Foramen and structures that pass through them
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
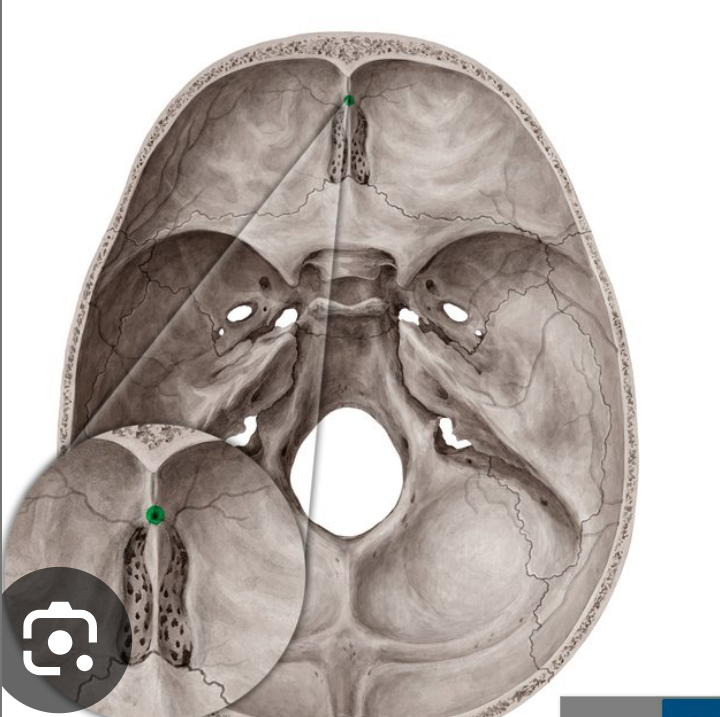
Foramen coecum
Nasal emissary vein
Cribiform plate:
Has 22 lobes. 11 on each side of the crista galli.
Content: Olfactory nerves (CN 1) and branches of the anterior ethmoidal artery, vein and nerve.
On the crista galli, a fold of the dura mater sits
Anterior ethmoid foramen
Content: Anterior ethmoidal artery, nerve and vein.
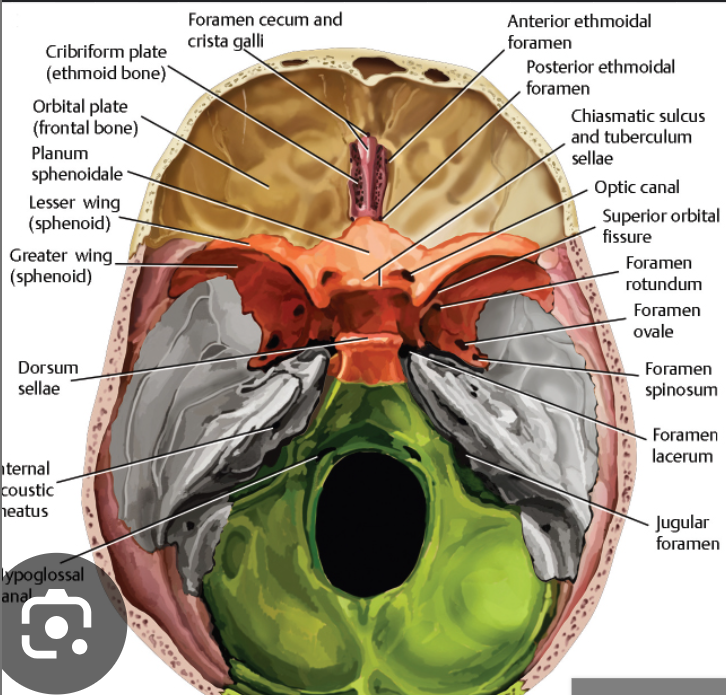
Posterior ethmoid foramen
Content: Posterior ethmoid artery, vein and nerve.
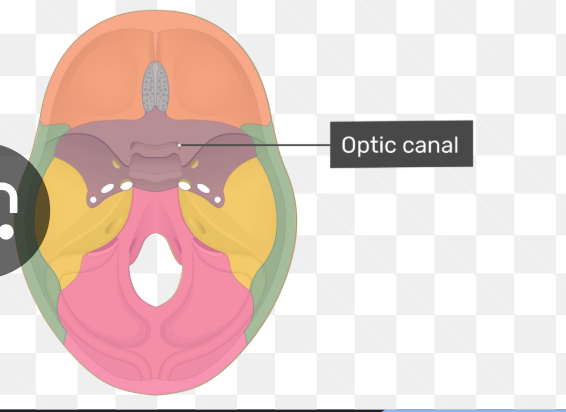
Opital canal
Content:
Optic nerve (CN II)
Ophthalmic artery
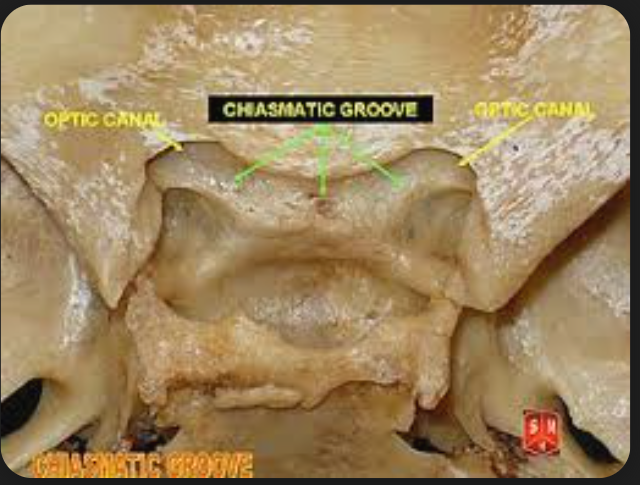
Chiasmatic groove
Thie crossing of the two optic right and left optic nerve .
