d. 2nd/3rd Tri Anat
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
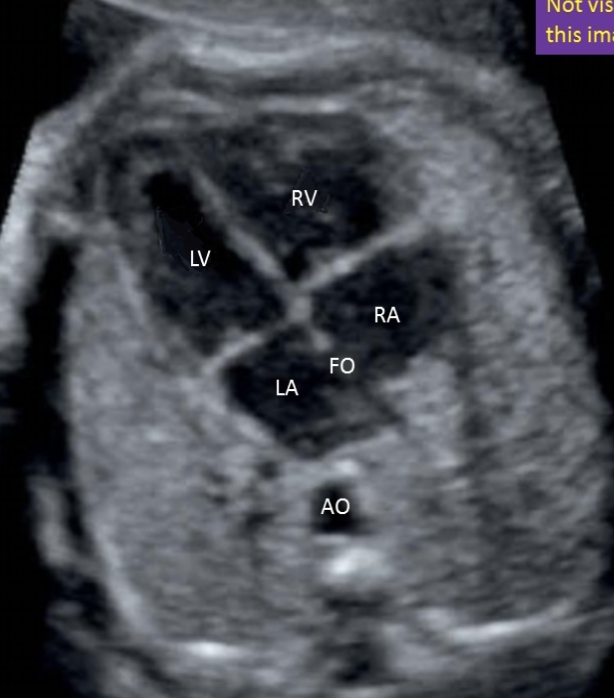
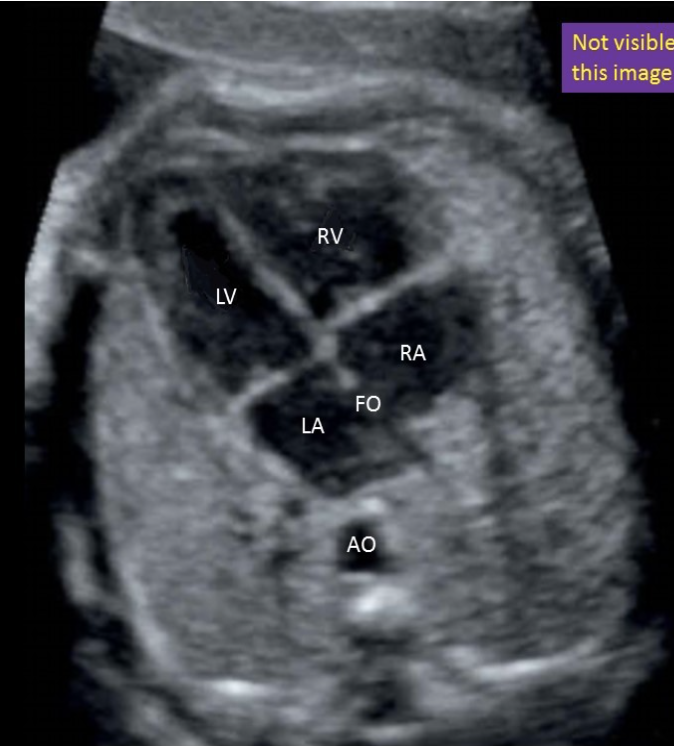
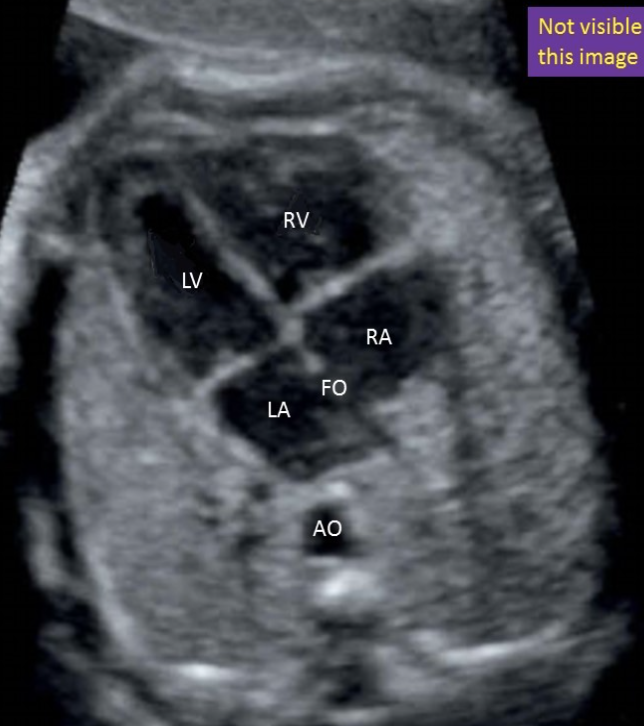
where is the left ventricle
a) top left
b) top right
c) bottom left
d) bottom right
a) top left
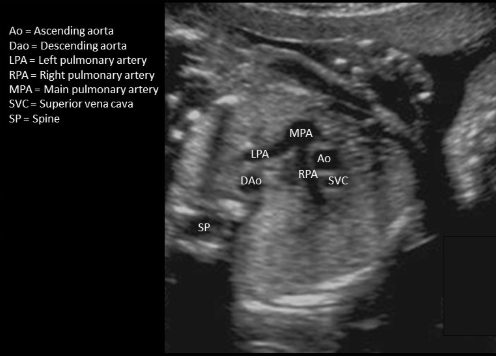
where is the right pulmonary artery
type in “on the side of ascending AO”
on the side of ascending AO
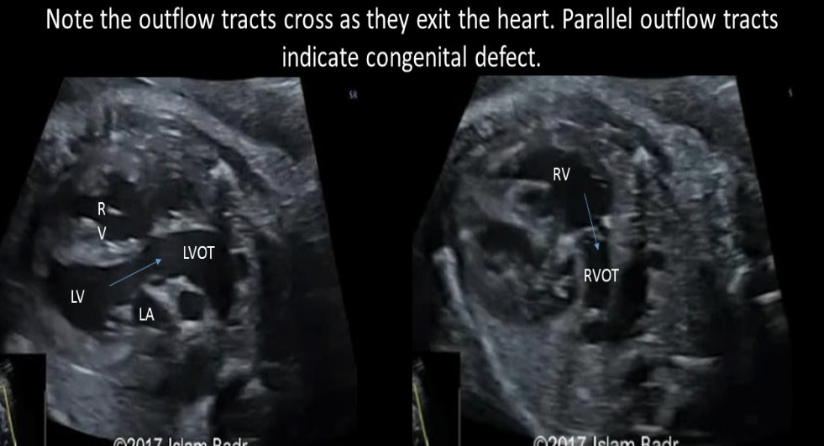
the proximal pulmonary artery + AO shows a normal appearance when
a) they exit the heart parallel to each other
b) the AO crosses anterior to the pulmonary artery as they both exit the heart
c) the pulmonary artery crosses anterior to the AO as they both exit the heart
d) the diameter of the AO is at least 2x the diameter of the pulmonary artery
c) the pulmonary artery crosses anterior to the AO as they both exit the heart
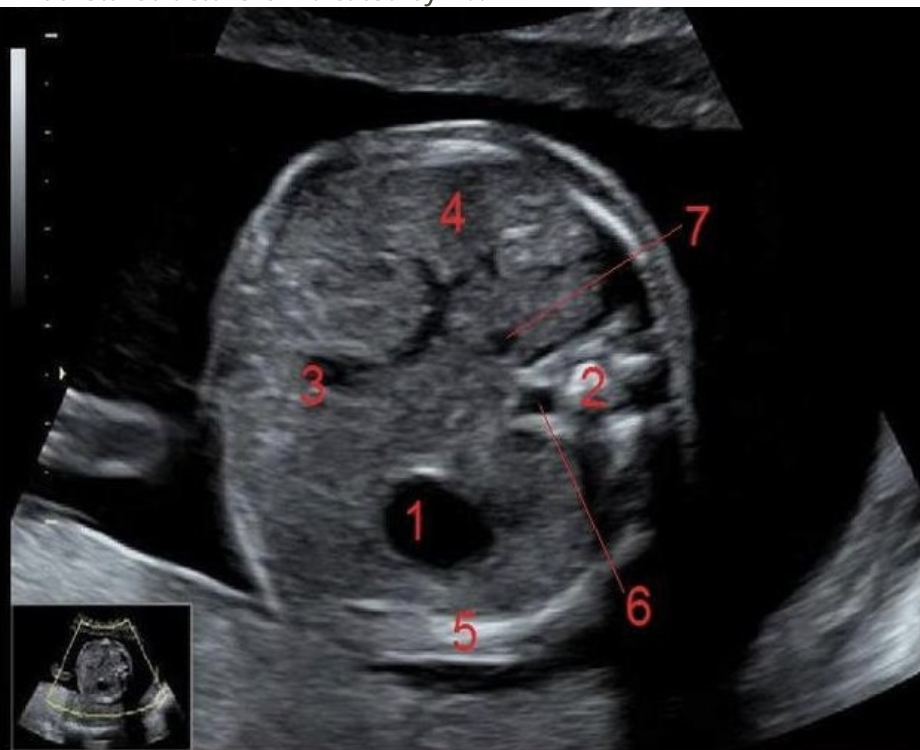
what is #5
a) stomach
b) hydronephrosis
c) lung tissue
d) bladder
d) bladder

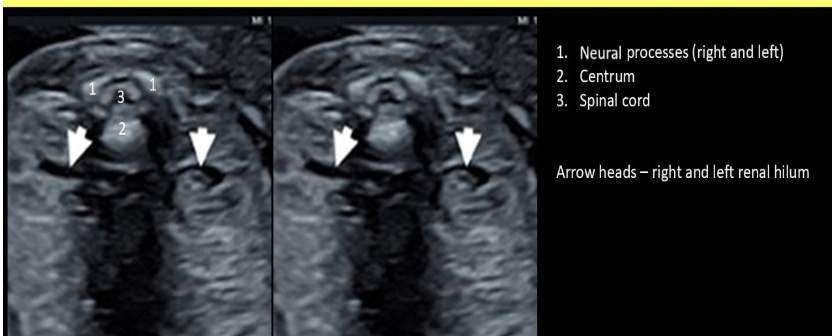
the normal spine has 3 ossification centers called
a) right + left neural processes and the centrum
b) medial + lateral neural processes and the centrum
c) anterior + posterior processes and the magnum
d) anterior + posterior neural processes and the centrum
a) right + left neural processes and the centrum
what is the functional unit of the placenta
a) cotyledon
b) lobe
c) nephron
d) lobule
a) cotyledon

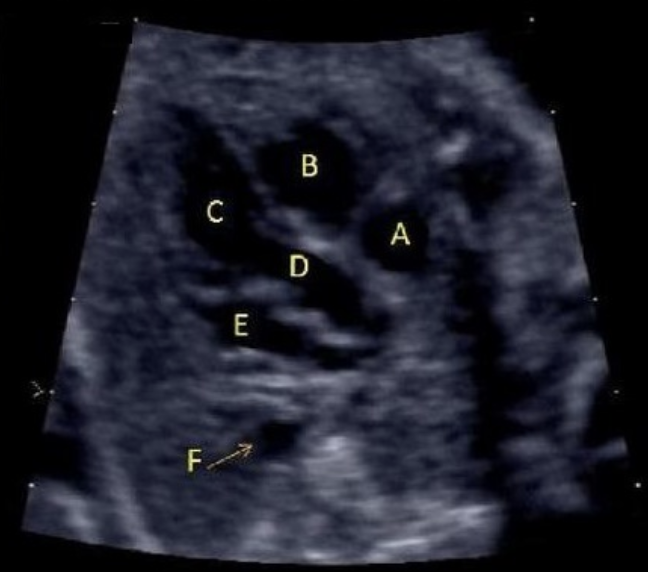
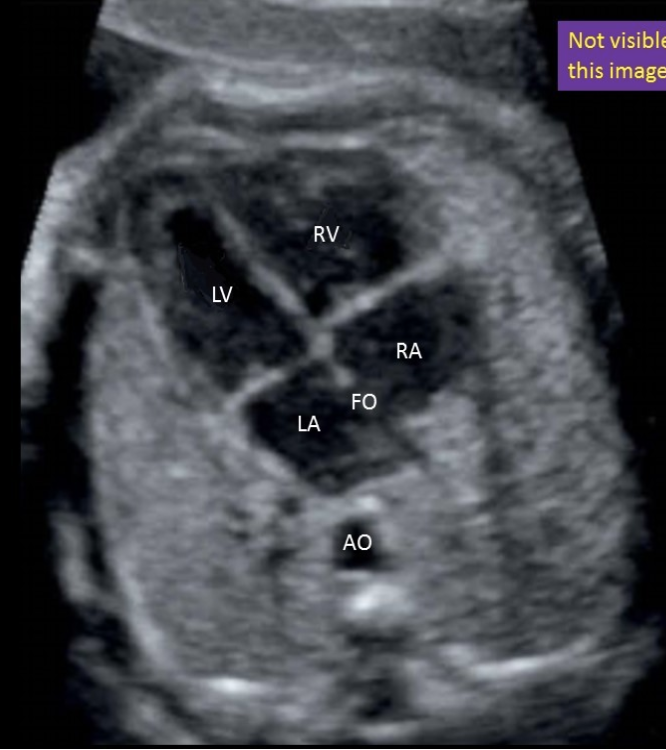
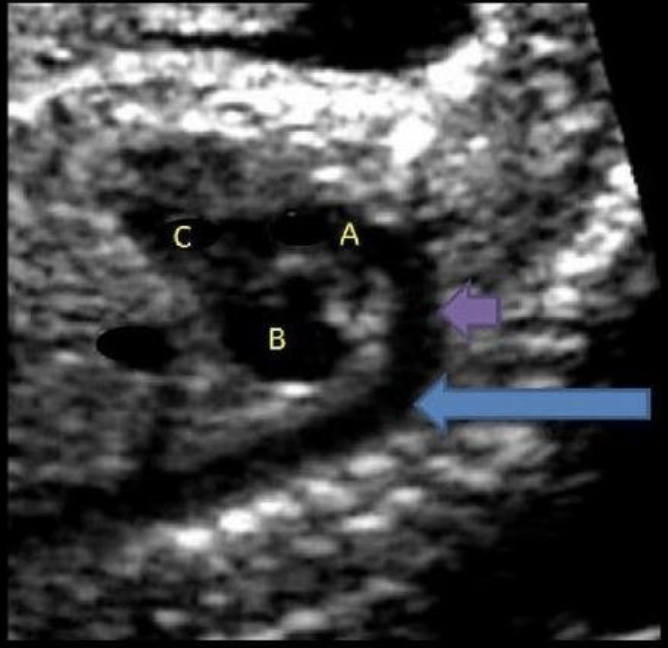
what is letter B
a) LVOT
b) RVOT
c) left ventricle
d) right ventricle
e) right atrium
d) right ventricle

what normal fetal structure produces AFP
a) kidneys
b) liver
c) pancreas
d) heart
b) liver

