Physics 2024
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
accelertion
The rate at which velocity changes
drag
resistance by friction from air or water moving over a surface
Gravity
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses.
reaction
a response to something
terminal velocity
the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity
air resistance
force that opposes the motion of objects that move through the air
elastic collision
A collision in which colliding objects rebound without lasting deformation or the generation of heat.
inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion
reference point
A place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion
thrust
push with force
at rest
The state of an object when it is not in motion
extension
stretching or elongation
initial velocity
the starting velocity
scalar
A physical quantity that has magnitude only.
unbalanced forces
forces acting on an object that combine and form a net force that is not zero
average speed
total distance divided by total time
final velocity
velocity of an object at the end of a time interval
kinetic
energy of motion
speed
The distance an object travels per unit of time
upthrust
A force that pushes things up in liquids and gases.
balanced forces
Equal forces acting on an object in opposite directions
force
A push or pull exerted on an object
net force
The combination of all forces acting on an object
vector
A quantity that has magnitude and direction
deceleration
negative acceleration
free fall
the motion of a falling object when the only force acting on it is gravity
newton
SI unit of force
stationary
standing still; not moving
velocity
Speed in a given direction
Displacement
Distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point.
friction
A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact
normal force
the force perpendicular to a surface that prevents an object from falling through the surface
stretch
make long, longer or bigger
weight
A measure of the force of gravity on an object
force
an interaction between 2 systems and as a consequence it can change a system’s motion
contact forces
forces that have an effect only on objects that they touch
non-contact forces
the objects don't physically come into contact, e.g. gravity, magnetic force
Distance
is the actual path taken between two points A to B
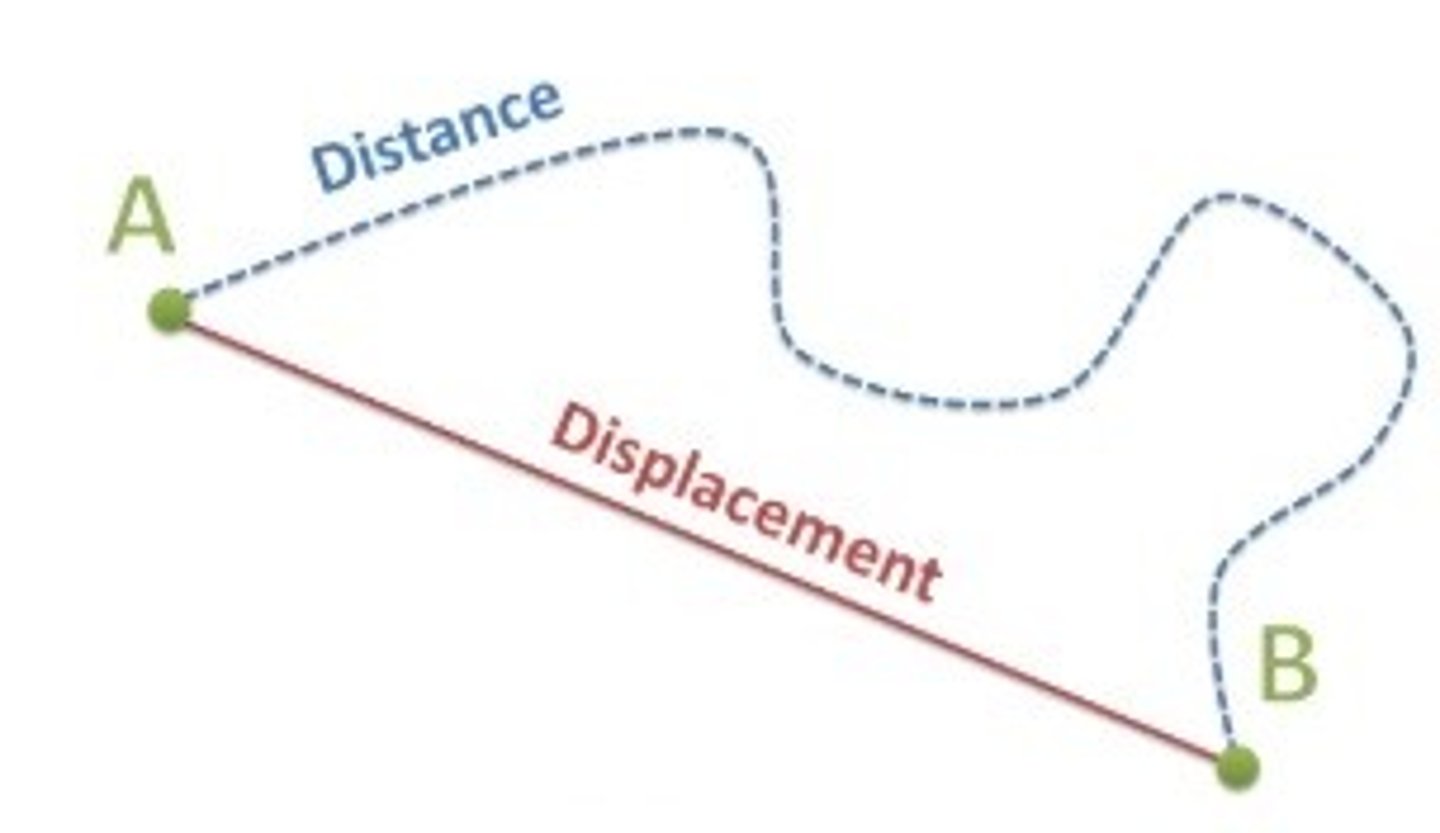
Distance is a ____quantity - it only has ____ and not a direction
scalar
magnitude
Displacement
is the straight line journey from one point to another
The displacement B to A is the exact reverse of A to B (same magnitude but opposite direction)
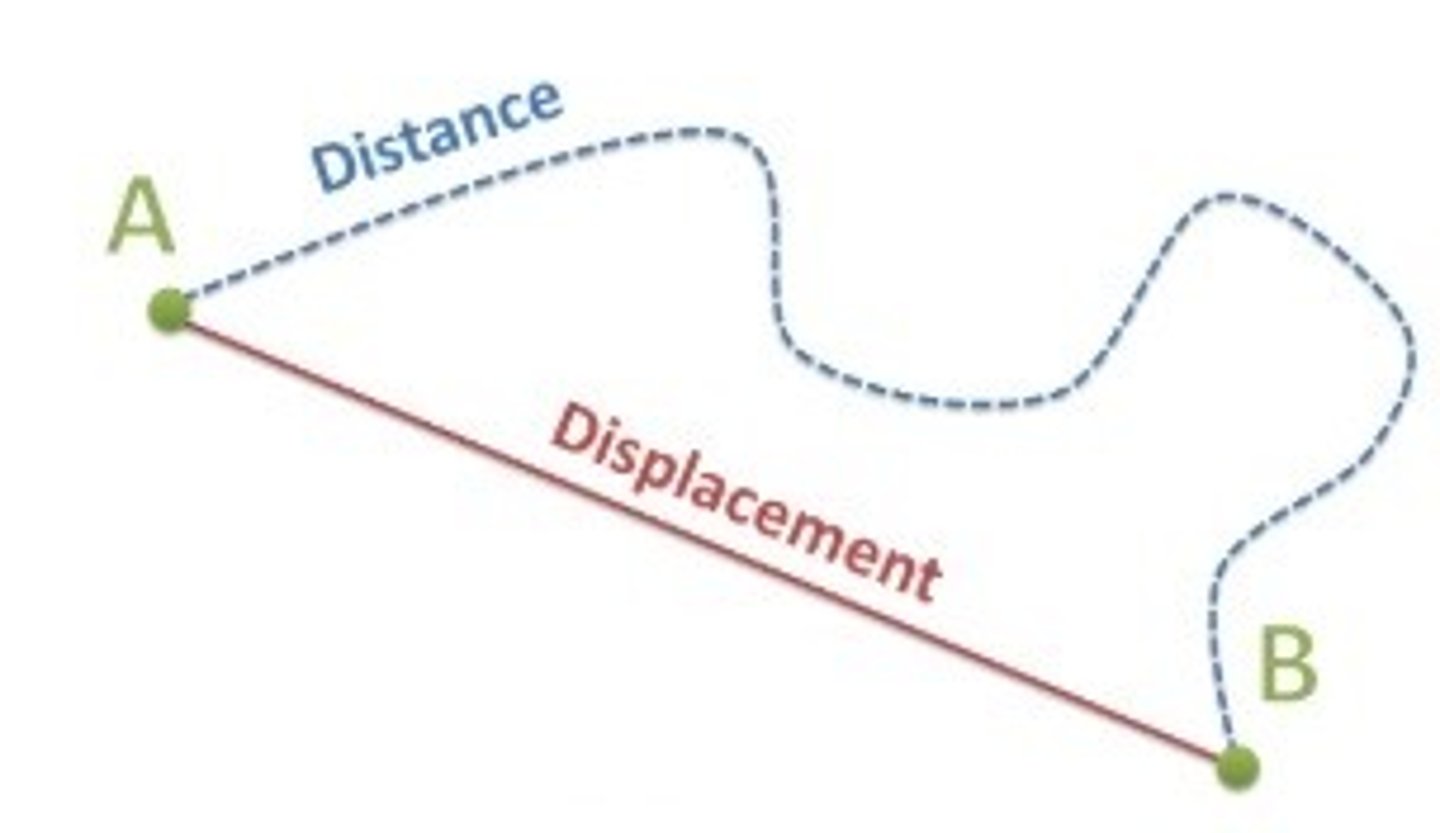
The displacement is a _____ - it has a ____ and ______
vector, magnitude, direction
All vectors can be represented by ....
arrows showing the size and direction
scalar quantity
a quantity that can be described by magnitude only and has no direction
Examples of scalar quantities

vector quantities

examples of contact forces
friction, reaction force, upthrust, tension, air resistance
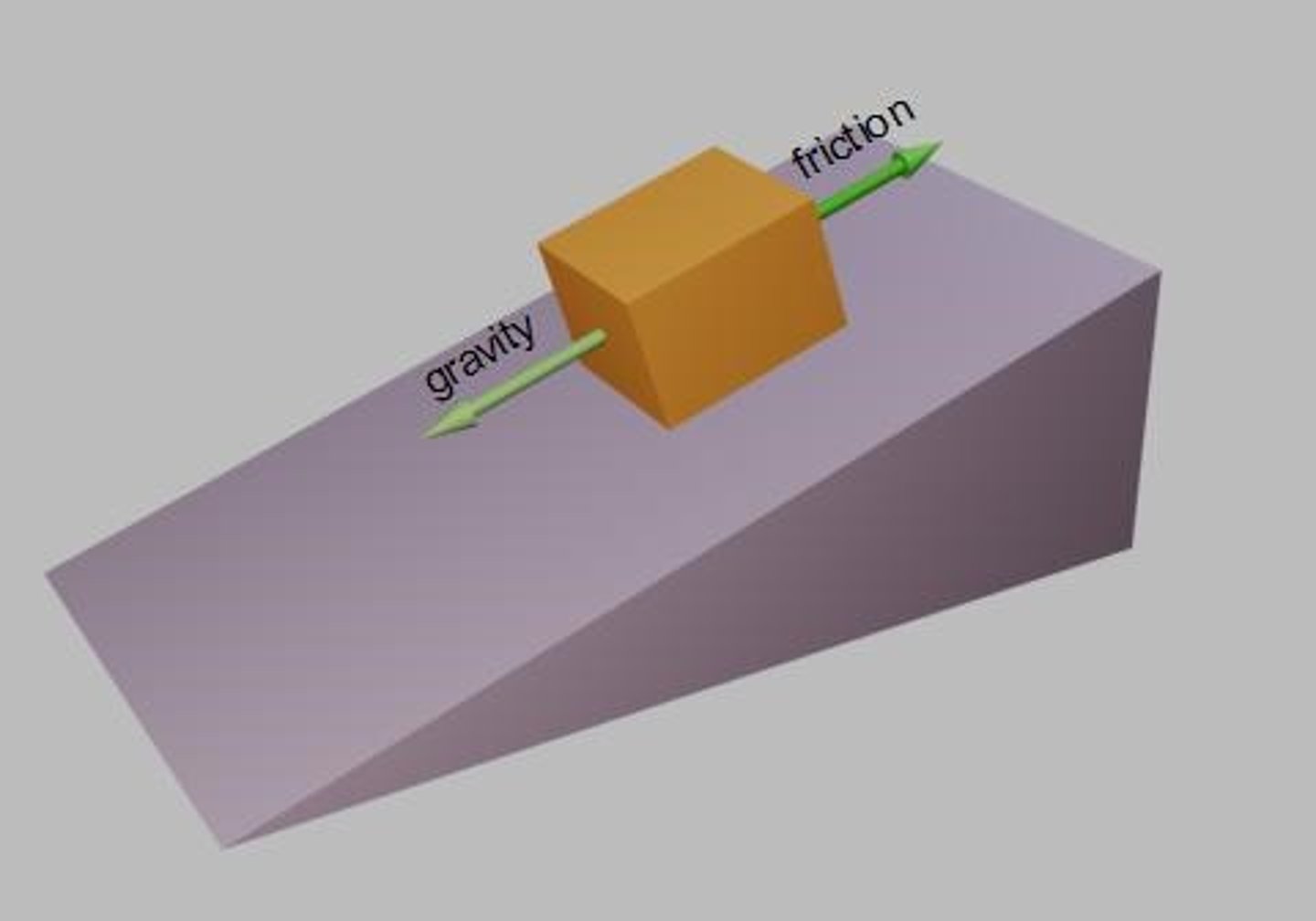
Friction
A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact
Two objects sliding past each other experience friction forces. For example, a box sliding down a slope.
reaction force
force acting in the opposite direction
An object at rest on a surface experiences reaction force. For example, a book on a table.
