Topic 2B- Co-ordination & Response
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
2.10 What is the central nervous system?
-It includes the brain and spinal cord
-the spinal cord extends down the base of the brain and is formed from a bundle of neurones which branch off different parts of the body
2.10 What is the brain made up from? And what is responsible for?
billions of interconnected neurones and is responsible for controlling complex behaviours.
2.10 What are the different regions of the brain?
-cerebral cortex or cerebrum
-the cerebellum
-medulla oblongata
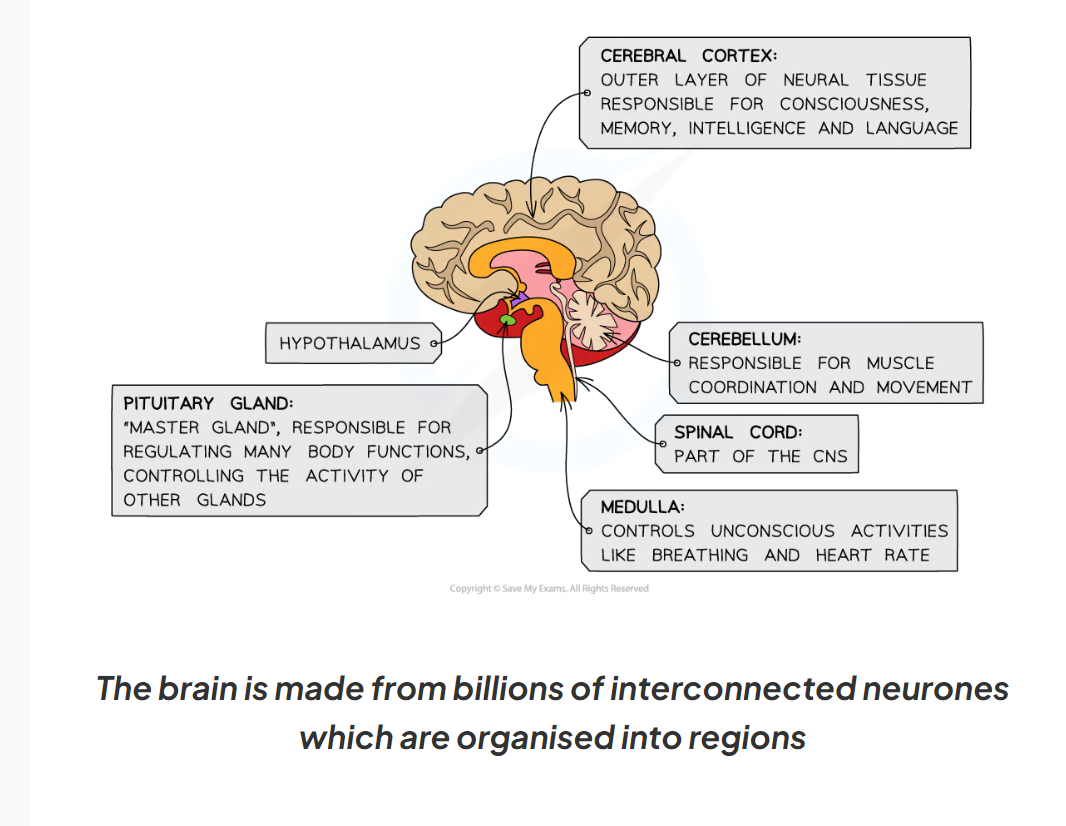
1.10 What is the cerebral cortex / cerebrum?
-this is the outer layer of the brain which is divided into 2 hemispheres (left and right)
-it is highly folded and is responsible for higher-order processes such as intelligence, memory, consciousness and personality
2.10 What is the cerebellum?
-this is underneath the cerebral cortex
-responsible for balance, muscle coordination and movement.