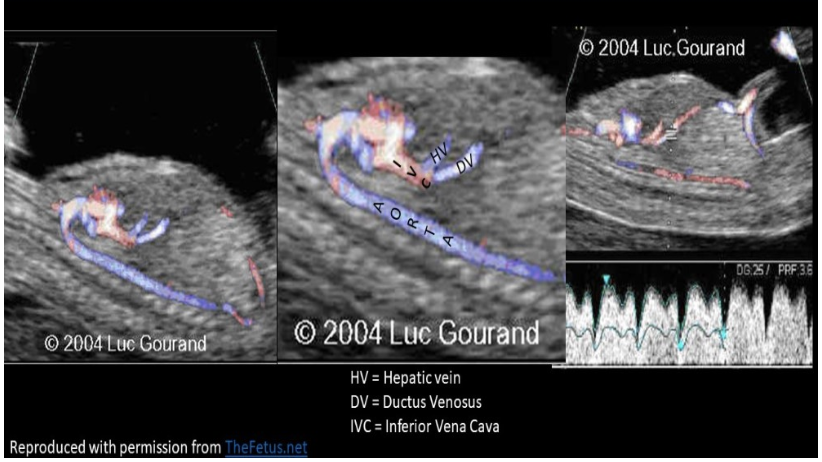
which describes the vessels that allows some umbilical blood to bypass the fetal liver in fetal circulation
a) foramen ovale
b) ductus venosus
c) ductus arteriosus
d) umbilical vein
b) ductus venosus
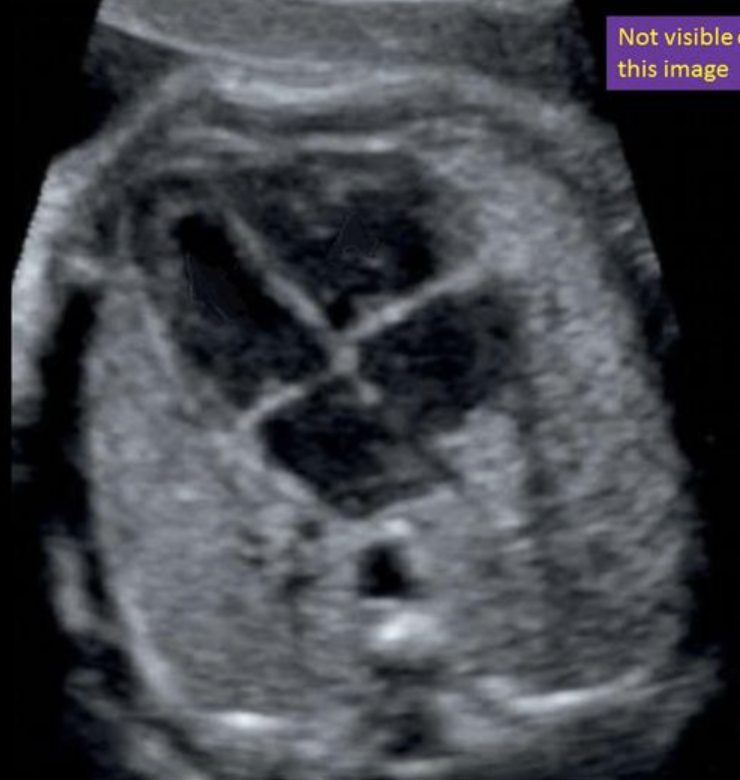
where is the right ventricle
a) top left
b) top right
c) bottom left
d) bottom right
b) top right
which hormone stimulates the formation of the cervical mucous plug found with pregnancy
a) progesterone
b) bHCG
c) estrogen
d) oxytocin
a) progesterone

what is #6
a) IVC
b) AO
c) spinal cord
d) spine
b) AO
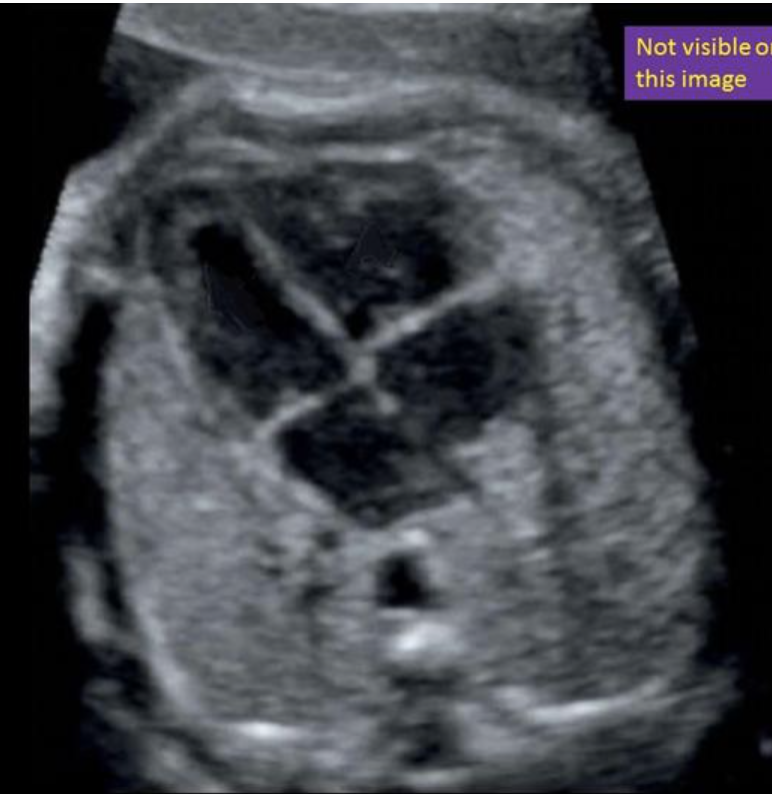
where is the foramen ovale
a) between the 2 atrium
b) between the 2 venticle
c) between the left atria + ventricle
d) between the right atria + ventricle
a) between the 2 atrium
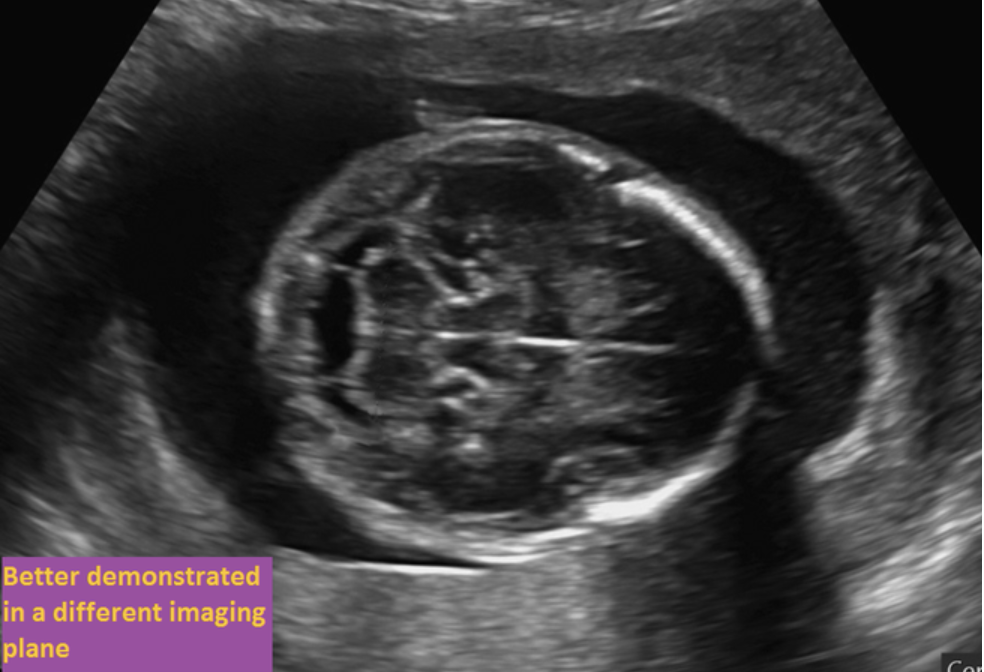
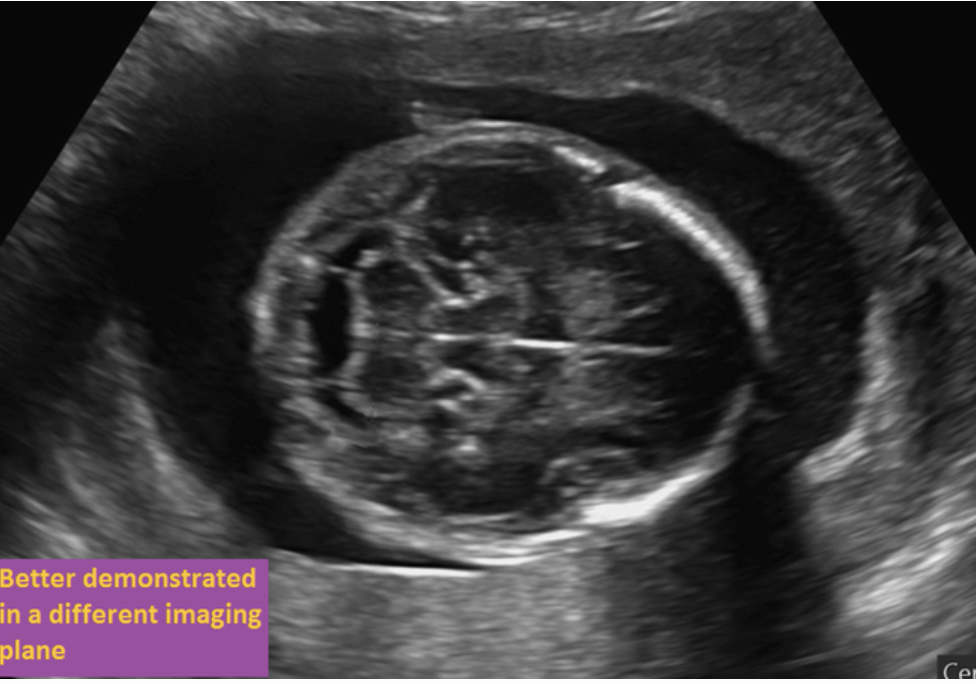
where is the choroid plexus
“imaged better in a different plane”
axial plane superior to this one
imaged better in a different plane

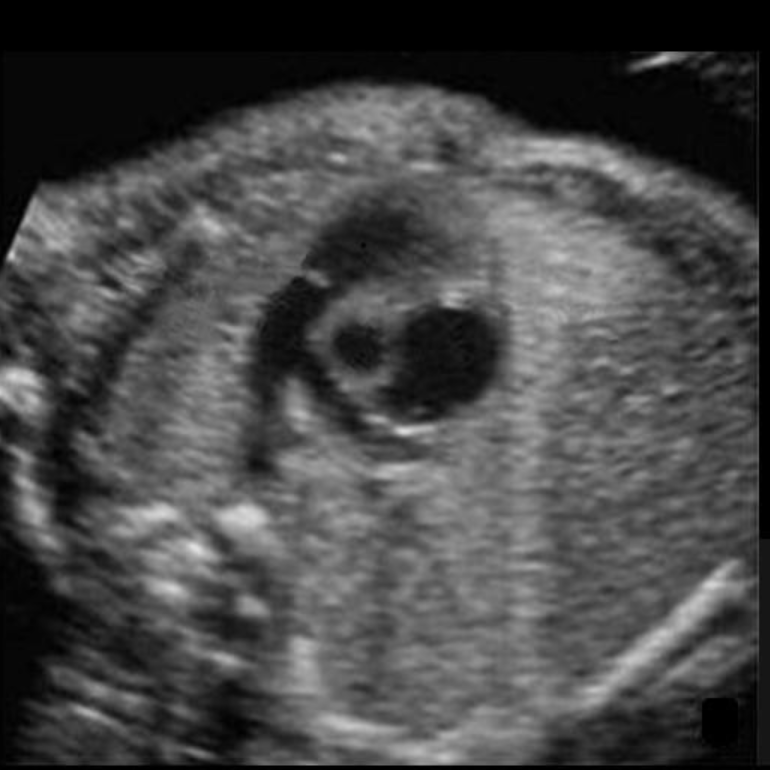
where is the right ventricle
write “the most anterior spot on the picture”
the most anterior spot on the picture
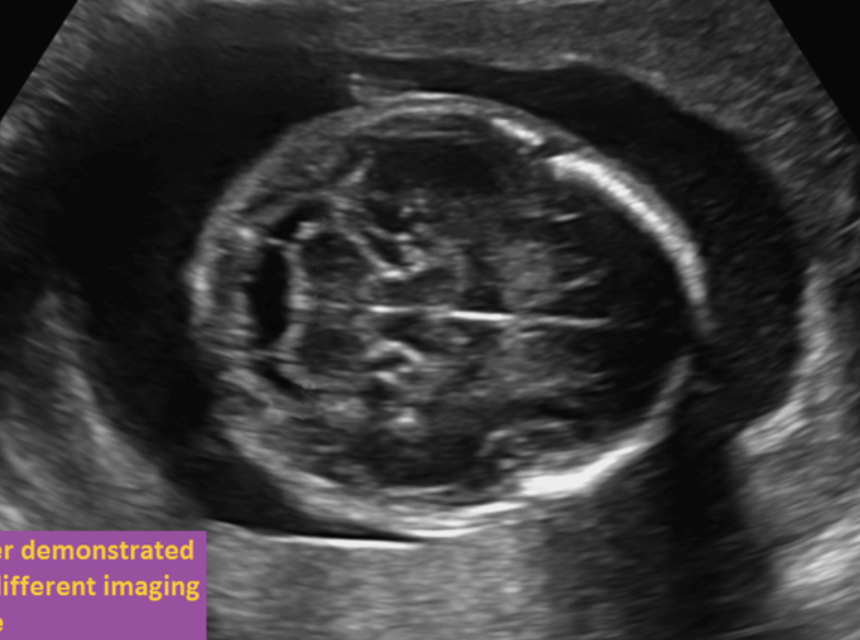
if the fetus is in breech position, where is the left lobe of the cerebellum
a) top
b) bottom
b) bottom

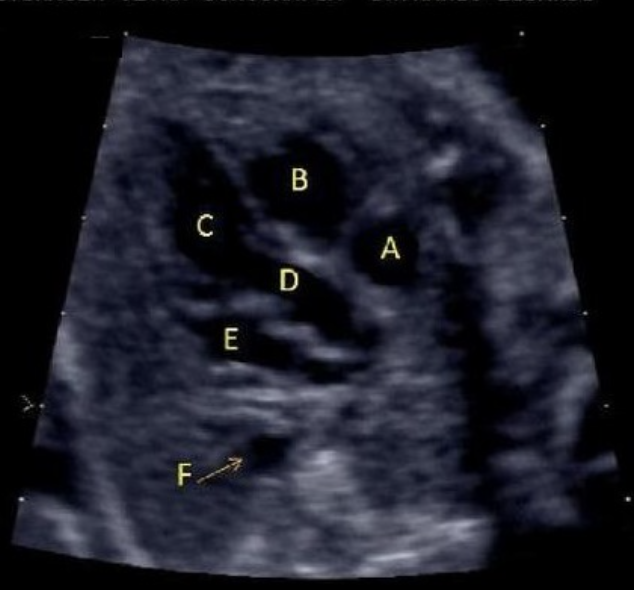
what is letter E
a) left ventricle
b) LVOT
c) RVOT
d) right atrium
e) left atrium
e) left atrium

in a normal pregnancy, the placental thickness should relatively be equal to the
a) cervix length
b) gestational age in weeks + 10mm
c) gestational age in weeks
d) fetal head circumference
b) gestational age in weeks + 10mm

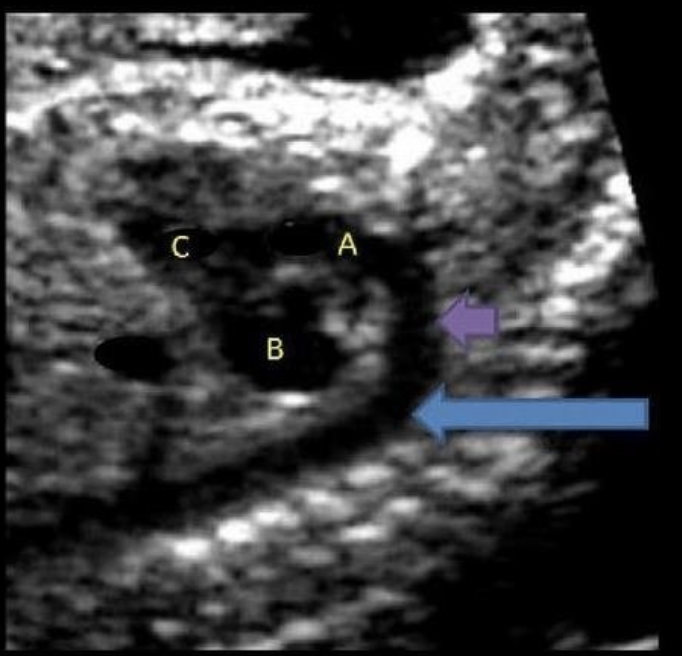
letter C is what
a) left atrium
b) left ventricle
c) right atrium
d) right ventricle
b) left ventricle

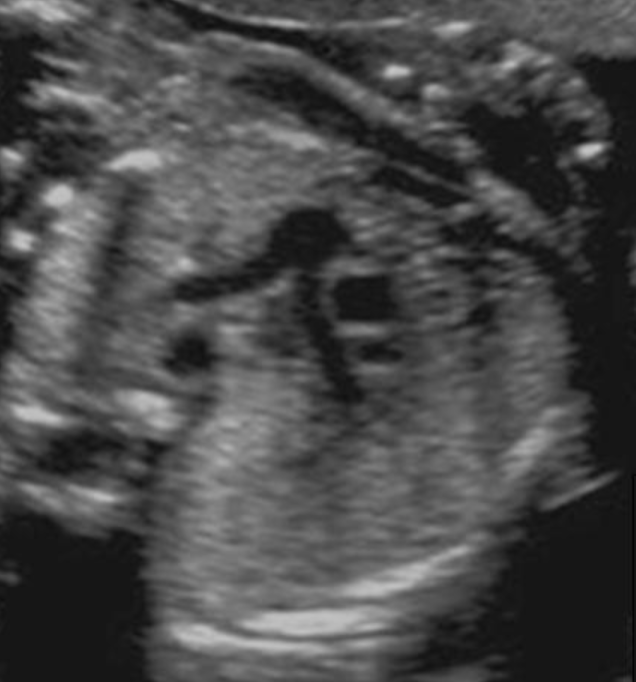
where is superior vena cava
type “next to ascend AO w/o branches”
next to ascend AO w/o branches
at what gestational age does the fetus completely take over the amniotic fluid production
a) 12 weeks
b) 20 weeks
c) 24 weeks
d) 16 weeks
d) 16 weeks

