Chapter 8 and 9: DNA and genomics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Structure of a nucleotide
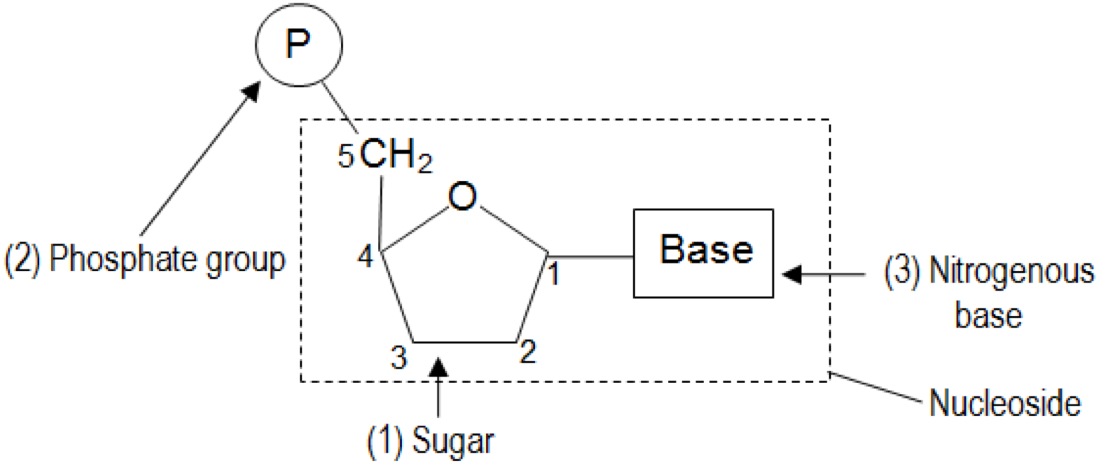
Deoxyribonucleotides have -OH Group at C2. T/F?
F. Ribonucleotides have -OH group at C2. Deoxyribonucleotides only have H.
What are the purines?
Adenine and guanine
What are the pyrimidines?
Cytosine and thymine
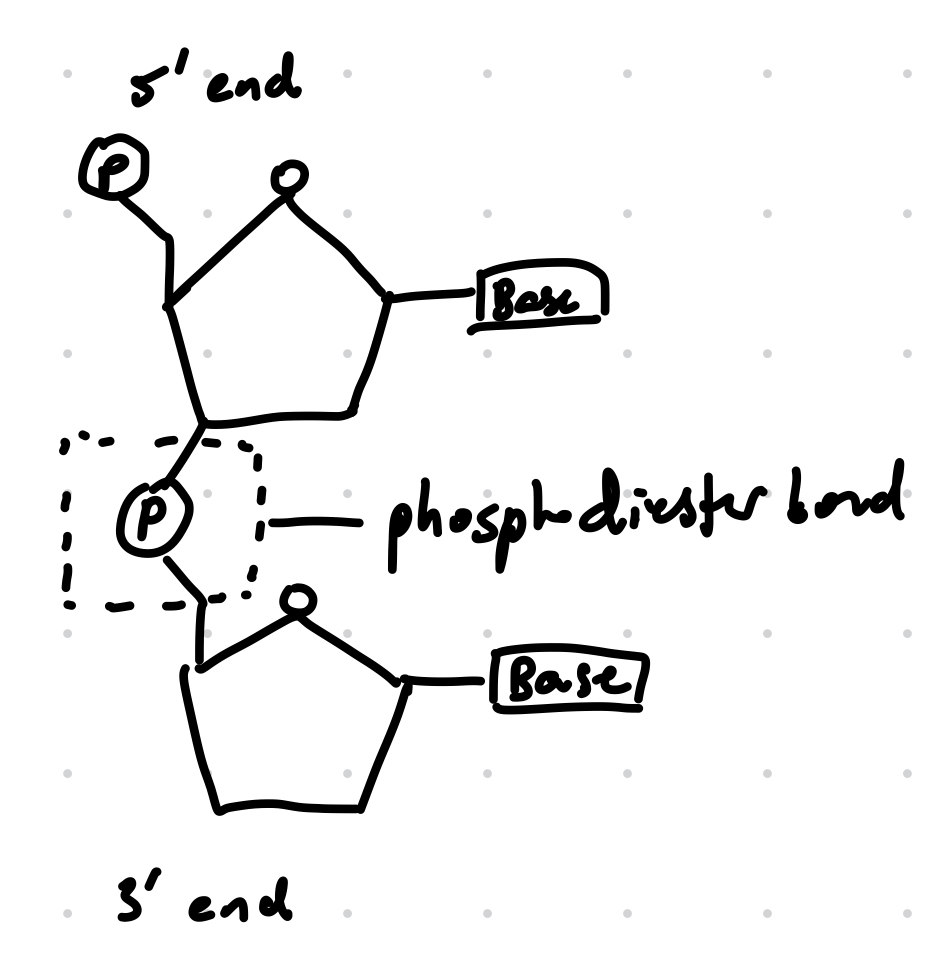
What is the bond that links adjacent nucleotides?
Phosphodiester bond
Draw a short segment of RNA and label the phosphodiester bond
What ratios are 1:1?
Purine: pyrimidines; A:T; C:G
Explain the importance of the ratios A to T and G to C in DNA
Ratios of A to T and G to C is approximately 1:1 in DNA
Indicating CBP whereby A base pairs with T and C base pairs with G
H bonds formed between complementary base pairs help to stabilize structure
Pairing between a purine and a pyrimidines will ensure DNA molc has a constant width of 2.0nm
RNA is ___ stranded but can ___ back upon itself and have ___ stranded regions
Single; fold; double
What is semi-conservative replication?
Both DNA strand separate by breaking of hydrogen bonds
Each strand acts as a template for synthesis of new strand through CBP
New DNA molecule consists of 1 original strand and 1 newly synthesised strand
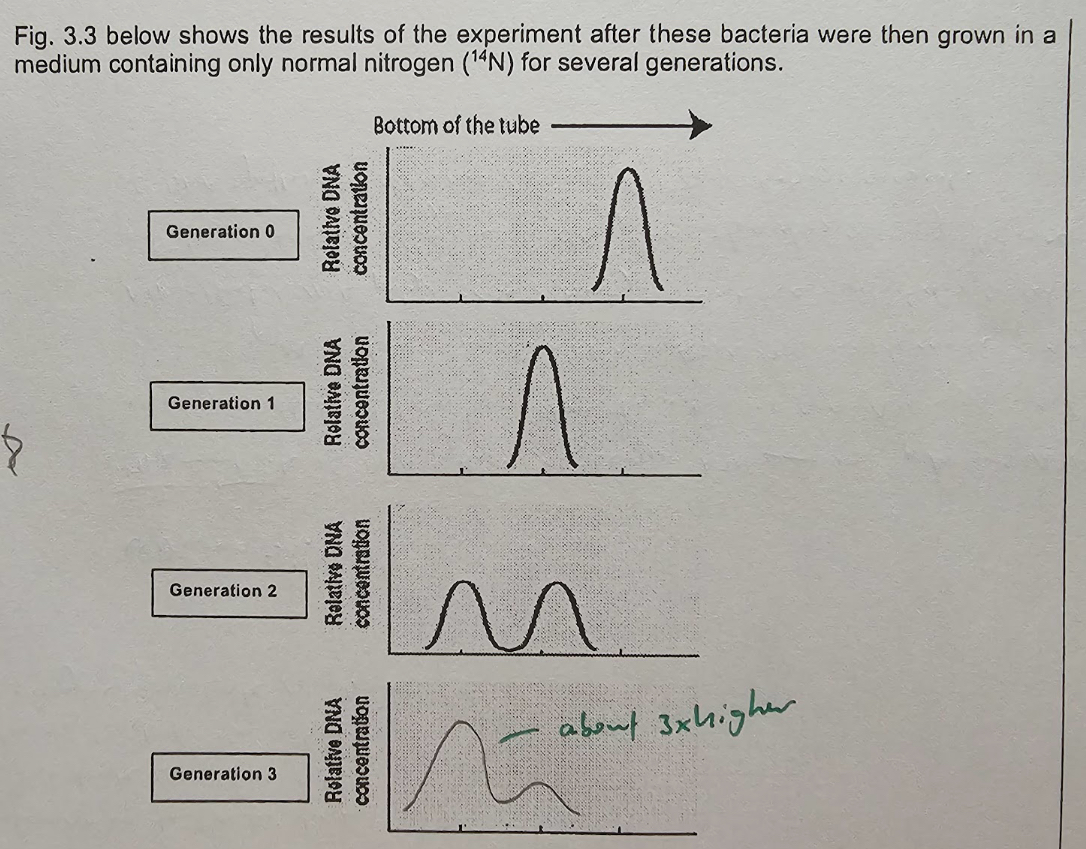
Explain the Uv absorption peaks observed in gen 1 and gen 2
