Microbiology Chapter 1
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
what is microbiology?
the study of small life
Micro- small
Bio- life
Logy- study
HUMAN USES OF MICROORGANISMS (3)
biotechnology, genetic engineering, bioremediation
what are the three areas of food microbiology
food safety, food spoilage, and food fermentation
what is food safety
effects food to make humans sick due to pathogens and may not by physically apparent (bad microorganisms)
what microorganisms does food safety include
Bacteria, fungi, protozoa, parasites, viruses
what is food spoilage
mainly effects quality of food product; does not have ability to cause sickness due to not being pathogens; may not cause illness to us but instead cause spoilage to the food product (bad smell, flavor) (the ugly- make food ugly)
what microorganisms does food spoilage include
bacteria
fungi
what is food fermentation
like yeast, bacteria found in yogurt
what microorganisms are involved in food fermentation
bacteria and fungi
areas of work for food microbiologist?
wide variety and range of possible work area
○ Quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA)
○ Food safety- make sure food is safe (life international trading)
○ Food regulations
○ Analytical labs
○ R&D
○ Teaching and research
in microorganism terms, first we started with —> then we got
prokaryotes which evolved to give us eukaryotes
what are the 2 major cell lines
prokaryotes and eukaryotes
prokaryotes are defined by what
no nucleus
what microorganism is always a prokaryote
bacteria
bacteria are
single celled
eukaryotes are characterized by what
having a true nucleus
eukaryotes include
algae
fungi
protozoa
helminths
algae are
photosynthetic organisms
fungi are
Microscopic like mold and yeast
Macroscopic like mushrooms and puffballs
protozoa are
animal like, mostly single cells
helminths are aka
worms
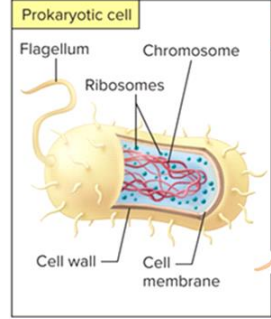
prokaryotes size and components
smaller than eukaryotes and no nucleus or organelles
have ribosomes, chromosomes, cell wall, and cell membrane
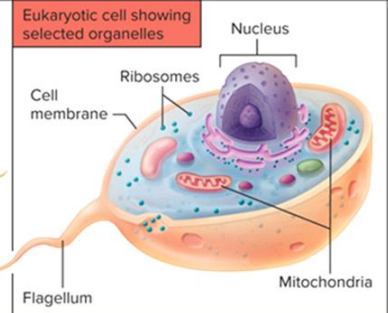
eukaryotes size and characteristics are
bigger than prokaryotes and more complex
have organelles like mitochondria
have nucleus
can be unicellular or multicellular
what are viruses
tiny, noncellular, parasidic things
viruses are not considere what? why?
not considered alive because they cannot survive on their own. They need a host to rely on
why do we classify viruses with microbes?
very tiny and sometimes smaller than bacteria and are microscopic and cause disease
viruses are not made of
cells! cannot replicate on their own!! They are made of a nuclear envelope to encompass their genetic material
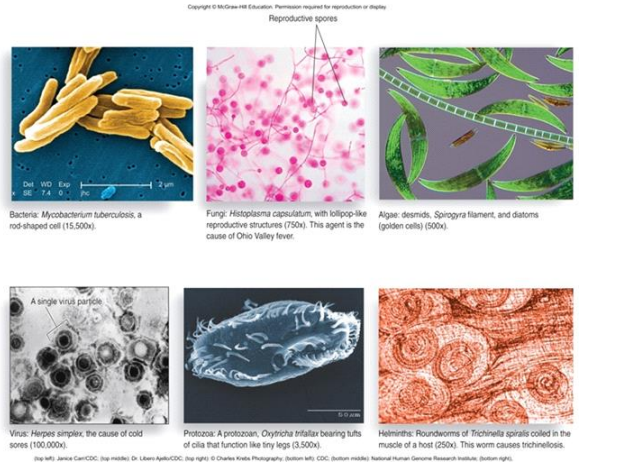
what are the 6 types if microbes
bacteria
fungi
algea
virus
protozoa
helminths
what size range do microbes belong in
10nm to 10mm
small ones (NM) are usually viruses
bacteria usually micrometers
eukaryotes tend to be the larger ones
microbes are involved in what that is key to nutrient and energy flow of ecosystem
photosynthesis and decomposition
photosynthesis and which microbes an do it
light fueled conversion of carbon dioxide to organic matter
algea
some bacteria
decomposition
breakdown of dead matter and waste into simpler compounds
microbial lifestyles (3)
most live freely (not bound to a host)
often share nutrients and habitats with other organism
parasites live on or in Host organism
microbes that live freely means what
not bound to a host
Relative harmless
Often beneficial
Some EVEN ESSENTIAL
parasites do what to host
Usually cause damage
Cause Infection, disease
what are pathogens
microbes that do harm (to humans or animals)
NOW WE LOOK AT HISTORY OF MICROBIOLOGY
in the past 300 years, main 3 prominent discoveries made in microbiology
Microscopy
Scientific method
Microbiology lab techniques
Created first microscope in 1590
Hans and Zacharias Janssen
First to observe living microbes in 1675
Antoine Van Leeuwenhoek
made single lens magnified up to 300x
Antoine Van Leeuwenhoek
what were the 4 major questions scientist wanted to know?
