Topic 2C - Cells and control: THE EYE
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
2.15 What is the eye?
a highly specialised sense organ containing receptor cells that allow us to detect the stimulus of light
2.15 Where are the two main receptors in the eye located? & What are they?
They are located in the retina
-Rods cells which are sensitive to light
-Cone cells which can detect colour
2.15 Label this diagram of an eye
2.15 What is the function of the cornea?
Transparent lens that refracts (behind) light as it enters the eye
2.15 What is the function of the iris?
Controls how much light can enter the pupil
2.15 What is the function of the iris?
Control how much light enters the eye
2.15 What is the function of the lens?
Transparent disc that can change shape to focus light on to the retina
2.15 What is the function of the retina?
Contains light receptors - cone (detects colour) and rod cells (detect light intensity)
2.15 What is the function of the optic nerve?
A sensory neurone that carries impulses between the eye and the brain
2.15 What is the function of the pupil?
A hole that allows light to enter the eye
2.15 What is the function of the suspensory ligaments?
ligaments that connect ciliary muscles to the lens
2.15 What is the function of the ciliary muscle?
a ring of muscle that contracts and relaxes to change the shape of the lens
2.15 What is the pupil reflex?
The pupil reflex is a reflex action to protect the retina from damage by light
2.15 What is the eye’s response to dim light?
-radial muscles contract
-circular muscles relax
-pupil widens
-more light enter the eye
2.15 What is the eyes response to bright light?
-radial muscles relax
-circular muscles contract
-pupil narrows
-less light enters the eye
2.15 How does the eye adapt when an object is close up?
-the ciliary muscles contract
-suspensory ligaments slack
-lens gets fatter
2.15 How foes the eye adapt when an object is far away?
-ciliary muscles relax
-suspensor muscles are pulled tight
-lens gets thinner
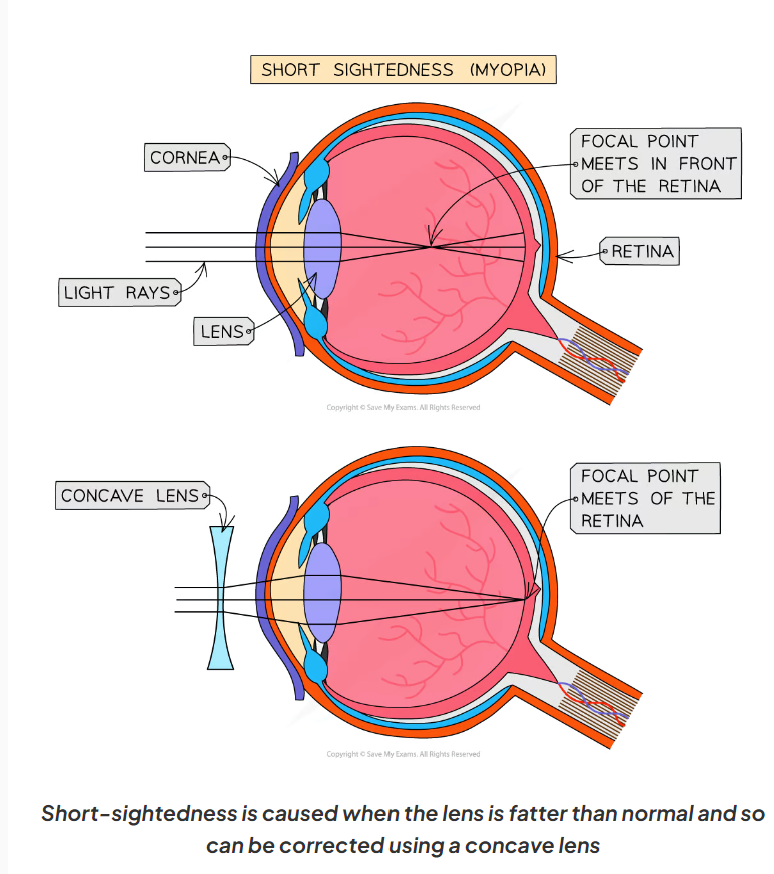