During semiconservative replication, original 15N-15N DNA strands unzipped and served as templates for formation of new strands
Since only 14N DNA present in medium resulting DNA molecules in gen 1 were hybrid DNA molecules, consisting of 1 original 15N strand and 1 newly synthesised 14N strand
Each hybrid DNA molecule from gen 1 unzipped and used as templates for DNA replication
50% of DNA in gen 2 were made up of hybrid 14N-15N DNA → middle peak; the other 50% were made up of light 14N-14N DNA → leftmost peak
Why is DNA a suitable store of information?
Can be replicated accurately so that daughter cells have identical copies of DNA as parent cell
Stable molecule → can be passed on to next generation without loss of coded info
Backup of code
Coded information can be easily accessed
What enzymes are involved in DNA synthesis?
Helicase, topoisomerase, primase, DNA polymerase, another DNA polymerase, DNA ligase
Types of DNA mutations
Single base substitution, inversion, insertion, deletion
Effects of DNA mutations
Frameshift mutation, missense mutation, silent mutation, nonsense mutation
Which globin is affects in sickle-cell disease?
B
Describe the changes in DNA, mRNA and AA in sickle cell disease
CTC to CAC, GAG to GUG, Glutamate to valine
Explain the significance of change in AA to the properties of Hb
Charged, hydrophilic glutamate is replaced by non-polar, hydrophobic valine