2.10 What is the medulla oblongata?
-this region controls unconscious activities such as heart rate and breathing
2.10 Label this diagram of the brain and explain what each part does
2.11 Why is our understanding of the brain imitated?
-the brain is very complex and very delicate
-different regions can’t be studies in isolation
2.11 what can be used to study the brain?
specialised scanners can be used to study the brain without having to resort to surgical intervention
2.11 What are the different scanner?
CT, PET and MRI
2.11 What are CT scanner and how are they used?
-CT scans produce 3D images of the brain from multiple different directions
-a scan produced in this way show physical structures of the brain and allows visualisation of any tissue damage
-the scans doesnt directly show the fuctions of the regions of the brain, however
2.11 What is a PET scanner?
-they detect gamma rays that radiate from chemical tracers (glucose)
2.11 What are PET scanners used?
-before going into the scanner the patient consumes the tracer (e.g radioactive glucose)
-this travels to any area of the body which has high levels of metabolic reactions / is using more glucose (particularly the brain)
-PET scanners detect gamer rays that radiate from the chemical tracer (glucose)
2.12 Give 4 reasons why treating damage and diseases to the CNS is very difficult
-cancerous tumours can be located deep into the brain or spinal cord, therefore cannot be surgically removed
-tissues in the nervous system don’t repair the same way that other tissues do
-we don’t exactly know which regions of the brain are responsible for which function.
-due to the delicate nature of nerve tissues, any potential treatment carries risks of further damage, which can lead to increased problems
accidental damage could lead to speech or motor issue, or changes to personality which permanent
