Week 3- Chemical processes in estuaries
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is fluorines behaviour like
Conservative
What is fluorine conc like in seawater v riverwater
Higher conc in seawater
What is irons behaviour like in seawater
Non conservative
Why is irons behaviour non conservative
Lost in upper estuary
Why is irons loss unlikely due to oxidation of Fe(II) to Fe(III)
As river water contain oxygen at rate of Fe(II) oxidation is fast
What is irons loss more likely to be due to
Coagulation of colloidal Fe(III) as river water mixes with seawater
What is the makeup of iron like in the solution
Most Fe lost is Fe(III)
Conc of Fe (II) is still high
When does concentration of Fe(II) decrease
With increasing stability
How do ligand affect iron concentrations
Fe (III) is stabilised by ligands and stop it from dissolving
Fe(II) is more stable
Effects the ratio of different irons
What behaviour does silicon show
Conservative and non-conservative
What evidence is there for the behaviour of silicon
Danshuei estuary
Conservative behaviour in March
Elbe estuary
Evidence for removal of dissolved silicon in early autumn
What do areas of silicon removal lead to
Diatom blooms
Give an example of a estuary with extreme silicon removal
Charlotte Harbour (Florida)
How can you trace large river plumes
Using the conservative behaviour of silicon
In Narragansett Bay what are a source of dissolved silicon in spring bloom and a net sink of dissolved and biogenesis silica
Marshes
Are anthropogenic inputs usually a source of silicon
No
In the rappahannock estuary what is the input of dissolved silicon due to
Desorption and dissolution
How can Si isotopes be used to study nutrient utilisation and remineralisation of biogenic silicon
Even though dissolved silicon shows conservative behaviour, silica preferentially use lighter Si isotopes to form frustules so the remaining dissolved silicon is enriched by heavier isotopes
What does behaviour of dissolved silicon changing over the year reflect
Rate of biological uptake/ remineralisation
Residence time of water within estuary
Turbidity
How does turbidity affect the behaviour of dissolved silicon
Particle loading may affect light penetration= River biological production is inhibited by turbidity
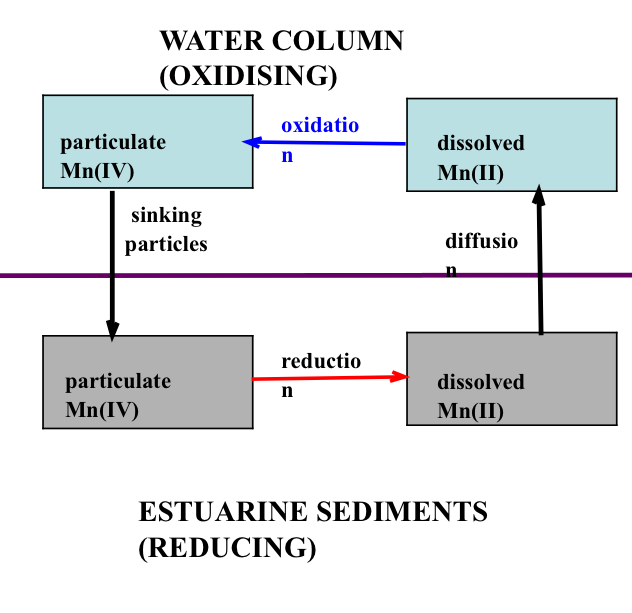
Why does manganese undergo intensive cycling in estuaries
Chemistry is linked to changes in redox
How do you describe the oxidising and reducing behaviour in manganese
Both takes place
Oxidising- Mn4+ thermodynamically stable, as MnO2 it has low solubility and Mn4+ forms particles or coats them
Reducing- Mn2+ thermodynamically stable, as Mn2+ it is soluble and can diffuse and advect in solution
Why are many estuarine sediments reducing
Due to high rates of burial of organic carbon
What takes place to manganese in anoxic sediment
Mn5+ is reduced to Mn2+ which is soluble
When is max concentrations of dissolved manganese seen
Intermediate sediments
What is the lifetime of manganese like
Long enough to be observed
What is a change in Mn oxidation state accompanied by
Phase change
What is the overall cycling of manganese like
What are the kinetics of Mn2+ like
Slow= can persist at concs higher than predicted by thermodynamics
Where can high concentrations of Mn2+ be found
Water column if circulation is restricted e.g. fjord
In bottom waters with low oxygen
Describe the tamar river and estuary
6km from north Devon coast
Main freshwater input to Plymouth
Catchment: agriculture, woodland, abandoned mines
Upper estuary: tidal mudflats and reed beds
Lower estuary: inhabited, dockyards, military port, mudflats
What is gauged daily flow like in Tamar river like
Variable but is a seasonal cycle
What do the 10 surveys show about estuarine mixing in the Tamar
Large seasonal variability due to runoff, residence times and point source
Nitrate shows conservative behaviour
Silicon shows conservative behaviour but not in summer
Phosphate has non conservative behaviour
What is the behaviour of nitrate and nitrite in 2018/19
Behaviour similar but concentrations different
What was the behaviour of phosphate like in 2019
Not conservative
All addition
How does nitrate behave in Tamar
Conservatively
What does student data show about nitrate
Does not show conservative behaviour in summer
How does phosphate behave in Tamar estuary
Non conservative manner