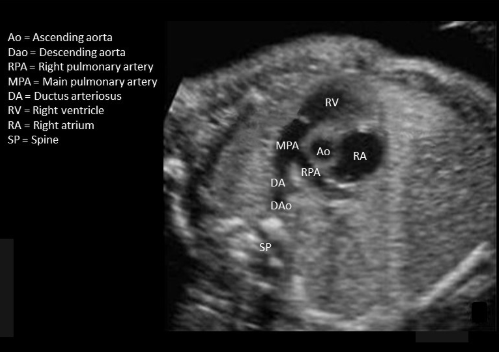
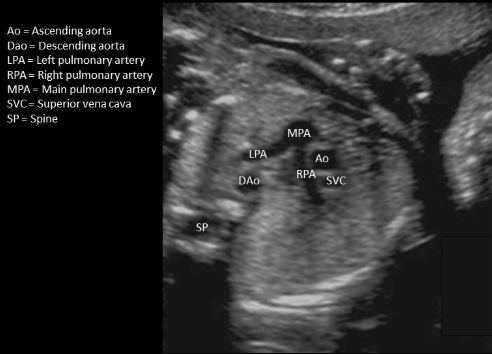
where is ascending AO - not seen in this image
type “seen in LVOT tract + aortic arch view”
this is descending AO
seen in LVOT tract + aortic arch view

the visualization of a normal stomach indicates a normal ___ is present
a) palate
b) colon
c) small intestine
d) esophagus
d) esophagus
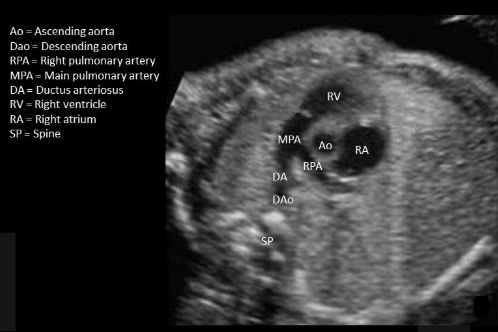
where is ductus arteriosus
type “MPA-DA-DAo”
MPA-DA-DAo
the normal heart occupies about ___ of the fetal chest
a) 33%
b) 55%
c) 60%
d) 25%
a) 33%
the fetal testicles normally descend into the scrotum before ___ weeks gestation
a) 26
b) 22
c) 16
d) 34
d) 34

the normal flow direction through the fetal foramen ovale is
a) left to right atrium
b) pulmonary artery to AO
c) right to left atrium
d) umbilical vein to fetal IVC
c) right to left atrium

the level of amniotic fluid continues to rise throughout pregnancy until approximately ___ weeks in gestational age where it will plateau then decline until birth
a) 16
b) 20
c) 28
d) 33
d) 33
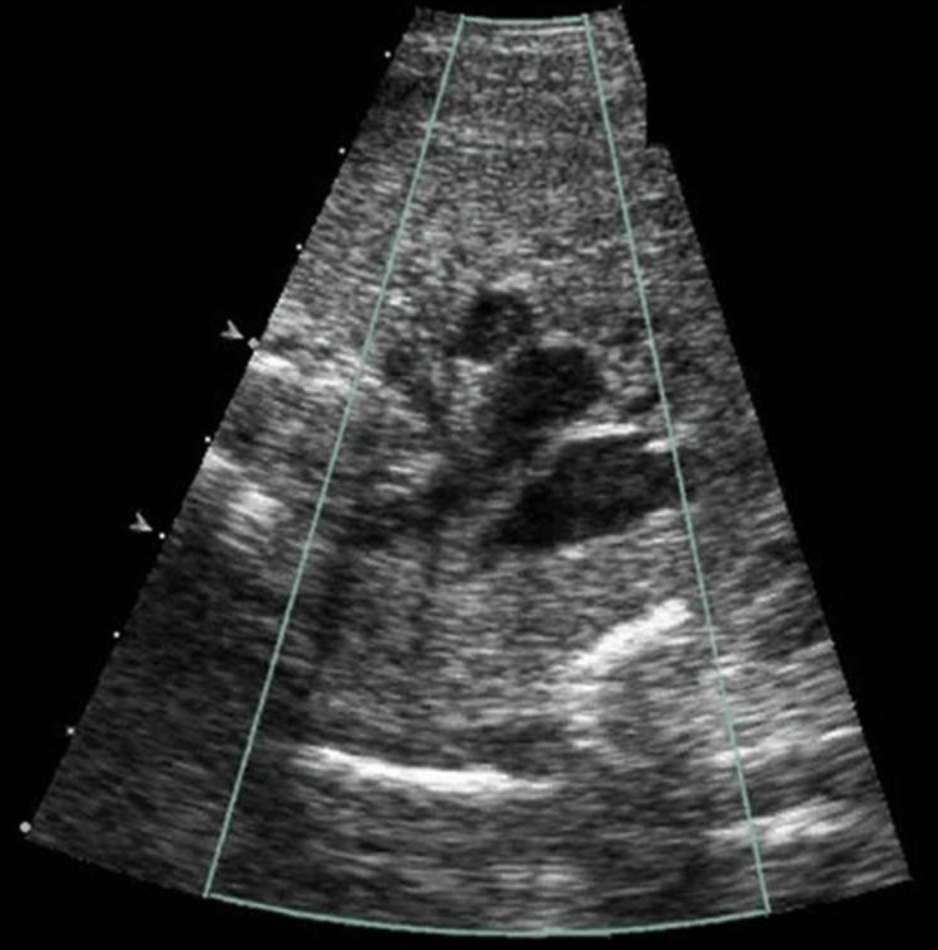
the blue arrow is
a) main pulmonary artery
b) aortic arch
c) descending aorta
d) ascending aorta
c) descending aorta
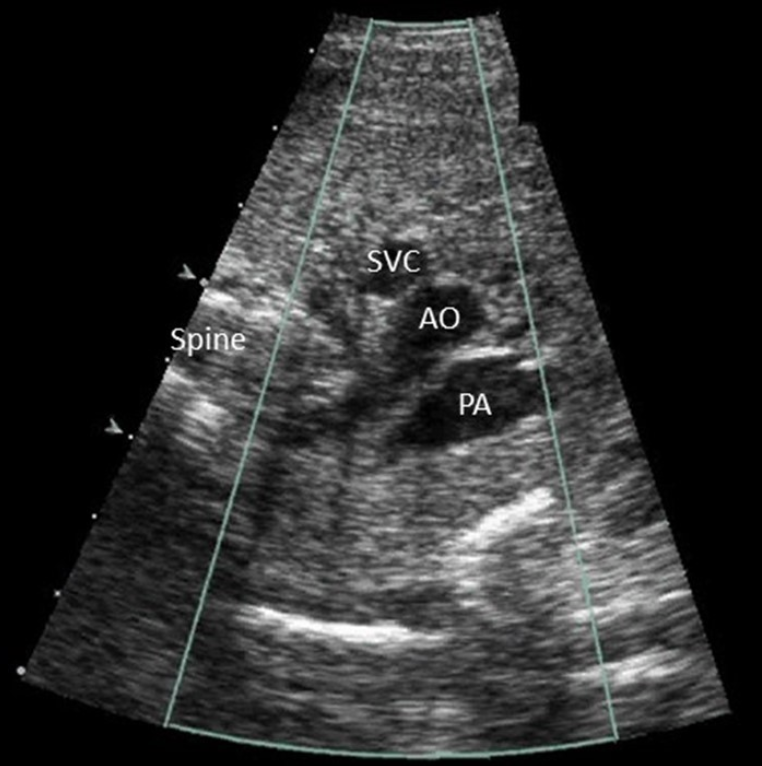
where is the AO in this 3 vessel view - which dot is it
a) top
b) middle
c) bottom
b) middle
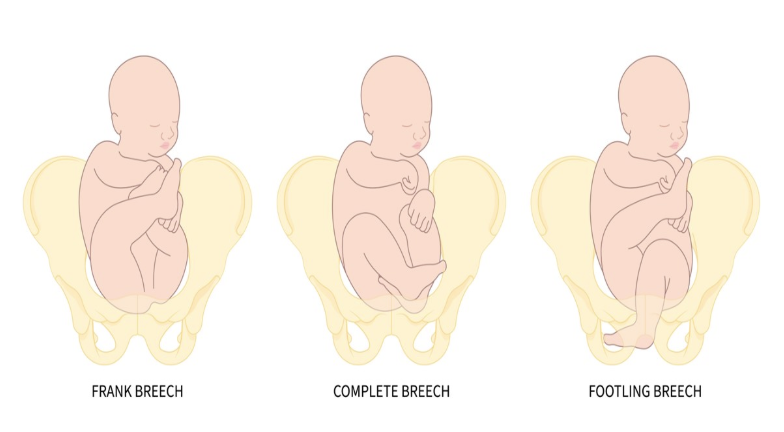
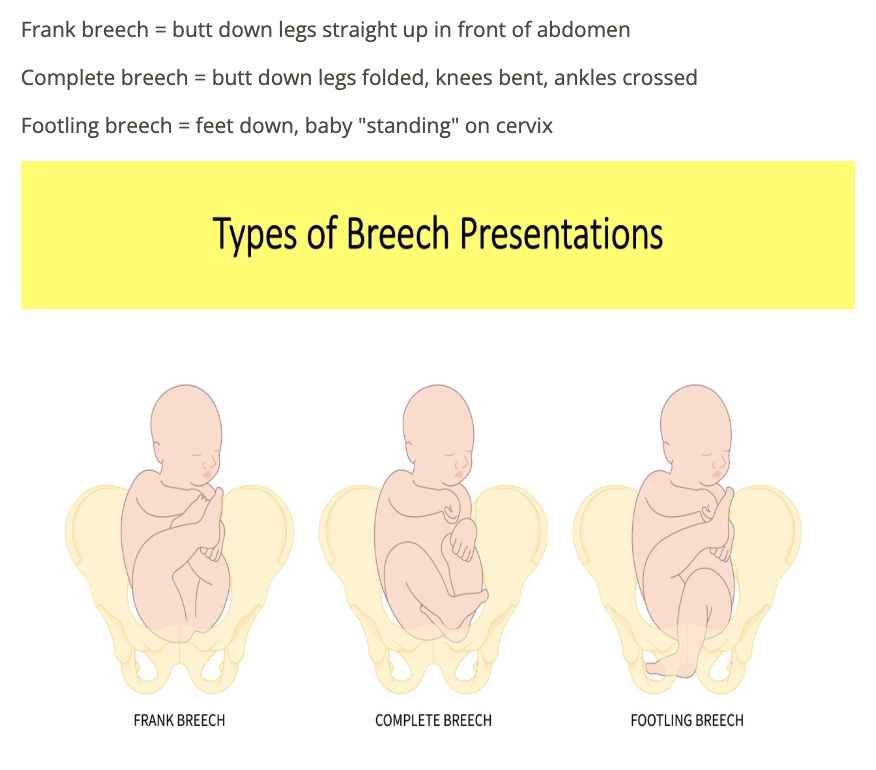
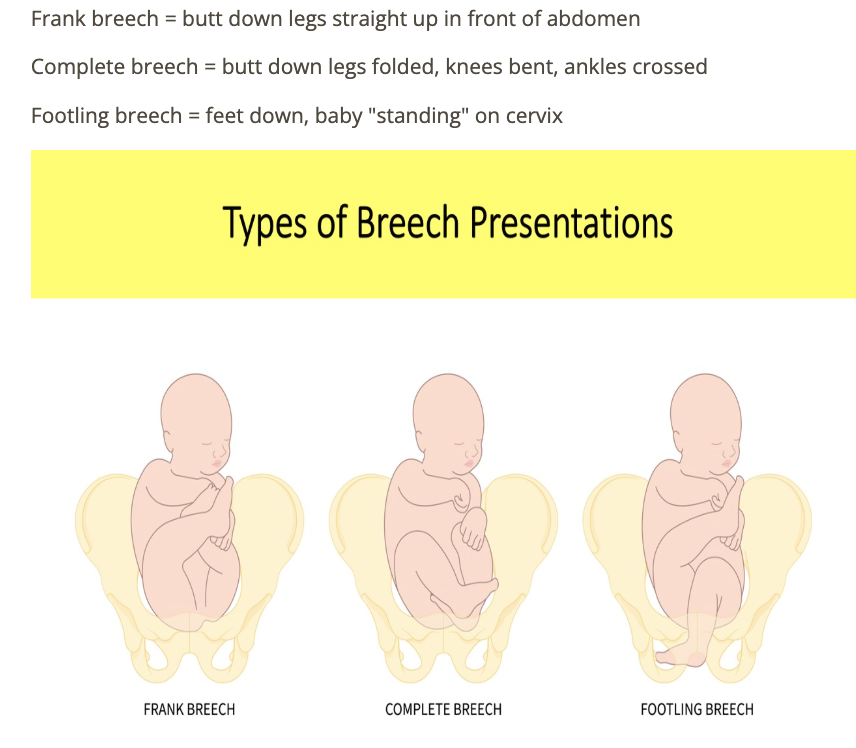
which type of breech is defined as fetus w/1 or both feet in the lower uterine segment
a) frank
b) partial
c) footling
d) complete
c) footling
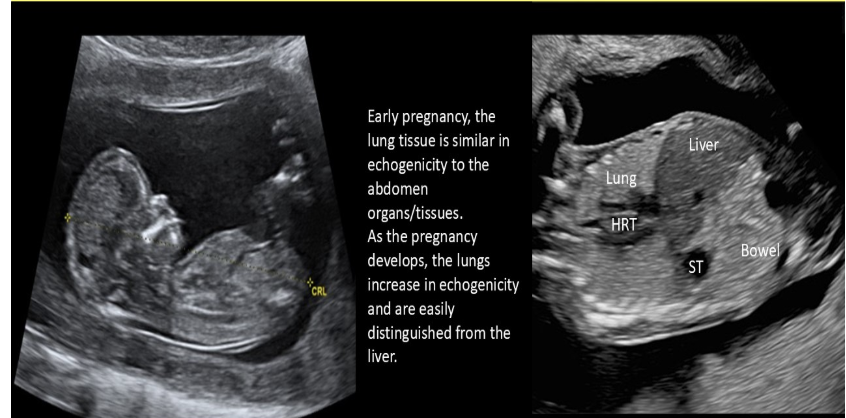
as the pregnancy advances, the sonographic appearance of fetal lungs will
a) decrease in echogenicity
b) become more anechoic
c) become increasingly heterogeneous
d) increase in echogenicity
d) increase in echogenicity
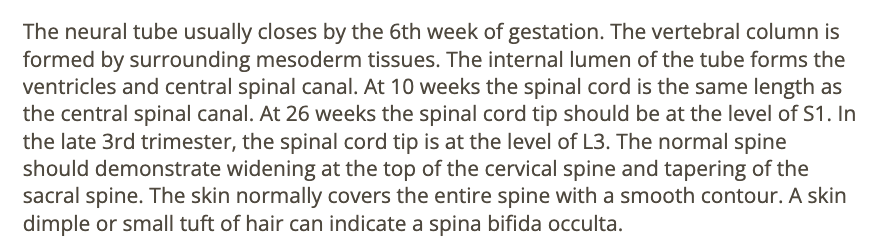
all describes a normal fetal spine except
a) in late 3rd trimester, the spinal cord tip is at level L3
b) widening of proximal spine
c) a skin dimple on the back marks the tip of normal spinal cord
d) tapering of the sacral spine
c) a skin dimple on the back marks the tip of normal spinal cord
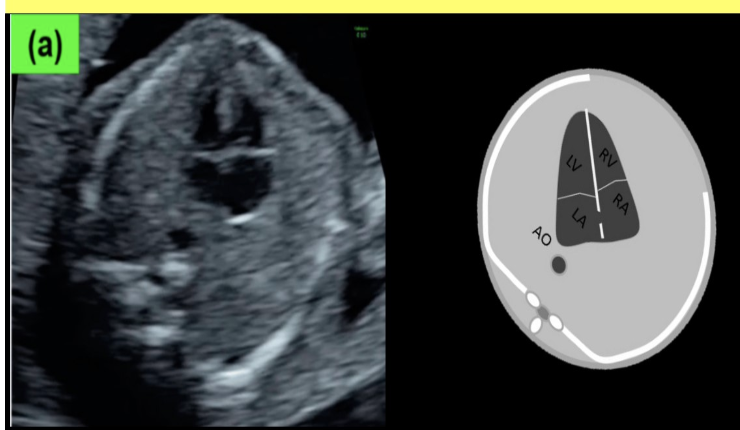
in a normal 4 chamber heart view, what cardiac chamber is closest to the spine
a) right ventricle
b) left ventricle
c) left atrium
d) right atrium
c) left atrium
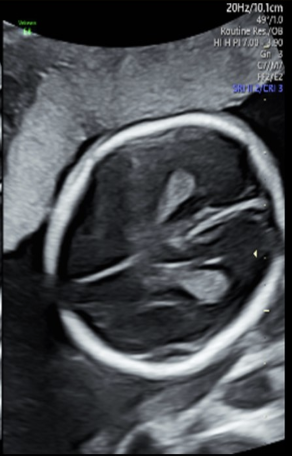
which normal cranial structures are identified within the lateral ventricles bilaterally
a) lobes of thalamus
b) choroid plexus
c) cerebellar pedicles
d) cavum septum pellucidum
b) choroid plexus
which type of breech is it when the fetus is butt first with legs extended adjacent to fetal abdomen
a) partial
b) complete
c) frank
d) footling
c) frank
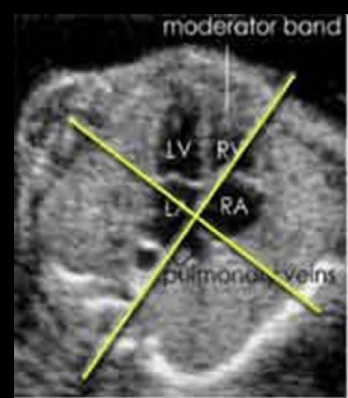
the fetal heart normally sits at a ___ degree angle in the chest with the apex pointed toward the left anterior chest wall
a) 30
b) 45
c) 60
d) 90
b) 45
normal amniotic fluid levels are mandatory for proper development of the fetal
a) lungs
b) kidneys
c) bladder
d) digestive tract
a) lungs

