Chemistry of Prostaglandins
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Arachidonic acid
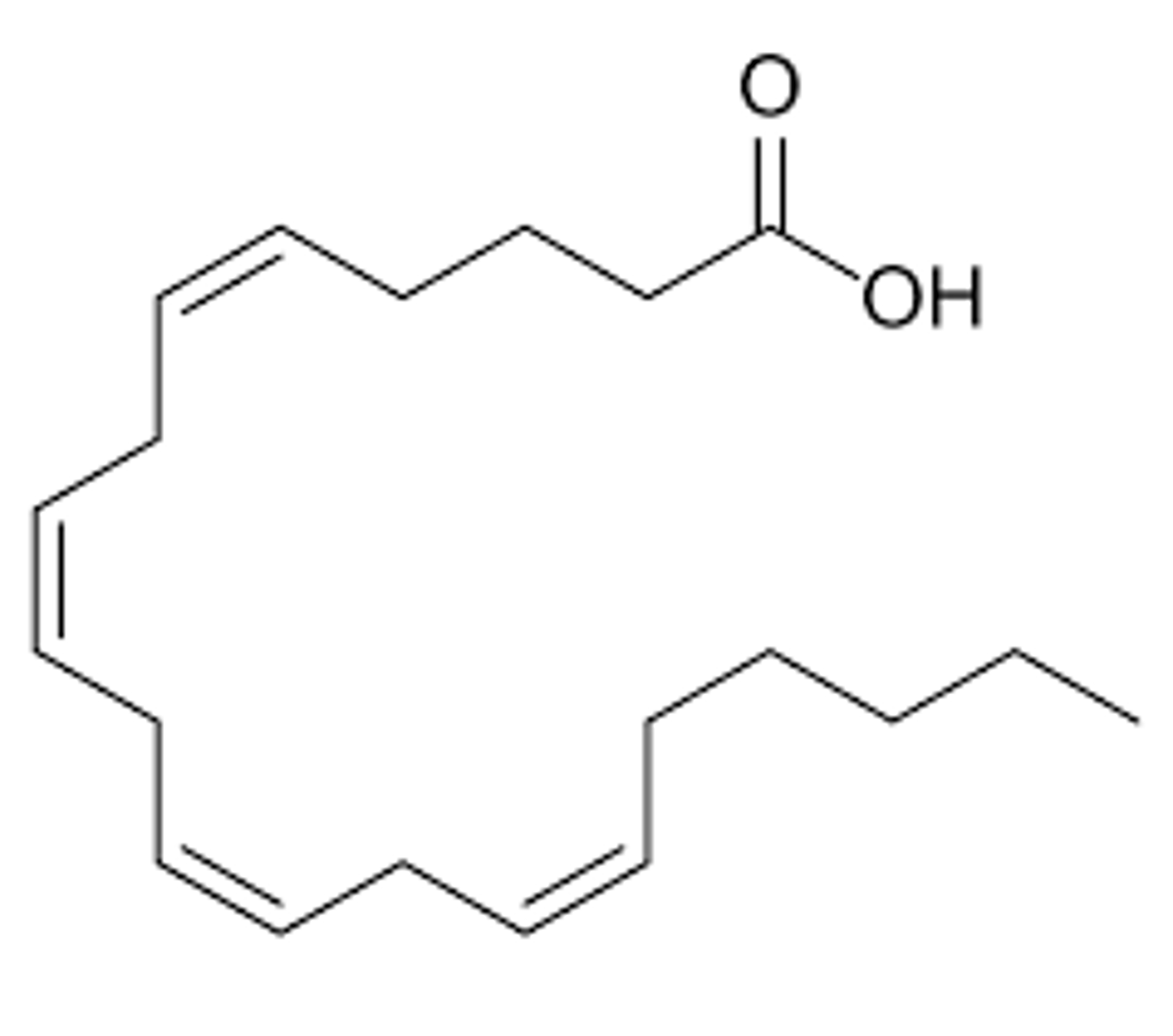
PGG

PGH

PGF2alpha
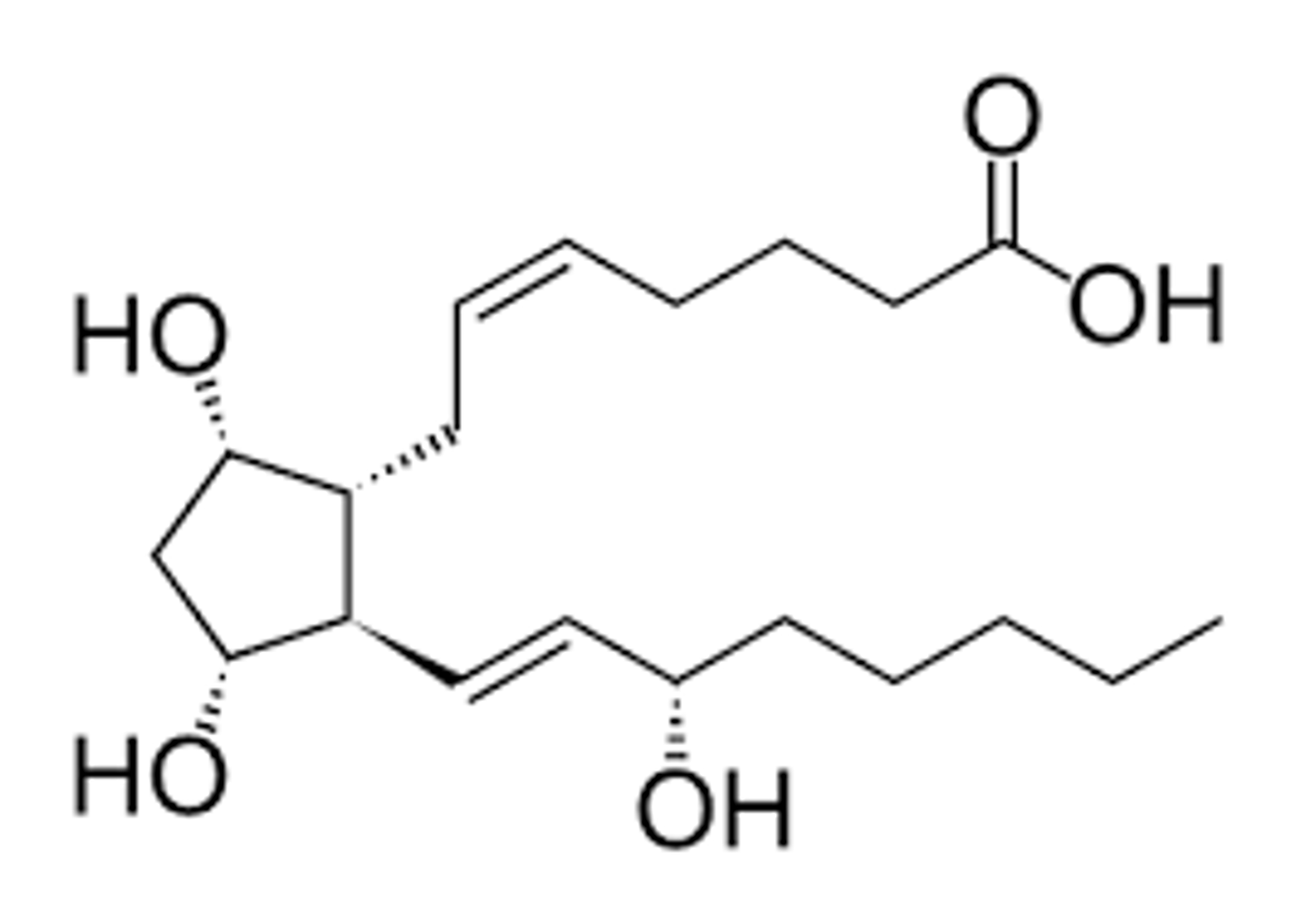
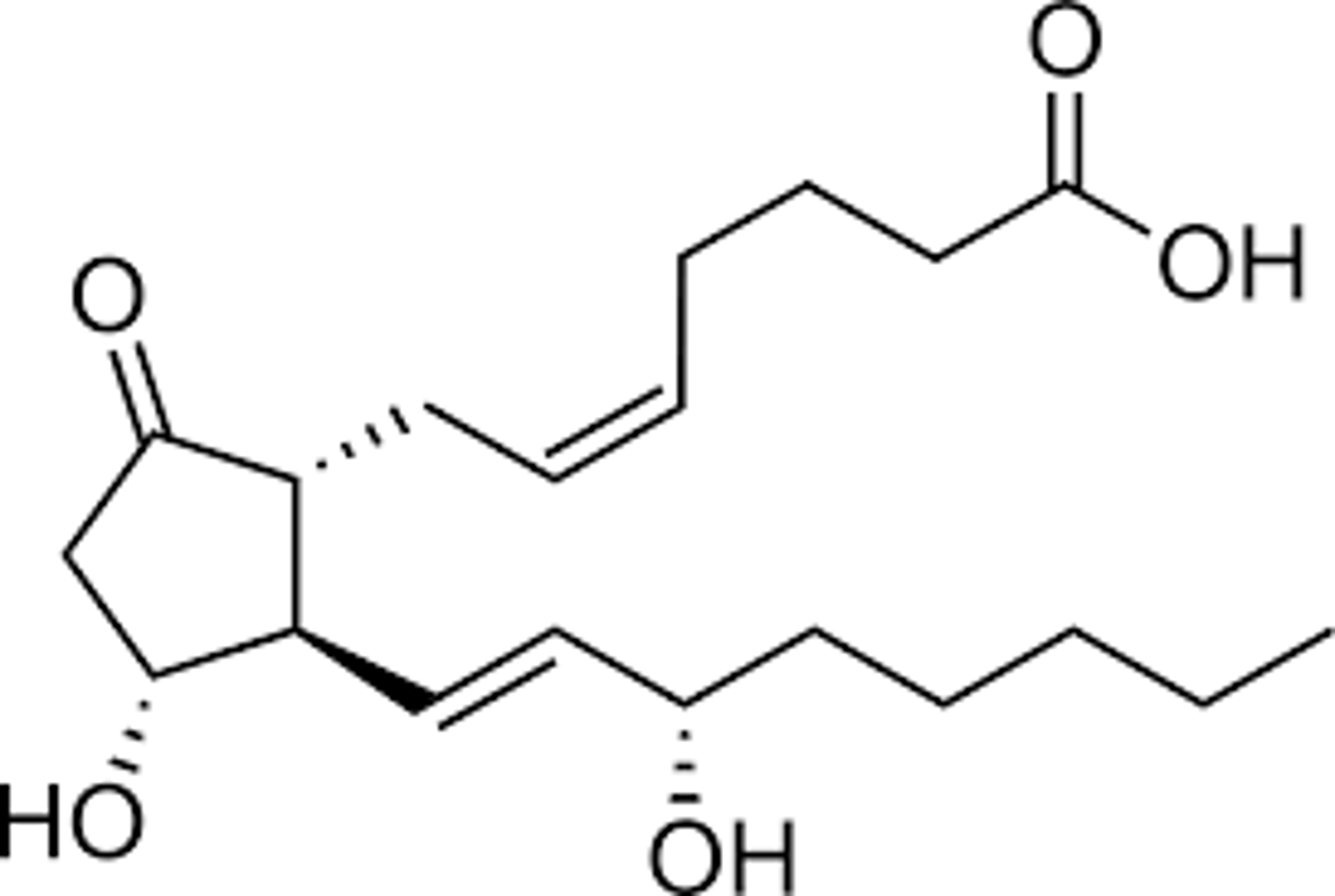
PGD2
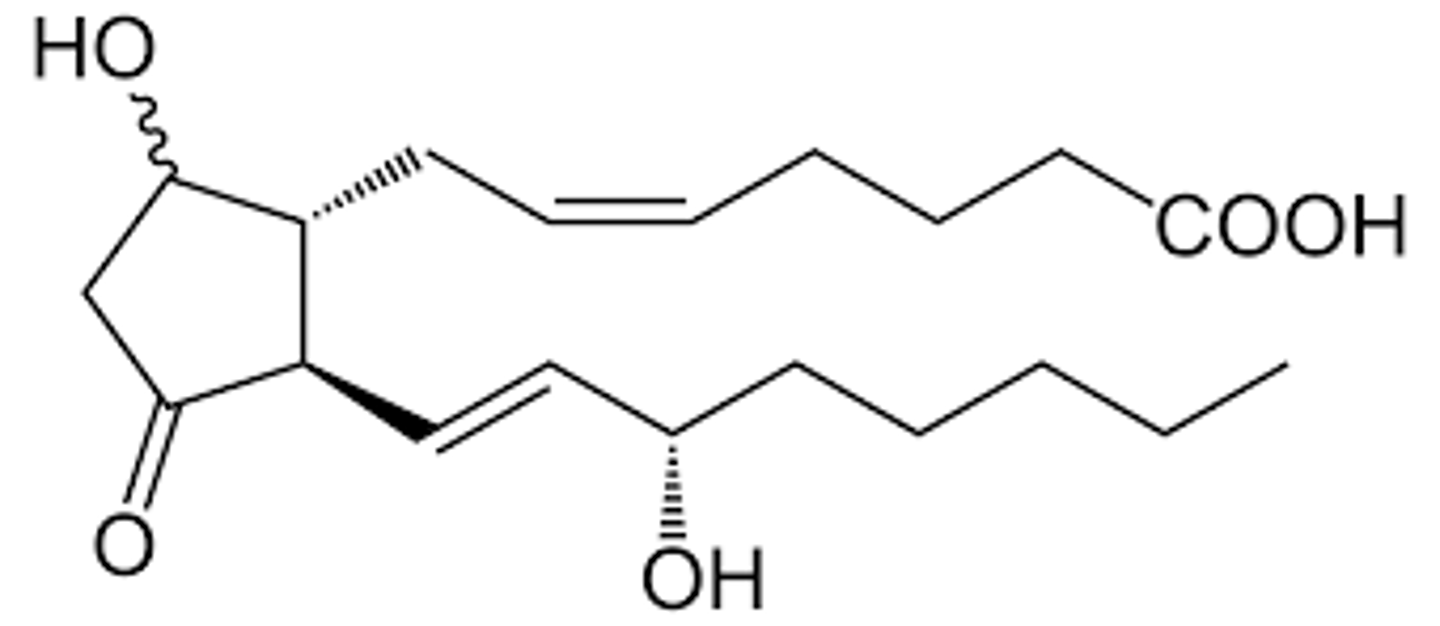
PGE2
Alprostadil
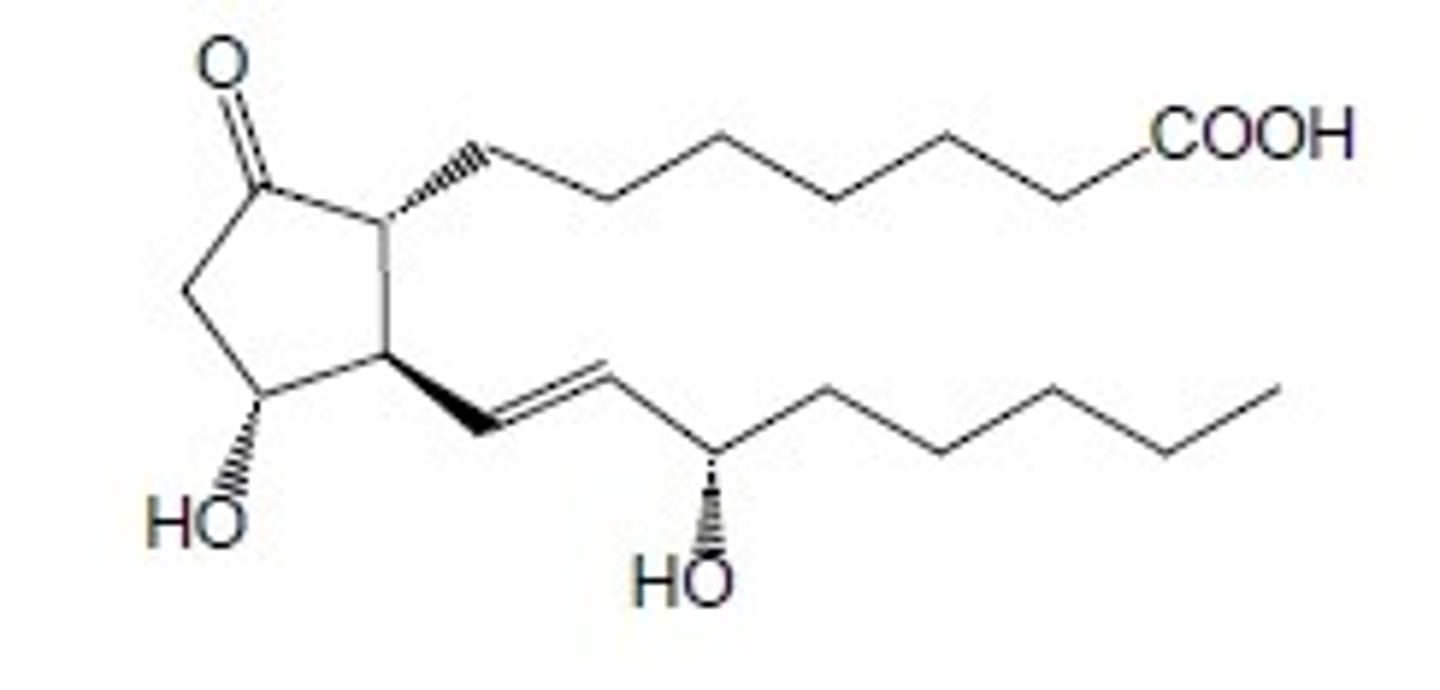
Misoprostol
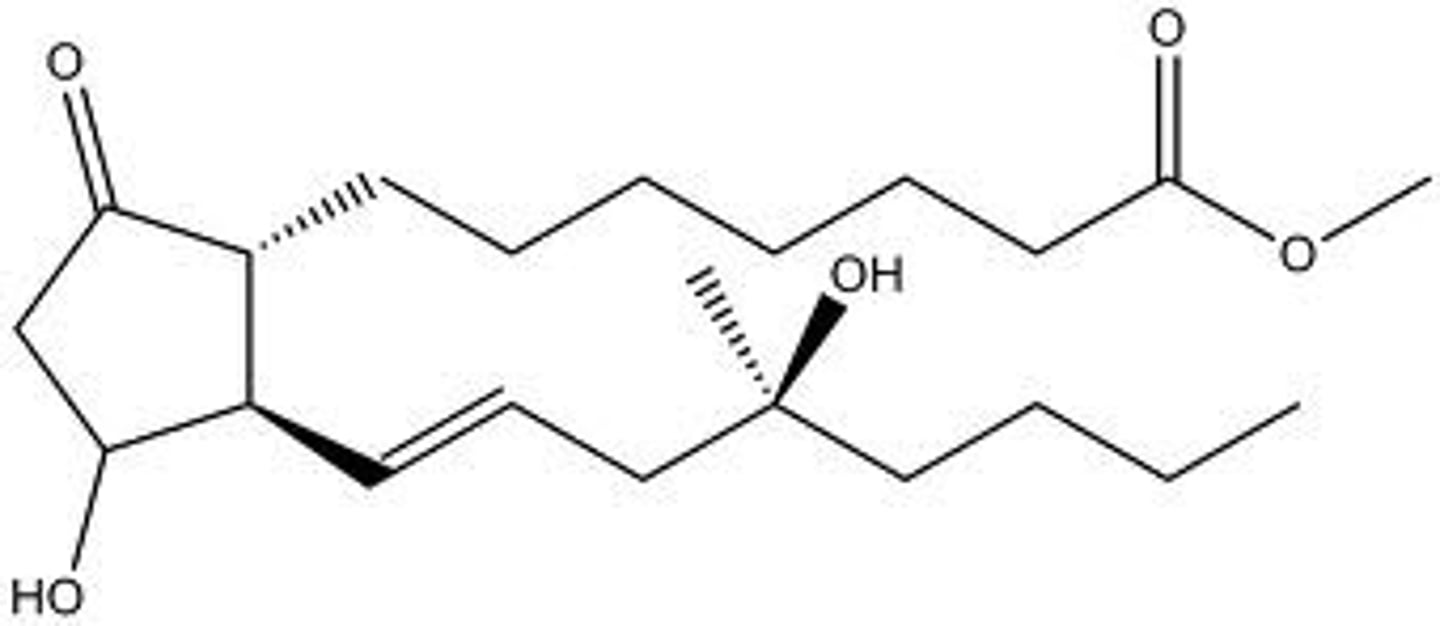
Dinoprostone
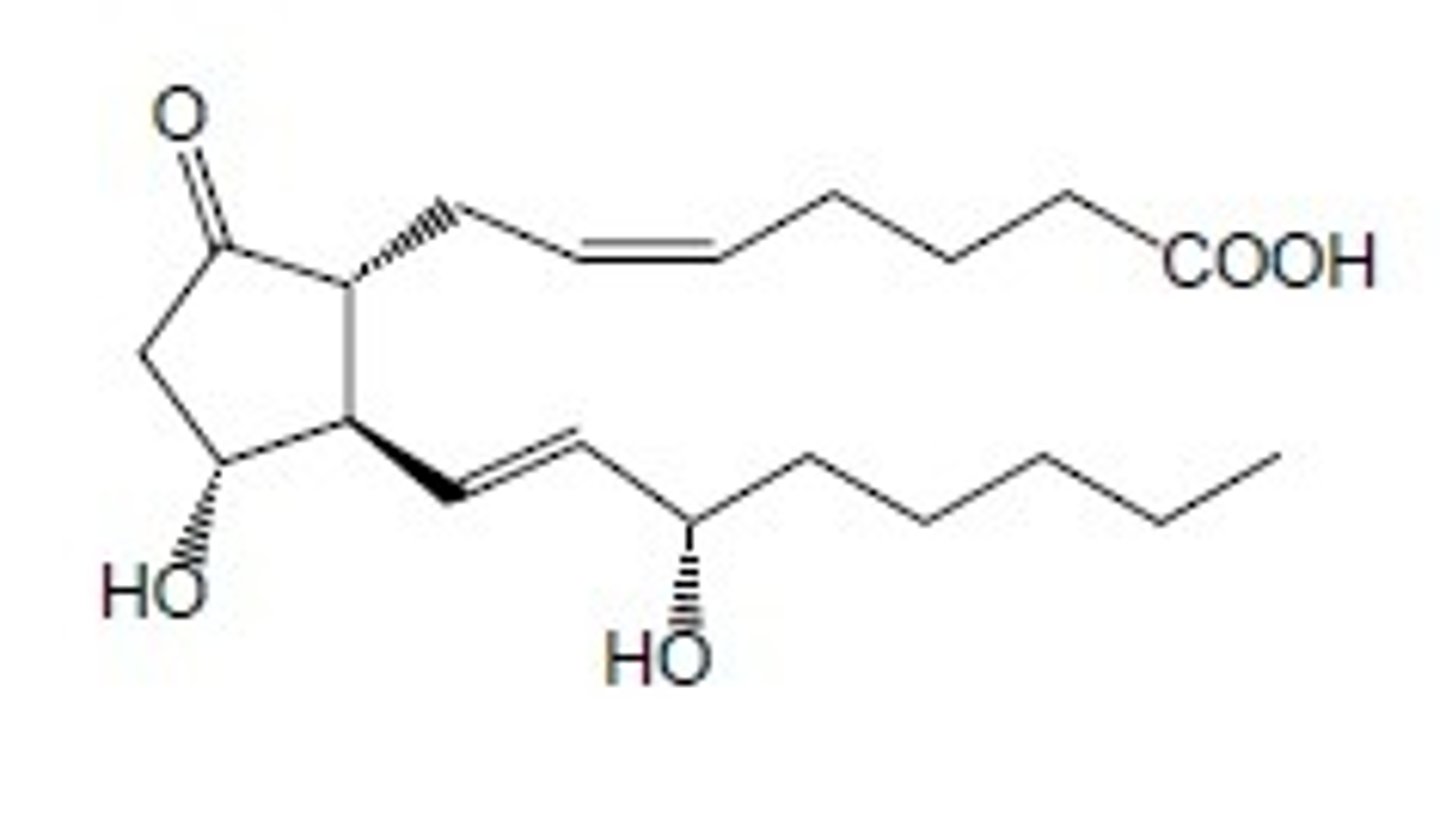
Sulprostone
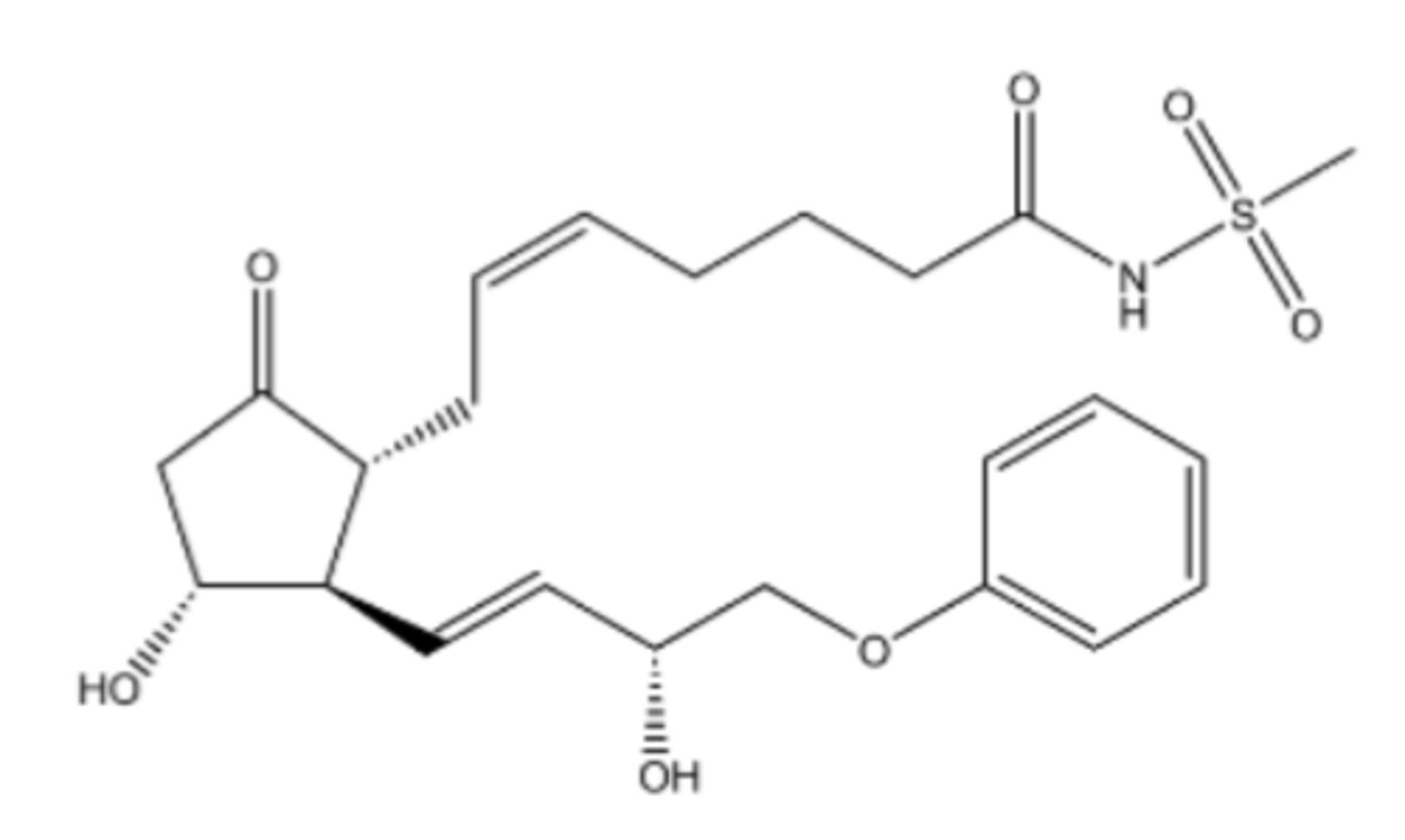
Latanoprost
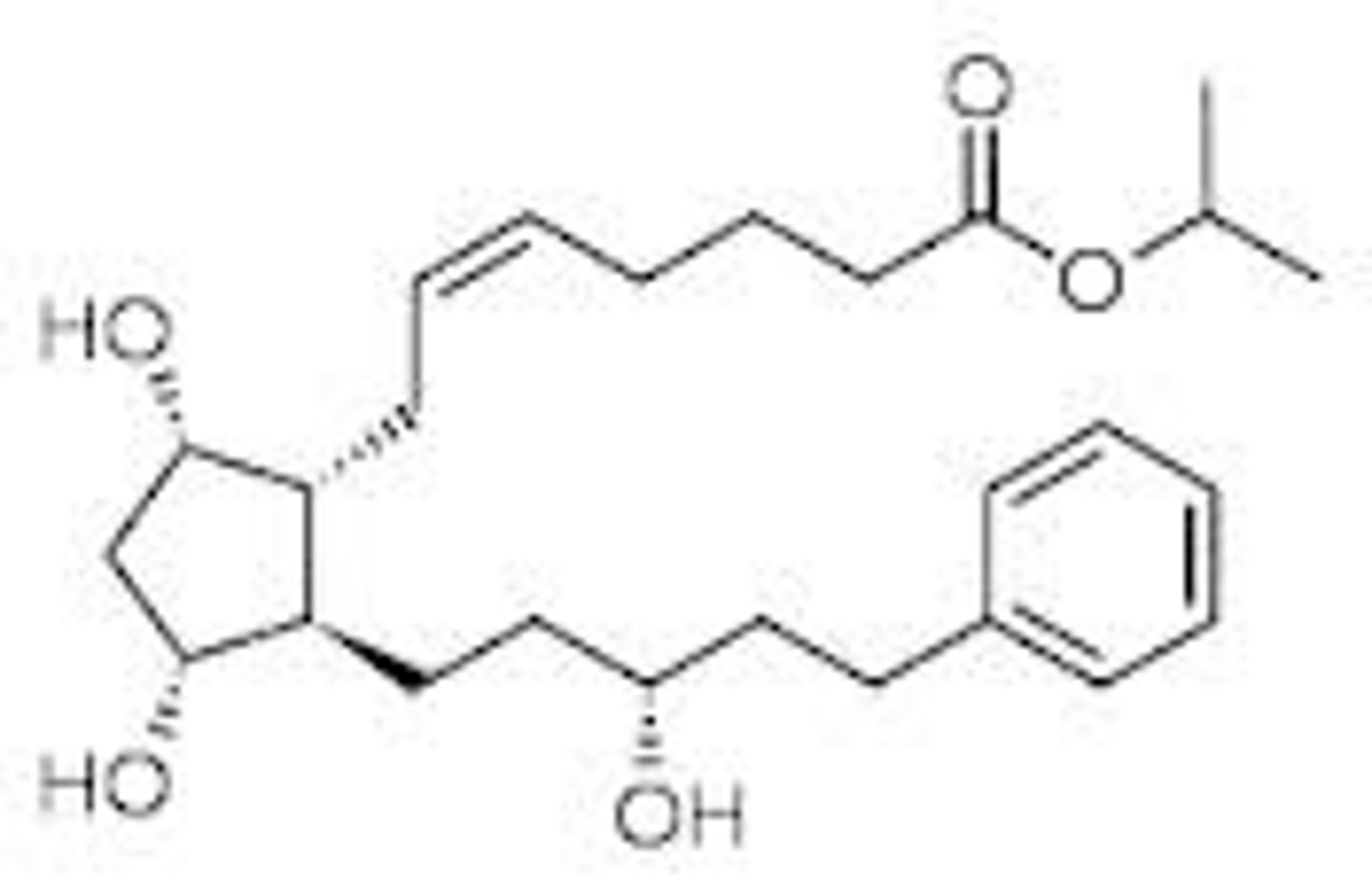
Latanoprostene
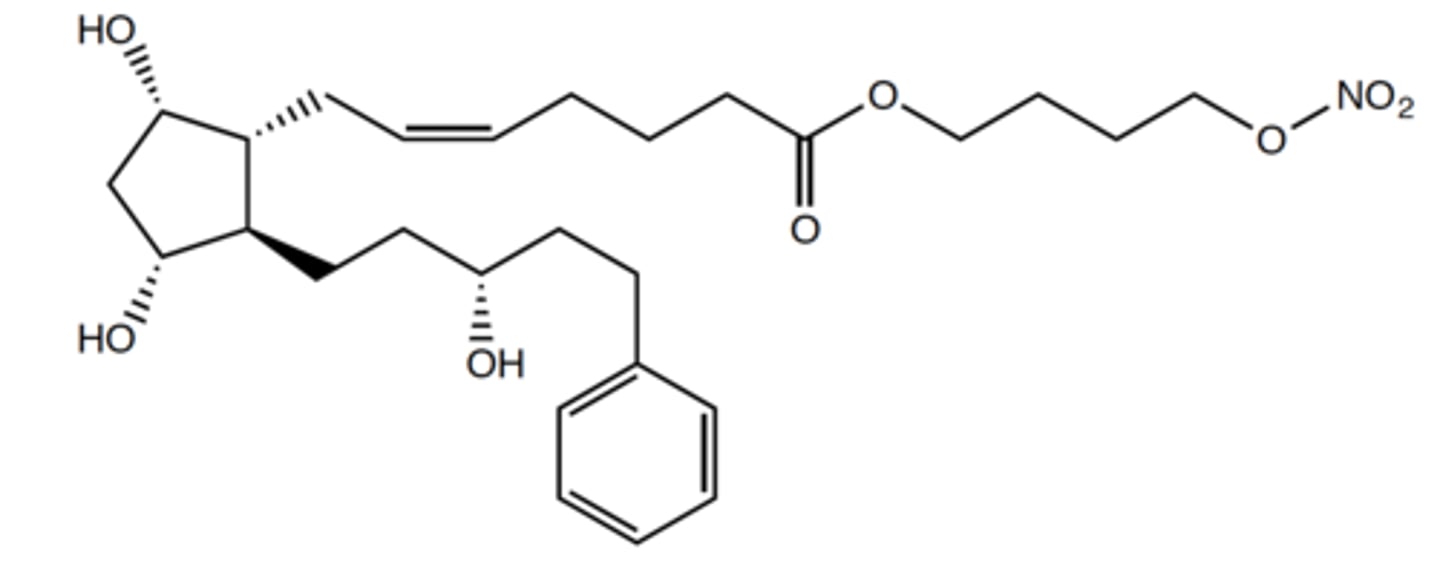
Bimatoprost
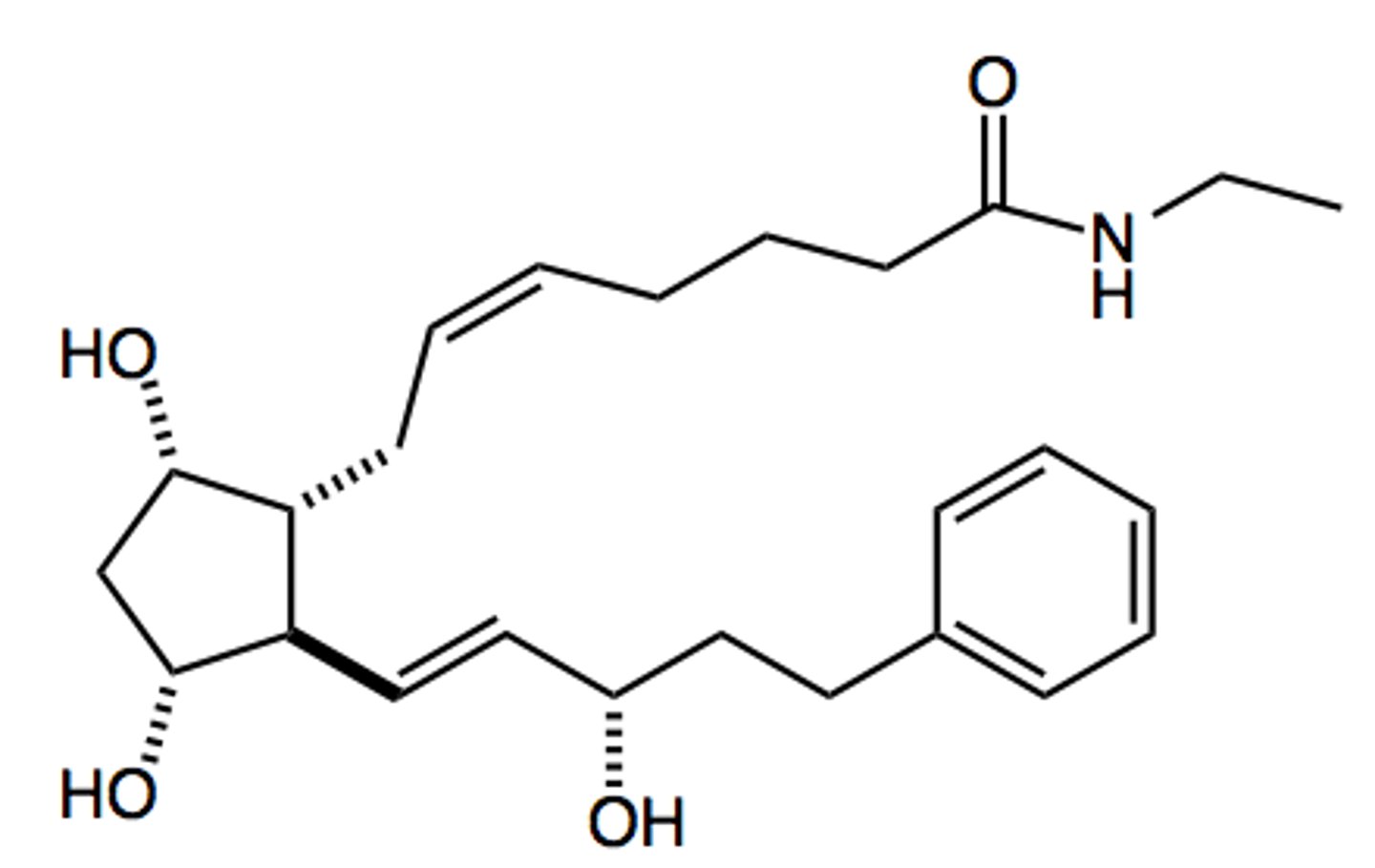
Prostacycin (PGI2)
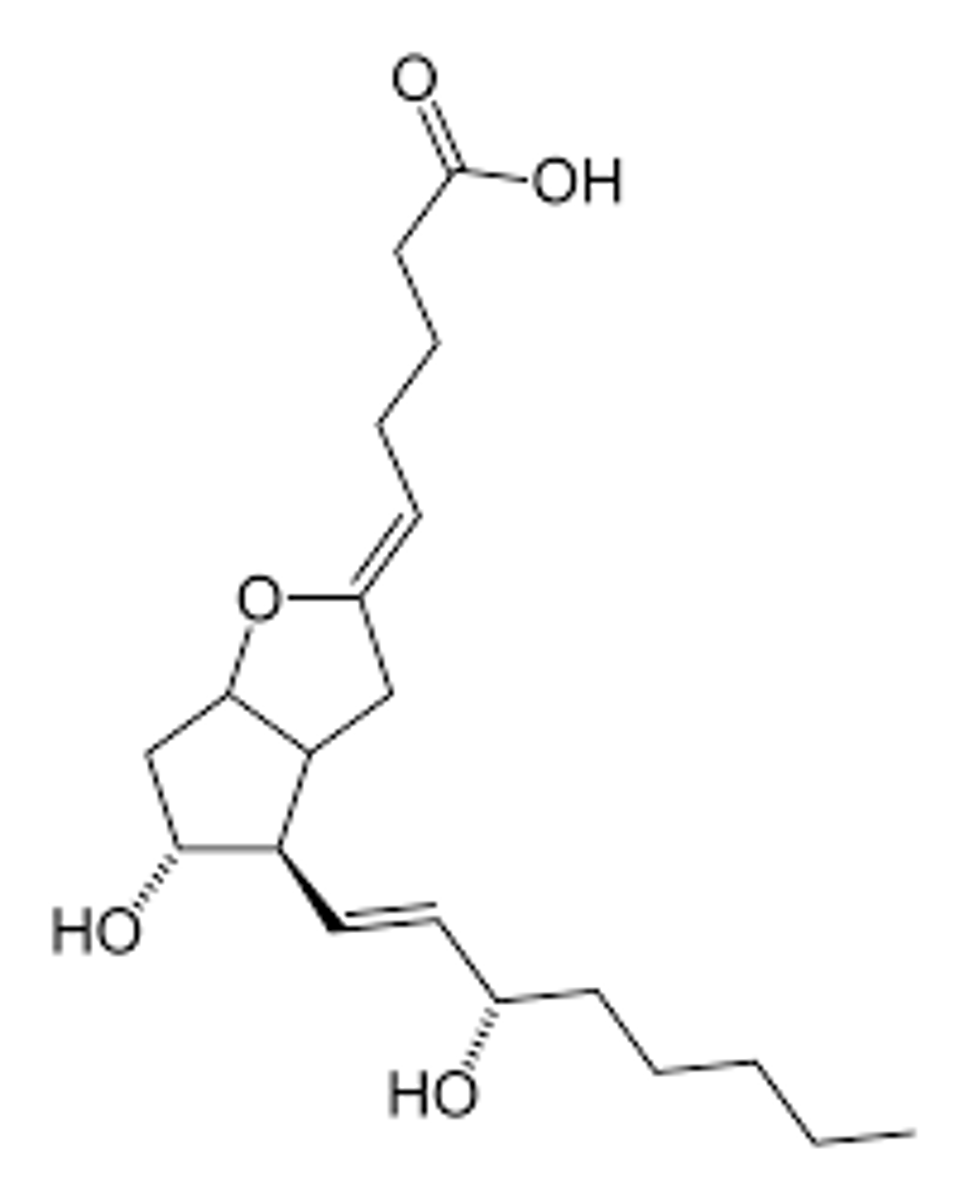
Epoprostenol
