DT 2.1 Technical Principles p2
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topics 2,3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
what are smart materials (next few cards on this)
materials that react to a change in their environment such as temperature, light pressure or electrical input. reactions inc. change in colour, shape or resistance
define electroluminescent (or EL)
materials that provide light when exposed to a current
examples of electroluminescent materials
EL wire (thin copper wire core coated in phosphor powder - produces glowing light when exposed to AC)
EL flexible films or thin panels - light emitting phosphor sandwiched between pair of conductive electrodes and subjected to an AC to create light. brightness depends on voltage
other e.g. are LEDs, OLEDs, phosphorescent materials
Advantages of EL films replacing LCD displays
they are flexible, do not generate heat and are more reliable
define quantum tunnelling composite (QTC)
materials that can change from electrical conductors to insulators when under pressure
what is QTC and how does it work
flexible polymers that contain conductive nickel particles that can be either a conductor or insulator.
nickel particles make contact with each other and are compressed when force applied leading to increase in conductivity.
when force removed, material returns to original state and becomes electrical insulator
what are shape memory alloys (SMA)
SMAs return to original shape if heated
Nitinol is a common one made from titanium and nickel
uses of SMAs
medical applications like medical fastenings used in bone fractures
what is polymorph and how is it made
is a thermoforming polymer supplied in granular form. when heated in water to 62*C it softens and forms pliable volume of material which can be moulded and shaped.
solidifies on cooling and can be modelled and shaped
if reheated in water, becomes pliable again
uses of polymorph
useful for model making and prototyping
define photochromic pigment + e.gs
these change colour in response to light exposure
e.g. sunglasses - change in response to UV radiation
define thermochromic pigment + e.gs
change colour in response to change in heat and can be engineered to specific heat ranges
e.g. baby bottles to give indication of temp of milk
e.g. thermochromic mugs which respond to boiling water and change colour
define micro-encapsulation
tiny microscopic droplets containing various substances applied to fibres, yarns and materials, including paper and card.
protects and controls release of chemicals like vitamins, therapeutic oils, moisturisers, antiseptics, and anti-bacterial chemicals (released through friction)
define biomimicry
taking ideas from and mimicking nature - for inspiration for new materials, structures and systems
e.g. of biomimetic material
Fatskin, developed by Speedo, mimics shark’s sandpaper like skin by reducing drag in water used in performance enhancing swimwear
what are composites
when 2 or more materials are joined together to create a new enhanced material
1 material = the matrix, other = the reinforcement
what is carbon-fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP), how it is made, properties, uses
consists of woven carbon fibre strands encased in a polymer resin
carbon fibre strands = very high tensile strength and the polymer resin is lightweight and rigid
used in sports equipment like tennis rackets where strength to weight ratio is important
what is Kevlar, properties, uses
a lightweight flexible and extremely durable aramid fibre that has excellent resistance to heat, corrosion and damage from chemicals and a high tensile strength to weight ratio
often used in protective clothing like police body armour, where fibre often woven in a lattice that provides protection against knife attacks, bullets etc..
glass reinforced plastic (GRP) how its made, properties, uses
composite of glass fibres and a polyester resin
glass fibres create rigidity and the resin makes GRP tough and lightweight
is difficult to recycle because process of combining fibres and resin = irreversible
used in surfboards, canoes and car bodywork
what are technical textiles
engineered with specific performance characteristics that suit a particular purpose or function
define interactive (or integrated) textiles
fabrics that contain devices or circuits that respond and react with the user
e.g. of this
conductive fibres and threads (made from carbon, silver and steel) can be woven into textile fabrics and made into clothing or conductive threads that can be sewn into a product to connect to a circuit
define microfibres
extremely fine lightweight synthetic fibres, usually polyester or nylon
properties and e.gs of microfibres
excellent strength-to-weight ratio, water-resistance and breathability
used throughout textiles industry from clothing to cleaning cloths
what are phase-changing materials (PCMs) + an e.g.