Superior orbital fissure
Content: CN III, IV, V1 (first trigeminal nerve) , vi and Superior orbital vein
CN 3- Oculomotor nerve
CN 4- Trochlear nerve
CN V 1- Ophthalmic nerve
CN 6- Abducens nerve
Superio orbital vein

Revision on the Cranial nerves:
There are 12 cranial nerves
CN 1- olfactory nerve
CN 2- optic nerve
CN 3- oculomotor nerve
CN 4- trochlear nerve
CN 5- Trigeminal nerve——— V1: Ophthalmic nerve. V2: Maxillary nerve. V3: Mandibular nerve.
CN 6- abducens nerve
CN 7- Fascial nerve
CN 8- Vestibulocochlear nerve
CN 9- Glossopharyngeal nerve
CN 10- Vagus nerve
CN 11- Accessory nerve
CN 12- Hypoglossal nervd
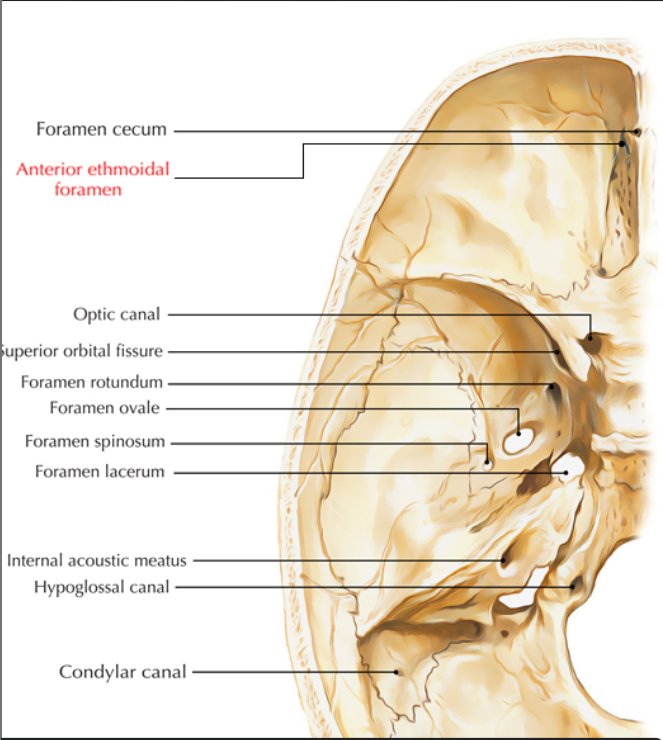
Foramen Rotundum
Content: Maxillary nerve (CN V/2)
Foramen ovale
Contents: Acronymn : MALE
M- Mandibular nerve (V/3),
A- Accessory menigeal artery
L- Lesser petrosal nerve
E- Emissary vein
Foramen spinosum
Contents:
Middle meningeal artery and vein.
Meningeal bramch of mandibular nerve.
Foramen Lacerum
Greater, lesser and deep petrosal nerve.
Note: This formamen is usually closed (sphenopetrosal synchodrosis)
Carotid canal:
Contents:
Internal carotid artery.
Internal carotid nerve plexus.
Hiatus os the lesser petrosal canal
Content:
Lesser petrosal nerve
Hiatus for the greater petrosal nerve
Greater petrosal nerve
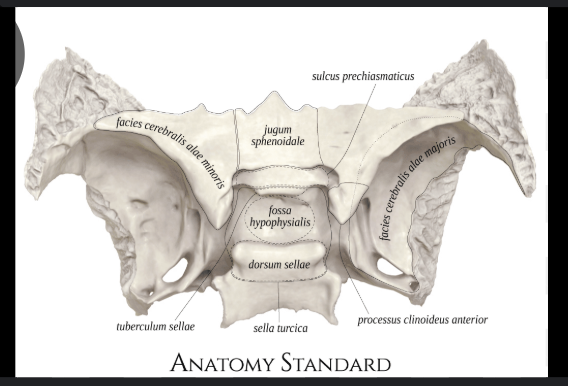
Hypophysial fossa
Where the pitutary gland sits on
Foramen magnum
Content:
vertebral artery
Anterior and posterior and spinal arteries.