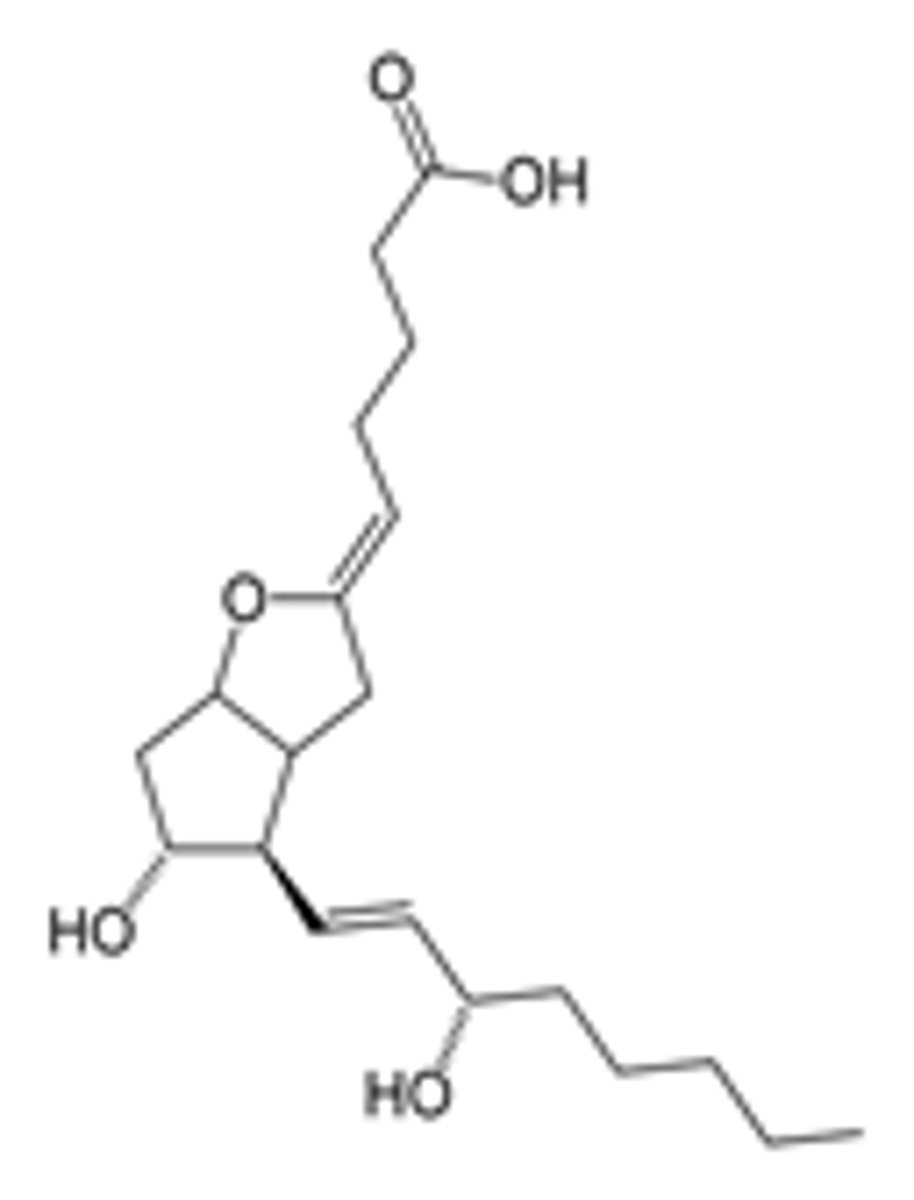
Iloprost
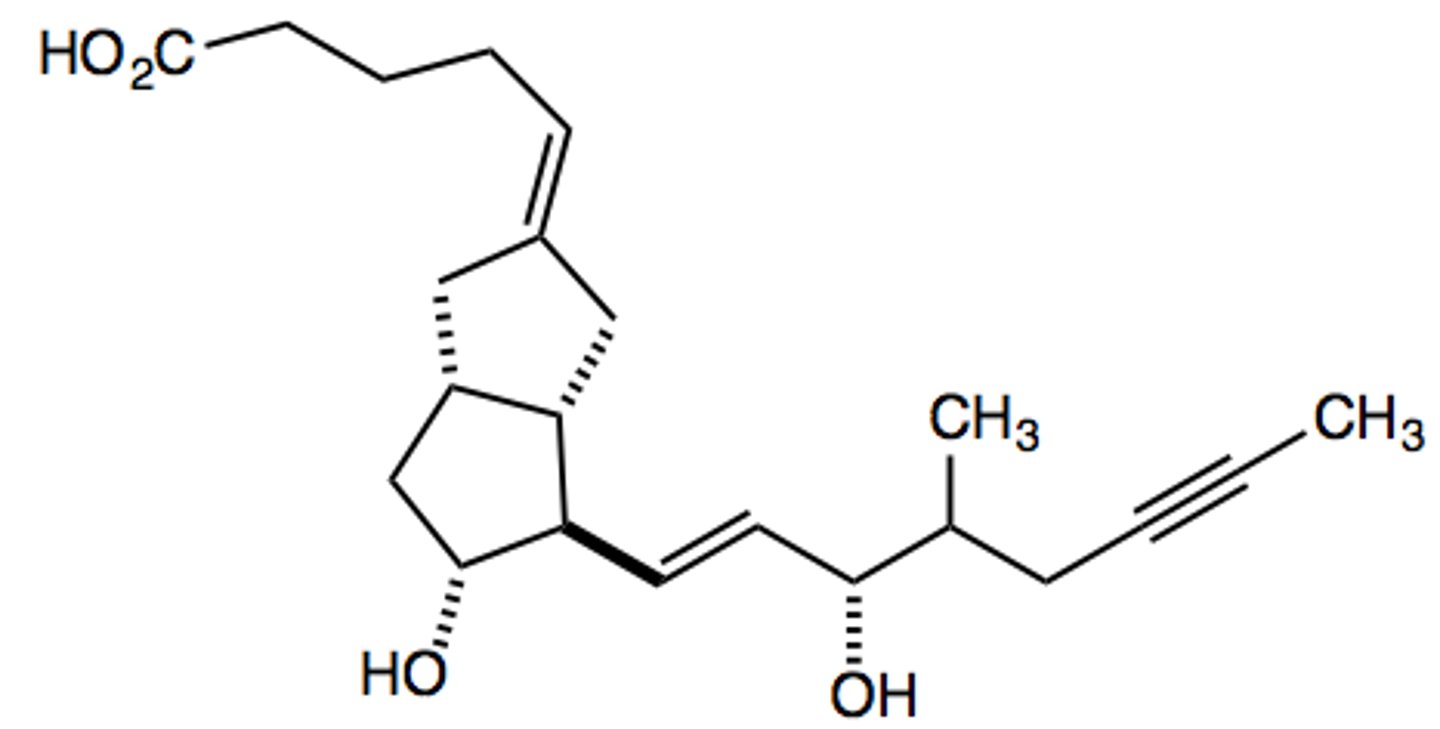
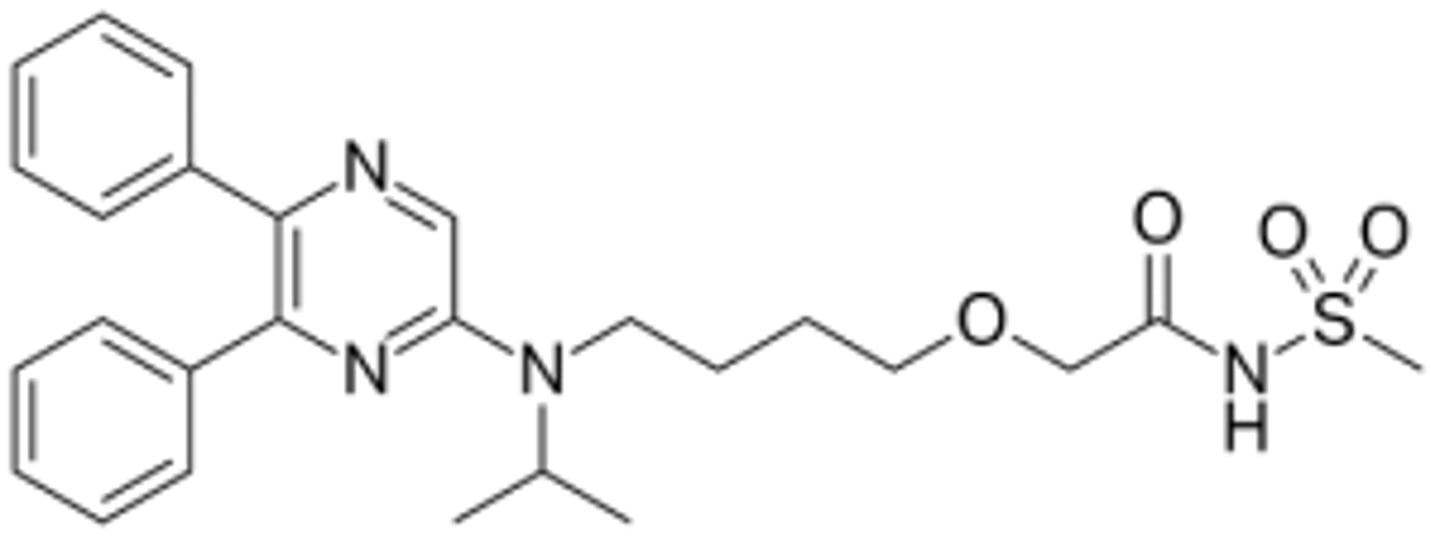
Selexipag
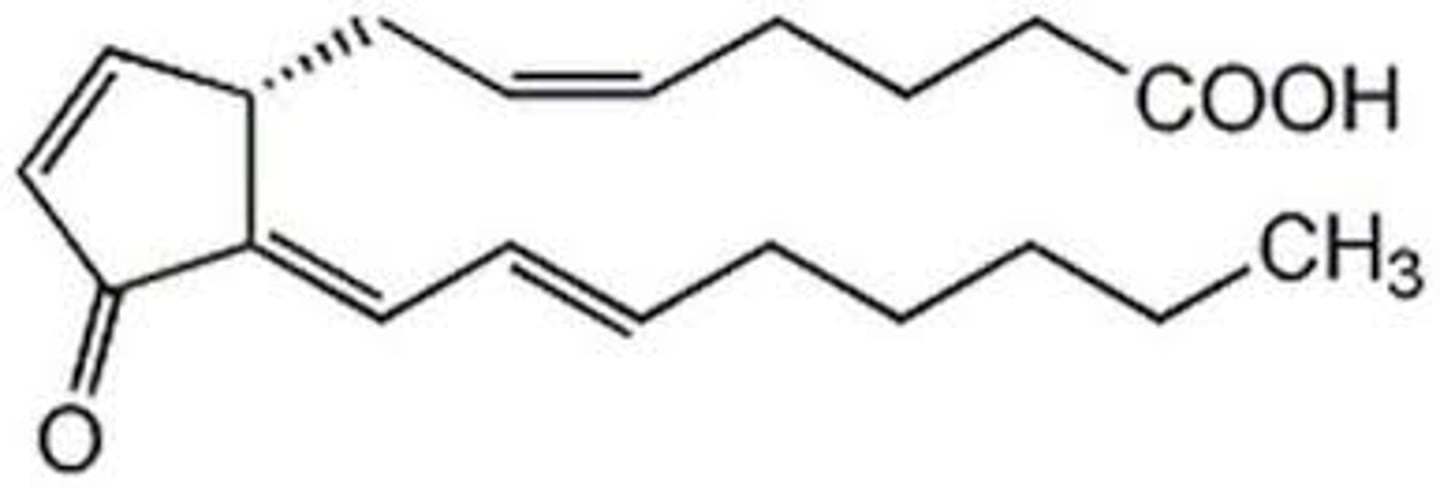
PGJ
TXA2
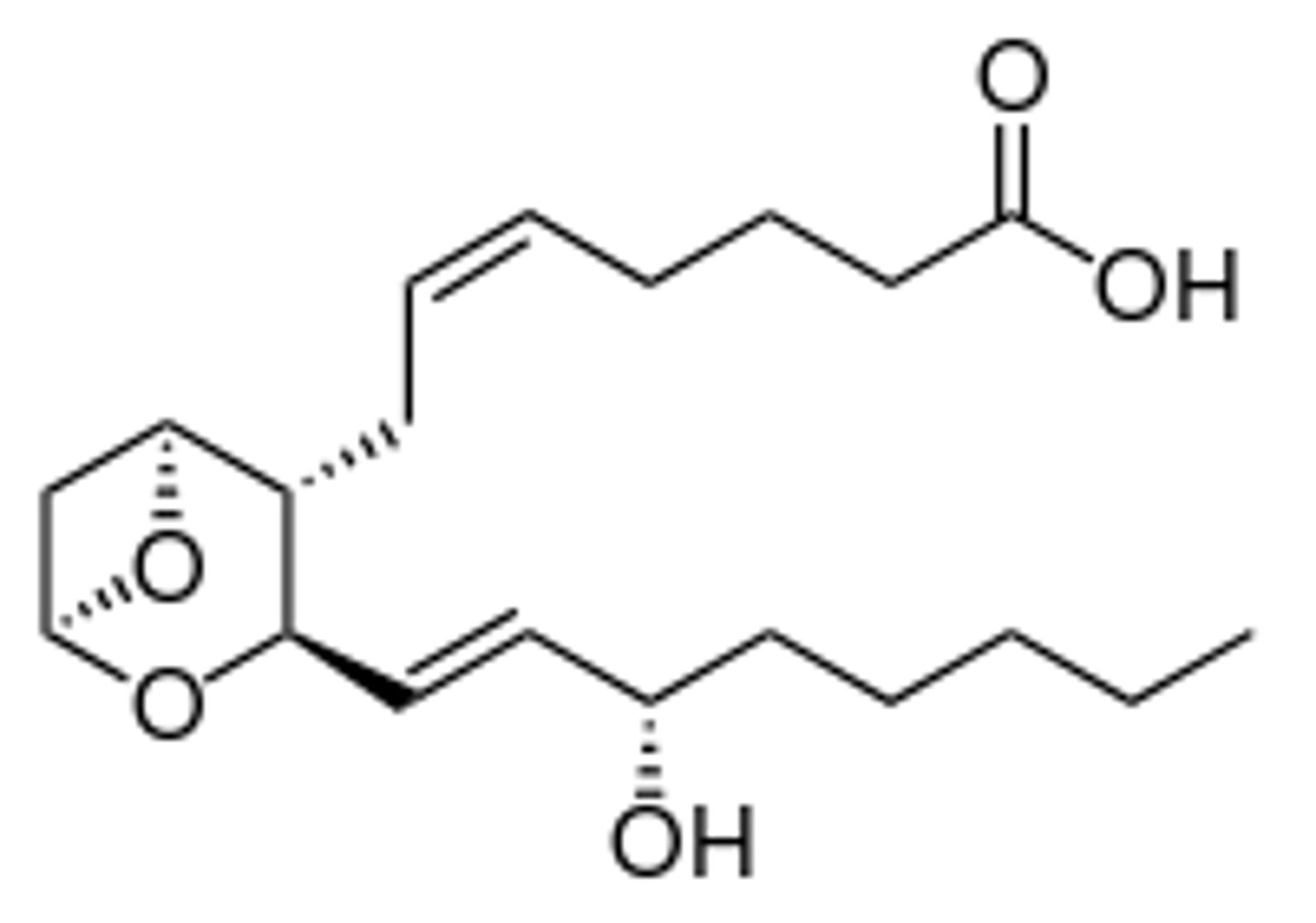
TXB2

Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
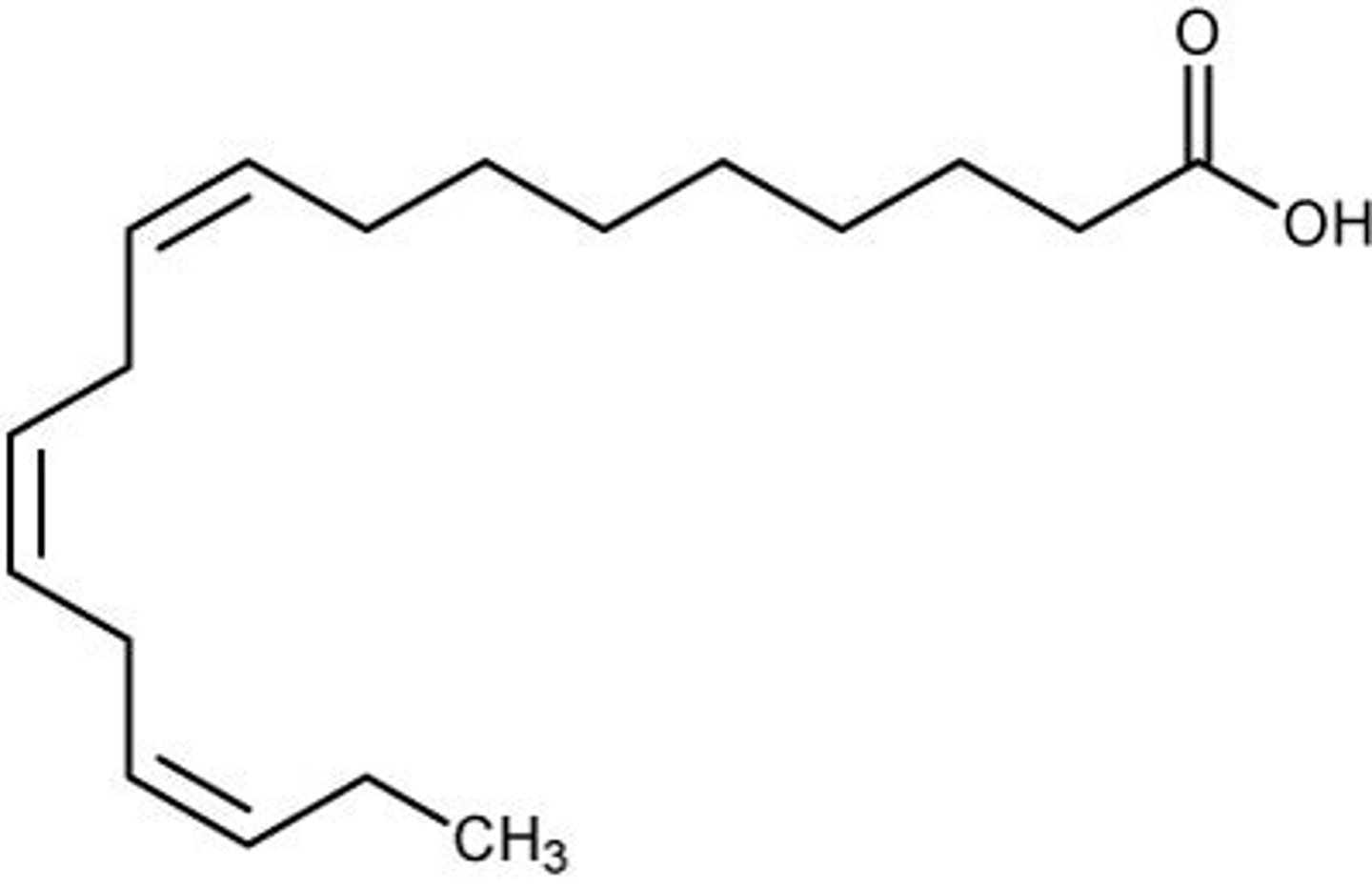
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
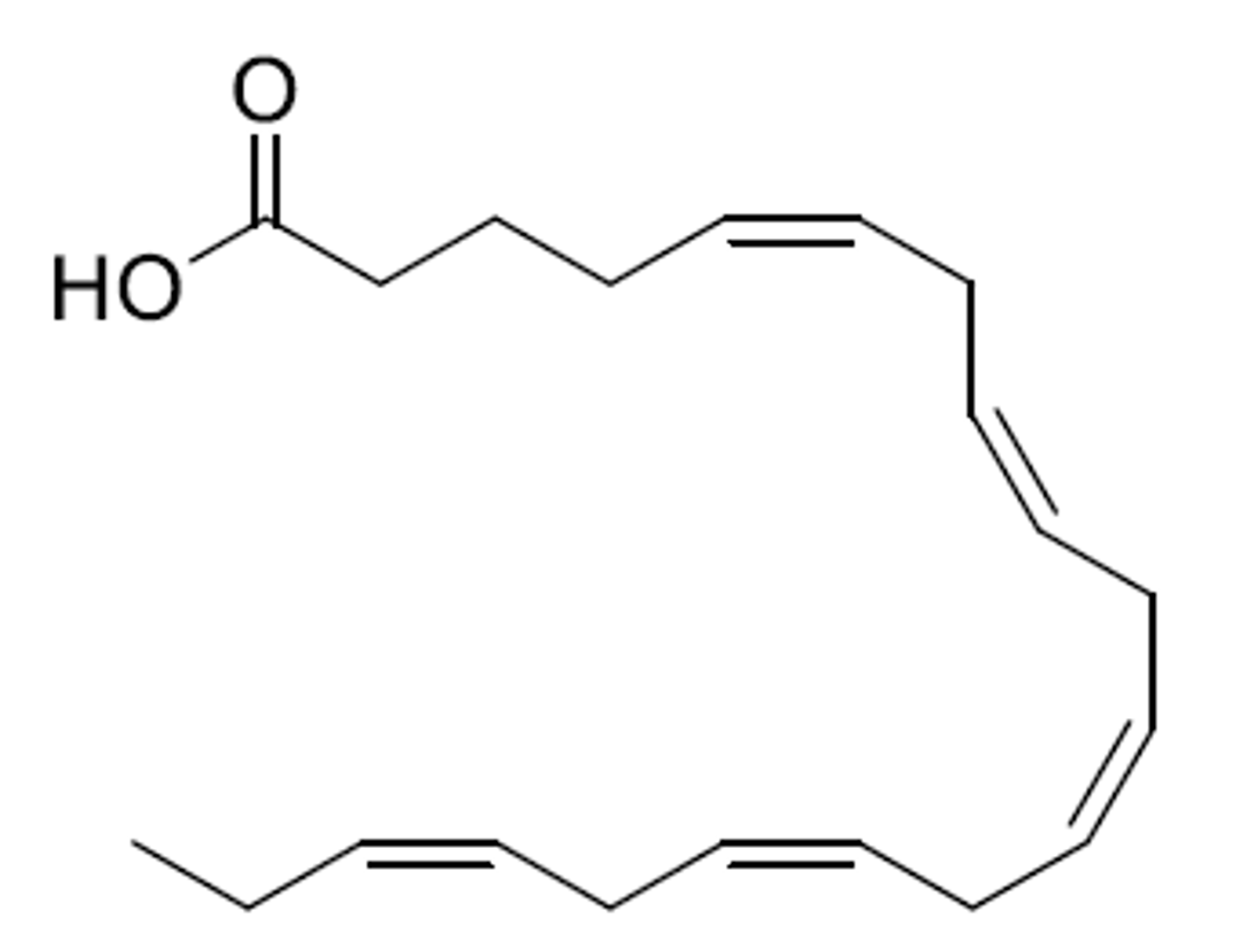
Docohexaenoic acid (DHA)
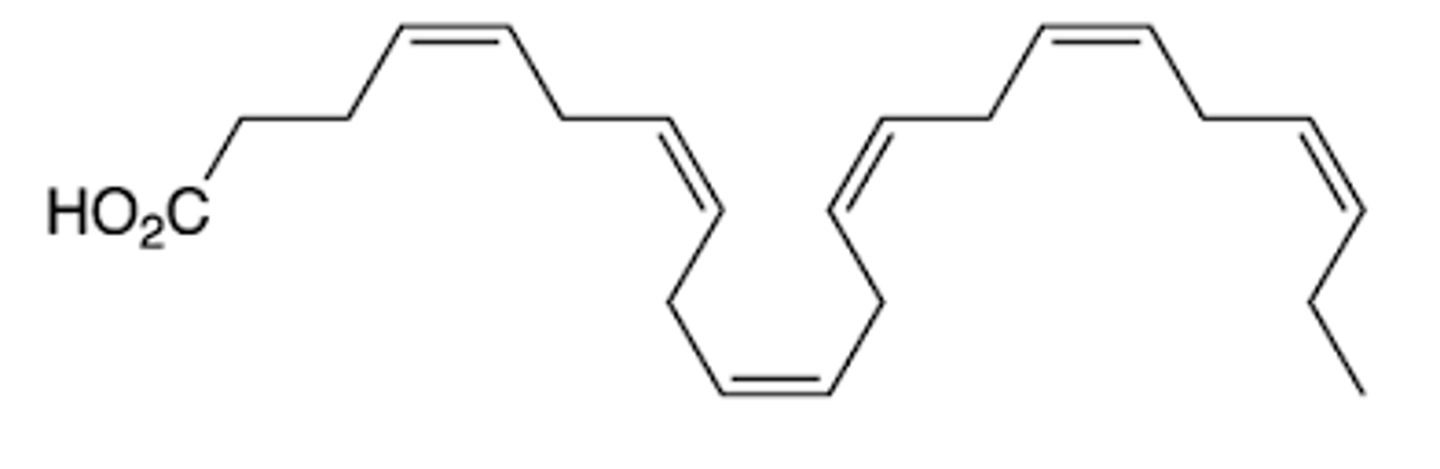
Zileuton
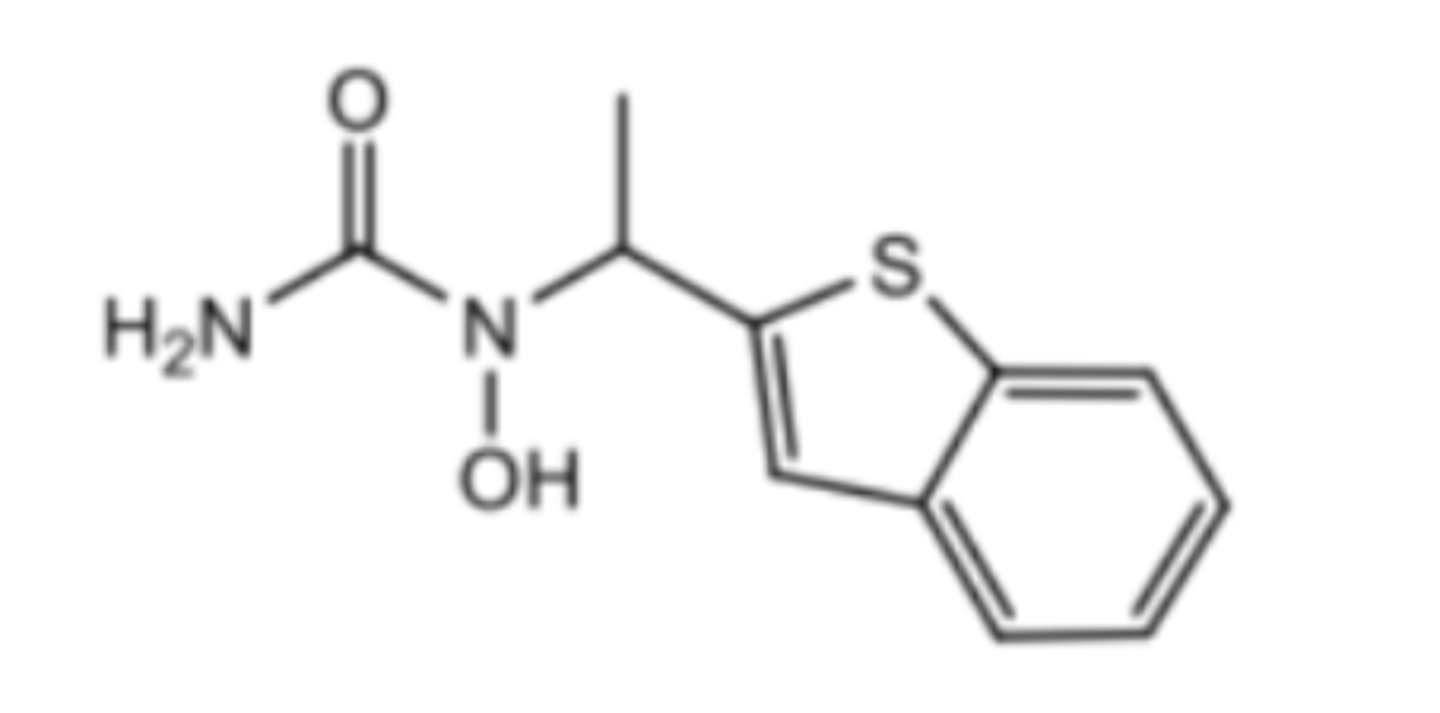
Montelukast
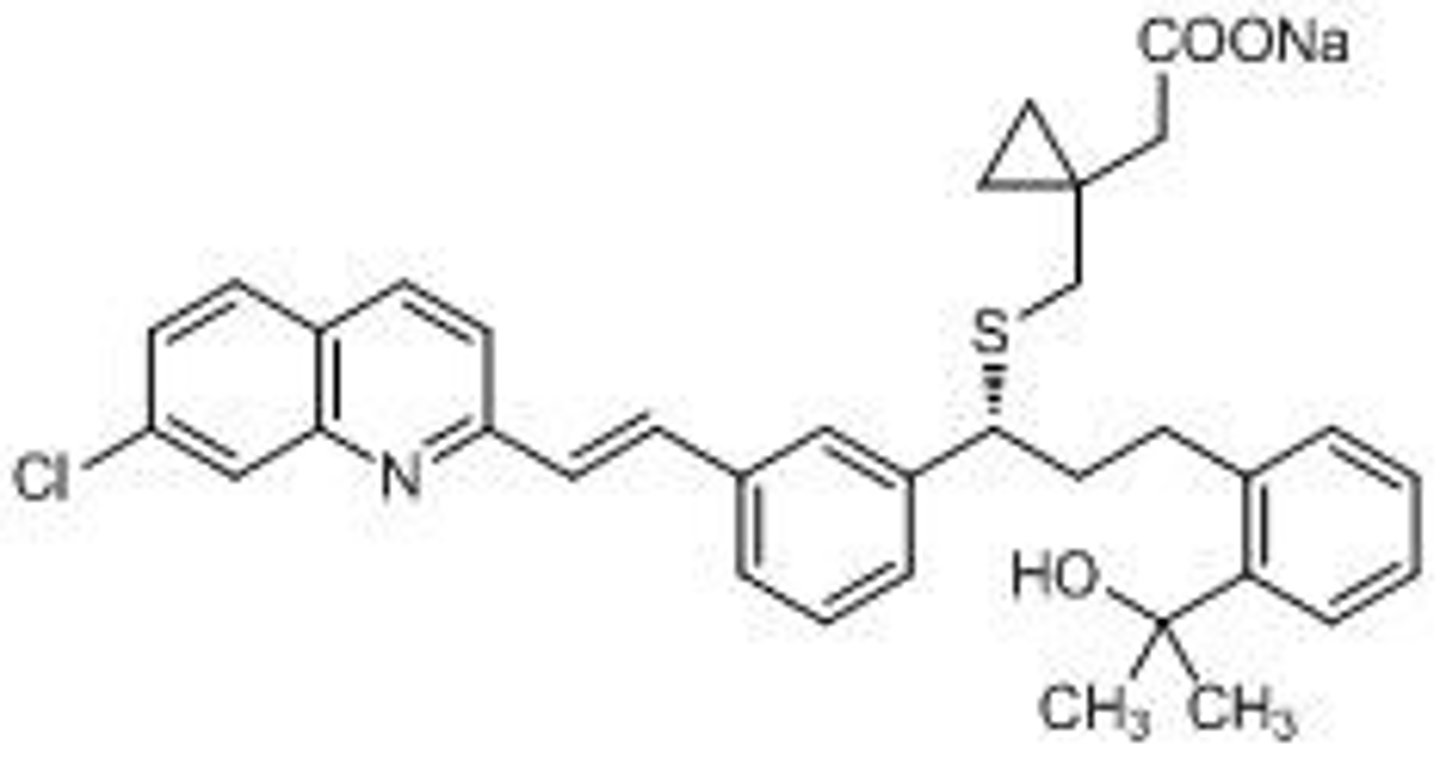
Zafirlukast
What are prostaglandins derived from?
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)
What prostaglandins are formed in the liver?
