Unit 3 (6/24) - patient protection and radiation protection of imaging personnel (copy)
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
Holistic patient care
treat the pt as a whole person rather than a. Body part
Ex: your pt is Mr. Smith, not the ankle x-ray
Effective Communication & Body Language (10 steps)
Introduce self
Address pt properly
Ease patient stress & anxiety
Understanding & dignity
Clear & concise instructions
Increase their cooperation
Give time to ask questions
Gain trust
Be professional, present, & aware of body language
Reduce repeats
Patient motion: involuntary
caused by muscles, not controllable
Heart
Digestive
Chills
Tremors
Spasms
Pain
Withdrawal
Correcting involuntary motion
decrease exposure time & increase imaging receptor speed
Voluntary motion
controlled motion
Lack of control caused by:
Age
Breathing
Anxiety
Discomfort
Fear
Mental instability
Correcting voluntary motion:
Gaining patient cooperation & use of proper immobilization
Immobilization
piggostat
Papoose/octostop
Sponges & sandbags
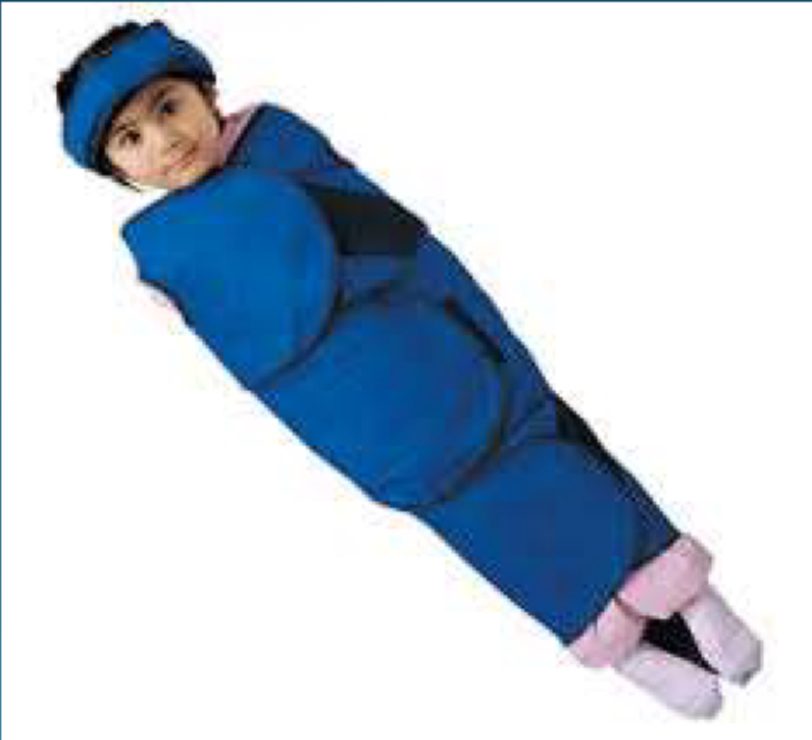
Mummy wrap/ bunny wrap
Tape
Velcro straps
Radiolucent plexiglass
Have non-radiology employee help hold
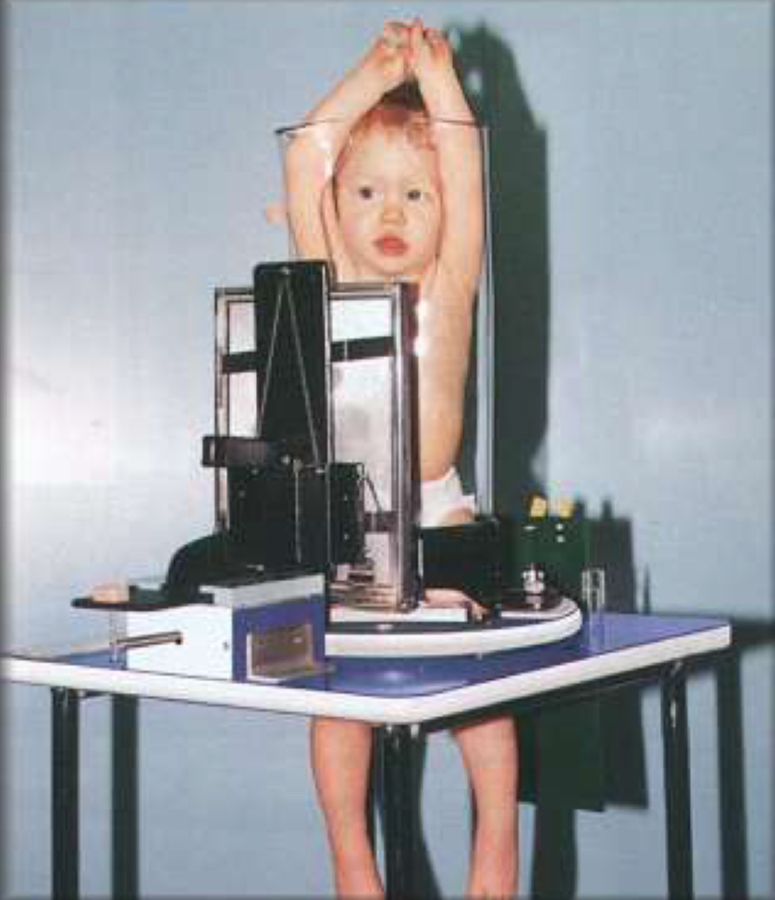
What immobilization is this
Piggostat
What immobilization is this
Octostop