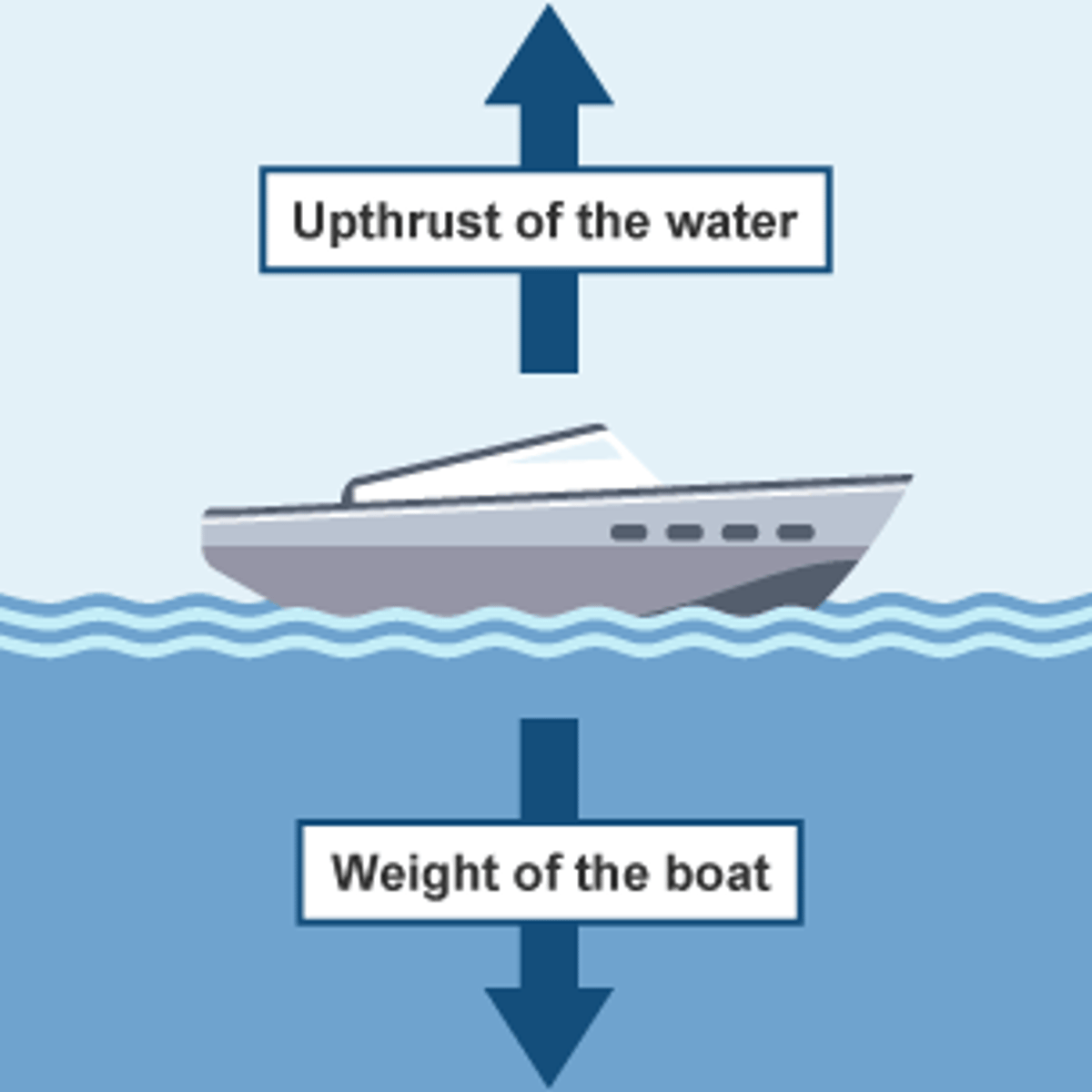
Upthrust
A force that pushes things up in liquids and gases.
An object that is partly, or completely, submerged in fluid experiences a greater pressure on its bottom surface than on its top surface. This causes a resultant force upwards. This force is called upthrust.
tension
stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object
An object that is being stretched experiences a tension force. For example, a cable holding a ceiling lamp.
air resistance
force that opposes the motion of objects that move through the air
An object moving through the air experiences air resistance. For example, a skydiver falling through the air.
non-contact forces are ...