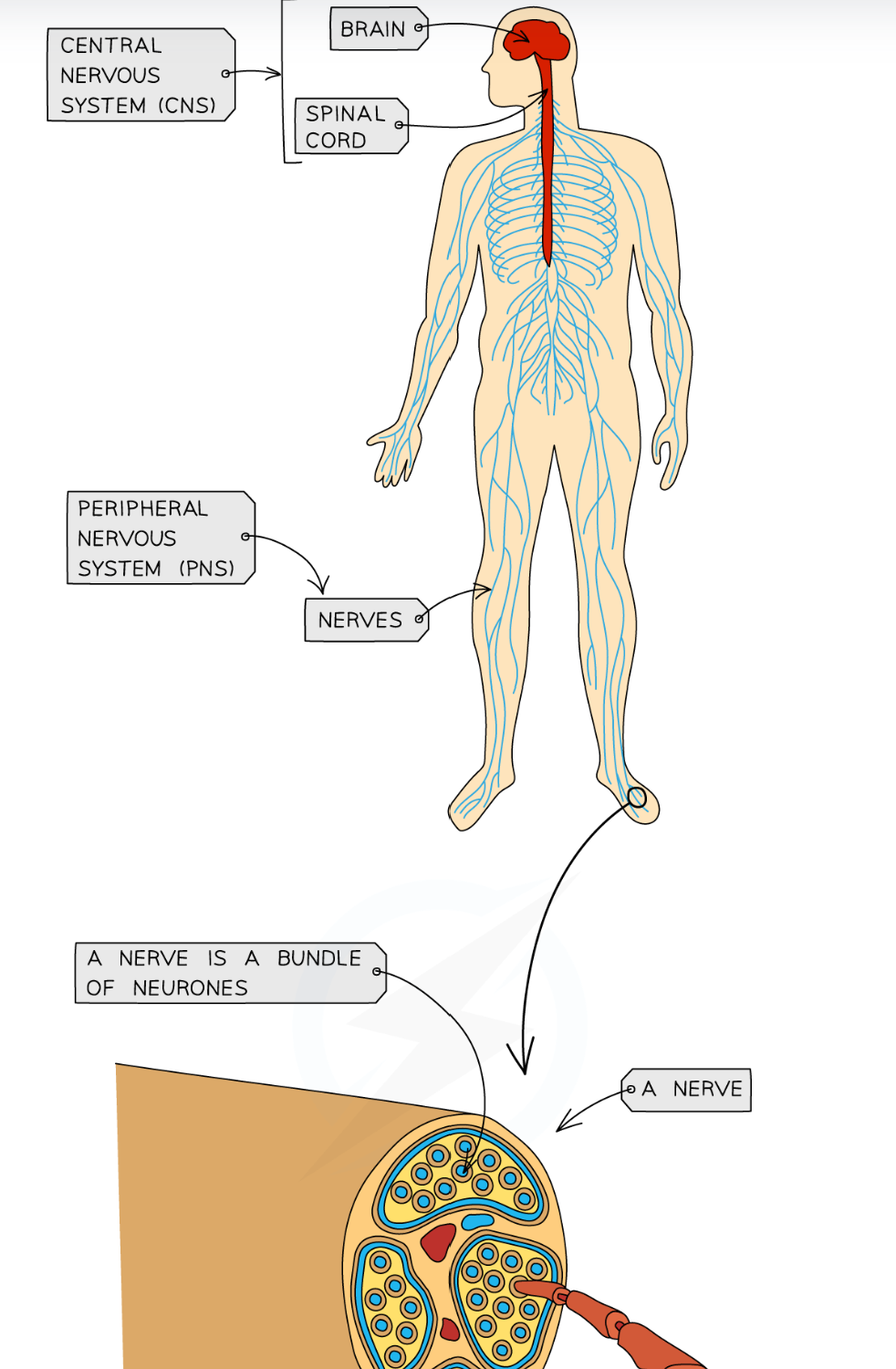
2.13 What does the nervous system consist of?
-central nervous system (CNS) - the brain and spinal cord
-Peripheral nervous system (PNS) - all the nerves in the body
2.13 How is information sent through the nervous syste,?
Through electrical impulses - these are electrical signals that pass along the nerve cells (known as neurones)
a bundle of neurones is kwon as a nerve
2.13 What is the purpose of the CNS?
Acts as a central coordinating centre for the impulses for the impulses that come in from (or sent out to) any part of the body