Spinal root of accessory nerve
Transition between the medulla oblangata and spinal ord
Meninges (dura mater, arachnoid matter, pia matter).
Internal vertebral venous plexus.
Tectorial membrane and alar ligaments.
Jugular foramen:
Contents: Cranial nerve 9, 10, 11 and Jugular vein
CN 9- Glossopharyngeal nerve.
CN 10- Vagus nerve.
CN 11- Accessory nerve.
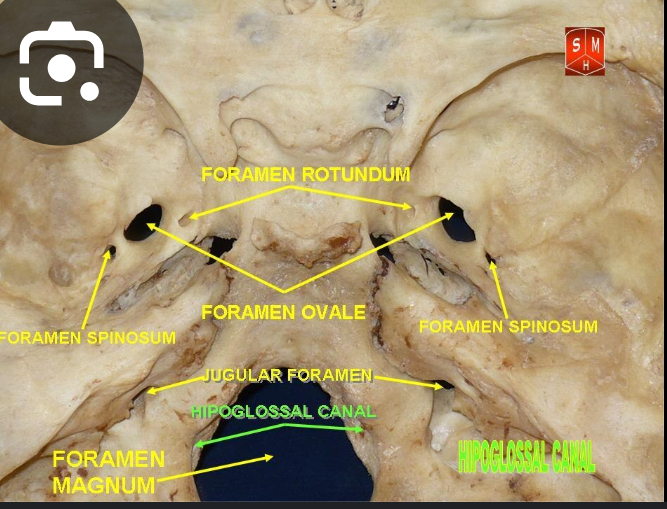
Hypoglossal canal:
Hypoglossal nerve (CN 12)
Internal acoustic meatus and canal
Facial nerve (CN 7).
Vestibulocochlear nerve
Labrinthine artery.
Exit to vestibular aqueduct
Endolymphatic duct
Mastoid canal
Emissary vein
Condylar canal
Emissary vein
Petrotympanic fissure
This is where the branch of the facial nerve called the chorda tympani exits the skull through
Fossula petrosa
This is a tiny fossa located between the jugular fossa and the carotid cana;.
Content: The inferior ganglion of the glossopharngeal nerve (CN 9) sits here.
Tympanic canaliculus
This originates at the fossula petrosa, and the tympanic branch of CN 9 passes through it.
Inside the tympanic cavity, it forms the plexus on the inner side of the tympanic membrane (eardrum) called the tympanic plexus. From the tympanic plexus, a branch called the lesser petrosal nerve exits the tympanic cavity through the canal for the lesser petrosal nerve.
The tympanic nerve, which is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve CN 9, originates from the inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Mastoid canaliculus
auricular branch of CN 10 passes through it
Musclotubarian canal
On the superior half of this canal, the tensor tympani muscle is found.
The inferior half is the eustachian tube.
Jugular fossa
It lodges the bulb of the internal jugular vein and the superior ganglion of the CN 9 and 10.
Stylomastoid foramen
Found between the stylod process and the mastois process.
It is the external opening of the facial canal.
The facial nerve exits sthe skull through it.
Tympanic cavity (Theory)
The ear is split into 3 parts:
External
Middle ear - also called the TYMPANIC CAVITY.
Inner ear
The middle ear lies within the temporal bone and extends from the tympanic membrane (eardrum) to the internal wall of the inner ear.
The main function of the middle ear is to transmit vibrations from the tympanic membrane (eardrum) to the inner ear via the auditory ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes).
TYMPANIC CAVITY:
The tympanic cavity is a narrow air-filled chamber in the petrous part of the temporal bone. This cavity has 2 parts:
Tympanic cavity proper.
Epitympanic recess- this is the space superior to the tympanic cavity.
Contents of the tympanic cavity
Ear ossiscles.
Stapedius and tensor tympani muscles
Chorda tympani nerve (a branch of the facial nerve CN7).
Tympanic plexus of nerve (arises from the CN 9- glossopharyngeal nerve)
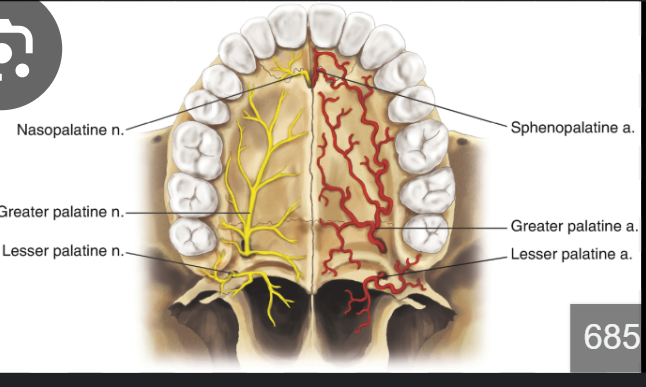
Incisive canal
Connects the oral cavity with the nasal cavity.
Content: nasopalatine nerve, artery and vein
Mastoid foramen
Emissary vein