Gravitational force, magnetic force, electrostatic force
Gravitational force
an attractive force that acts between any two masses

electrostatic force
attraction or repulsion of particles or objects because of their electric charge.
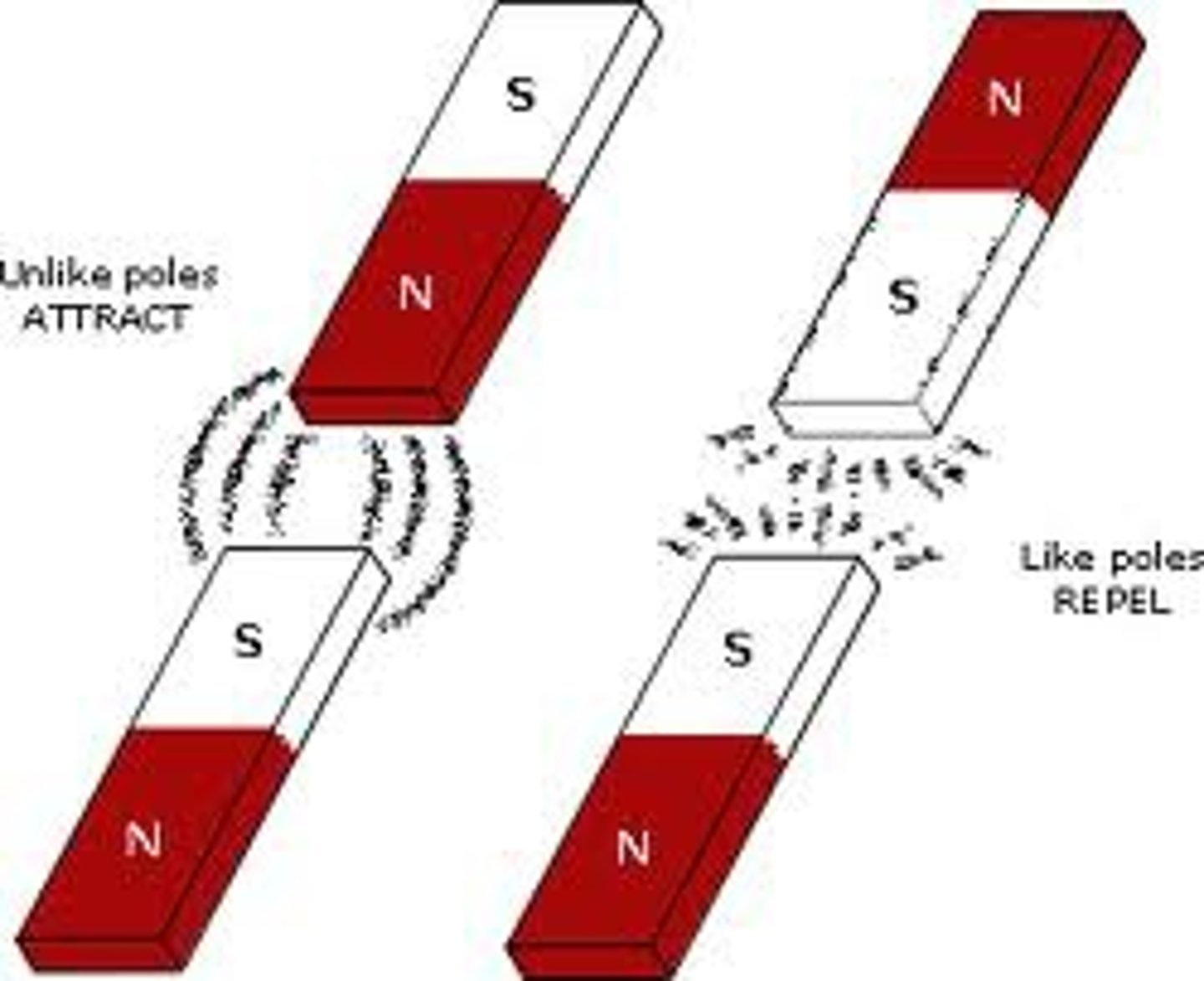
magnetic force
the attraction or repulsion between magnetic poles
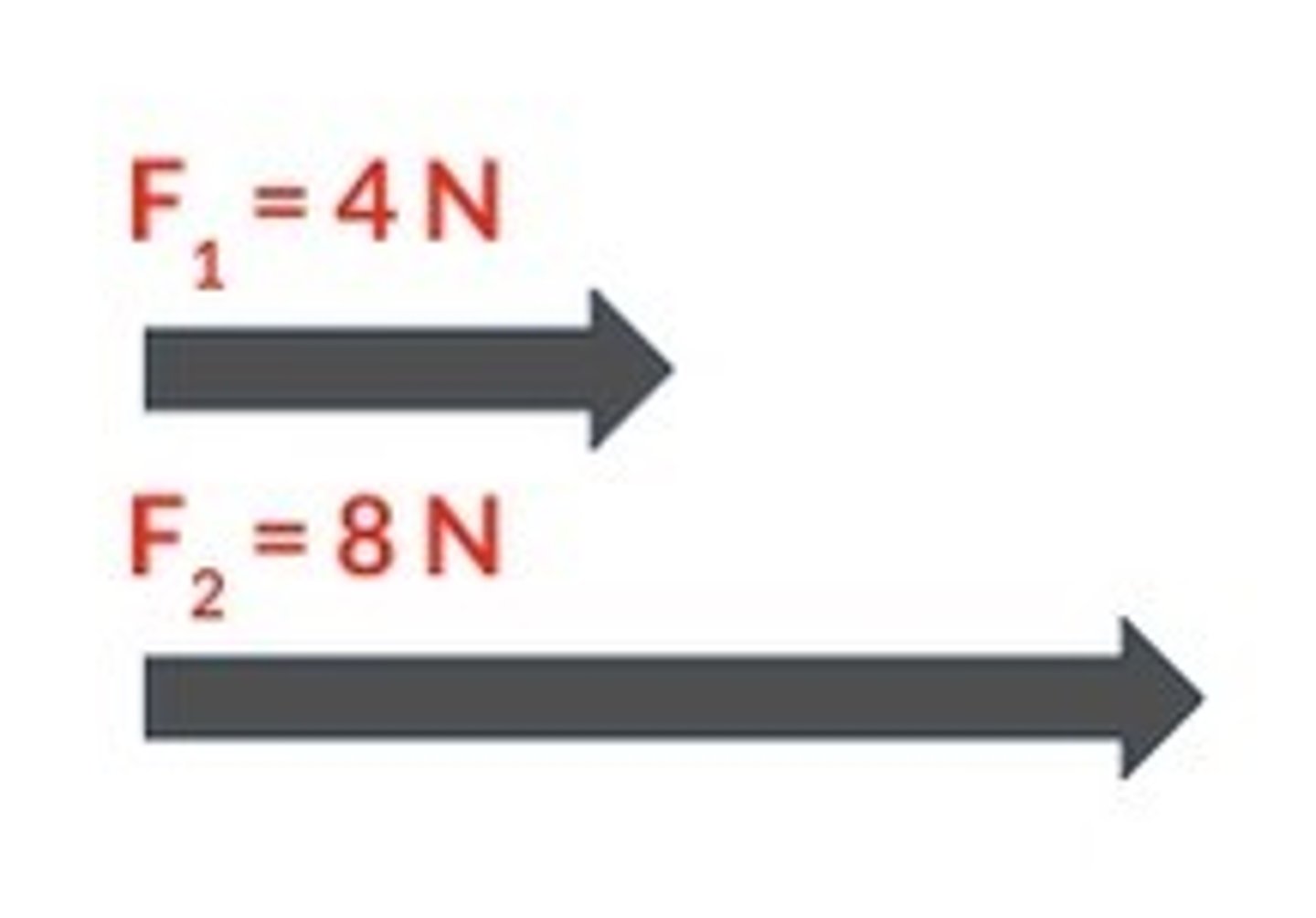
Are forces vector or scalar quantities? And what are they measured in?
Forces are vectors because they have both a size and a direction
Forces are represented using arrows
Forces are measured in newtons (N)
free body diagram
a diagram showing all the forces acting on an object
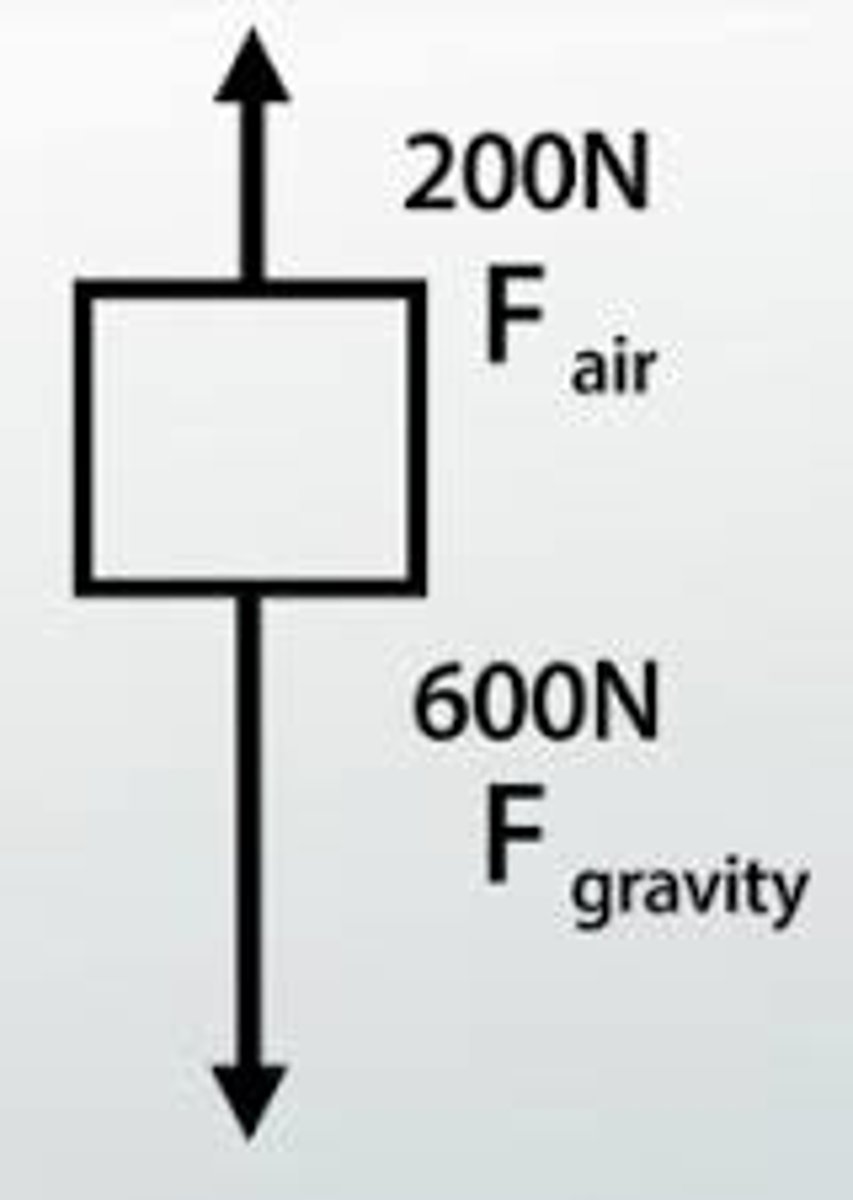
What forces are acting on a stationary student sat on a stool?