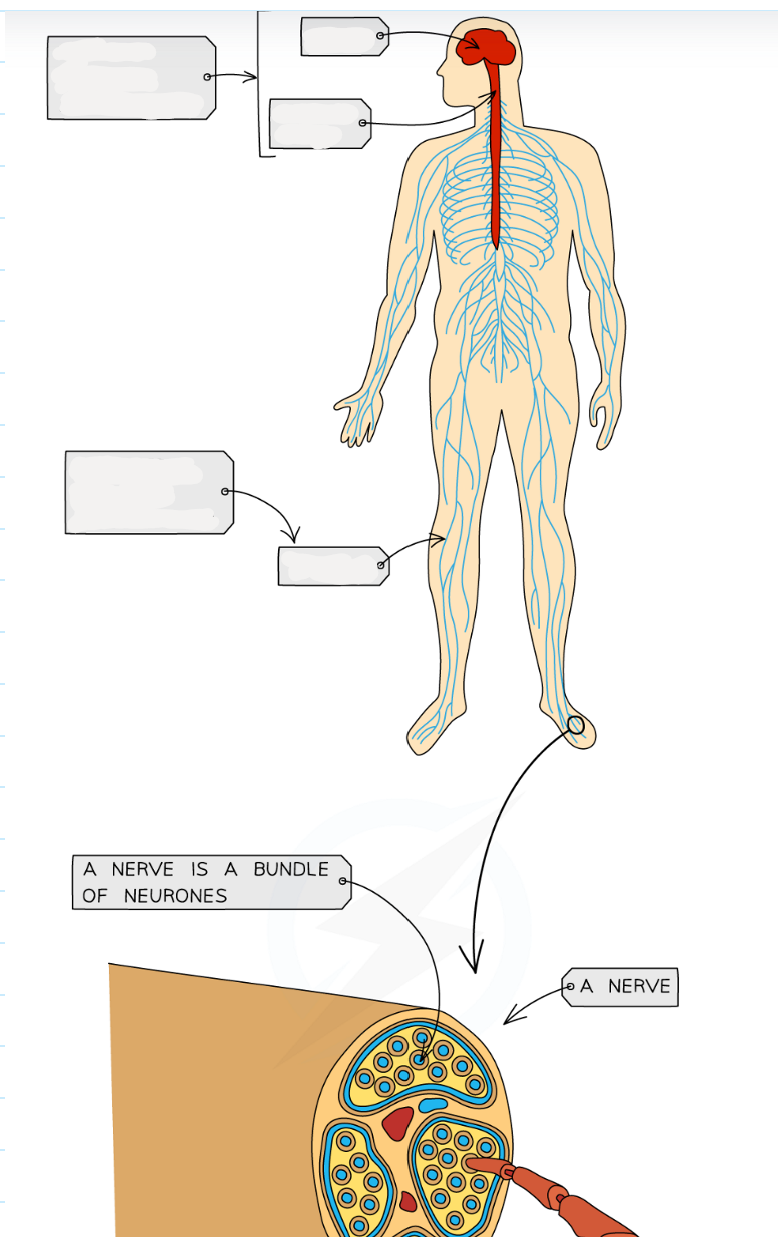
2.13 Label
2.13 What is a stimulus?
a change in an organisms surroundings
e.g:
-light: colour (wavelength)
-sound
-temp
-chemicals (taste)
-pressure/ touch (kinetic energy)
2.13 What is a response?
a reaction to a stimulus. EG muscle contraction, movement of gland
2.13 Give some examples of responses
coughing, blinking, sneezing, swallowing, knee jerking, pupil constriction (getting smaller)
2.13 what is the process to respond to a stimulus?
1) stimulus: heat from hot pan