what is the function of the choroid plexus
a) releasing multiple types of hormones that control fetal growth + metabolism
b) production of cerebrospinal fluid
c) releasing multiple types of hormones that control fetal circulation + blood pressures
d) releasing multiple types of hormones that control fetal lung maturation
b) production of cerebrospinal fluid
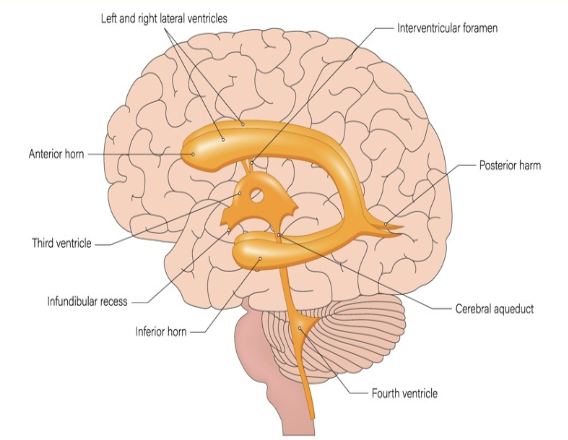
the aqueduct of sylvius connects the __ in the brain
a) 3rd + lateral ventricles
b) lateral + 4th ventricles
c) 4th ventricle + cisterna magna
d) 3rd + 4th ventricles
d) 3rd + 4th ventricles
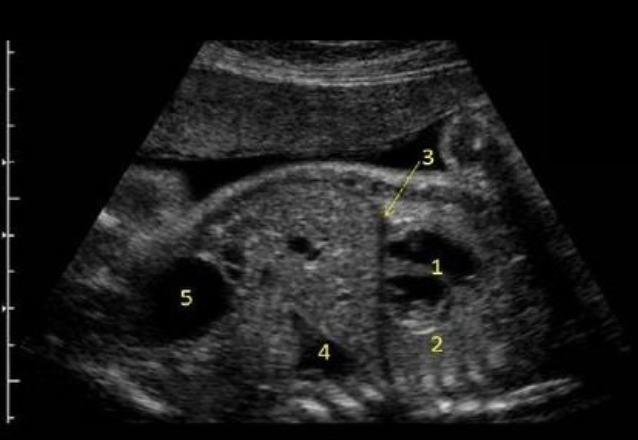
the normal corpus luteal cyst seen in pregnancy begins to regress at ___ weeks gestation and should be totally resolved by week
a) 14, 16
b) 16, 20
c) 12, 16
d) 20, 28
a) 14, 16
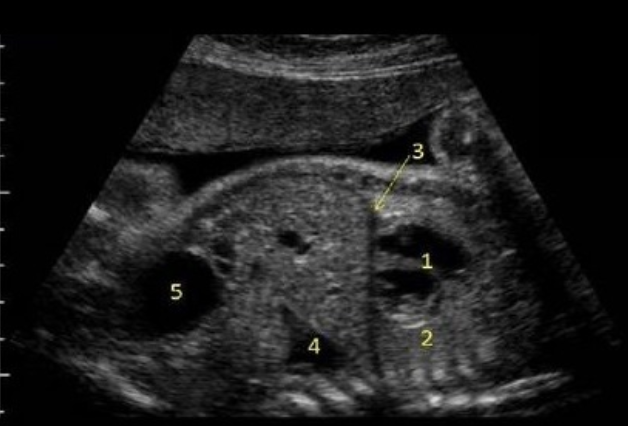
what is #1
a) bladder
b) stomach
c) heart
d) rhombencephalon
c) heart

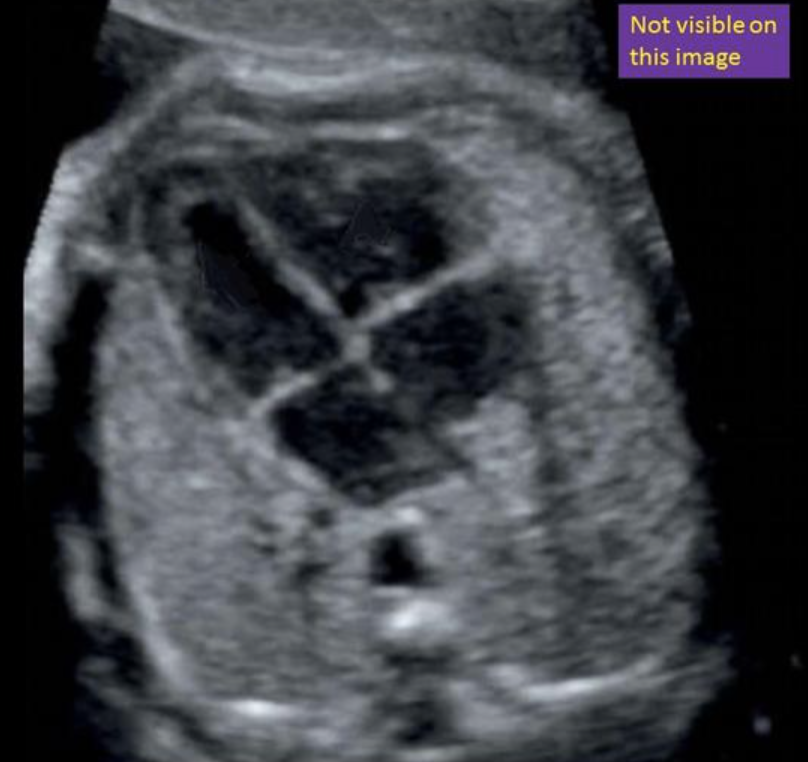
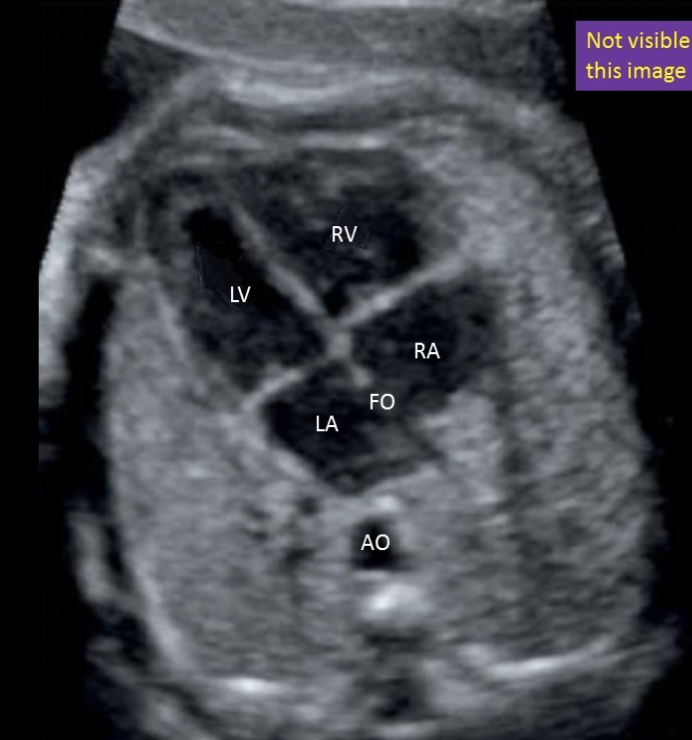
where is the inferior vena cava
“not visible w/4CH view”
inferior to right atrium
not visible w/4CH view

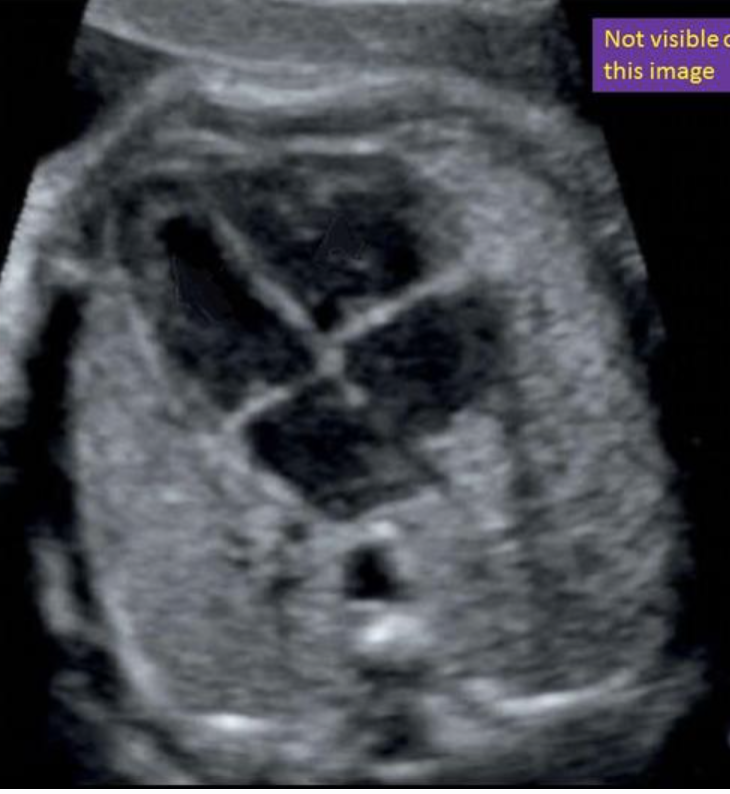
where is the right atrium
type “bottom right”
bottom right
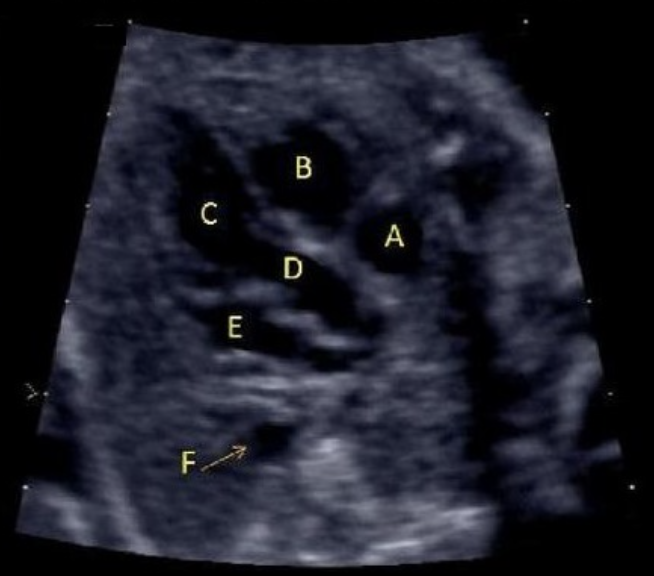
what is letter F
a) LVOT
b) left atrium
c) ascend aorta
d) coronary sinus
e) right atrium
c) ascend aorta

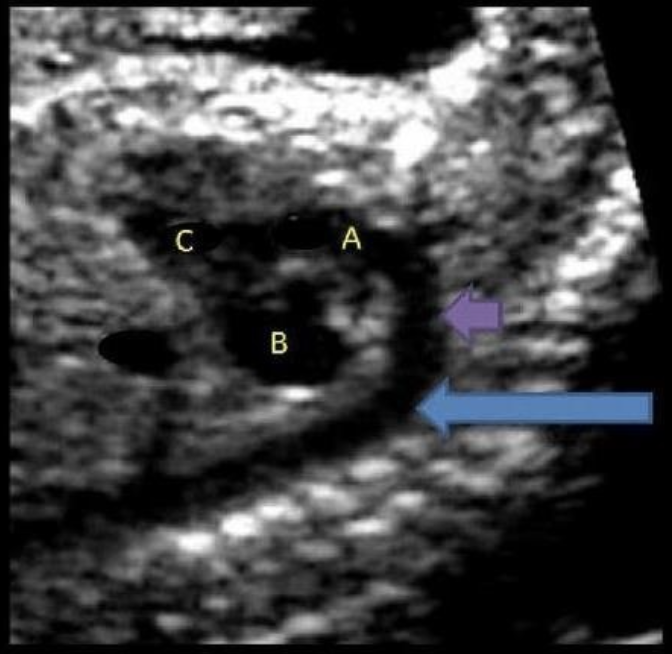
what is letter B
a) left atrium
b) left ventricle
c) right atrium
d) right ventricle
a) left atrium

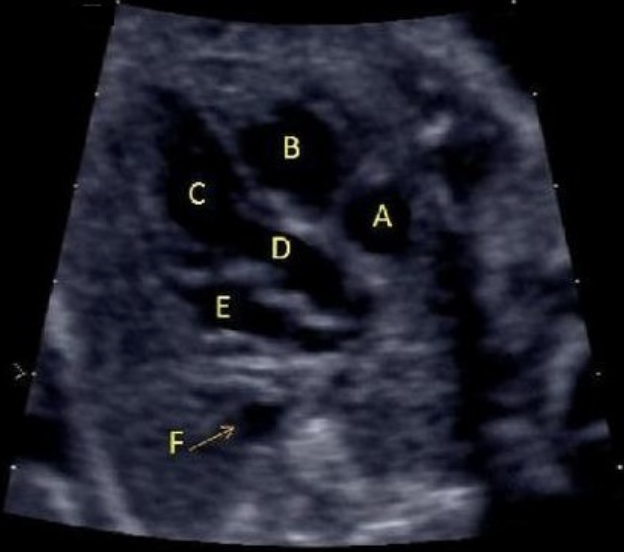
letter A is
a) left atrium
b) RVOT
c) LVOT
d) right ventricle
e) right atrium
e) right atrium

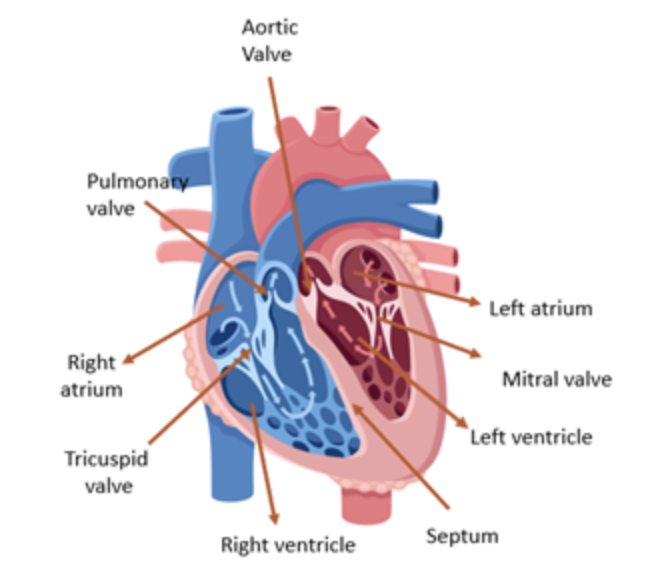
the right atrium receives blood from
a) SVC
b) pulmonary veins
c) pulmonary arteries
d) ductus arteriosus
a) SVC

