Unit 10 Review: Thermochemistry and States of Matter
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
What is energy and what are its units?
Energy is the capacity to do work, and its units include Joules (J), calories (cal), and kilowatt-hours (kWh).
What is thermochemistry?
Thermochemistry is the study of the heat energy associated with chemical reactions and changes in state.
What is heat energy and what are its units?
Heat energy is the energy transferred between systems or objects with different temperatures, measured in Joules (J) or calories (cal).
What is the conversion between Joules and calories?
1 calorie is equal to approximately 4.184 Joules.
What is the definition of a calorie and what is a nutritional 'Calorie' equal to?
A calorie is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. A nutritional 'Calorie' (Cal) is equal to 1,000 calories.
How is energy stored in chemical bonds?
Energy is stored in chemical bonds as potential energy, which can be released when bonds are broken.
What happens when chemical bonds are formed?
When chemical bonds are formed, energy is released, often in the form of heat.
What is the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics?
The Zeroth Law states that if two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
What is thermal equilibrium?
Thermal equilibrium is the state in which two bodies in contact do not exchange heat energy, indicating they are at the same temperature.
What is temperature and how does it differ from heat energy?
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance, while heat energy is the total energy transferred due to temperature difference.
What are the differences among the system, boundary, and surroundings?
The system is the part of the universe being studied, the boundary is the separation between the system and surroundings, and the surroundings are everything outside the system.
How does heat flow in an endothermic process?
In an endothermic process, heat flows from the surroundings into the system.
How does heat flow in an exothermic process?
In an exothermic process, heat flows from the system into the surroundings.
What is the sign for an endothermic process?
The sign for an endothermic process is positive (+).
What is the sign for an exothermic process?
The sign for an exothermic process is negative (-).
What happens to the kinetic energy of the surroundings in an endothermic process?
In an endothermic process, the kinetic energy of the surroundings decreases.
What happens to the kinetic energy of the surroundings in an exothermic process?
In an exothermic process, the kinetic energy of the surroundings increases.
What is specific heat capacity?
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
What are the units of specific heat capacity?
The units of specific heat capacity are Joules per gram per degree Celsius (J g^-1 °C^-1).
What is the formula for specific heat capacity?
The formula for specific heat capacity is q = mcΔT, where q is heat energy, m is mass, c is specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
What is a calorimeter?
A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction.
What is calorimetry?
Calorimetry is the science of measuring heat changes during chemical reactions or physical changes.
How much heat is transferred when a 24.7 kg iron bar is cooled from 880°C to 13°C?
The heat transferred can be calculated using the specific heat formula: q = mcΔT.
Is the process of cooling the iron bar endothermic or exothermic with respect to the system?
The process is exothermic with respect to the system, as heat is released to the surroundings.
What happens when a sample of aluminum absorbs 9.86 J of heat and its temperature increases from 23.2°C to 30.5°C?
The specific heat capacity can be calculated using the formula q = mcΔT, where q is the heat absorbed.
What is the specific heat capacity of aluminum?
0.90 J g-1 K-1
How much energy does an 8.29 g sample of calcium carbonate absorb when its temperature increases from 21.1°C to 28.5°C?
50.3 J
What is the specific heat of ethanol if a 25.0 g sample absorbs equal heat energy as water and its temperature rises from 21.6°C to 29.9°C?
Calculated based on the heat absorbed and temperature change.
Why does the temperature of ethanol increase more than that of water when both absorb equal amounts of heat energy?
Ethanol has a lower specific heat capacity than water.
Which substance requires the smallest amount of heat to increase its temperature by 10°C: lead, water, sulfur, or arsenic?
Lead, with a specific heat capacity of 0.128 J g-1 °C-1.
Which substance can absorb the most energy in a temperature increase of 1 K among aluminum, silver, copper, and carbon (graphite)?
The substance with the highest specific heat capacity.
What will be the final temperature of 1.5 kg of ethanol at 37°C after adding 8.0000 x 10^4 J of energy?
Final temperature calculated using specific heat capacity.
If equal masses of two substances absorb 25 J and the temperature of A increases by 4°C while B increases by 8°C, what can be inferred about their specific heats?
The specific heat of A is double that of B.
Which metal undergoes the smallest change in temperature when equal masses are subjected to the same amount of heat?
The metal with the higher heat capacity.
What is the First Law of Thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Describe a coffee cup calorimeter.
A device used to measure the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes.
What is the specific heat capacity of a metal if a 47.5 g sample at 425.0°C is placed in 1.000 L of water at 18.0°C and reaches equilibrium at 21.0°C?