Changes in the primary, secondary, tertiary structure as change in the R groups and bonds formed affect the way the polypeptide folds
At low O2 concentrations, loss of O2 from HbS results in conformational change and hydrophobic patches on HbS stick out
Hydrophobic areas of different HbS molecules stick together and HbS polymerizes, forming absorbable, long, rigid, rod-like fibres that distorts the shape of biconcave RBC and make it sickle shaped
Effect of change in AA in Hb
Long insoluble HbS fibres within RBC → normal biconcave shape distorted into sickle shape
Sickle RBC more fragile → shorter lifespan → shortage of RBC and poor O2 transport → anaemia
Sickle RBC are pointed and elongated → may get lodged in small blood vessels → interfere with blood circulation → organ damage
Characteristics of genetic code
Every code is a triplet code
Code is universal
Code is degenerate
Code is non-overlapping
Code is continuous
Includes ‘stop’ and ‘start’ sequences
Name the start codon and the corresponding amino acid
AUG, methionine
Name the stop codons
UAG, UAA, UGA
Aneuploidy
Condition where the cell does not have a chromosome number that is a multiple of the haploid number. There are extra or fewer chromosomes present compared to the wild type.
Non-disjunction
When homologous chromosomes/ sister chromatids fail to separate properly to opposite poles. Can occur during meiosis or mitosis/