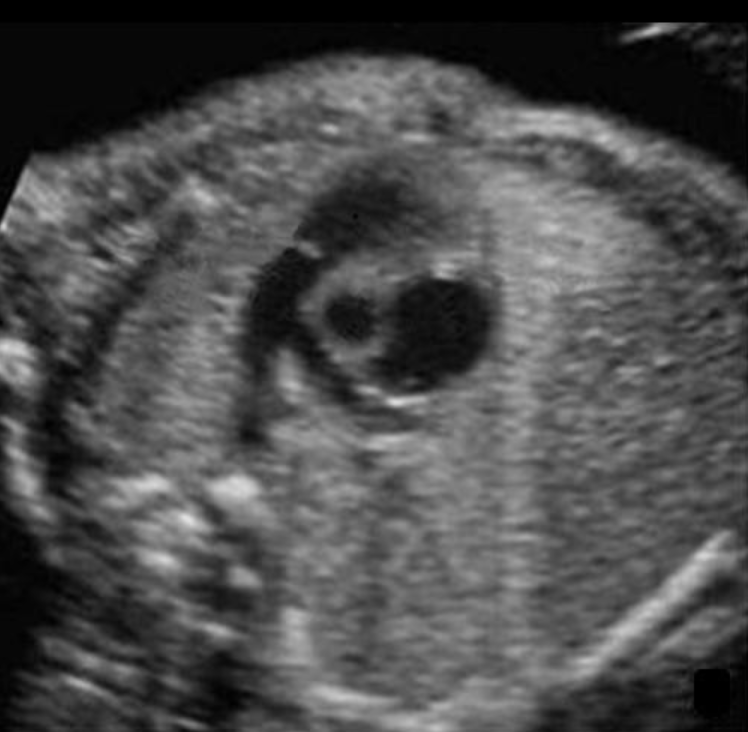
where is the descending AO
under ductus arteriosus
under ductus arteriosus
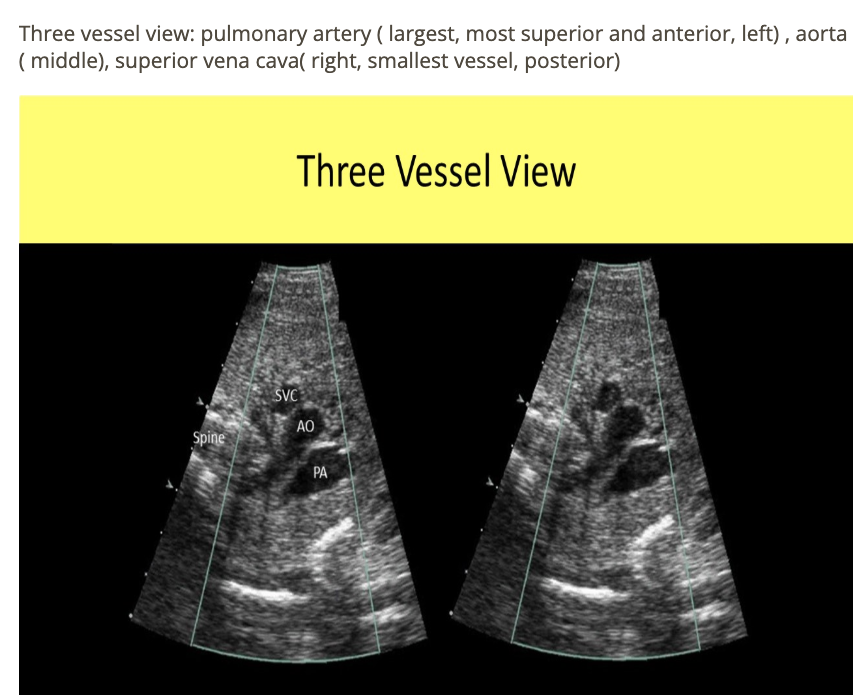
the 3 vessel view of the fetal heart shows all except
a) inferior vena cava
b) superior vena cava
c) pulmonary artery
d) AO
a) inferior vena cava
in some adults, Meckel’s diverticulum can be identified as a remnant of fetal embryology. what causes this anatomic variation?
.
a) the placental umbilical cord attachment persists as a diverticulum in the ileum portion of the bowel
b) the placenta persists as a diverticulum in the ileum portion of the bowel
c) the gestational sac persists as a diverticulum in the ileum portion of the bowel
d) the yolk sac persists as a diverticulum in the ileum portion of the bowel
d) the yolk sac persists as a diverticulum in the ileum portion of the bowel
which cardiac chamber is normally located most anterior in the fetus
a) left ventricle
b) left atrium
c) right ventricle
d) right atrium
c) right ventricle
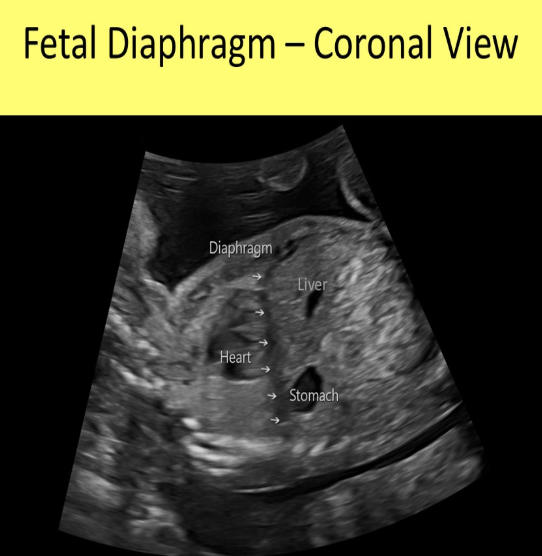
which describes the normal fetal diaphragm
a) hyperechoic dome shaped structure w/the top of the dome facing cephalad
b) hyperechoic linear structure that separates the abd from the chest
c) hypoechoic dome shaped structure w/the top of the dome facing cephalad
d) hypoechoic cup shaped structure w/the bottom of the cup facing caudal
c) hypoechoic dome shaped structure w/the top of the dome facing cephalad
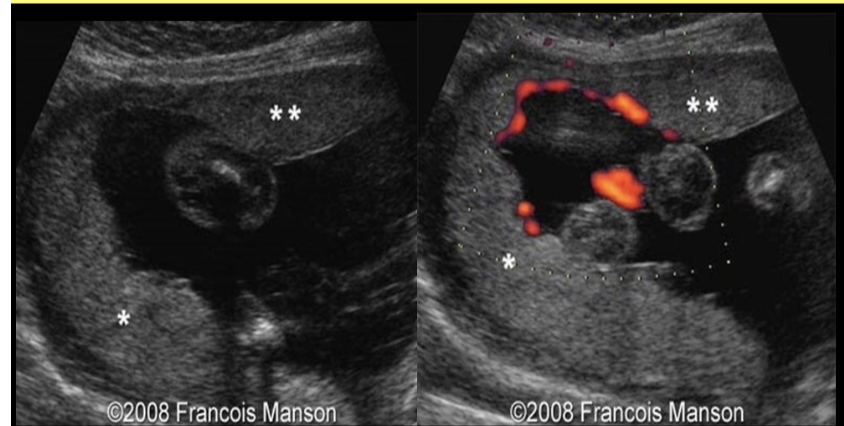
which is described as ectopic lobes of placenta tissue separate from the main placenta
a) placenta previa
b) placenta accreta
c) succenturiate placenta
d) placenta increta
c) succenturiate placenta

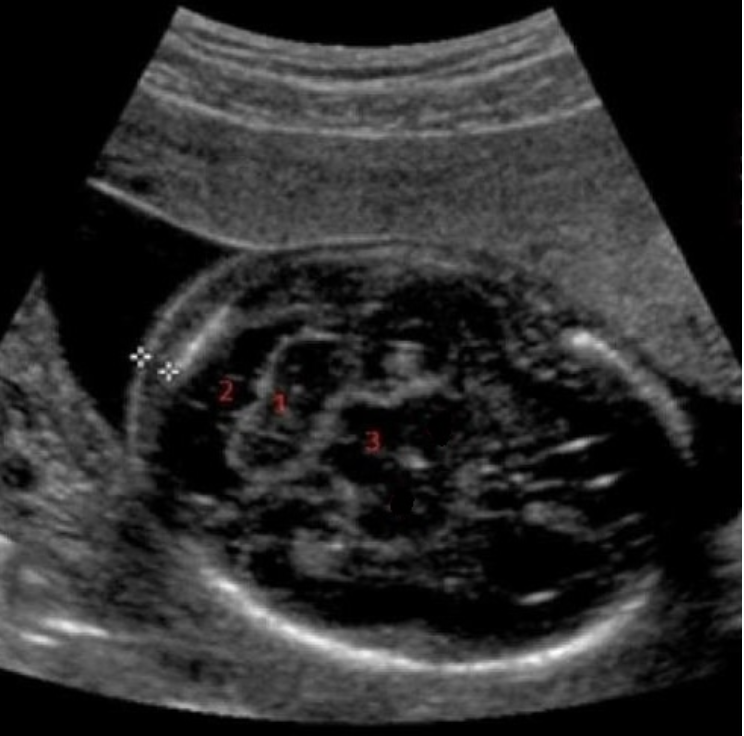
what is #2
a) caudate nucleus
b) cisterna magna
c) cerebellum
d) nuchal skin fold
b) cisterna magna

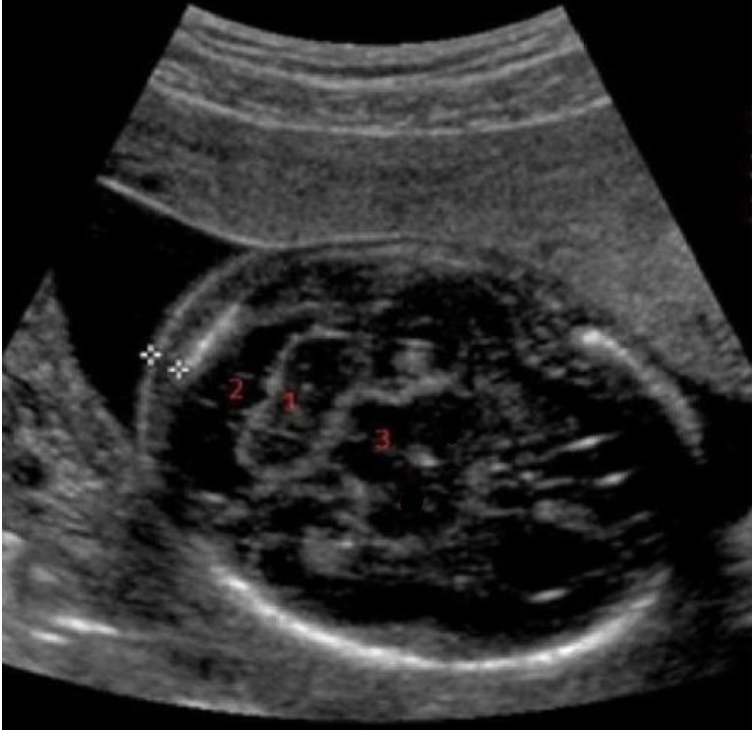
what is #1
a) nuchal skin fold
b) cerebellum
c) caudate nucleus
d) cisterna magna
b) cerebellum

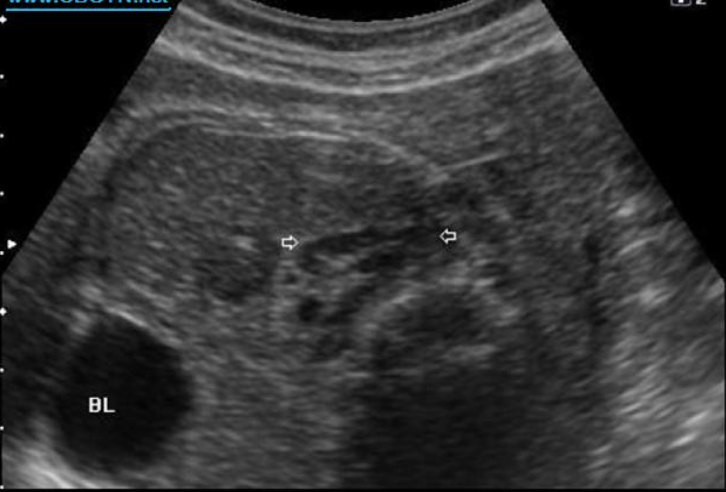
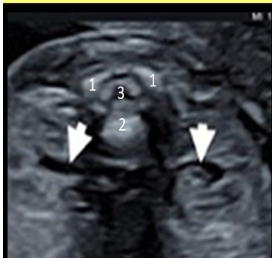
what are the white arrows pointing to
a) neuroblastoma
b) normal adrenal gland
c) normal kidney
d) collapsed bowel
b) normal adrenal gland
in normal pregnancies, fetal age derived from biometric measurements should be within ___ of the average fetal parameter age for that measurement
a) 15%
b) 5%
c) 7.5%
d) 10%
d) 10%
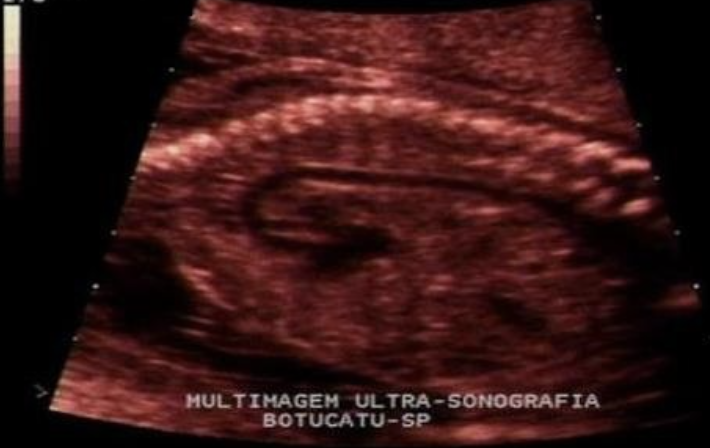
the image is taken from ___ view to evaluate ___
a) sagittal, AO
b) sagittal, IVC
c) coronal, AO
d) coronal, IVC
a) sagittal, AO

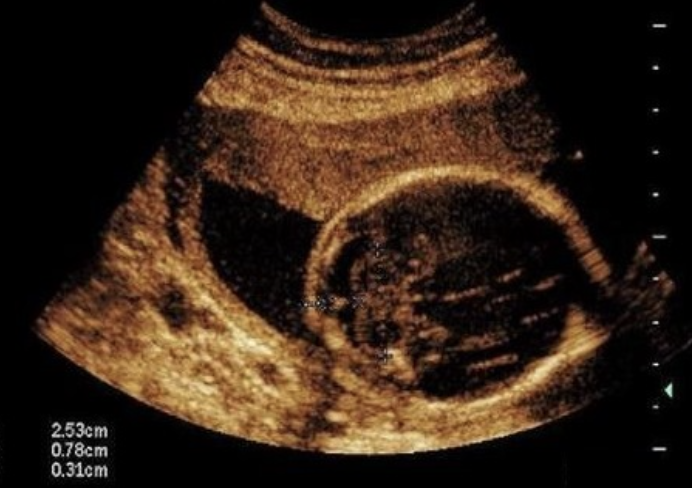
where is the placenta
a) low lying
b) posterior
c) anterior
d) fundal
c) anterior
the cisterna magna is enlarged if it measures more than
a) 5mm
b) 7mm
c) 10mm
d) 12mm
c) 10mm

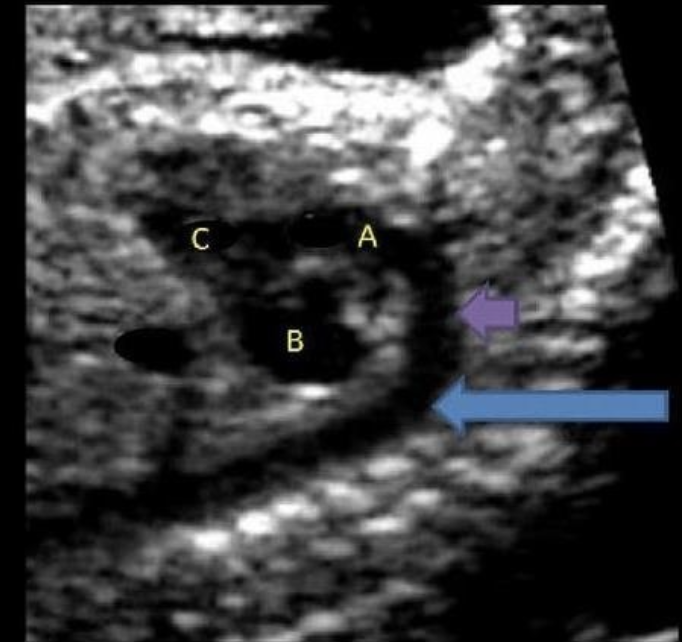
what is letter A
a) descending AO
b) ascending AO
c) main pulmonary artery
d) aortic arch
b) ascending AO

