Reproductive Organs and Associated Pelvic Structures - BPK 326
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
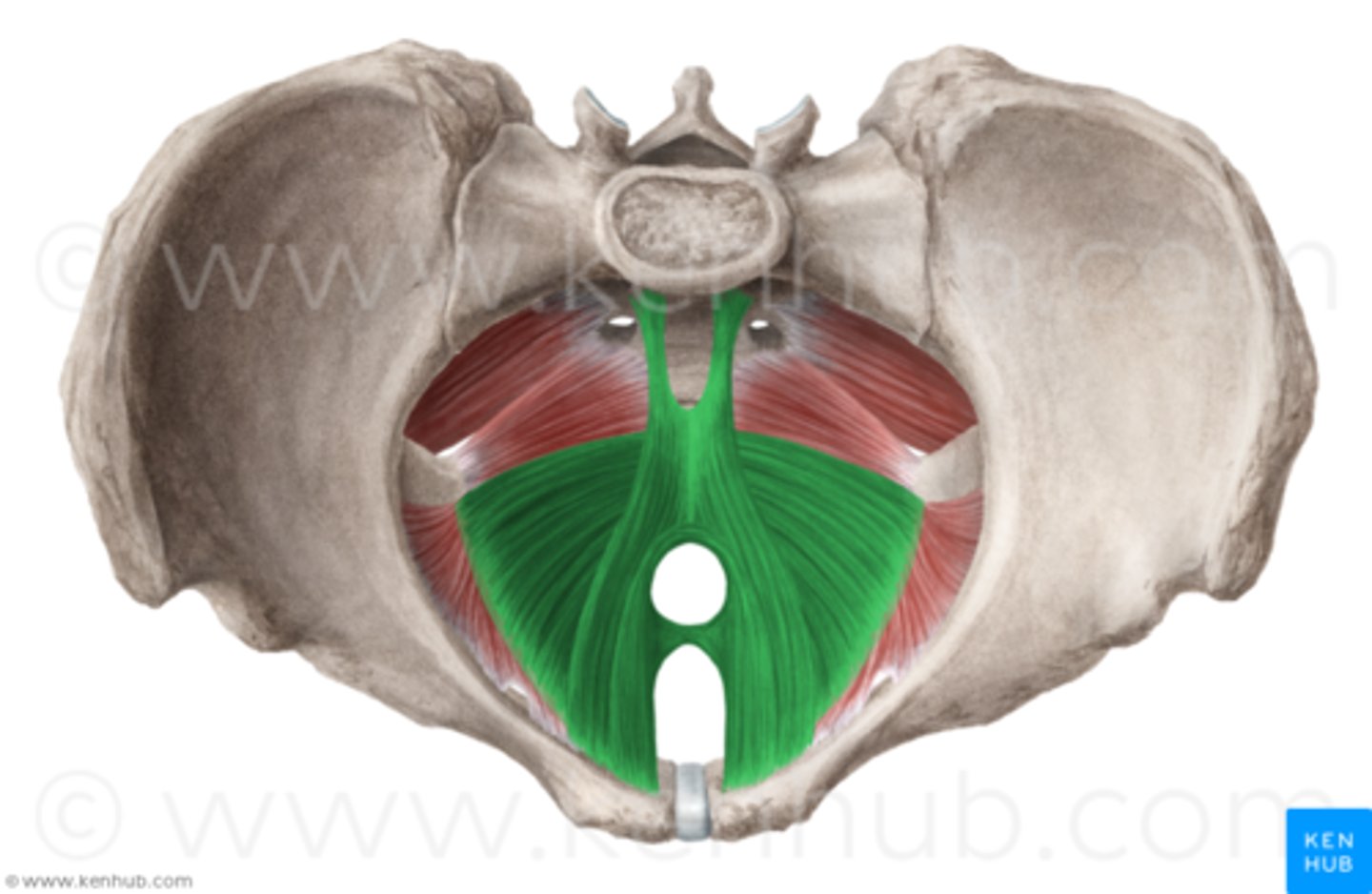
pelvic diaphragm (pelvic floor)
muscles create a muscular trampoline (supporting organs of pelvis)
- voluntarily controlled and exercised (kegal exercise)
- crucial to continence (bladder and bowel control) and sexual function
3 groups of pelvic diaphragm
pelvic diaphragm
urogenital diaphragm
sphincter and erectile muscles of urogenital tract
levator ani group
puborectalis
pubococcygeus
iliococcygeus
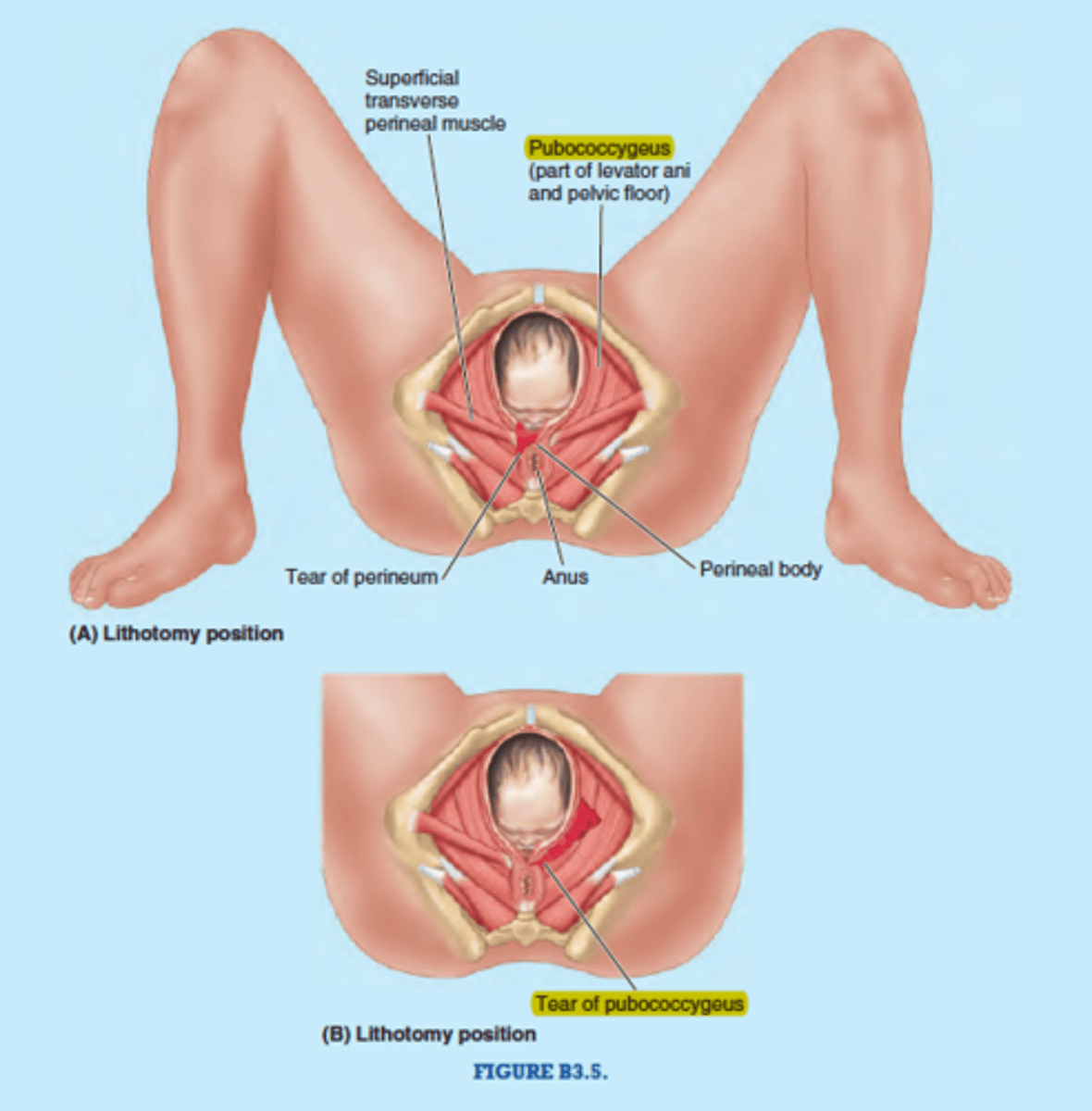
pelvic floor injury
common consequence of vaginal delivery
- puborectalis and pubococcygeus are most common muscles damaged
- causes incontinence and sexual dysfunction
compared to cesarean section
- vaginal devilry is associated with 2 fold increase risk of pelvic floor dysfunction
- combo of aging and birth
uterus
- fundus and cervix
womb
- contains the developing fetus during gestation
- 50-200g non-pregnant, expands a lot and weighs 1kg at birth
- fundus = top part connects to ovaries through fallopian tubes