Is spontaneous generation of microbial life possible?
What causes fermentation?
What causes disease?
How can we prevent infection and disease?
what was the idea of spontaneous generation
Early belief some life forms could arise from vital forces in nonliving or decomposing matter
○ Flies from manure
○ Mushrooms on rotten log
○ Maggots on meat
who disproved spontaneous generation?
Louis Pasteur- THEORY OF BIOGENESIS- the idea that living things can only arise from other living things
theory of biogenesis
the idea that living things can only arise from other living things
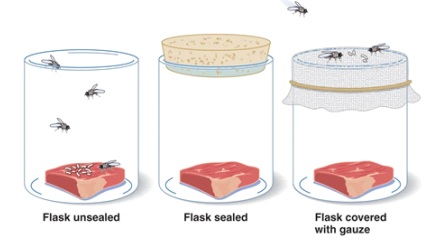
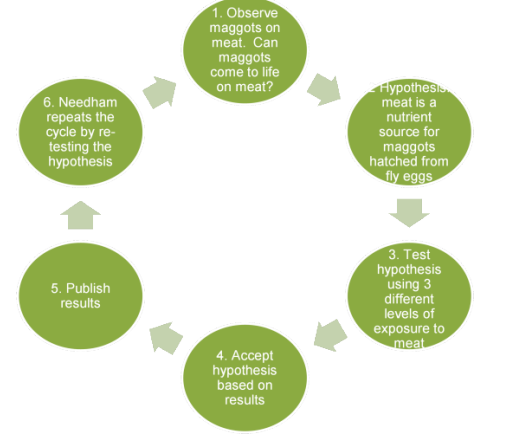
francesco redi experiment about spontaneous generation
Decaying meat isolated from flies-----> maggots never developed
Meat exposed to flies---> soon infested
so saw that maggots were from the flies and not the mean
scientist began to doubt spontaneous generation
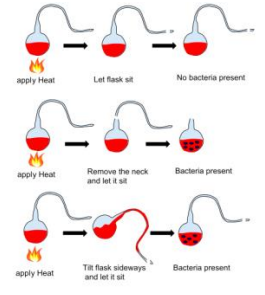
louis pasteur experiment concerning spontaneous generation
proved it NOT TRUE
Used swan-necked flask that remained upright, no microbial growth appeared When flask tilted, dust from the neck bend seeped back into the flask and clouded the infusion with microbes within a day
what is the scientific method
-A scientific approach to explain how and why an observed phenomenon occurs
-Uses hypothesis to predict what will happen under known conditions
-A lengthy process of experimentation, analysis, and testing
-Result either support or refute hypothesis
hypothesis
possible explanation that can be supported or refuted by observation and experimentation
goes from Hypothesis--> theory----> law
what are the 6 basic steps of the scientific method
1. Observation leads to question
2. Question generates hypothesis
3. Hypothesis tested through experiment
4. Accept, reject, or modify hypothesis based on results
5. Publish results
6.repeat
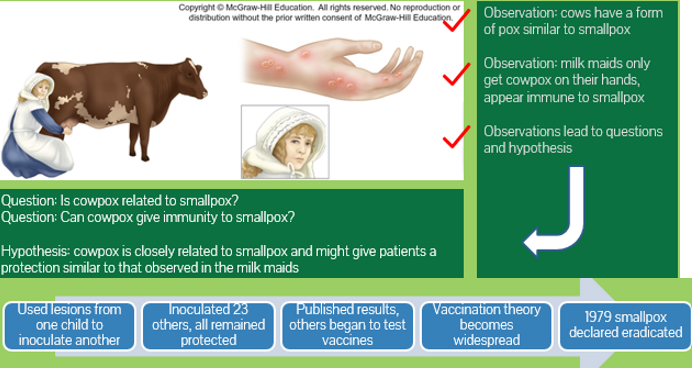
what did edward jenner do?