encapsulated droplets on fibres and materials that change between liquid and solid within a temperature range
absorb energy during the heating process (returning to liquid) and release energy to environment during cooling (returning to solid)
e.g. cold weather clothing - encapsulated into fabric, allow body heat to be stored and then released when needed
what are breathable fabrics (+commonly used one) properties, uses
Gore-Tex consists of 3 or more fabrics laminated together with the breathable hydrophilic membrane in the middle (this is a solid structure that stops water passing though but at the same time can absorb and diffuse fine water vapour molecules)
means sweat and perspiration and permeate out but moisture from rain etc.. cant enter
therefore used in high performance clothing and footwear - helps regulate body temp by maintaining constant temp by allowing flow of air in and out
how is sun-protective clothing made and further enhanced - why does this work
clothes are made from tightly woven or knitted fabrics as this is most effective at blocking out the sun’s harmful UV rays as gaps much smaller preventing rays getting through
elastane fibres used to reduce spaces further making fabrics even more protective
define aramid fibres, Nomex as a n example + properties of Nomex
aramid fibres - non-flammable heat resistant fibre
Nomex is an aramid synthetic fibre primarily used where heat and flames resistance is essential. e.g. firefighters’ uniform and racing car drivers’ clothin
extremely strong and can withstand very extreme conditions
what are geotextiles
woven or bonded, synthetic or natural, permeable fabrics made originally for use with soil with the ability to filter, separate, protect and drain
uses of geotextiles
in civil engineering, road and building construction and maintenance
e.g. control of coastal erosion and drainage; and control of embankments on the sides of roads
what is Rhovyl + properties
non-flammable, synthetic fibre which is crease resistant, has good thermal and acoustic properties, is anti-bacterial and comfortable to wear
uses of Rhovyl
construction of fibre gives fabric ability to wick away moisture like perspiration through fabric.
also dries quickly and does not retain odours making it ideal for socks
what is a system
a set of parts which work together to provide functionality to a product
purpose of electronic systems
to provide functionality to products and processes
what are subsytems
electronic systems can be broken down into these
and can then be classified as inputs, processes and outputs
subsystem - the interconnected parts of a system
what are system/block diagrams + signals
to show how subsystems are connected and signals flow between them
signals = digital or analogue
what can process subsystems be made from
microcontrollers, microprocessors, computers
define microcontroller
a miniaturised computer, programmed to perform a specific task, and embedded in a product
what is an Integrated circuit (IC)
e.g. microcontroller
a miniaturised, highly complex circuit with small pin connections in a single component
some functions programming devices can do + example applications for these
counting - sports scoreboard, digital clock, pedometer
switching - night light, electric kettle, automatic door
timing - security light, burglar alarm, cooking timer
what does a sensor do + name the 2 types
produces an electrical signal which can be analogue or digital
define digital sensor
a sensor that detects yes/no or on/off situations
define analogue sensors
sensor used to measure how big a physical quantity is. e.g. light and temperature
what is an LDR + uses
an analogue sensor used to sense light level
used in streetlamps, night lights, digital clocks (for brightness control), CCTV cameras (to switch to night vision mode)
what is a thermistor + uses
an analogue sensor to sense temperature
used in ovens, room thermostats, electric heaters and car engines
2 types of thermistors
negative temperature coefficient (NTC) type: resistance falls as temp increases
PTC type: resistance increases as temp increases
what does an output subsystem do
converts electrical signals into a desired function
types of output subsystems + uses
buzzers - produce sound outputs. useful for providing feedback that a user has pressed a button.