2) receptors: detect this stimulus (generate an electrical impulse), via sensory neurone
3) coordinator: relay neurone, via motor neuron
4) effector: eg muscle or gland
5) response: eg muscle contraction
2.13 In what form does information travel through the nervous sytem?
electrical impusles
2.13 What are impulses?
-electrical signals which travel through the nervous system in nerve cells
-impulses travel very fast and allow a rapid response
2.13 What are receptors? Where are they found?
detects stimuli (change in the environment)
-convert the stimuli (eg light energy) into an electrical impulse
-found in the eyes, ears, skin and noise
2.13 What types of energy do these receptor detects?
-tongue
-eye
-skin
-ear
-tongue: chemical
-eye: light
-skin: heat, kinetic (pressure)
-ear: sound
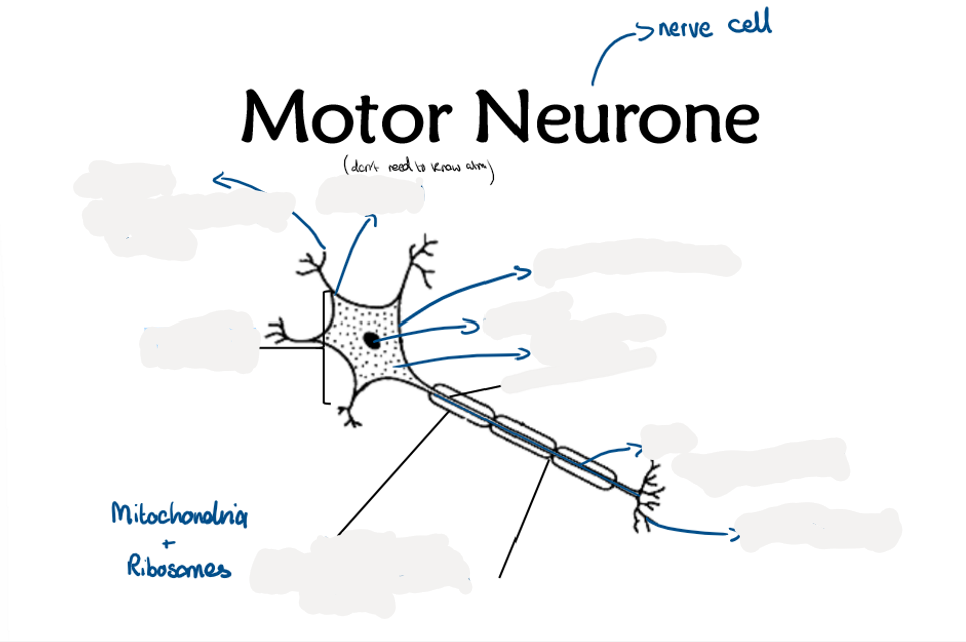
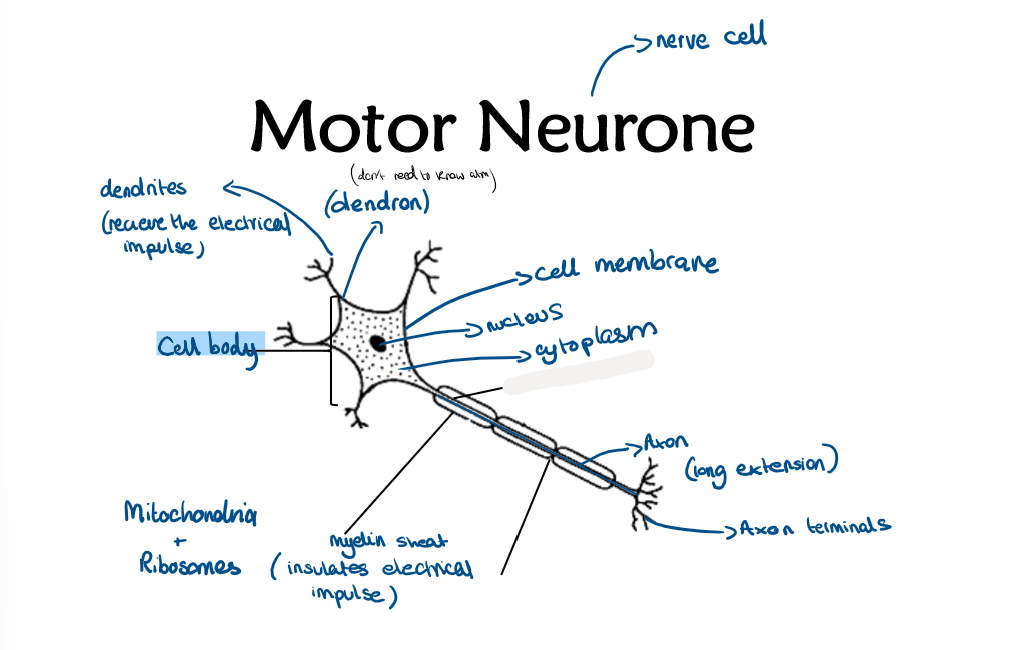
2.13 Label this diagram of a motor neurone
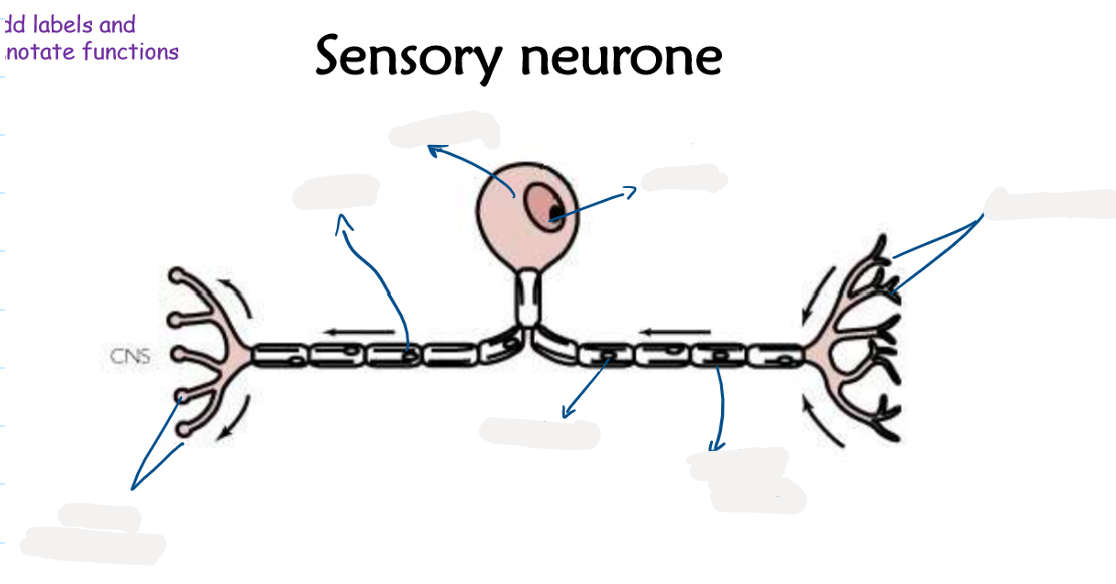
2.13 Label this diagram of a sensory neurone
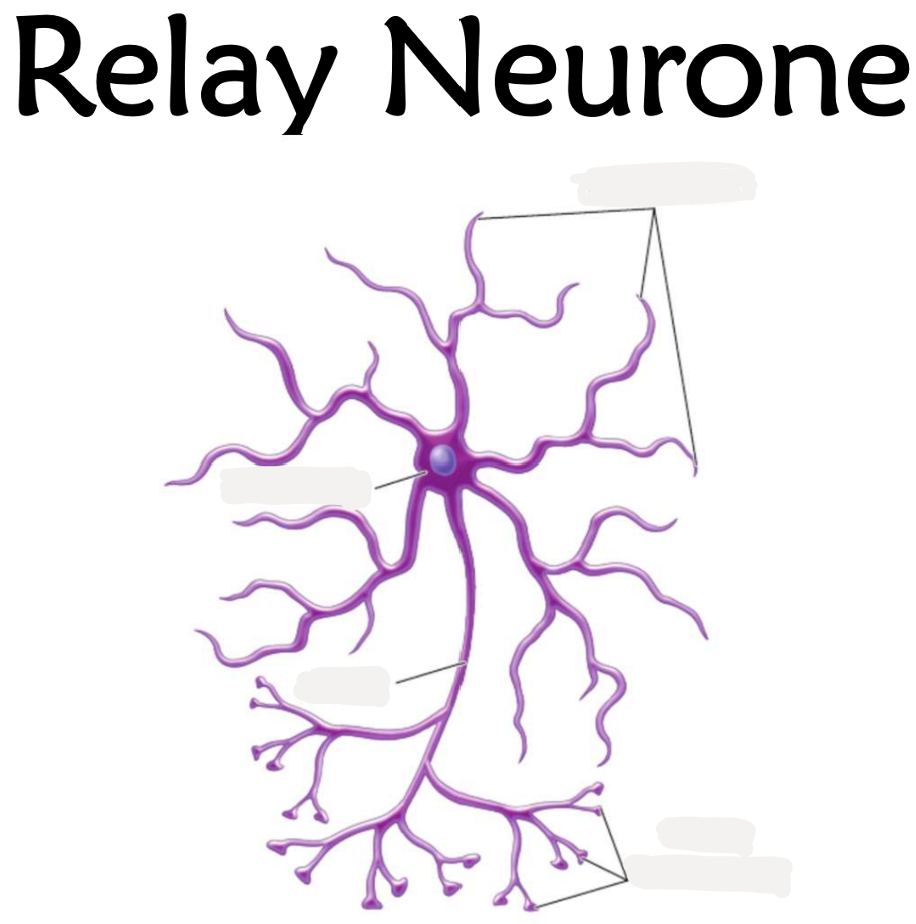