- cervix is connected to vagina
- uterus changes size dramatically during pregnancy (10 months baby loses weight)
complications of pregnancy
rapidly expanding uterus compresses adjacent organs compromising function and creating complications
- shortness of breath
- heart burn (kicking stomach, pushing acid into esophagus)
- reduced stomach capacity
- impaired intestinal transit and constipation
broad ligament
sheet like fold of peritoneum
- extends from the sides of the uterus to the lateral wall and floor of the pelvis
- holds uterus in position
round ligament
true ligament
- extends from lateral aspects (horns) of the uterus to the labium majorum
- extend anteriorly
- pain in pelvis / labia due to baby growing (tugging on them)
uterine prolapse
due to damage in pelvic floor muscles and or ligaments
- uterus collapses into vagina (outside of vagina)
fallopian tubes
aka uterine tubes
- transport the fertilized ovum from the ovaries to the body of the uterus
- 10cm long
- bilateral
4 divisions prox to dis
- infundibulum
- ampulla
- isthmus
- intramural
ectopic pregnancy
aka tubal pregnancy
- egg implants on the wall of fallopian tube
- results in death of embryo
- life threatening for mother (tubes can burst)
- appendix lies very close to right ovary and uterine tube
- tubal pregnancy can be misdiagnosed as appendicitis
tubal ligation
aka tubes tied
- surgical method of birth control
- ovas that are released simply degenerate and are absorbed
abdominal - part is cut or removed
laparoscopic - cauterized or cut
vagina
fibromuscular tube
- 7-10 cm in length
- facilitates childbirth, menstruation, sexual intercourse, sexual pleasure
cervix
separates uterus and vagina
- dilates during labour to admit the passage of the baby into the birth canal
- check routinely for cervical cancer (Pap smear)
normal - smooth, glistening surface, small and round = never been pregnant
HPV infection - large and bloody opening (for non-invasive cancer)
vulva
external female genitalia
- mons pubis
- clitoris
- labia minor
- labia majora
- vaginal orifice
female genital mutilation
remove clit
remove vaginal tissue and clit
sewing shut, small hole for excretion
stretched labia
- common in immigrant countries. (African, Middle East and Asia)