Calculated based on heat transfer between the metal and water.
What is the final temperature of 25.0 g of iron at 398 K placed in 50.0 g of water at 298 K in an insulated coffee cup?
Final temperature calculated using specific heat capacities of iron and water.
What is a phase change?
A transition between different states of matter.
List and define the six types of phase changes and classify them as exothermic or endothermic.
Melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, sublimation, deposition.
What is the difference between evaporation and boiling?
Evaporation occurs at the surface at any temperature; boiling occurs throughout the liquid at a specific temperature.
What happens to temperature during a phase change?
Temperature remains constant during a phase change.
What happens to the kinetic energy of particles during a phase change?
Kinetic energy changes as particles transition between states.
What happens between particles during the melting process?
Particles gain energy and overcome intermolecular forces.
What happens between particles during the vaporization process?
Particles gain enough energy to break free from the liquid state.
What happens between particles during freezing?
Particles lose energy and form a structured arrangement.
What happens between particles during condensation?
Particles lose energy and come closer together to form a liquid.
What is the formula for determining the heat absorbed during melting?
Q = m * L_f, where L_f is the latent heat of fusion.
What is the formula for determining the heat released during freezing?
Q = m * L_f, where L_f is the latent heat of fusion.
What is the formula for determining the heat absorbed during vaporization?
The formula is Q = m * ΔH_vap, where Q is the heat absorbed, m is the mass, and ΔH_vap is the heat of vaporization.
What is the formula for determining the heat released during condensation?
The formula is Q = m * ΔH_cond, where Q is the heat released, m is the mass, and ΔH_cond is the heat of condensation.
What sequence occurs when water droplets form on the wall above a simmering pot of soup?
C) Vaporization, then condensation.
What happens to water molecules when an ice cube melts in a beaker?
C) The molecules become randomly arranged and slide past each other.
How much energy is required to melt a 20.0-pound bag of ice at 0°C?
Energy required = mass (kg) heat of fusion. Convert 20.0 pounds to kg (20.0 lb 0.4536 kg/lb). Use the heat of fusion for ice (334 J/g).
How much energy is released by 50.0 g of condensing water vapor?
Energy released = mass (g) * heat of vaporization. Use the heat of vaporization for water (2260 J/g).
How do you calculate the mass of liquid water at 100°C that can be converted to vapor by absorbing 2.40 kJ of heat?
Use the formula: mass = Q / ΔH_vap, where Q is 2400 J and ΔH_vap is 2260 J/g.
How many joules of heat energy are required to heat 15.00 g of lead from 25°C to its melting point (327°C) and melt it?
Calculate using the specific heat formula: Q = m c ΔT for heating, then add Q = m * ΔH_fusion for melting.
How many joules of heat energy are released as 55.0 g of water cools from 135°C to -13°C?
Calculate using Q = m c ΔT for the cooling process.
What happens to the kinetic energy of particles between minute 0 and minute 2 in a cooling graph?
The kinetic energy decreases as the temperature drops.
What is the kinetic molecular theory for solids and liquids?
In solids, particles vibrate in fixed positions; in liquids, particles are close but can slide past each other.
Rank the states of matter from lowest to highest kinetic energy.
Solid < Liquid < Gas.
What must be present between individual particles of solids and liquids that is not assumed to exist between gas particles?
Intermolecular forces.
What are allotropes? Provide examples.
Allotropes are different forms of the same element in the same physical state. Examples include carbon (diamond and graphite) and oxygen (O2 and O3).
What are pressure-temperature (P-T) phase diagrams?
P-T phase diagrams show the phases of a substance at different pressures and temperatures, differing from heating and cooling curves which show temperature changes over time.
What is the triple point in a P-T phase diagram?
The triple point is the specific temperature and pressure at which all three phases (solid, liquid, gas) coexist in equilibrium.
What is the critical point in a P-T phase diagram?
The critical point is the temperature and pressure at which the distinction between liquid and gas phases disappears.
What is the normal melting point?
The normal melting point is the temperature at which a substance changes from solid to liquid at 1 atm pressure.
How does the shape of a P-T phase diagram differ for substances with different densities in solid and liquid states?
For substances where solid density is greater than liquid density, the solid-liquid line slopes left; for those where liquid density is greater, it slopes right.
What is enthalpy and what are its symbols for endothermic and exothermic reactions?
Enthalpy (H) is the total heat content of a system. A positive change (ΔH > 0) indicates an endothermic reaction, while a negative change (ΔH < 0) indicates an exothermic reaction.
What is heat of reaction?
Heat of reaction is the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction.