2.16 What is sort-sightedness?
-also known as myopia
-happens when the lens is more curved than normal or the eyeball is too long
-this means the light is refracted too much
-so the focal point falls in front of the retina (rather than on the retina)
-meaning that distant objects appear blurry
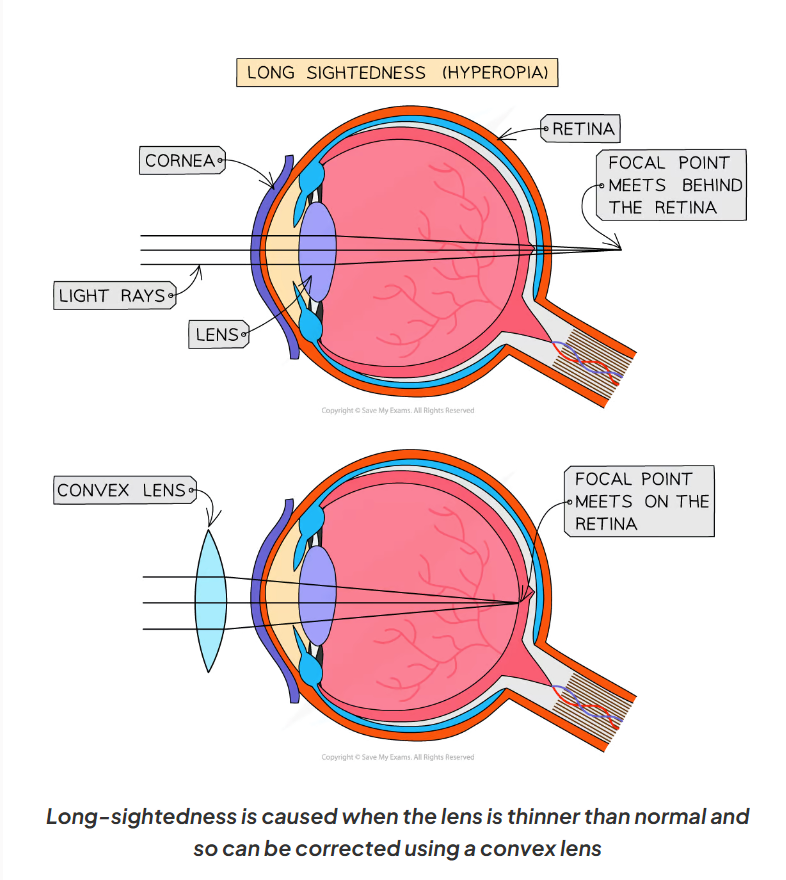
2.16 What is long-sightedness?
-also known as hyperopia
-happens when the lens is less curved than normal or the eyeball is too short
-this means the light is not refracted enough
-so the focal point falls behind the retina (rather than on)
-meaning the close objects appear blurry
2.17 How can short-sightedness be treated?
It can be corrected using contact lenses or glasses with a concave lens
2.17 How can long-sightedness be treated?
it can be corrected using contact lenses or glasses with a convex lens
2.17 Here is a diagram of how short-sightedness affects the structure of the eye and how it can be corrected
2.17 Here is a diagram of how long-sightedness affects the structure of the eye and how it can be corrected
2.16 What is colour blindness?
-the inability to distinguish between certain colours and in rare cases, the inability to see colours at all
-it is genetically inherited but can also develop over time
-there are several different types of colour blindness
2.17 How can colour blindness be treated?
-there is no cure (bc the cone cells cannot be replaced)
-people who are colour blind mostly try to find ways to live with it
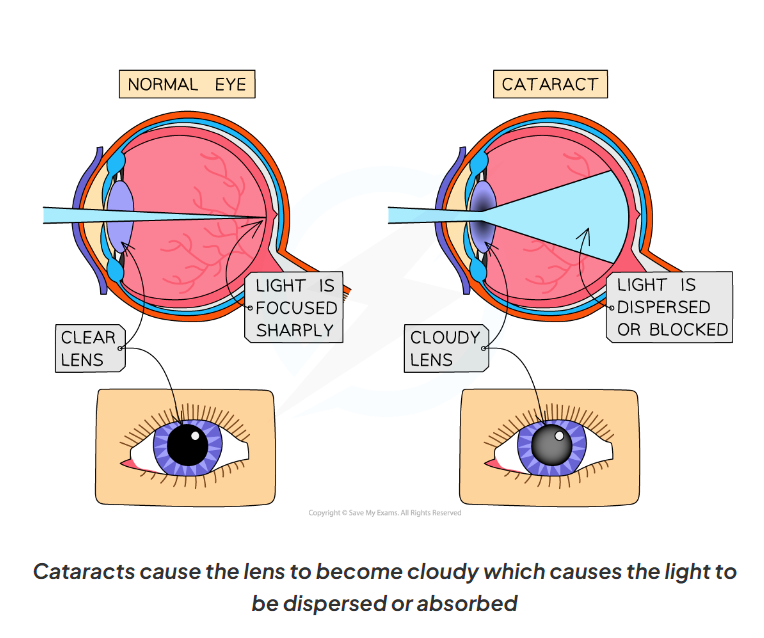
2.16 What is cataracts?
-a condition where in which a build up in protein causes clouding of the lens
-a cloudy lens means that light is dispersed throughout the eye or absorbed by the lens, rather than being sharply focused to one particular part
-this often results in blurry vision
-eventually if left untreated cataracts can lead to blindness
2.17 How can cataracts be treated?
-It can be corrected by replacing the cloudy lens with an artificial one
2.17 Here is a diagram of the structure of a normal eye vs a cataracts eye