penis
contains erectile bodies - tissues containing vascular space that can be engorged with blood (tumescence - erection)
- corpora cavernosa
transverse section of penis
corpus cavernosa
corpus spongiosum
corpus cavernosa - dorsal, lateral enlargement (one on each side)
- contain large vascular sinuses (allows penis to fill with blood)
- largest portion of the penis
corpus spongiosum - ventral
- contains urethra
- continuous with glans, both have less tunic covering relative to the corpus cavernosum
root of penis
contains two crura
one bulb
slide 16
prepuce / foreskin
covers majority of the glans
- uncircumcised, foreskin attaches to fascia overlying the body of the penis
- arose from religious and social convention
benefits - reduced risk of urinary tract infection, penile cancer, sexual transmitted diseases (HIV)
risks - infection, permanent disfiguration, impaired sexual pleasure or function
urethra
extends from internal urethral office of bladder to external urethral orifice of the glans
4 parts
- preprostatic (intramural) urethra (surrounded by internal urethral sphincter)
- prostatic urethra
- membranous urethra (surrounded by external urethral sphincter)
- spongy (penile) urethra
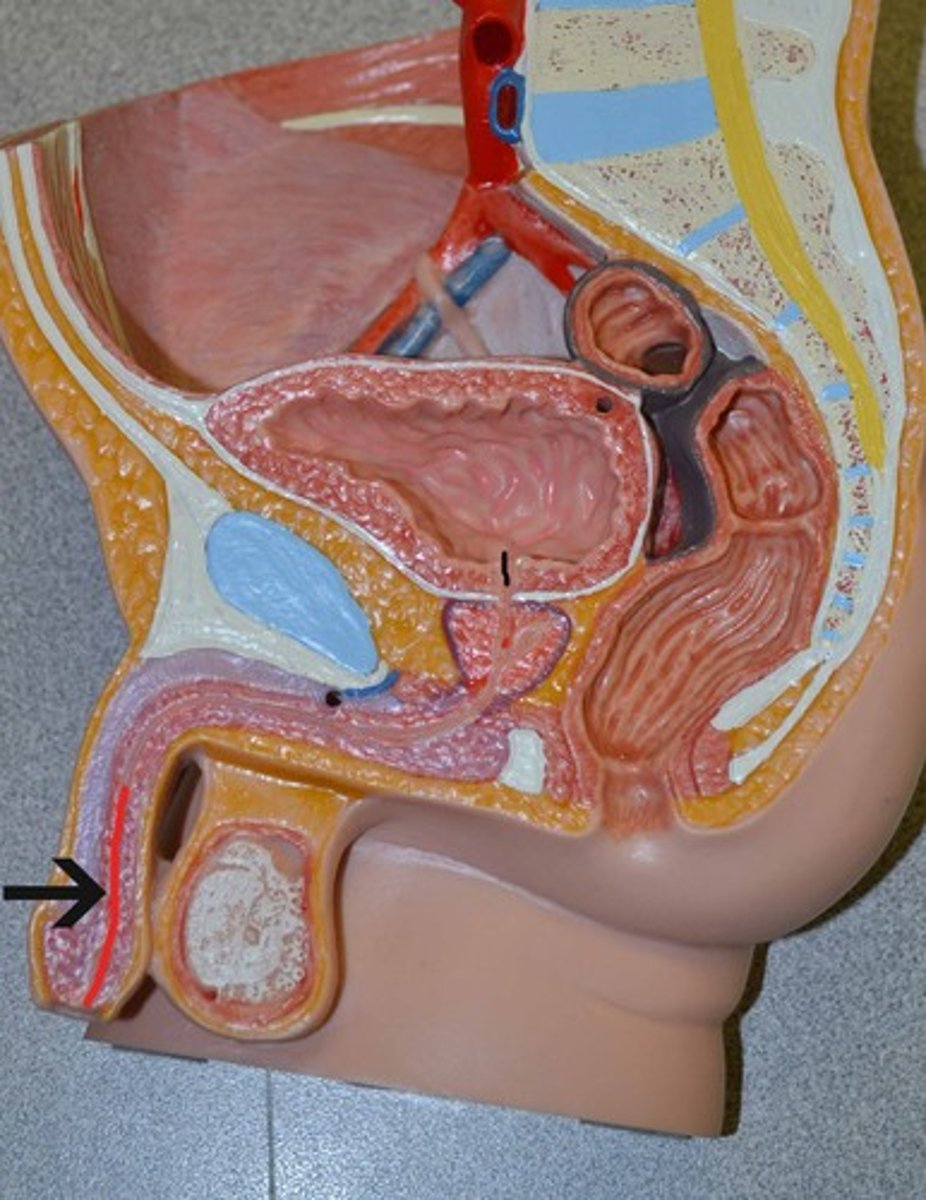
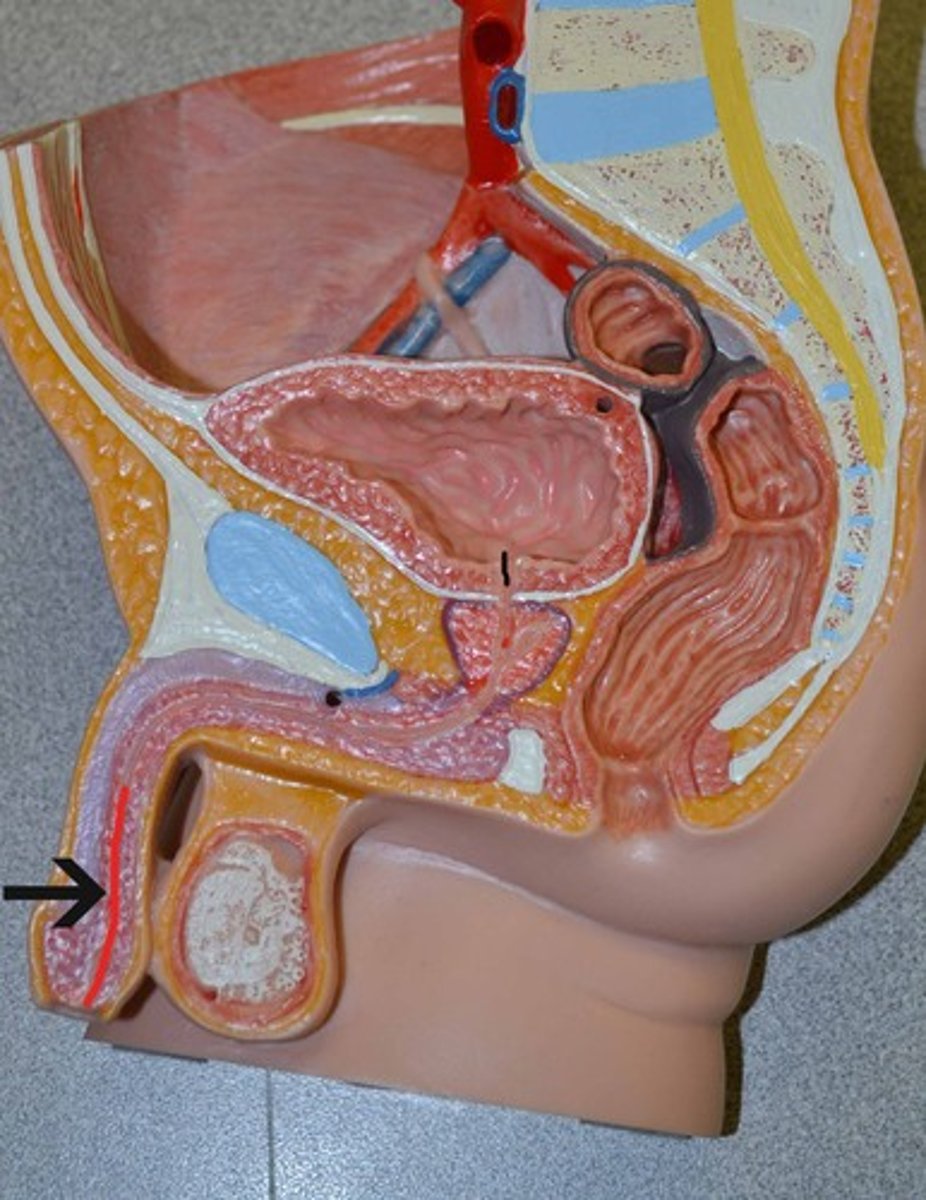
prostatic urethra
contains urethral crest - where prostatic ducts open bilaterally
- contains seminal colliculus, where ejaculatory ducts open
affected by benign prostatic hyperplasia
- non cancerous increases in prostate size
- results in waking up in the middle of the night to urinate, urinary hesitancy (hard to stop/start pee), intermittent urine flow
ejaculatory duct
formed by the merger of seminal vesicle duct with vas deferens
spongy urethra
Cowper's glands (bulbourethral glands)
- eject lubricating fluid into urethra
- two openings increase the size of the urethra, ampulla (proximally) and navicular fossa (distally in glans)
sperm track
testis - produce sperm
epididymis - matures sperm
vas deferens - moves sperm
ampulla
seminal vesicle - add secretion
ejaculatory duct
urethra
vas deferens ligation
vasectomy
- surgical form of birth control
- easy non-invasive
- can be reversible
egg track
ovary
fallopian tube - fertilization
uterus