What immobilization is this
Papoose
Beam limiting devices
limits primary beam to a smaller area
Decreases exposure by reducing the amount of tissue that is exposed to radiation
Reduces scatter
Types of beam limiting devices
aperture diaphragm
Cones
Collimators
Aperture diaphragm
flat lead w/ a hole cut in it & placed below the windows
Most common is RECTANGULAR
Square
Round
Reduces scatter
Cones
circular metal cylinders that connect to front of the use & limits the size of the beam
Can be flared or straight
Can be telescoped 10-12 inches to make field size smaller (extensive cylinder)
Cones have been replaced by ___
Collimators
Cones are mostly used in what
Dental radiography (but can be used for heel, skull, and spine images)
Collimators
also called light localizing variable aperture rectangular Collimators
Most versatile
Should not be opened larger than body part
2 sets of shutters 90 degrees from one another
Collimators can reduce exposure by what percentage?
20-30%
Over collimating (making it too small) can cause what?
Repeat images
Near (upper)
near x-ray production
Reduces exposure from off focus radiation!!!!
Far (lower)
located close to light source
Confines beam to area of interest
Skin sparing
minimizes the skin exposure by requiring a 15 cm distance from skin to Collimators
Spacer bars
Grids clean up__
Scatter
PBL
Positive beam limitation
Positive beam limitation
electronic sensors in the bucky that senses the size of the IR that is used & opens the Collimators appropriately
Slits of pegs
Reduces human error
Positive beam limitation (PBL) is also known as?
Automatic collimation
PBL/ automatic collimation is regulated to be within ___% accuracy
2%
Filtration
hardens the beam by cleaning up low energy (longer wavelength)
Reduces patient exposure to skin & superficial surface
Reduces absorbed dose
Lower energy photons provide no detail to the image!!!
Low energy=
Filtration
High energy=
Lead
Total filtration in the housing is ___ mm Aluminum (Al) equivalent for units that operate above 70 kVp
2.5
2 types of filtration
Inherent
Added
Inherent filtration
0.5 mm Al equivalent
Made up of glass envelope, insulating oil, & glass window
Added filtration
2.0mm Al equivalent Made up
Sheets of Al added outside the glass window above the collimator
Can be accessed by service person
Can be changed as tube ages
Mobile & fluoro require ___ mm Al filtration
2.5
NCRP report #____ lists minimum requirements for filtration
102
Radiation control for health & safety act of 1981 states___
The x-ray tube must have adequate filtration
HVL (half value layer)
measures beam quality or effective energy of the beam
Measured at least once a year by a physicist or if the tube is replaced/ repaired
1 HVL=
50%
2 HVL=
25%
3 HVL=
12.5%
4 HVL=
6.25%
2019 Shielding- AAPM (American association of physicists in medicine)
statement that shielding of patient gonadal or fetal shielding should be discontinued
What year was shielding discontinued?
2019
CARES committee
Communicating advances in radiation education for shielding
Radiosensitive organs
lens of eye
Breasts
Reproductive organs
2 types of shielding
Gonadal
Specific area
First step of gonadal protection is proper___
Collimation
Due to location of gonads, females receive__ MORE exposure than males
3x
Appropriate shield placement can reduce exposure by ___% in females, & ___% in males
female= 50%
Male= 90-95%

What type of shielding is this?
Flat contact/ fig leaf
What is the most effective position for flat shields?
AP/ PA recumbent position

What type of shielding is this?
Shadow shields
Shadow shields are not suitable for what procedures?
Fluoroscopy

What shielding is this?
Shaped shields
Shaped shields
contoured to enclose the male reproductive organs
Can be placed by the pt
When can shaped shields not be used?
During PA projections
What kind of shielding is this?
Clear shields (transparent lead-plastic material)
What type of shielding is this?
Lap shields (half)
Half Shield
used for gonadal protection of patient
Covers front or back of patient & is attached by Velcro strap or on wheels