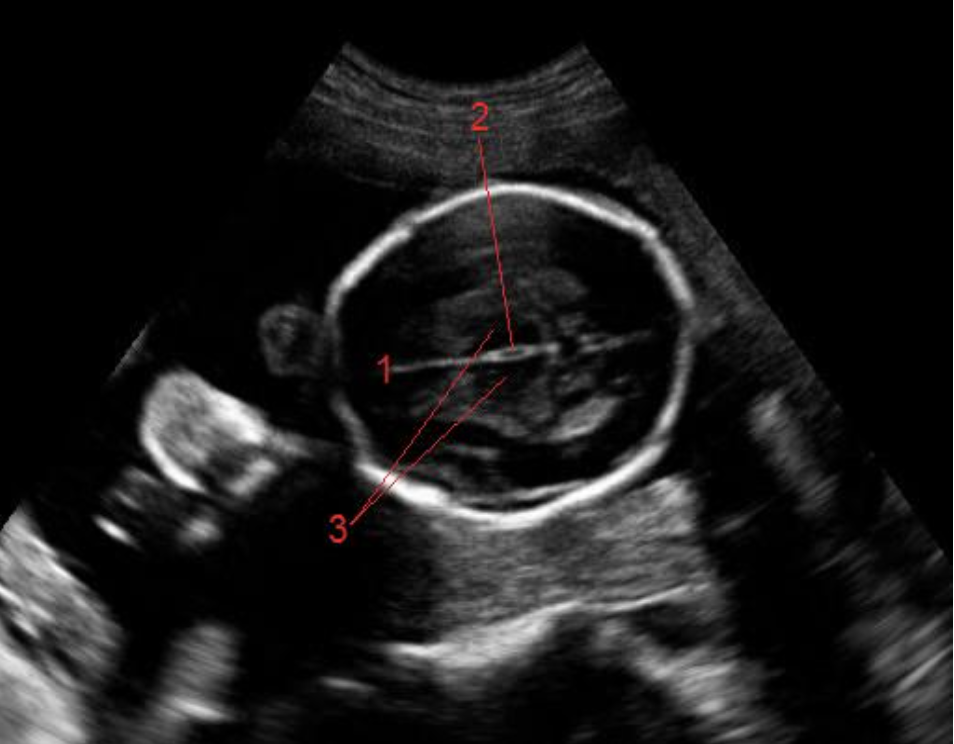
what is #2
a) fourth ventricle
b) caudate nucleus
c) third ventricle
d) corpus callosum
c) third ventricle

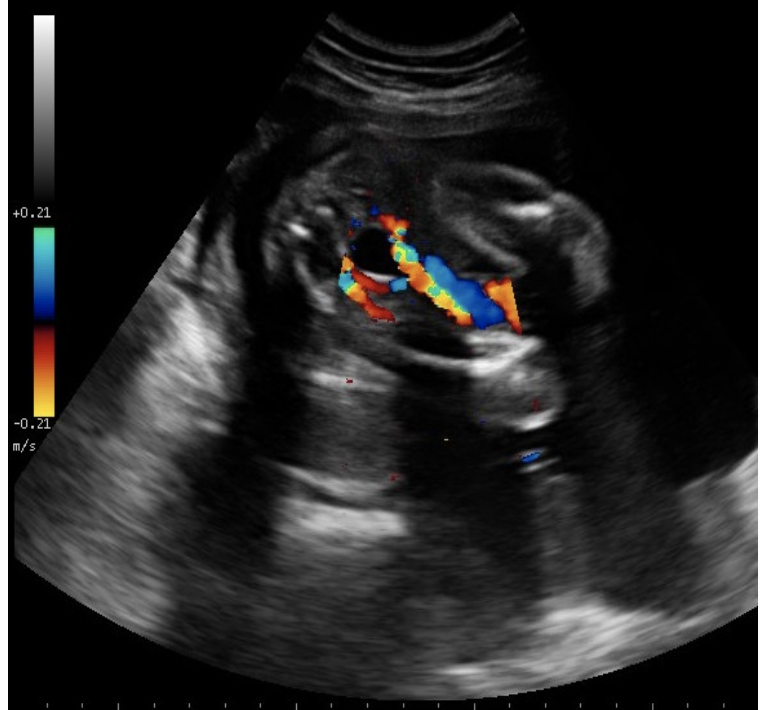
what is true
a) normal cord w/2 arteries
b) transverse view at the level of stomach
c) shows 2 vessel cord
d) shows lumbar spine + pelvic bones
a) normal cord w/2 arteries
the normal anterior-posterior renal pelvic diameter (APRPD) in a 2nd trimester fetus is ___ mm and ____ mm in a 3rd trimester fetus is considered normal
.
a) <2mm, <4mm
b) <8mm, <16mm
c) <4mm, <7mm
d) <10mm, <20mm
c) <4mm, <7mm

which cranial structure is considered abn if it increases in size between US exams performed at 20 and 28 weeks
a) choroid plexus
b) cerebellum
c) thalamus
d) lateral ventricle
d) lateral ventricle

on fetal US, the LVOT refers to the ____ and the RVOT refers to the ___
a) ascending AO, pulmonary artery
b) aortic valve, pulmonary valve
c) aortic arch, pulmonary vein
d) descending AO, peripheral pulmonary arteries
a) ascending AO, pulmonary artery
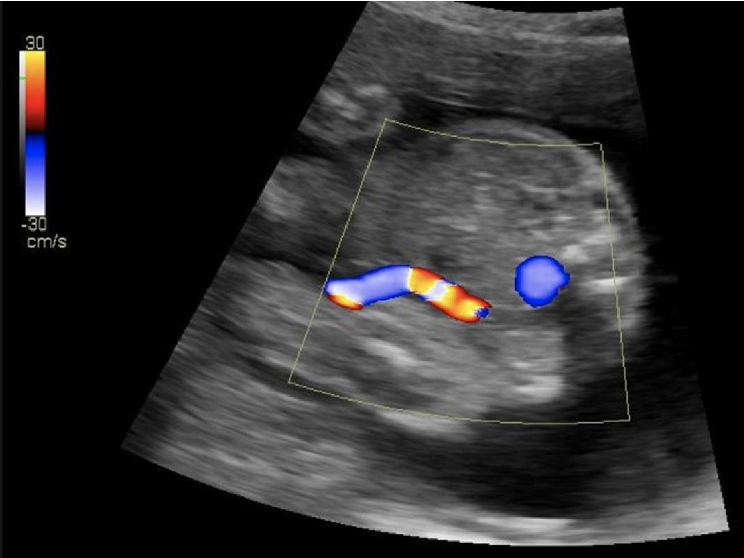
what is the blue circle
a) IVC
b) umbilical artery
c) AO
d) umbilical varix
c) AO

which type of breech when the fetus presents butt first sitting crossed legged w/knees bent
a) frank
b) footling
c) partial
d) complete
d) complete
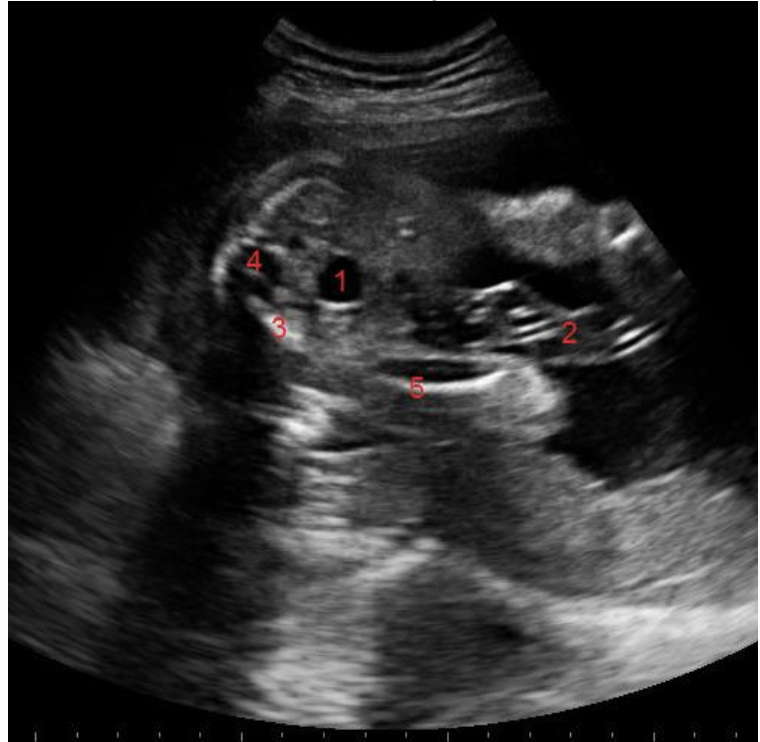
what is #3
a) cord
b) sacral spine
c) pelvic bone
d) lumbar spine
c) pelvic bone
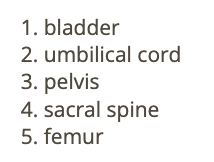
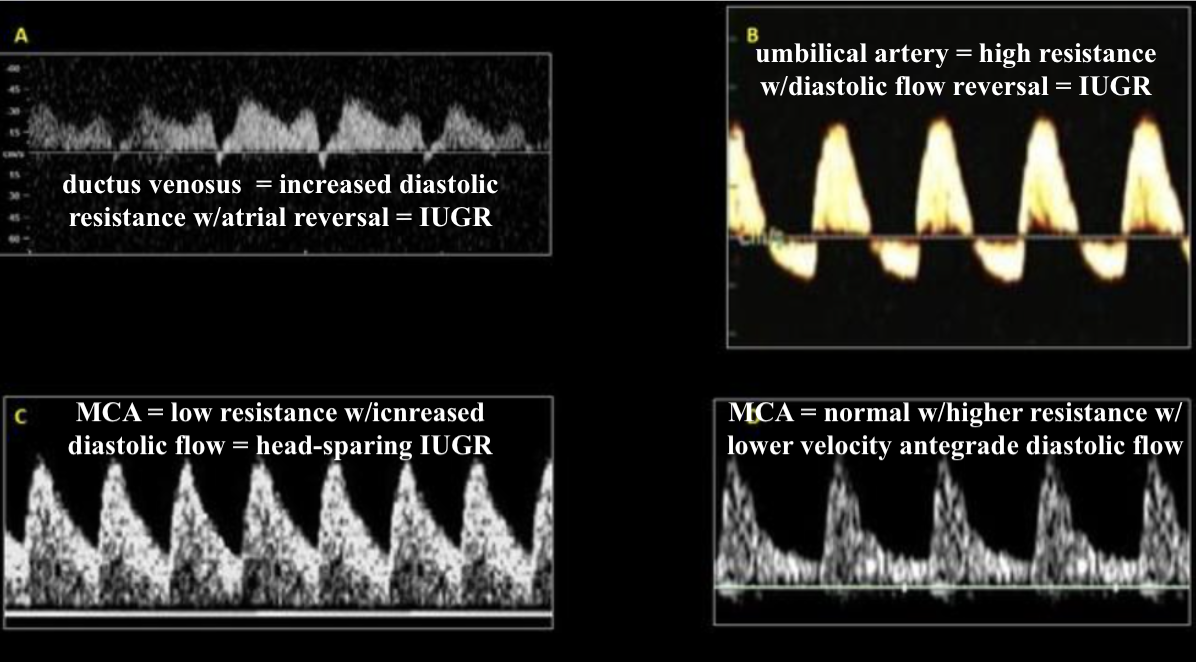
which is normal middle cerebral artery waveform
a) a
b) b
c) c
d) d
d) d
average normal heart rate in 2nd trimester is ___ BPM
a) 80-120
b) 120-160
c) 100-140
d) 160-200
b) 120-160
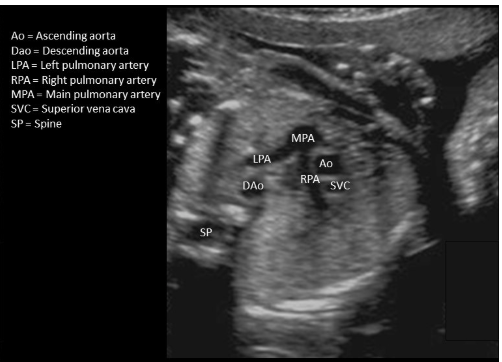
where is the ascending AO
type “MPA-AO-SVC”
MPA-AO-SVC
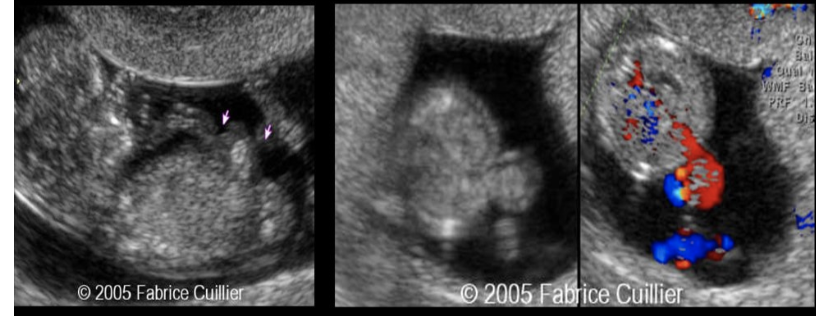
herniation of the midgut is an abn finding in gestations over ___ weeks in age
a) 8
b) 10
c) 12
d) 14
c) 12
what intracranial structure is located between the 2 lobes of the thalamus
a) pituitary gland
b) cisterna magna
c) 4th ventricle
d) 3rd ventricle
d) 3rd ventricle
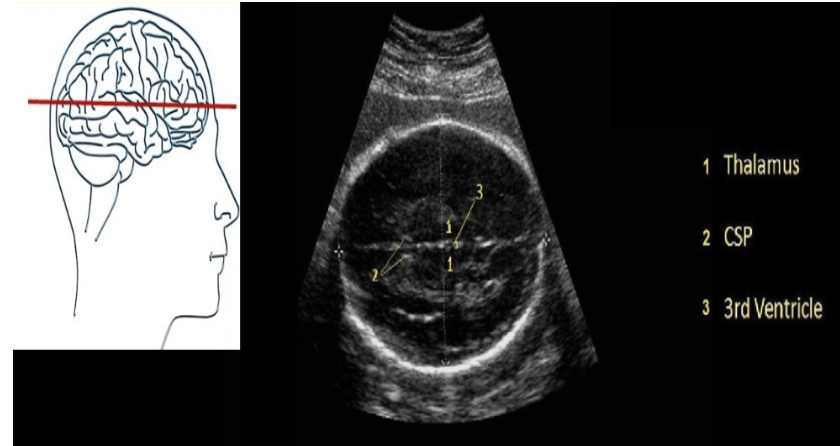
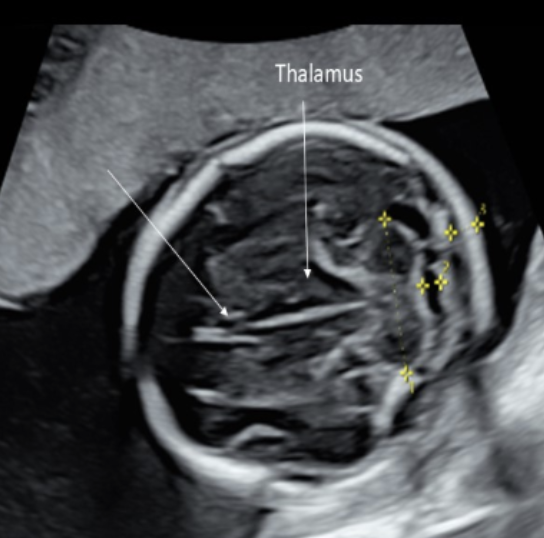
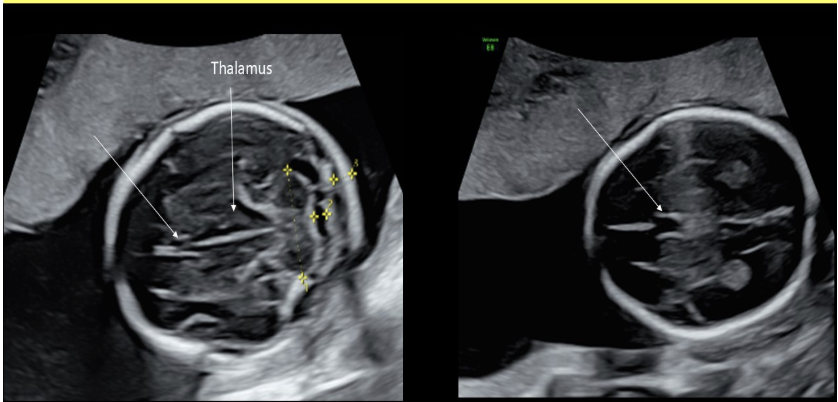
what intracranial structure is located anterior to the lobes of the thalamus
a) choroid plexus
b) 3rd ventricle
c) cavum septum pellucidum
d) cerebellum
c) cavum septum pellucidum
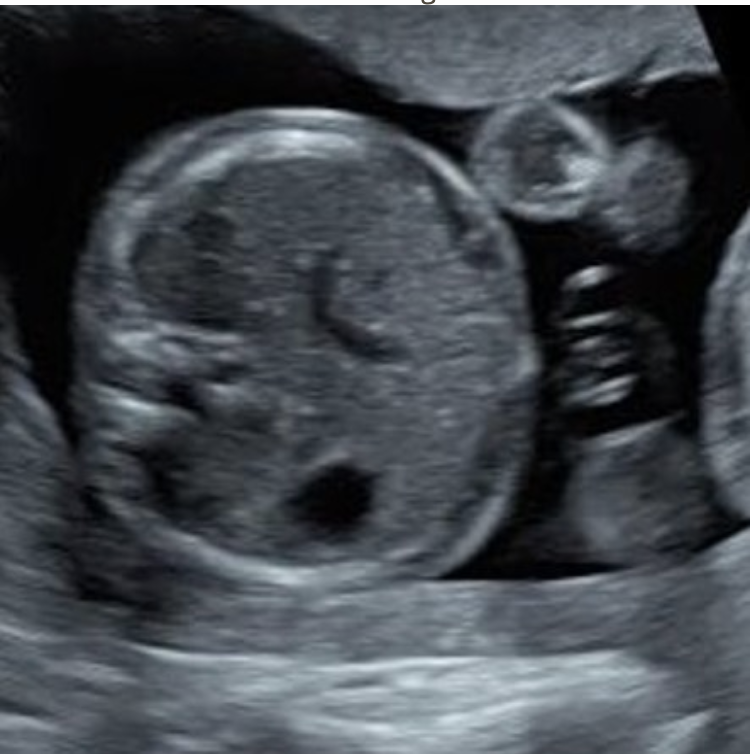
what is shown here
a) persistent right umbilical vein
b) ascites
c) pseudoascites
d) omphalocele
c) pseudoascites