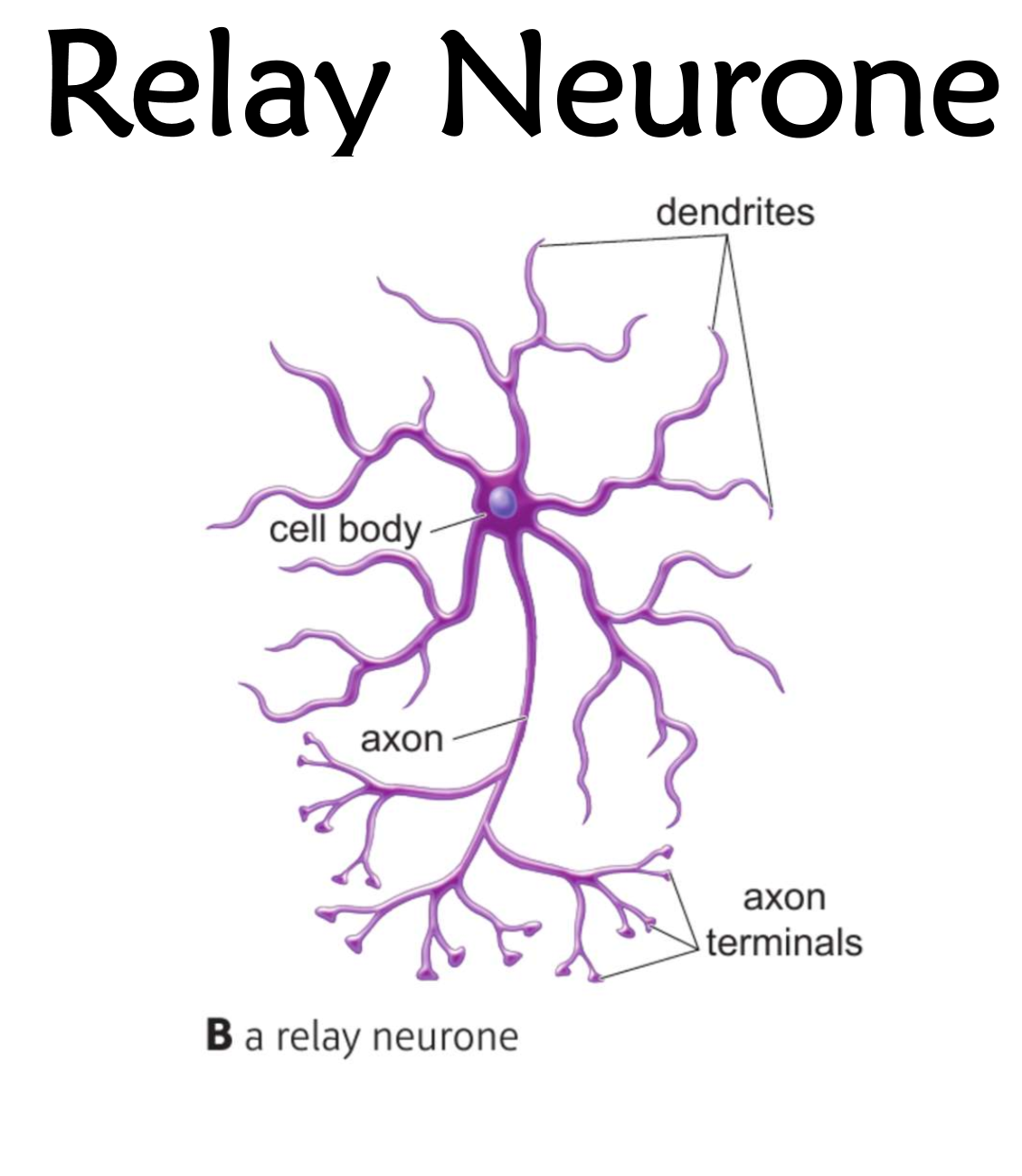
2.13 Labe this diagram of a relay neurone
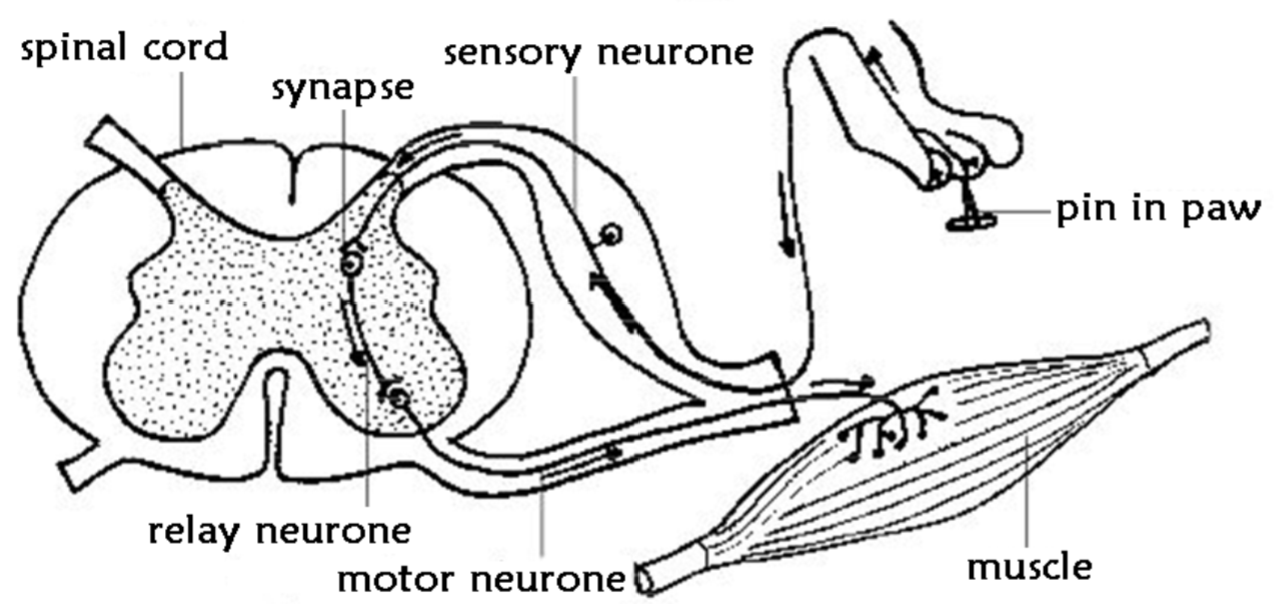
2.14 Explain the journey of an electrical impulse in a reflex arc
1) receptor generates an electrical impulse
2) via the sensory neurone
3) sensory neurone to relay neurone through synapse (gab between 2 neurone)
4) relay neurone to spinal cord then motor neurone through synapse
5) effector carries out response, eg muscle/ gland
2.14 Explain how the impulse travels through the synapse
1) Electrical impulse arrives at axon terminal