All prostaglandin products
What prostaglandins are formed in mast cells?
- PGE2
- PGD2
What prostaglandin is formed in the uterus?
PGF2alpha
What prostaglandin is formed in platelets?
TXA2
What prostaglandin is formed in vascular walls?
PGI2
Which prostaglandins are not biologically active?
- PGA
- PGB
- PGC
What does the number after the prostaglandin name indicate?
Number of double bonds
To what can PGH be converted?
- PGD
- PGE
- PGF
- TXA2
- PGI2
What are the key points of PGG and PGH?
- PGG is catalyzed by COX to create peroxide
- PGG is quickly converted to PGH by COX
- PGH is unstable
What are the key points of PGD2?
- Produced mainly in brain and mast cells
- Regulates inflammation
- Regulates sleep
- Aids in male sexual development
- May cause baldness if overexpressed
What are the key points of PGE2?
- Regulates inflammation
- Aids in muscle repair
- Induces vasodilation
What are the key points of PGF2alpha?
- Regulates menstrual cycle
- Accelerates/induces labor
- Abortifacient
- Regulates intraocular pressure
What are the key points of alprostadil?
- Endogenous prostaglandin
- Treats erectile dysfunction
- Vasodilation
- Applied intracavernosally or intraurethally
- PGE1 derivative
What are the key points of misoprostol?
- Prevents gastric ulcer formation
- Induces bicarbonate production in the stomach
- Ends early-term pregnancies
- PGE1 derivative
What are the key points of dinoprostone?
- PGE2 derivative