Is the reaction PbO (s) + C (s) + 106.8 kJ ➔ Pb (s) + CO (g) endothermic or exothermic?
The reaction is endothermic because it absorbs heat (106.8 kJ).
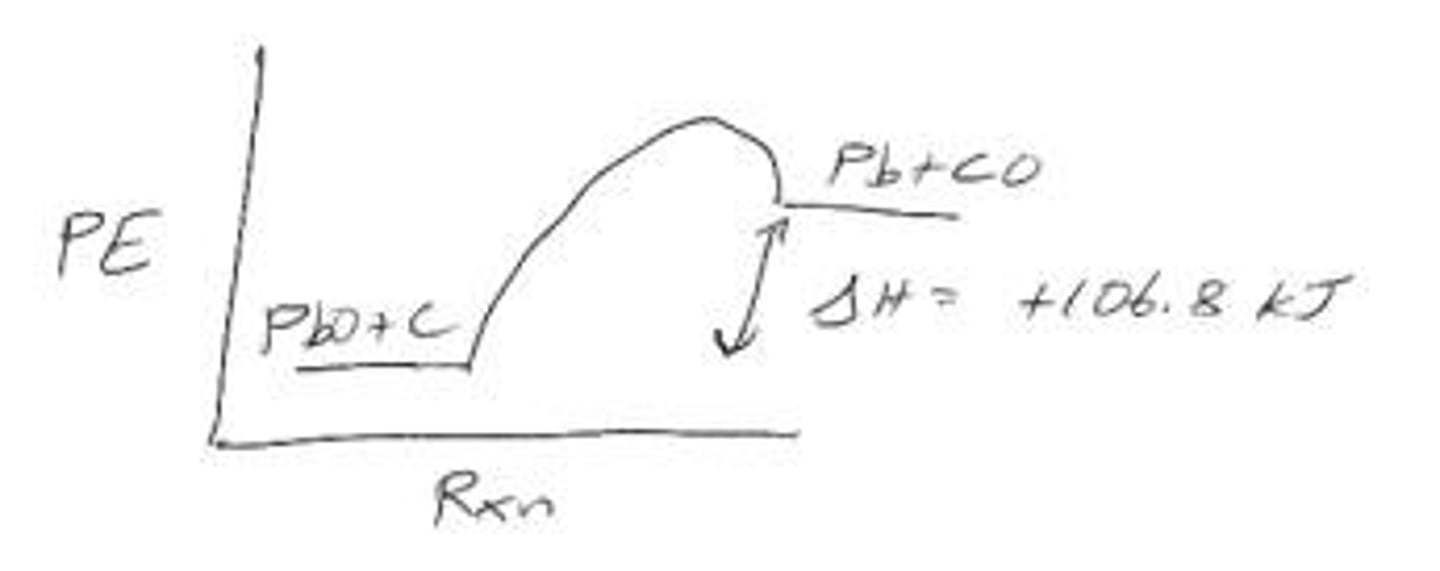

What is the enthalpy change for the reaction PbO (s) + C (s) + 106.8 kJ ➔ Pb (s) + CO (g)?
The enthalpy change is +106.8 kJ.
What is the reaction for the combustion of methane (CH4)?
CH4 + 2 O2 ➔ CO2 + 2 H2O
What is the enthalpy change for the complete combustion of methane?
ΔH = -212.8 kJ
Is the combustion of methane an endothermic or exothermic reaction?
Exothermic, because heat is released.
How many moles of oxygen are used if 452.0 kJ are produced in the combustion of methane?
2 moles of O2 are used.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction 2 Al (s) + 3 NH4NO3 (s) ➔ 3 N2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) + Al2O3 (s)?
ΔH = +2030 kJ.