2) Neurotransmitter (a chemical) is released into the gap between the neurones (the synapse)
3) The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse
4) Stimulates an impulse in the next neurone
2.14 What is a reflex action? Give some examples
a rapid automatic (or involuntary) response to a stimulus
e.g blinking, gaging, sneezing, withdrawal reflex
2.14 What is the purpose of a reflex action?
to protect form harm
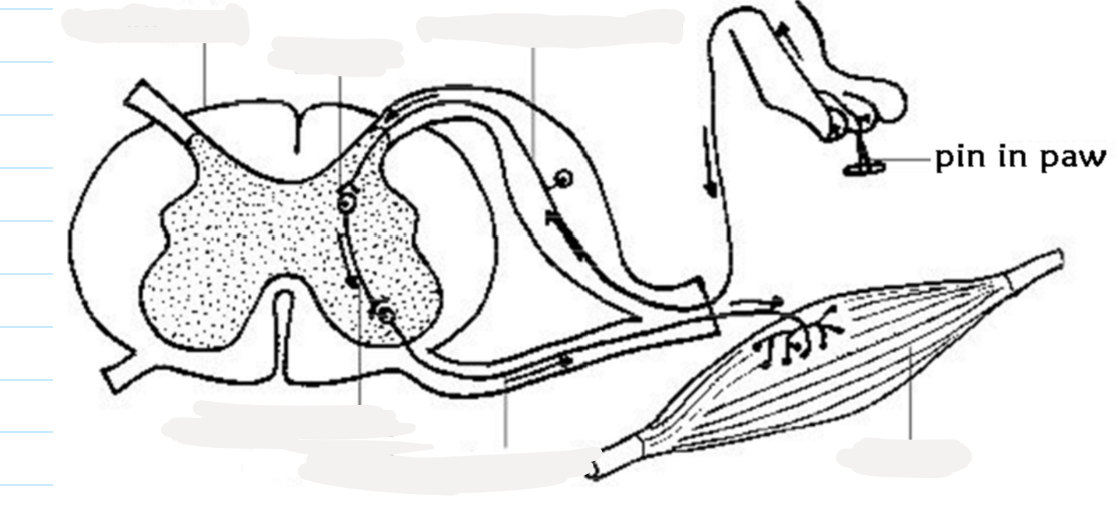
2.14 Label this diagram of the reflex arc