There are two forces to consider
the force of gravity downwards (the weight) and the normal contact force of the chair pushing you upwards
To simplify further, we only draw the forces and do not draw the body at all
This is called a free body diagram
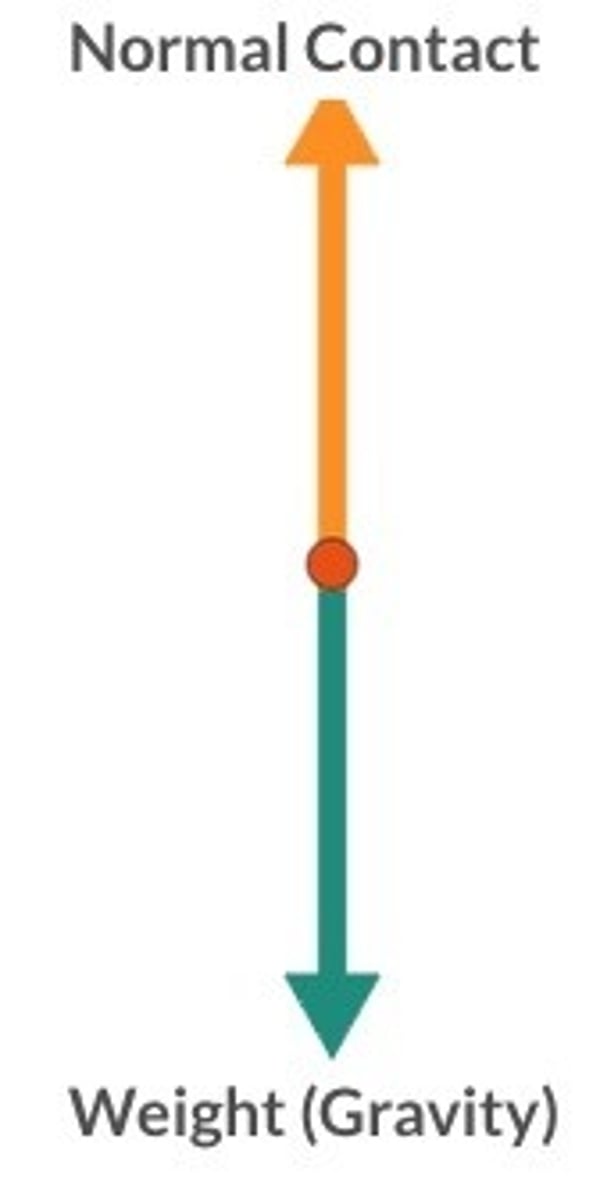
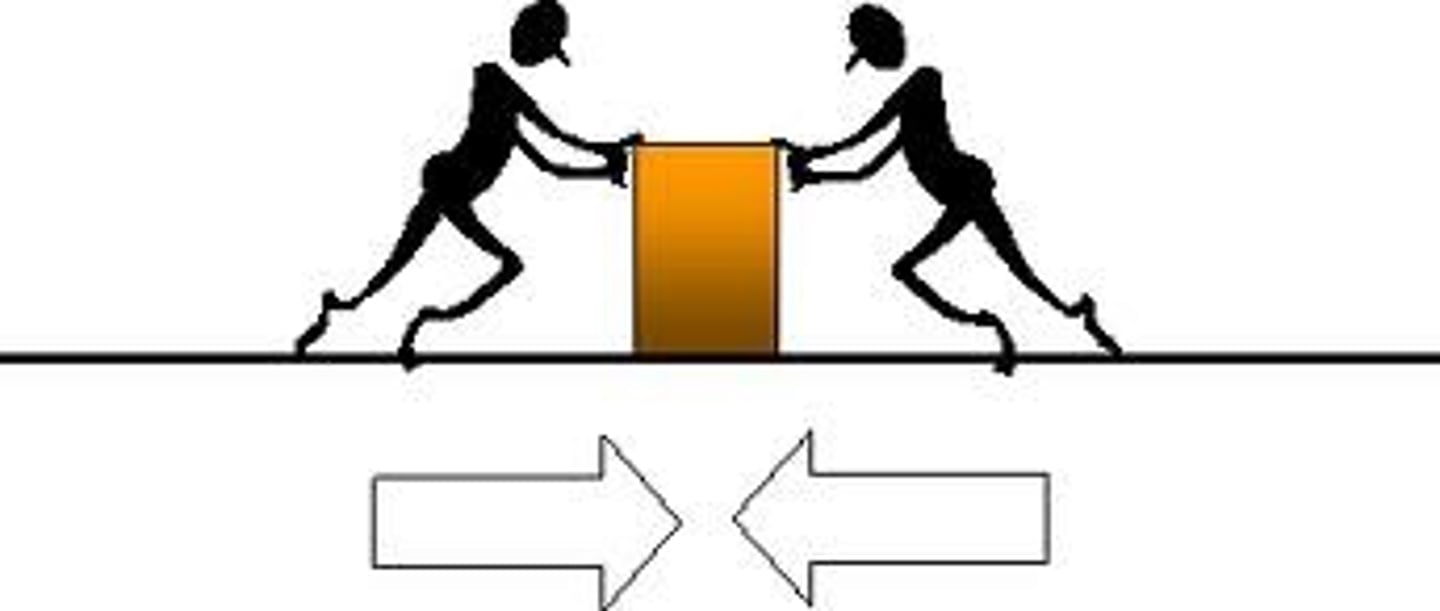
balanced forces
When forces add up to zero (the resultant force is zero) then we say that they are balanced
If forces are balanced then the object will not change its motion
If the object was stationary then it will remain stationary
If the object was moving then it will remain moving at a constant speed
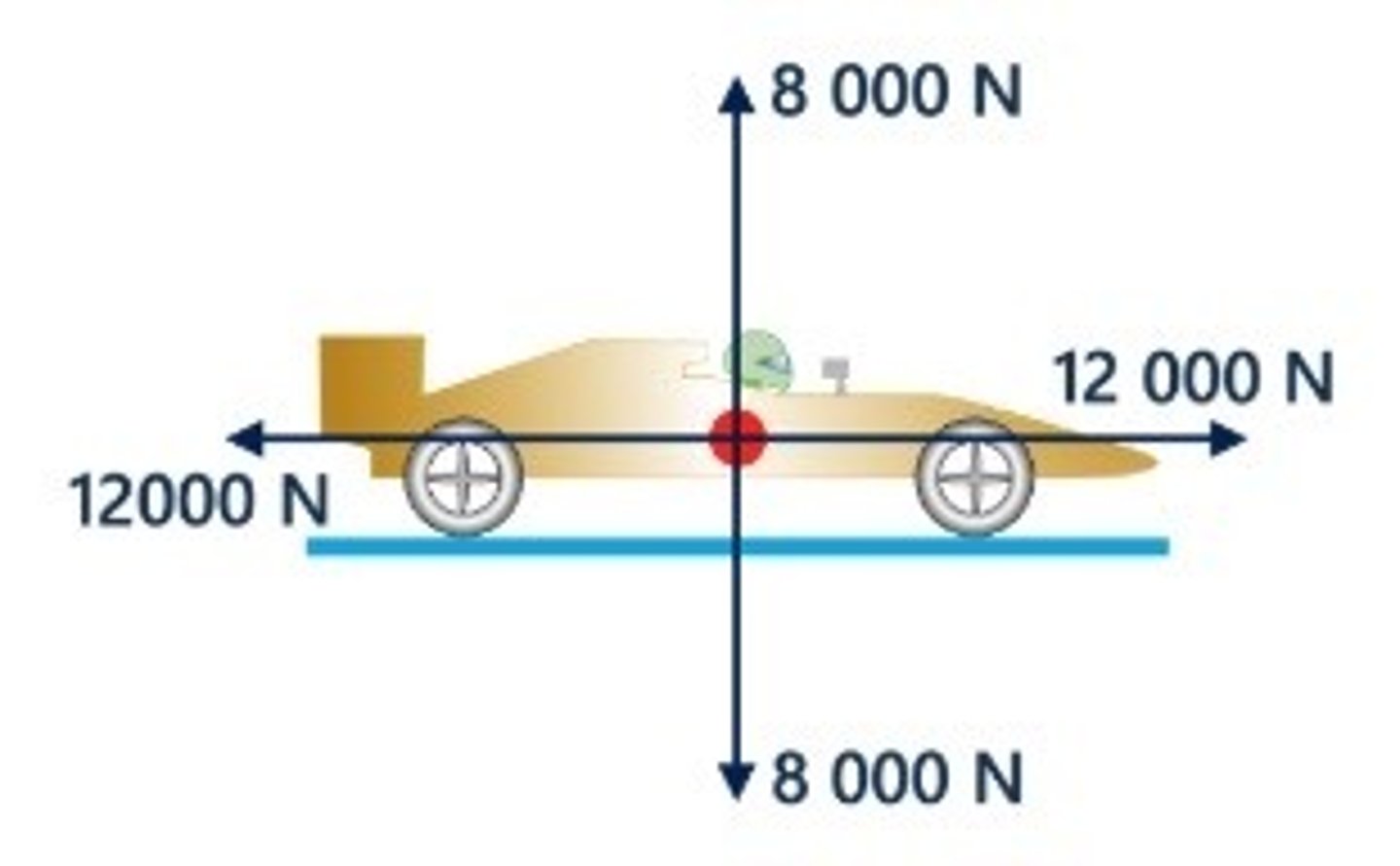
Newton's First Law