- Induces labor via cervical softening
- Abortifacient
What are the key points of sulprostone?
- PGE2 derivative
- Abortifacient
- Treats postpartum hemorrhage
What are the key points of latanoprost?
- PGF2alpha derivative
- Treats glaucoma/ocular hypertension
- Effects last 24 hours
- May cause gradual and permanent darkening of the iris
What are the key points of latanoprostene?
- Prodrug
- PGF2alpha derivative
- Treats glaucoma/ocular hypertension
- Converted into latanoprost acid and butanediol
What are the key points of bimatoprost?
- PGF2alpha derivative
- May also target prostamide receptors
- Treats eyelash hypotrichosis
- Treats glaucoma/ocular hypertension
What are the key points of iloprost and epoprostenol?
- PGI2 derivative
- Treats pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Treats peripheral vascular disease
- Inhaled or injected
- Short half-life (minutes)
What are the key points of selexipag?
- Selective prostacyclin receptor (IPr) agonist
- Prodrug
- Treats pulmonary hypertension
- Taken orally
- Long half-life (twice daily use)
- Metabolized by carboxylesterases in the liver
What are the key points of PGJ?
- PGD2 derivative
- Electrophilic center susceptible to nucleophilic attacks
- Can reduce pro-inflammatory activity
- Impacts PPAR-gamma pathway
- Impacts NF-kappaB pathway
What are the key points of TXA2?
- Target GPCRs
- PGH2 derivative
- Very short half-life
- Rapidly converted into TXB2 (inactive)