found in burglar alarms, microwave ovens, dishwashers and kitchen timers
LED produces a light output. available in range of colours, sizes, shapes
used as an indicator (i.e. as a ‘power on’ light in a product), or as a source of illumination e.g. torch
resistor must be used with an LED to limit current flow or LED will burn out
define feedback + why
achieving precise control by feeding information from an output back into the input of a control subsystem
allows a microcontroller to monitor the effect of the changes it makes to its output devices in order to achieve precise control over a system
an e.g. of feedback
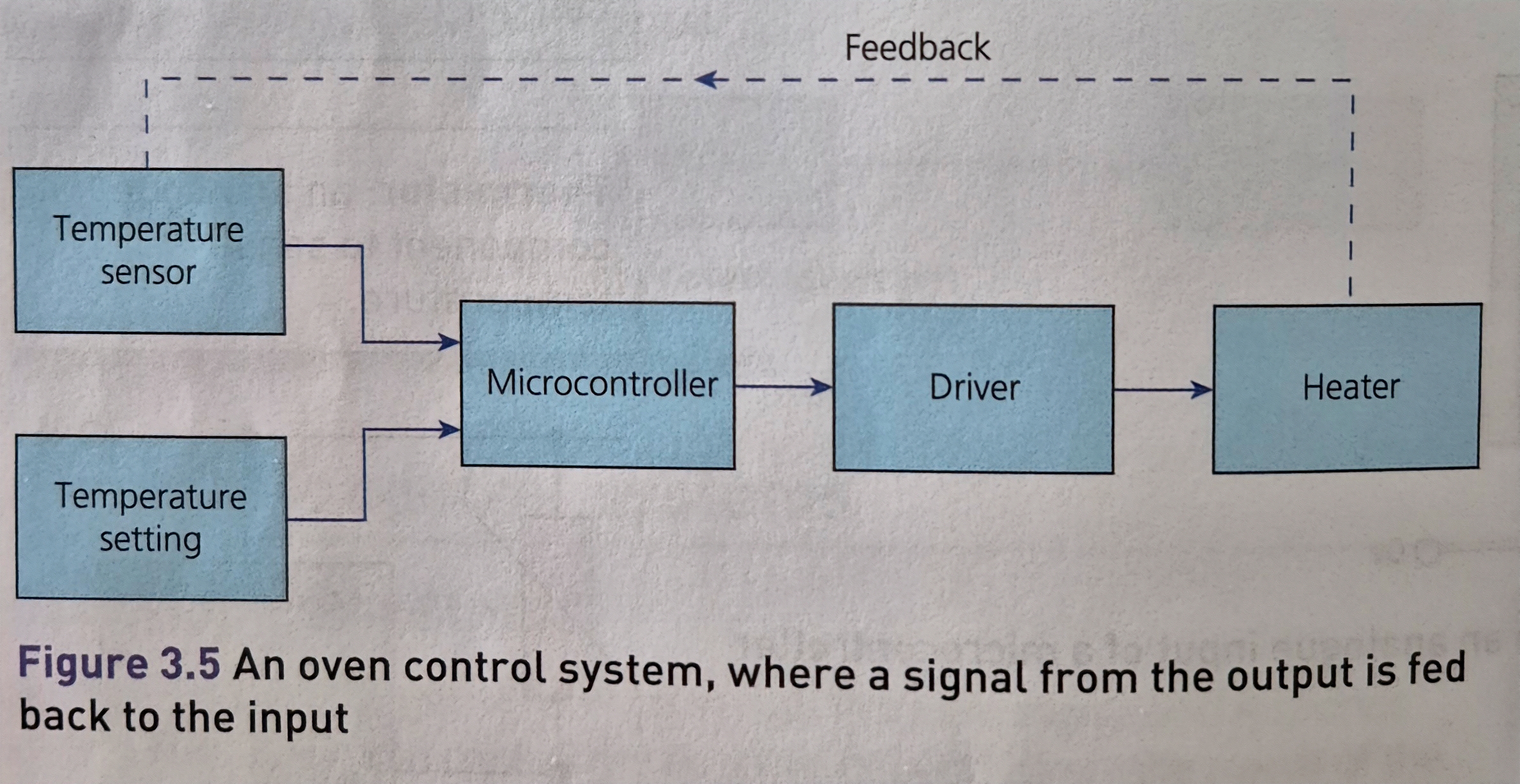
why is reprogramming microcontrollers useful
allows for updates, improvements and adjustments to the operation of devices without needing to replace hardware
enhances functionality and can adapt to new requirements
egs of products including microcontrollers
toasters, TVs, microwave ovens, hi-fi systems and cars
what is a Programmable interface controller (PIC)
a microcontroller used in many products - due to ease of use
define program (in terms of microcontroller)
a set of instructions which tells the microcontroller what to do
define subroutines(or macros)
a small sub-program within a larger program