What kind of shielding is this?
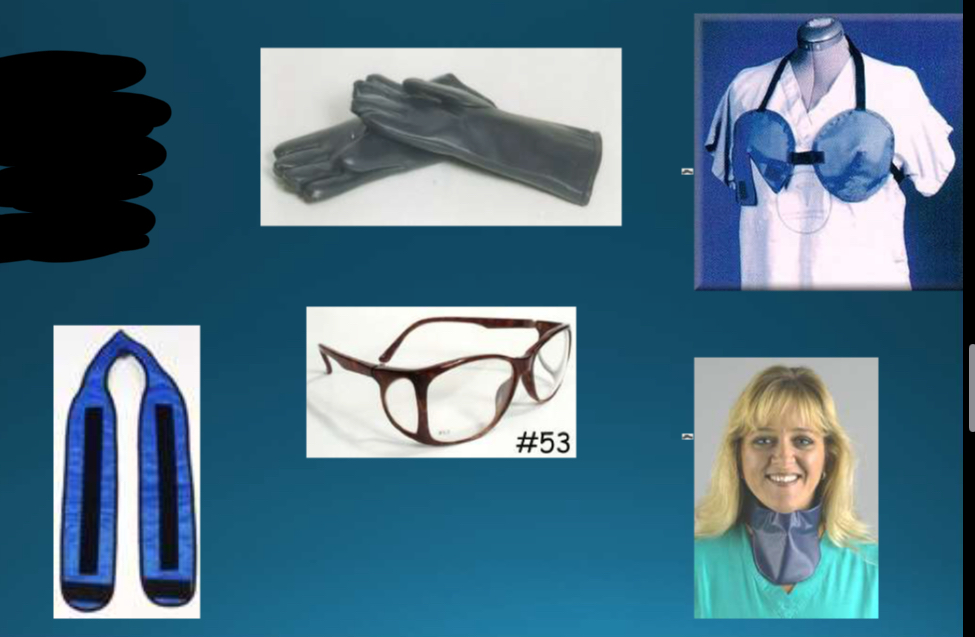
Specific area shields
Examples of specific area shields
Eyes
Breast
Thyroid
Gloves
Compensating filters
used when x-raying a part that has varying thickness to reduce dose & provide a uniform density across the image
Decreases entrance skin exposure
aluminum or lead-acrylic that is attached to the bottom of the collimator
4 types of compensation filters
Wedge
Through
Ferric
Boomerang
Wedge compensating filter
used for foot or spine
Trough compensating filters
bilateral wedge
Used for chest
Ferlic compensating filters
used for hips
Boomerang compensating filters
used for shoulders
kVp (kilovoltage peak)
quality of x-ray incr. with thicker body parts
Unit selected on operating console
Max possible energy of a photon that exits the x-ray tube
mA/ milliamperage
quantity of x-rays
Measurement of x-ray tube current or # of electrons crossing the tube from cathode
Selected on operating console
DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL TO PATIENT EXPOSURE
What is the quality of x-ray that increases w/ thicker body parts
kVp
What is the quantity of x-rays?
mA
mAs/ milliampere seconds
controls the amount of radiation produced by the x-ray tube
DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL TO PATIENT EXPOSURE
Increase in mAs= increase in
Dose
AEC/ automatic exposure control
cells that are selected on the operating console that will automatically select the mA, according to cell selection & body part
exposure index (EI)
the number that is found on the image after processing that measures receptor exposure
Under exposure will cause ____, which needs a repeat
Quantum noise (grainy appearance)
Extreme over exposure will cause ___, and needs to be repeated
Saturation
Use proper exposure factors
Makes optimal image w/ minimal dose possible
Sufficient penetration
When setting manual technique, measure the pt for accuracy
Reliable technique charts
Higher kVp= ____ for body parts
Lower mas
Image receptor exposure
increase in image receptor speed decreases patient exposure but decreases sharpness
200 or 400 speed image receptor
Correct processing
inadequate processing results in repeats
Rule of thumb is to use a grid when part thickness is over ___ cm @ ___ kVp or higher
over 10 cm @ 60kVp or higher
Grids
remove scatter
Improves contrast/ detail of image
Use lowest grid ratio appropriate for the body part
Grids __ patient dose, but improves the quality of the image which produces a better diagnosis
increase
Higher grid ratio=
Higher patient dose
Air gap technique
alternative to using a grid to clean up scatter
Air gap technique distance
4-6 inches (10-15cm) away from image receptor with 10-12 feet SID
Negative of air gap technique
the increase in magnification & not useful in kVp higher than 90
Repeats are unacceptable if done due to carelessness or poor judgement
Positioning
Technique
Repeat analysis (7)
Problems w/ positioning
Incorrect centering
Inappropriate technical factors
Improper collimation
Foreign bodies
Processing artifacts
Patient motion
Unnecessary exposures For chest x-rays
Pre admission
Pre employment
Routine health check ups
Screening for TB
Unnecessary exposure for lumbar x-rays
Pre employment
Unnecessary exposure for CT whole body scans
Check for disease
Minimal source to skin distance on a mobile fluoroscopy unit is
12 inches (30 cm)
The smaller the source to skin distance, the ___ the entrance exposure
Larger
Portable x-rays
Only perform on patients that cannot be transported to the department
Digital radiography
do not overexpose pt just because if can be manipulated
Utilize technique charts & grids
What is the largest exposure to patients in diagnostic radiology
fluoroscopy