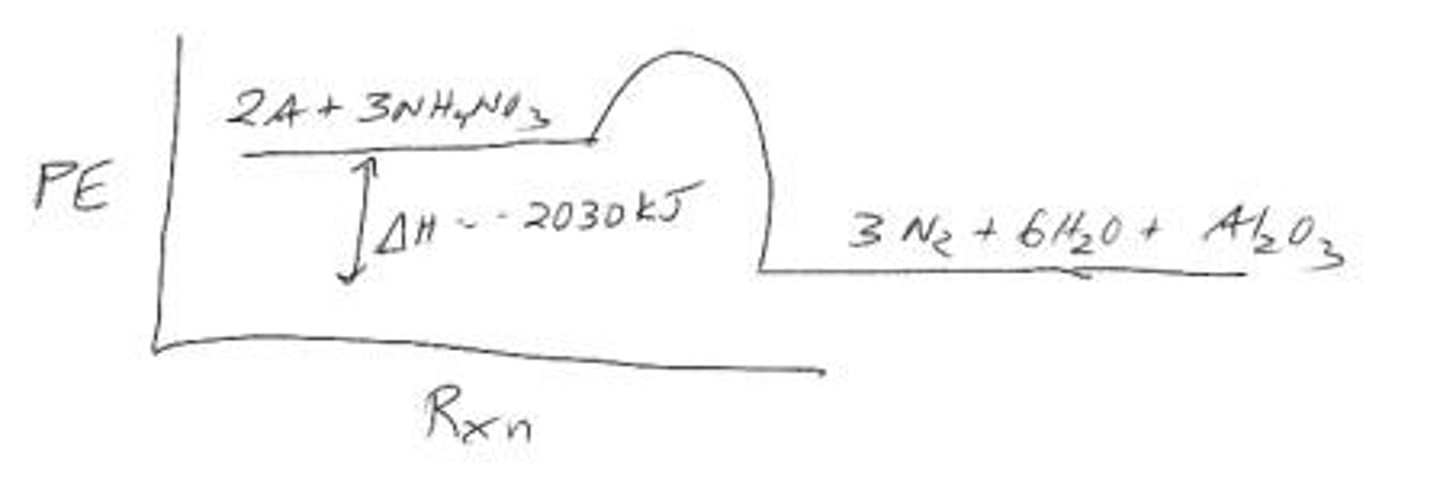
Is the reaction 2 Al (s) + 3 NH4NO3 (s) ➔ 3 N2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) + Al2O3 (s) endothermic or exothermic?
Exothermic, as heat is released.
What happens to the temperature of the surroundings during the reaction 2 Al (s) + 3 NH4NO3 (s)?
The temperature of the surroundings increases.
What is Hess's Law?
Hess's Law states that the total enthalpy change for a reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps, regardless of the pathway taken.
What is the enthalpy change for the reaction 2 SO3 (g) ➔ 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)?
ΔH = +197.8 kJ.
Is the reaction 2 SO3 (g) ➔ 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) endothermic or exothermic?
Endothermic, as heat is absorbed.
How many grams of SO3 react when 575 kJ of heat energy are absorbed?
To be calculated based on the stoichiometry of the reaction.
What is the enthalpy change for the dissolution of solid sodium hydroxide in water?
-44.4 kJ/mol.
If 13.9 g of NaOH dissolves in water, what is the resulting temperature change?
To be calculated based on the specific heat and mass of the solution.
What is the heat energy released or absorbed when 15.0 g of Al reacts with 30.0 g of Fe3O4?
-3363.6 kJ.
How do you determine the limiting reagent in a chemical reaction?
By comparing the mole ratio of reactants used in the balanced equation.
What is the balanced reaction for mixing 0.1000 L of 0.500 M HCl with 0.3000 L of 0.100 M Ba(OH)2?
2 HCl + Ba(OH)2 ➔ BaCl2 + 2 H2O.
What is the heat of reaction when 0.1000 L of 0.500 M HCl is mixed with 0.3000 L of 0.100 M Ba(OH)2?
-118 kJ.
What is the final temperature of the solution after mixing 0.1000 L of 0.500 M HCl with 0.3000 L of 0.100 M Ba(OH)2?
To be calculated based on the heat released and specific heat capacity.
What is the concentration of the excess reagent after the reaction occurs?
To be calculated based on the initial concentrations and the limiting reagent.
What is the pH of the solution after the reaction between HCl and Ba(OH)2?
To be calculated based on the remaining concentration of H+ and OH- ions.
What is the energy diagram for the reaction 2 Al (s) + 3 NH4NO3 (s) ➔ 3 N2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) + Al2O3 (s)?
It shows the energy of reactants, products, and the change in enthalpy.
What is the reaction equation for the oxidation of C6H4(OH)2?
C6H4(OH)2 (aq) + H2O2 (aq) ➔ C6H4O2 (aq) + 2 H2O (l)
What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) for the reaction C6H4(OH)2 ➔ C6H4O2 + H2?
ΔH = +177.4 kJ
What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) for the formation of H2O2 from H2 and O2?
ΔH = -191.2 kJ
What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) for the reaction H2 + ½ O2 ➔ H2O (g)?
ΔH = -241.8 kJ
What is the enthalpy change (ΔH) for the phase change from H2O (g) to H2O (l)?
ΔH = -43.8 kJ
What is entropy and what is its symbol?
Entropy is a measure of disorder or randomness in a system, symbolized as S.
What are the units for measuring entropy?
The units for entropy are typically joules per kelvin (J/K).