used the scientific method in disease control
Experiment 1
- Took scraping from cowpox blisters on a milk maid hand
- Inoculated the scrapings into a boy who had NOT had smallpox
- The boy developed minor symptoms but remained healthy
Experiment 2
- A few weeks later the child was exposed twice to pus from active smallpox lesion
- He did NOT acquire smallpox and appeared to have immune protection
what did joseph lister do (3)
-introduced aseptic techniques to reduce microbes in medical settings and prevent wound infection techniques
-chemical disinfection of hands prior to surgery
-use of heat for sterilization
what is the germ theory of disease
The idea that many diseases are caused by growth of microbes in the body- not sins, bad character, poverty, etc
what did robert koch study
causative agents of disease
how did louis pasteur contribute to the germ theory (4)
-Showed microbes caused fermentation and spoilage
- Disproved spontaneous generation of microorganisms
- Developed pasteurization
- Demonstrated what is now known as Germ Theory of Disease
what are contributions of Robert Koch (7)
•Simple staining techniques
•First photomicrograph of bacteria (both in and outside of diseased tissue)
•Techniques for estimating CFU/mL
•Use of steam to sterilize media
•Use of Petri dishes
•Techniques to transfer bacteria
•Bacteria as distinct species
what did robert koch contribute to the germ theory
Established Koch's postulates- series of experiments to determine if a pathogen is the cause of a disease - -Identified cause of anthrax, TB, and cholera
THE POSTULATES TIED THE DISEASE TO THE CAUSE
what are koch’s postulates
series of experiments to determine if a pathogen is the cause of a disease
what are Koch’s postulates (like the 3 specific ones)
1. Agent must be isolated in pure culture and grown outside the host
2.When agent is introduced into a healthy, susceptible host, the host must/should get the disease
3. Same agent must be found in the diseased experiment host
what is taxonomy
how we organize, classify, and name living things
what are the levels of classification (8)
domain (archaea, bacteria, and eukarya
kingdom
phylum or division
class
order
family
genus
species
who fathered taxonomy
carl von linne
what are the 3 concerns of taxonomy? (parts it focuses on)
classification, nomenclature, and identification
Classification
orderly arrangement of organisms into groups
Nomenclature
assigned names
Identification
determining and recording organism traits in order to place into taxonomic schemes
method of classification (phenotype) encompasses what?
***Analyze observable and biochemical properties
Observable characteristics
○ Size
○ Shape
○ Staining characteristics
Biochemical properties
○ Ability to ferment carbs
○ Carbon source used for growth
○ Enzymes
○ Biotyping
○ Serotyping
○ Phage typing
what does analitic methods of classification encompass?
***Analyze cell structure
Whole cell lipid analysis
Cell wall fatty-acid analysis
Whole cell protein analysis via mass spectroscopy
Enzyme and electrophoresis
what does genotyping method of classification encompass?
*look at the genetic information
*most accurate methods
DNA-DNA hybridization
Nucleic acid sequence analysis
Whole genome sequencing analysis
Plasmid analysis
Ribotyping
how are things names scientifically
using binomial nomenclature
BINOMIAL (SCIENTIFIC) NOMENCLATURE
Gives each microbe 2 names
-Genus- capitalized
- Species- lowercase
Both italicized (preferred) or underlined (when handwritten)
staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
- Listeria monocytogenes (L. monocytogenes)
- Salmonella enterica (S. enterica)
ALWAYS GIVE FULL NAME FIRST, THEN CAN USE ABBREVIATION IF MENTIONED AGAIN
They are named according to who discovered them, how the microbe looks, or the disease it causes
what two things do we use to explain ORIGIN AND EVOLUTION OF MICROBES
phylogeny and evolution
Phylogeny
○ Natural relatedness between groups of organisms
Evolution
-All new species originate from preexisting species
-Closely related organisms have similar features bc they evolved from common ancestral forms
evolution ___________ progresses toward greater complexiity
usually
what are the 5 kingdoms
Monerans
Prokaryotes, unicellular
Protists
Eukaryotes, mostly unicellular, can be photosynthetic or feed on others
Plants
Eukaryotes, multicellular, cell walls, photosynthesis
Fungi
Eukaryotes, multicellular, cell walls, NOT photosynthetic
Animals
Eukaryotes, multicellular, NO cell walls, NOT photosynthetic
monerans (characteristics)
a. Prokaryotes, unicellular
protist charcateristics
a. Eukaryotes, mostly unicellular, can be photosynthetic or feed on others
Plants characteristics
Eukaryotes, multicellular, cell walls, photosynthesis
fungi characteristics
Eukaryotes, multicellular, cell walls, NOT photosynthetic
animals
Eukaryotes, multicellular, NO cell walls, NOT photosynthetic