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
The car is either stationary or moving in a straight line at a constant speed.
unbalanced forces
If forces are unbalanced then the resultant force will be non-zero
The consequence will be that an object will change its motion
The object will accelerate or decelerate (negatively accelerate)
This means that the size and/ or the direction of the velocity will change
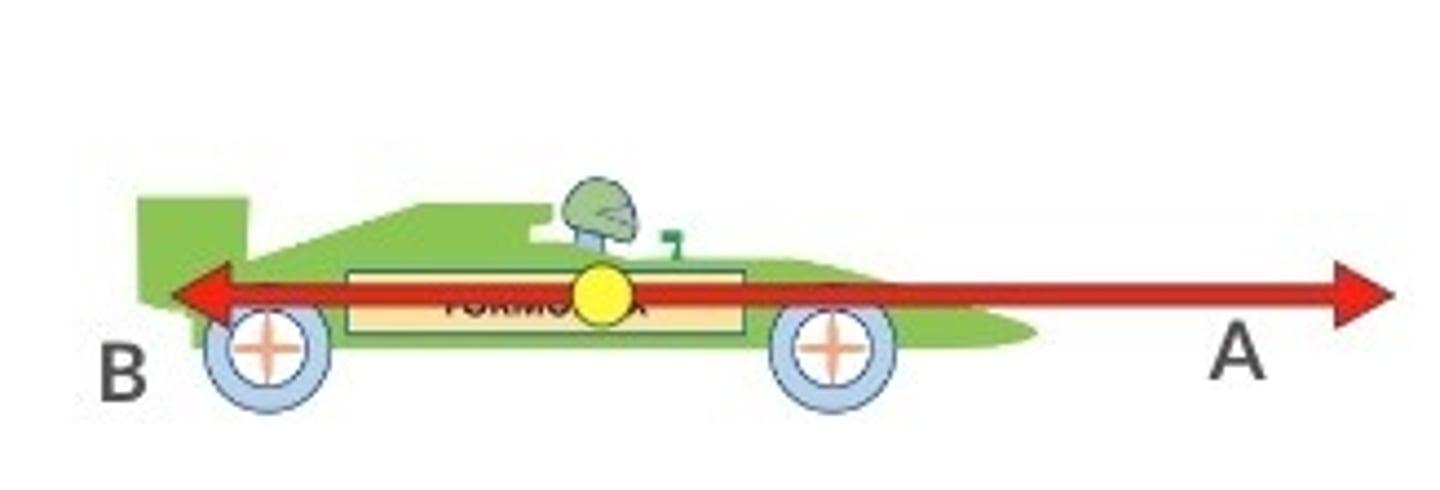
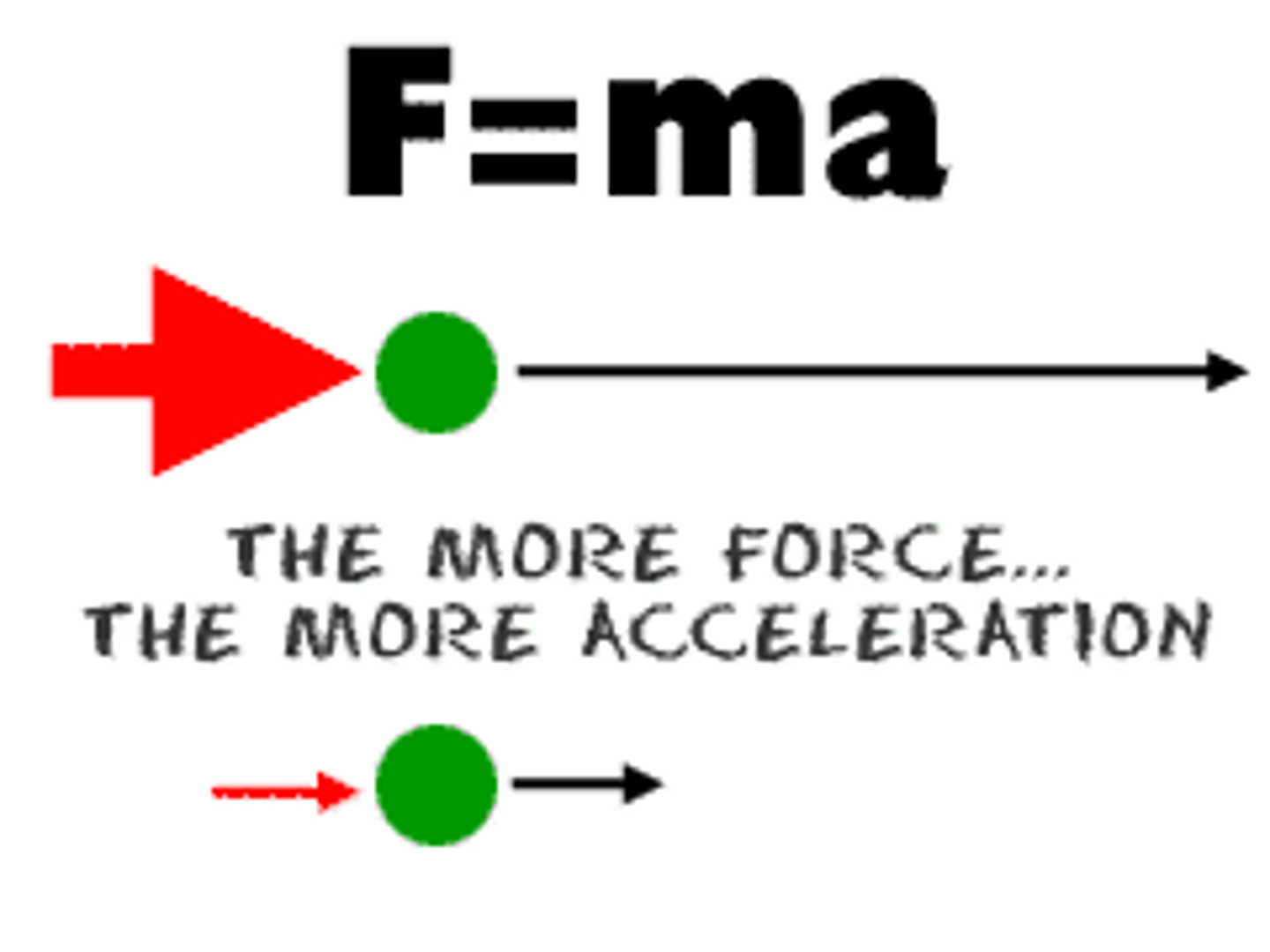
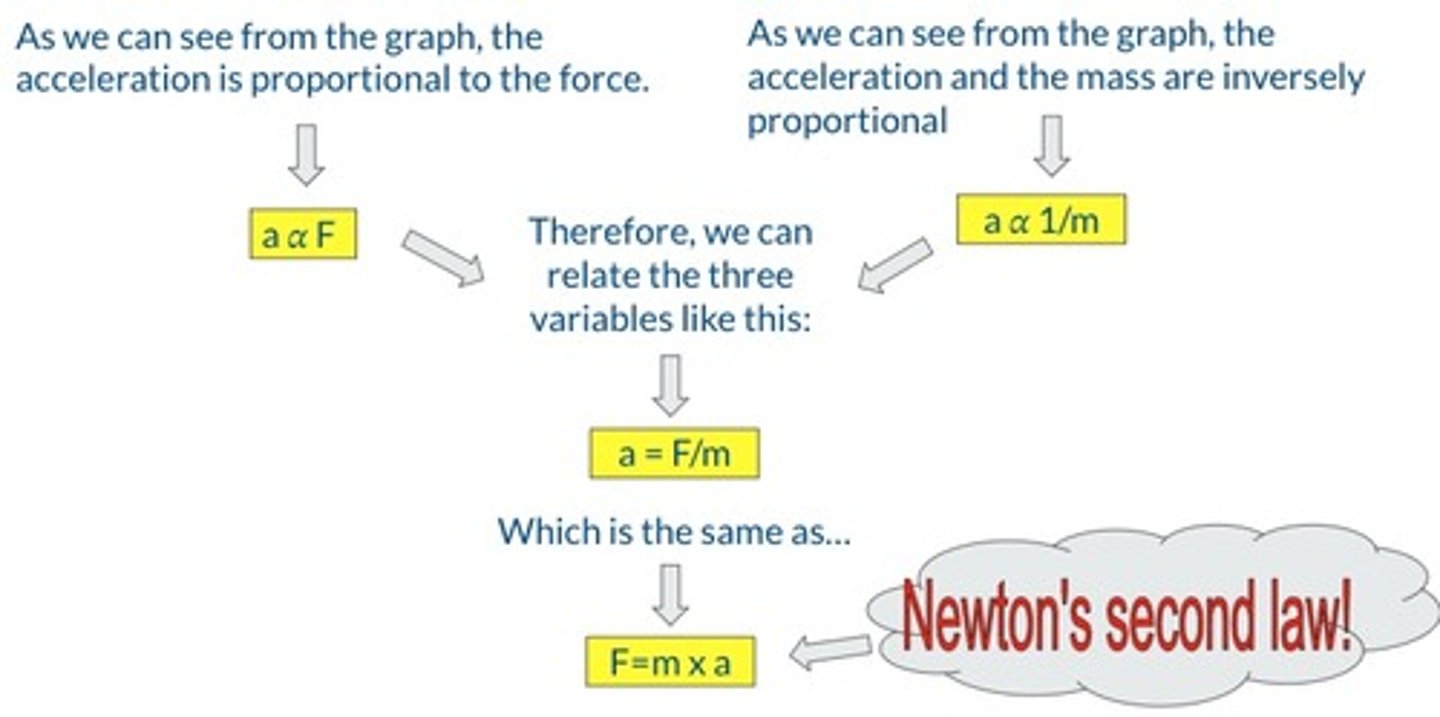
Newton's Second Law
Force = mass x acceleration
If the resultant force is non-zero, then the object must accelerate according to this formula.
SUVAT notation