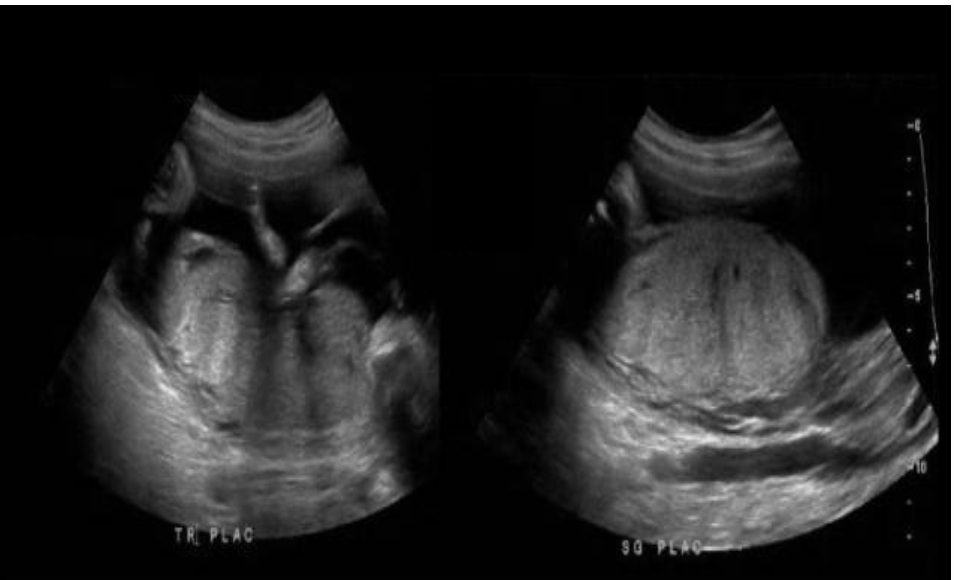
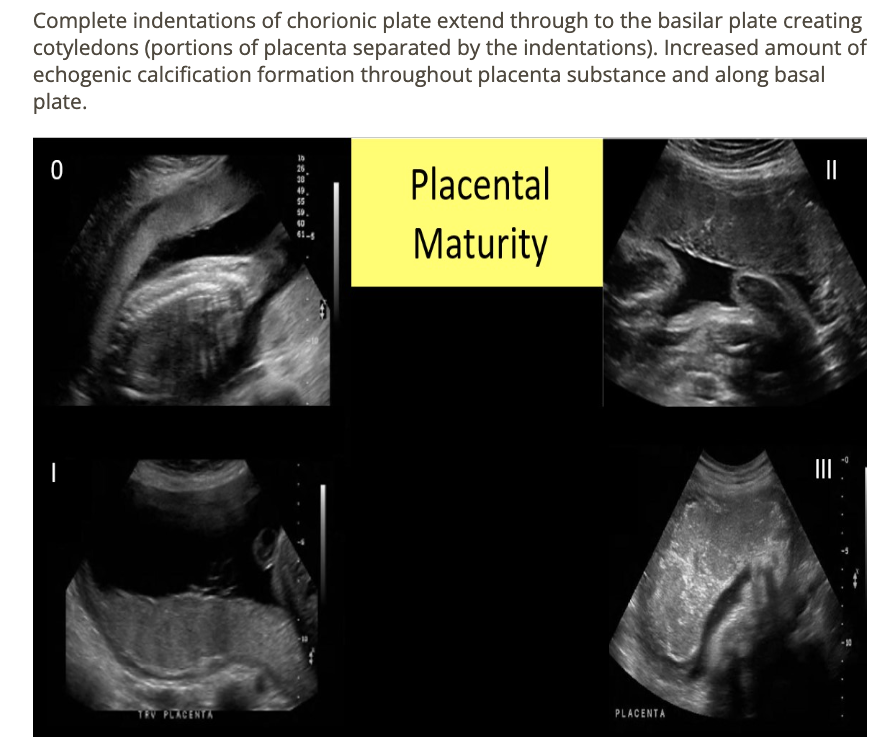
a pt is in her 2nd trimester and the placenta is being evaluated for grading. what grade is this
a) grade 0
b) grade 1
c) grade 2
d) grade 3
c) grade 2
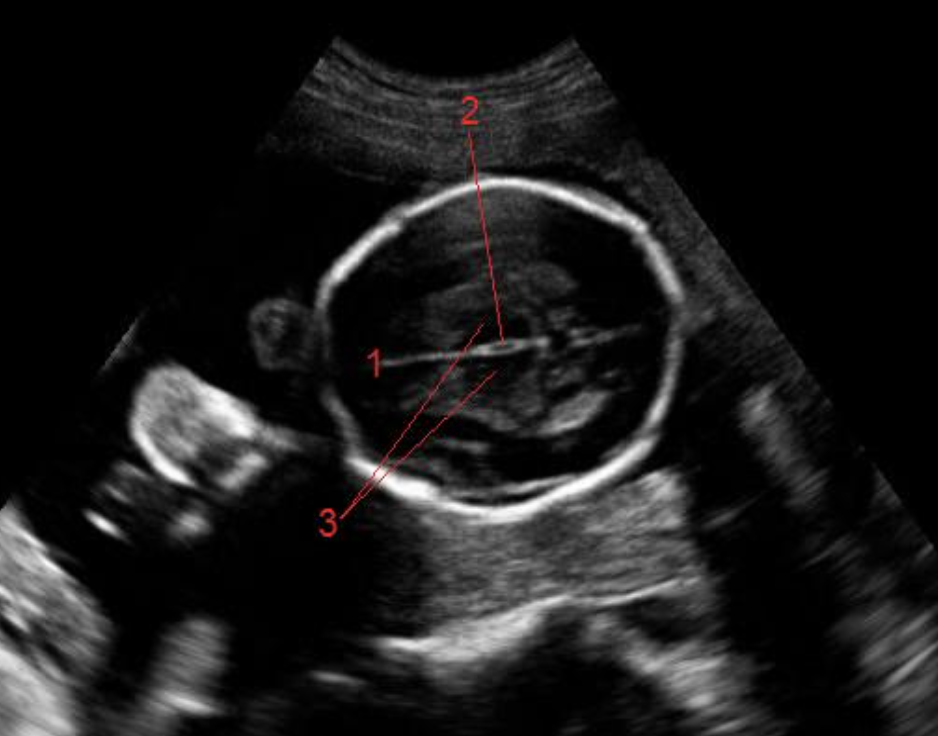
what is #1
a) cisterna magna
b) caudate nucleus
c) falx cerebri
d) corpos callosum
c) falx cerebri
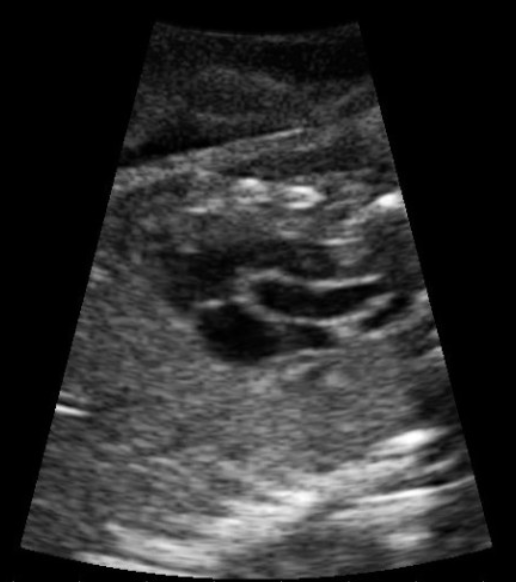
which cardiac view is this
a) LVOT
b) RVOT
c) ductus arteriosus
d) ductus venosus
a) LVOT

what is #2
a) lumbar spine
b) sacral spine
c) cord
d) extremity
c) cord

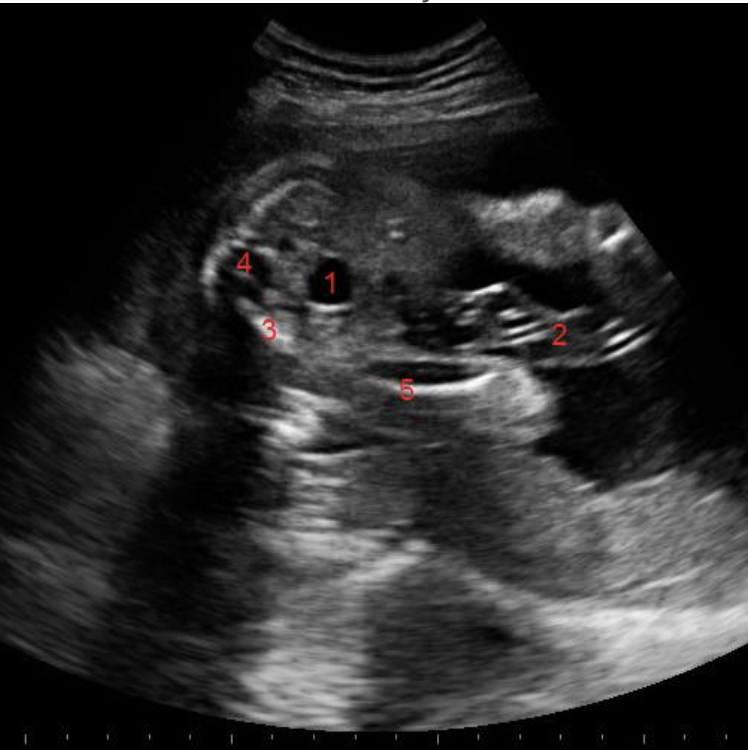
what is #5
a) rib
b) right lung
c) left lung
d) diaphragm
a) rib
chromosomal defects may be present in a pregnancy where the amnion + chorion have not completely fused by week __
a) 8
b) 12
c) 16
d) 20
c) 16

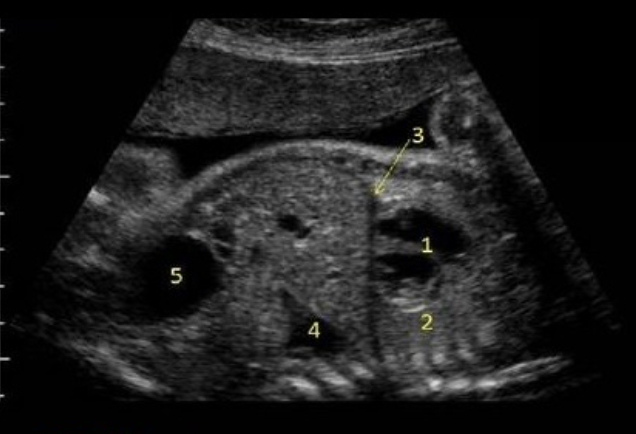
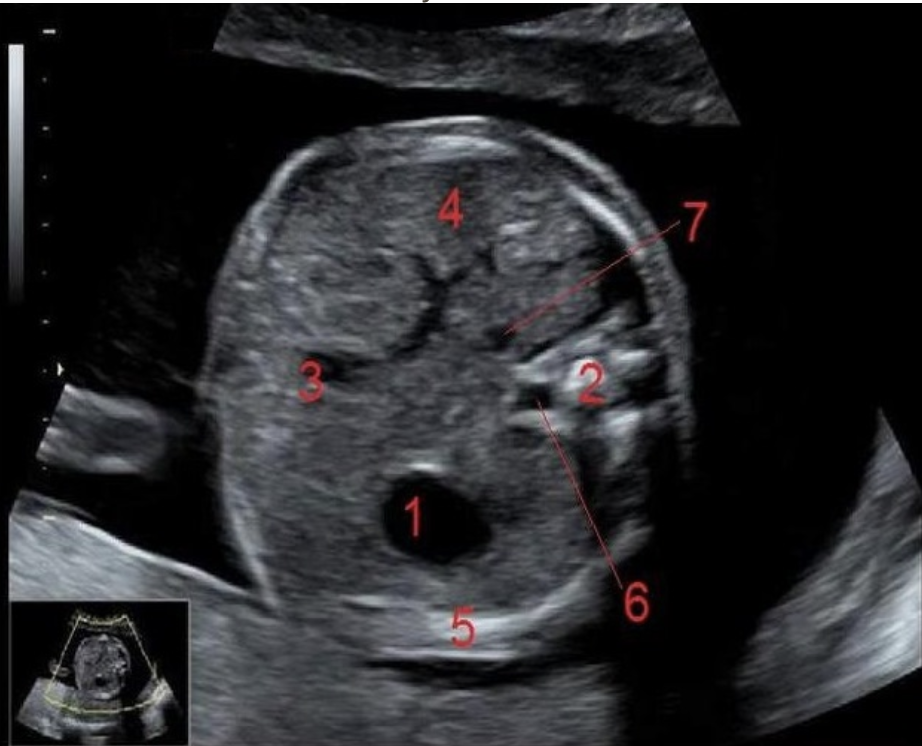
what is #4
a) hydronephrosis
b) bladder
c) stomach
d) lung tissue
c) stomach