What are the types of omega-3 fatty acids used in the body?
- Alpha-linolenic acid (AlA)
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
How do omega-3 fatty acids impact arachidonic acid metabolic pathways?
They compete for the same enzymes
What are RvE1/2?
- Anti-inflammatory
- Pro-phagocytosis
- EPA metabolites
What are RvD1/2/3/4?
- Anti-inflammatory
- Protect tissues
- Promote apoptosis
- Promote efferocytosis
- DHA metabolites
What is MaR1?
- Modulates nociception
- Protects tissues
- Promotes efferocytosis
- DHA metabolite
What is PD1?
- Anti-inflammatory
- Neuroprotection
- Promotes healing
- DHA metabolite
What is zileuton?
- 5-LOX inhibitor
- Manages and prevents asthma
- Prevents LTB4 and cysteinyl leukotrienes that play a role in bronchoconstriction
- Can cause liver toxicity
- Can cause suicidal thoughts and depression
What is zafirlukast?
- CysLT-1 receptor antagonists
- Long-term management of chronic asthma
- Metabolized by CYP enzymes in the liver
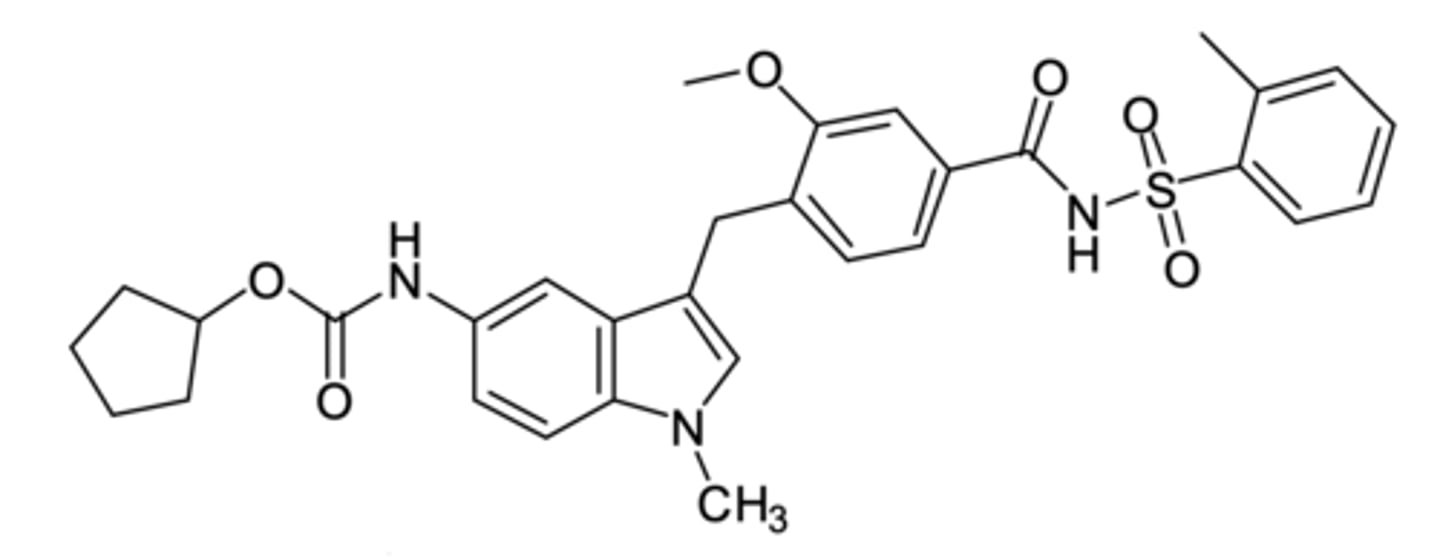
What is montelukast?
- CysLT-1 receptor antagonists
- Long-term management of chronic asthma
- Metabolized by CYP enzymes in the liver
- Treats allergic rhinitis
- Causes suicidal thoughts and depression (BBW)
What does COX-1 do?
- Gastric protection
- Renal blood flow
- Platelet aggregation
What is involved in the COX-1 pathway?
- PGE2
- PGI2
- TXA2
What does COX-2 do?
- Pain
- Fever
- Inflammation
What is involved in the COX-2 pathway?
- PGE2
- PGI2
- PGF2alpha