a _____ is needed to make an object accelerate
resultant force
practice calculating the acceleration of these boxes
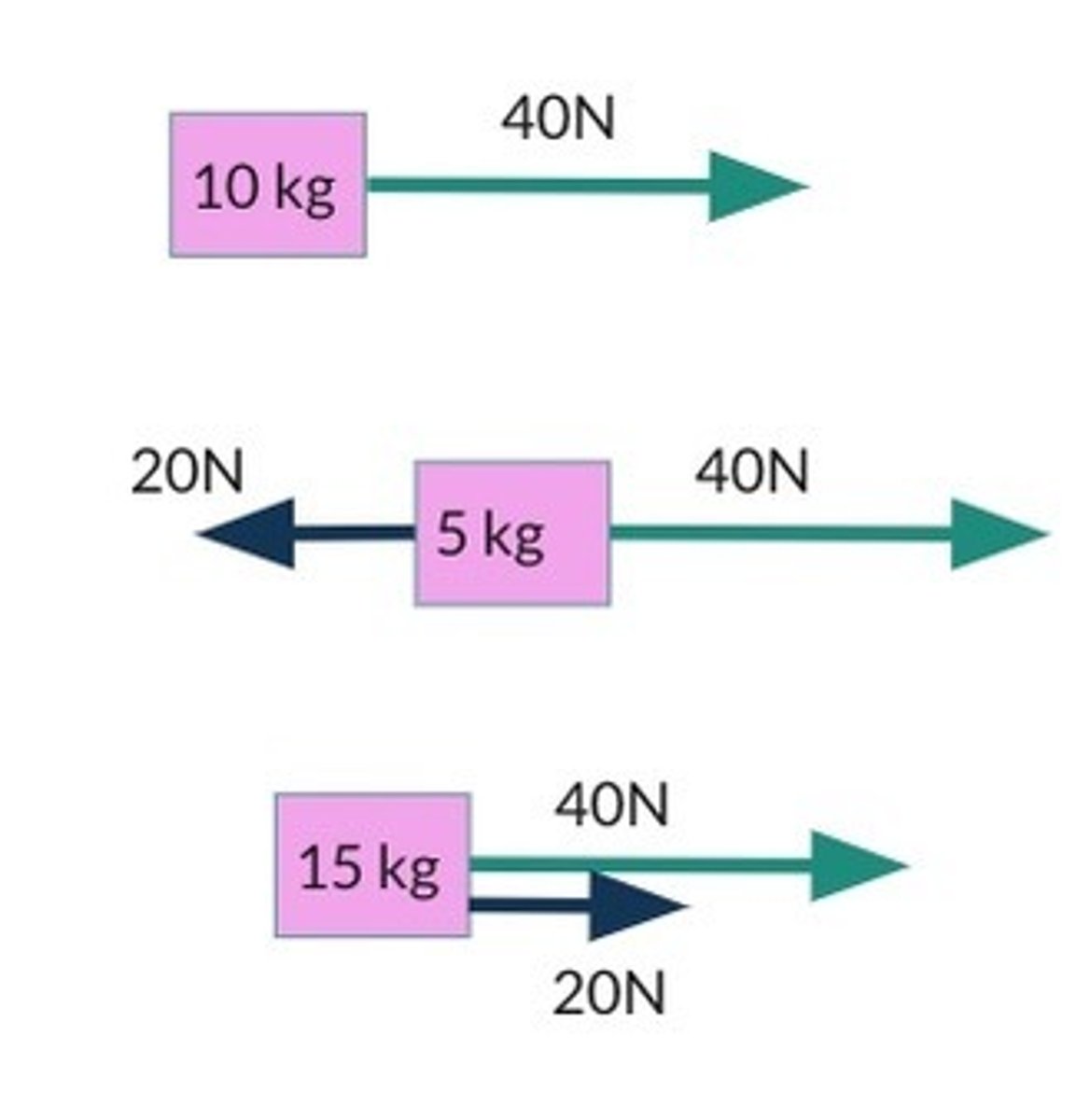
inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion - referred to as mass nowadays
Acceleration
Acceleration is the change in velocity over time
It is a vector quantity
There is an acceleration whenever there is a resultant force
Acceleration is measured in metres per second squared
This is written as m/s2 or ms-2 or m/s/s
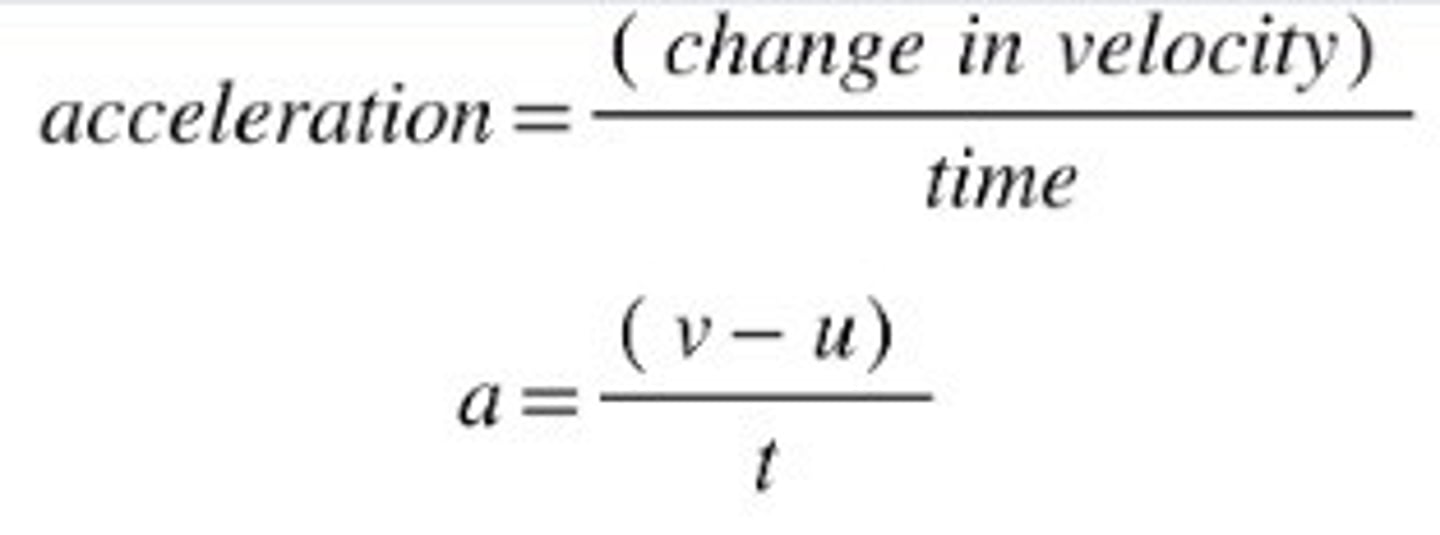
A car accelerates from 4 m/s to 24 m/s in 5 seconds. What is the acceleration of the car?
4 ms^-2
A car accelerates from 4 m/s to 24 m/s in 5 seconds. What is the acceleration of the car?
15 m/s