during renal development, the kidneys normally migrate from
a) the upper abd into an inferior retroperitoneal location
b) their origination point centrally in the abd to a more lateral location adjacent to the ribs
c) the pelvic region superiorly into the lower abd
d) the lower right side of the spine superiorly and separate once the fetus reaches 11 weeks
c) the pelvic region superiorly into the lower abd
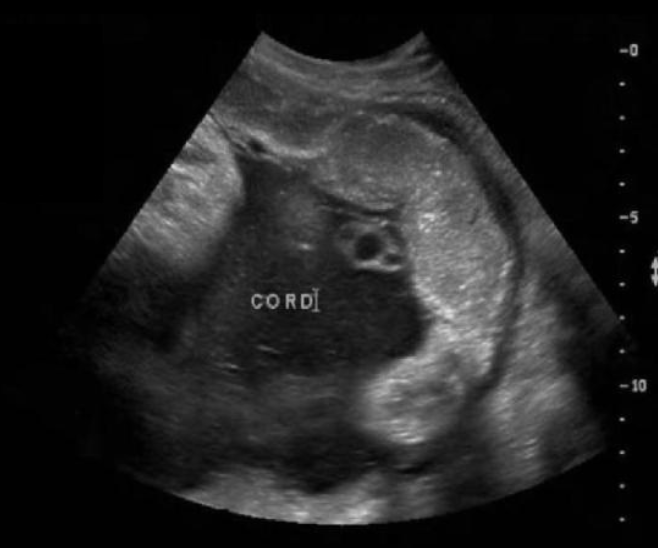
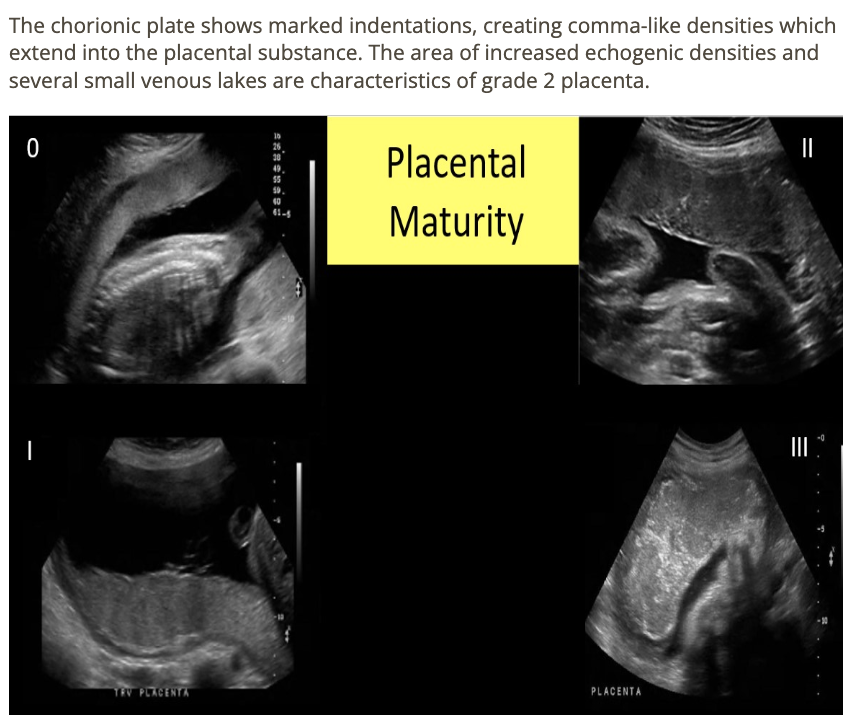
what grade is the placenta
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
d) 3
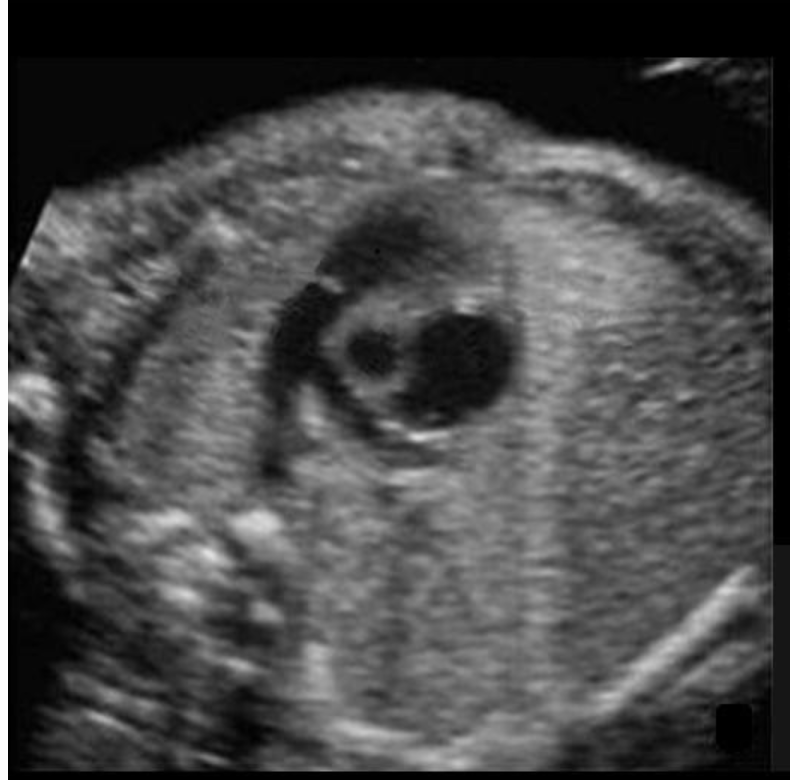
where is the ascending AO
type “between main pulmonary artery + right atrium”
descending ao is posterior to ductus arteriosus
between main pulmonary artery + right atrium
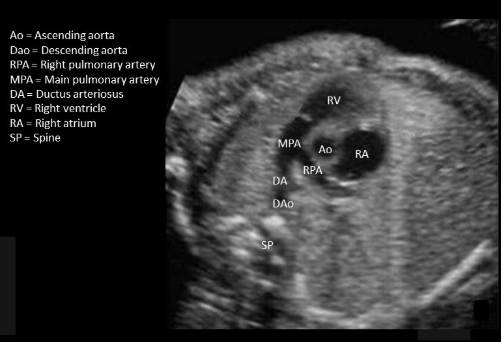
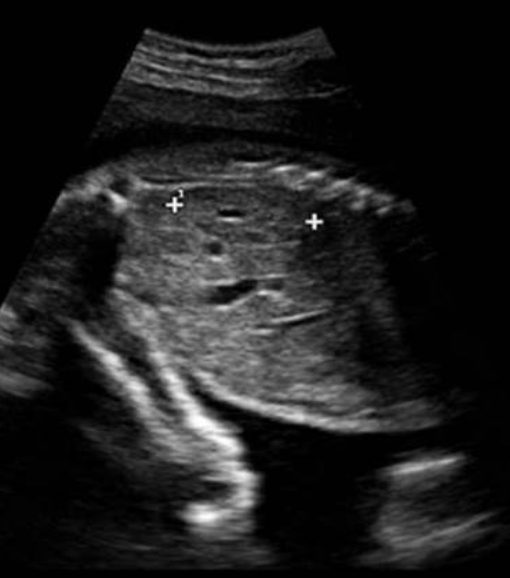
what is being measured
a) right kidney length
b) left kidney length
c) liver length
d) spleen length
a) right kidney length

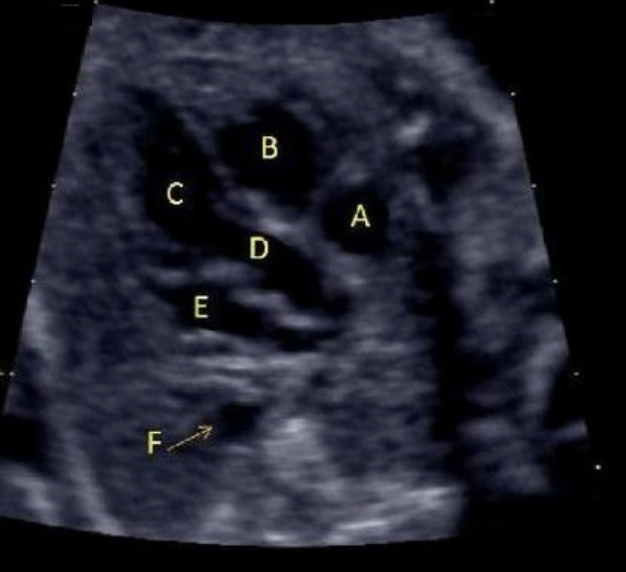
what is letter D
a) right ventricle
b) right atrium
c) left ventricle
d) LVOT
e) RVOT
d) LVOT

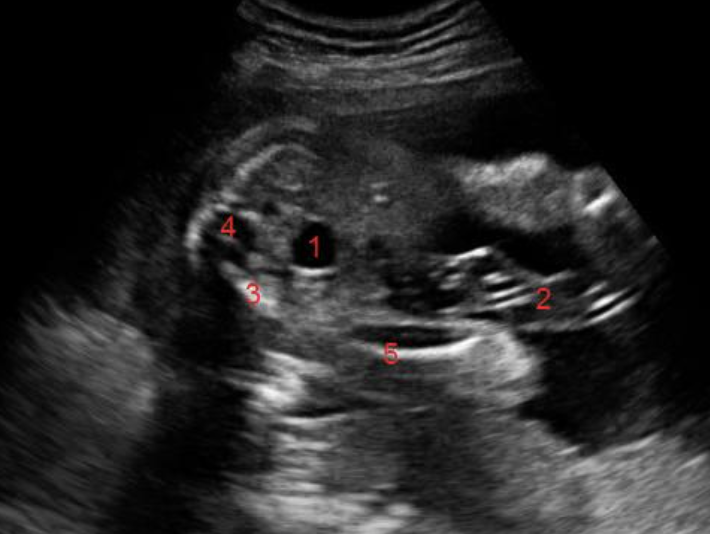
what is #4
a) cord
b) sacral spine
c) lumbar spine
d) pelvic bone
b) sacral spine

how many bones make up each fetal finger
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 5
b) 3

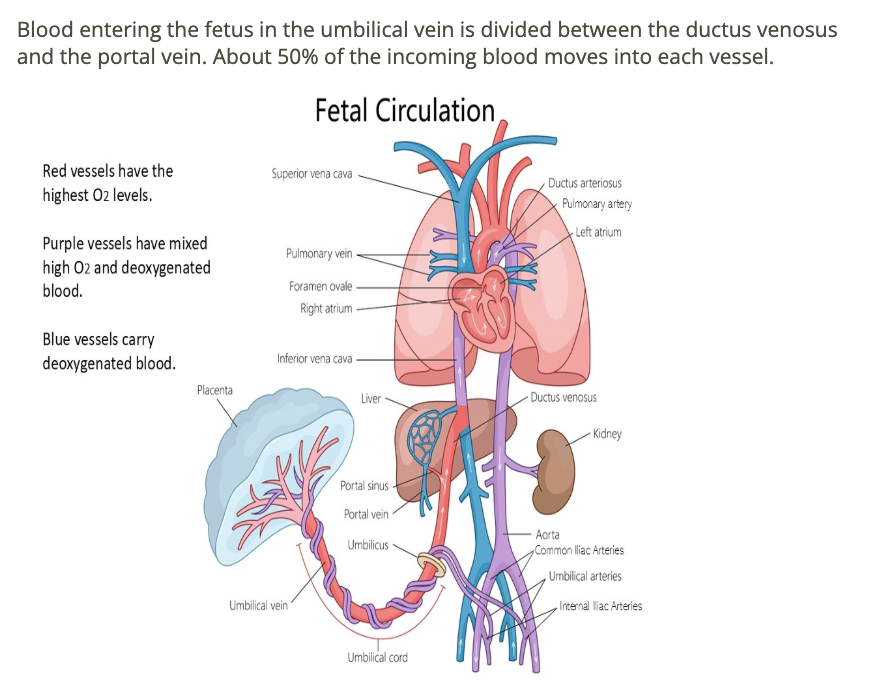
blood entering the fetus in the umbilical vein is divided between
.
a) PV + IVC
b) PV + ductus venosus
c) IVC + ductus venosus
d) PV + ductus arteriosus
b) PV + ductus venosus
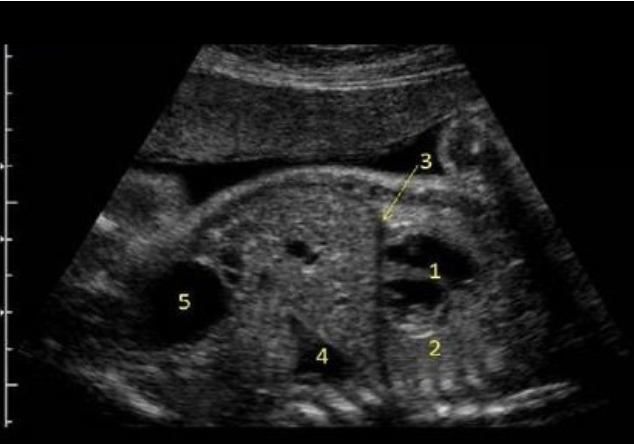
what is #2
a) diaphragm
b) lung
c) liver
d) thymus
b) lung

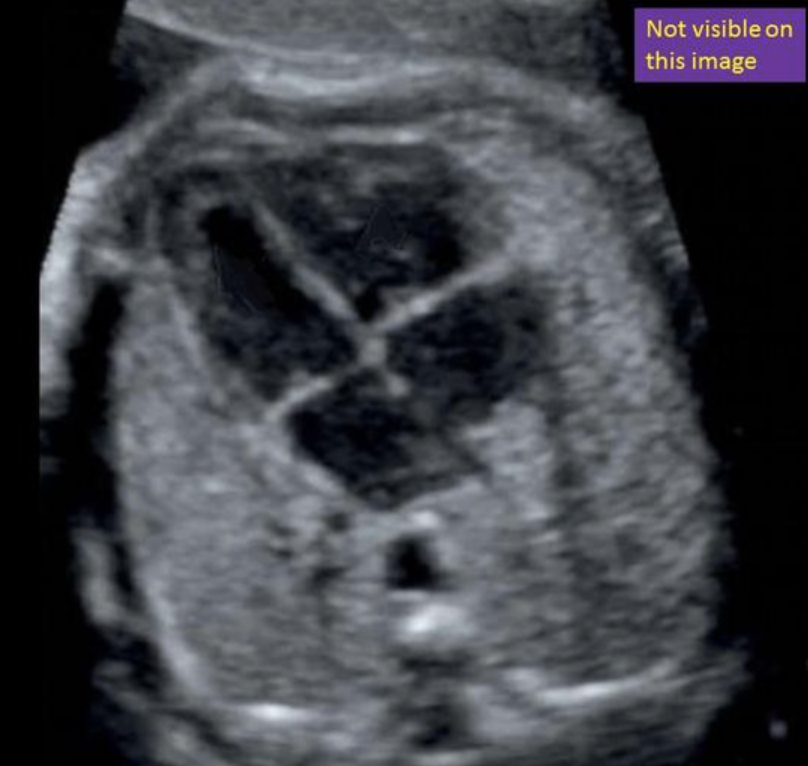
where is the descending AO
“between left atrium + spine”
4 chamber view = DEscending AO, not ascending
between left atrium + spine
which structure is considered the most reliable for determining fetal situs
a) AO + IVC
b) stomach + liver
c) stomach + heart
d) liver + GB
. the stomach and the heart are on the same side
a) AO + IVC

the ___ empties blood into the right atrium
the __ empties into the left atrium
.
a) IVC + SVC, pulmonary veins
b) pulmonary veins, IVC
c) tricuspid valve, mitral valve
d) IVC, SVC
a) IVC + SVC, pulmonary veins
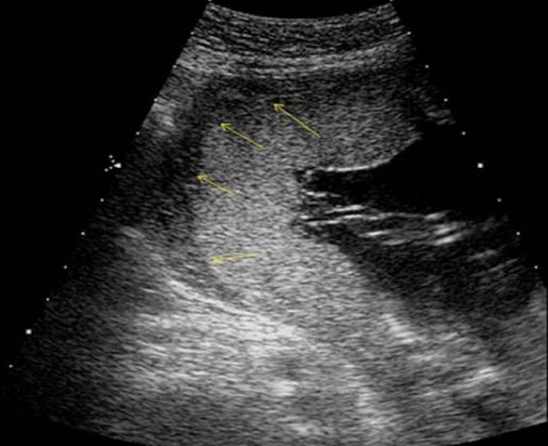
what are the arrows pointing to
a) hematoma formation w/placental abruption
b) normal retroplacental space
c) amnion + chorion junction
d) placental lake formation posterior to the placenta
b) normal retroplacental space
the __ is located between the right atrium + ventricle
the ___ is located between the left atrium + ventricle
a) tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve
b) mitral valve, tricuspid valve
c) mitral valve, aortic valve
d) tricuspid valve, mitral valve
d) tricuspid valve, mitral valve

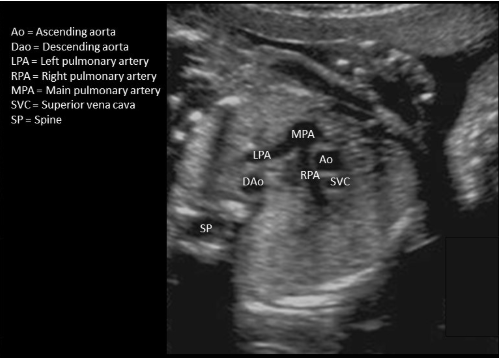
where is the left pulmonary artery
“branch closer to descending AO"
branch closer to descending AO
if the fetus is breech, where is the left lobe of the thalamus
The fetus is in breech position and facing the maternal left side
The '“fetal left side is posterior” and the fetal right side is anterior on the image.
fetal left side is posterior