An aircraft decelerates at 8 m/s2 for 6 seconds, from an initial velocity of 120 m/s. What is the final velocity of the aircraft?
72 m/s
A horse accelerates from 5 m/s to 17 m/s. The acceleration of the horse is 3 ms-2. For how many seconds was the horse accelerating?
4 seconds
mass
measures the number of atoms that something is made of and is the same everywhere in the universe
Weight
the pull of gravity on a mass and depends on the gravitational field strength g, so will be different up a mountain, on the Moon, in space…
They are connected using Newton 2
“g” is also called the acceleration due to gravity and is 9.8 N/kg or 9.8 m/s2 on Earth (or just 10 N/kg)
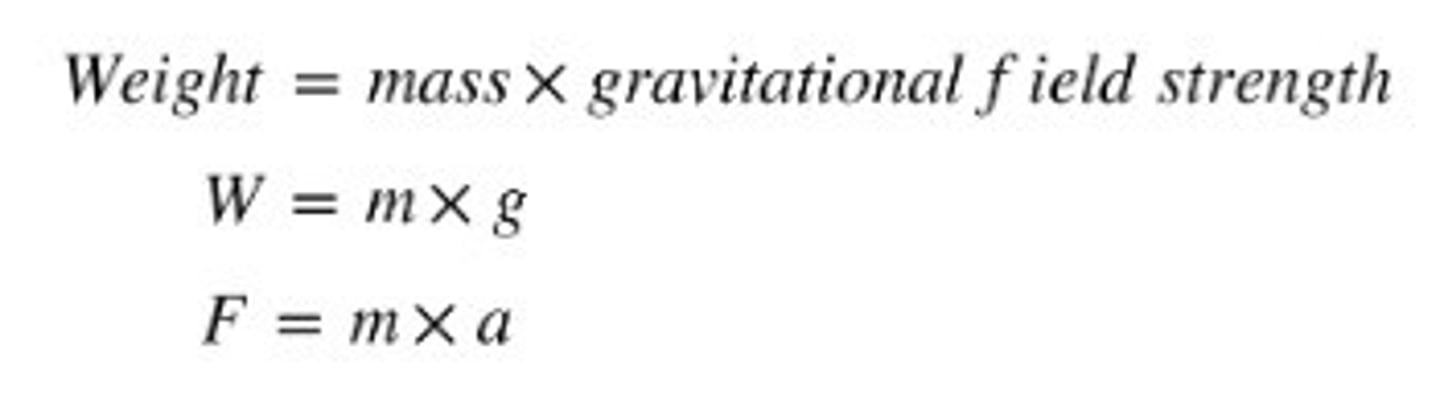
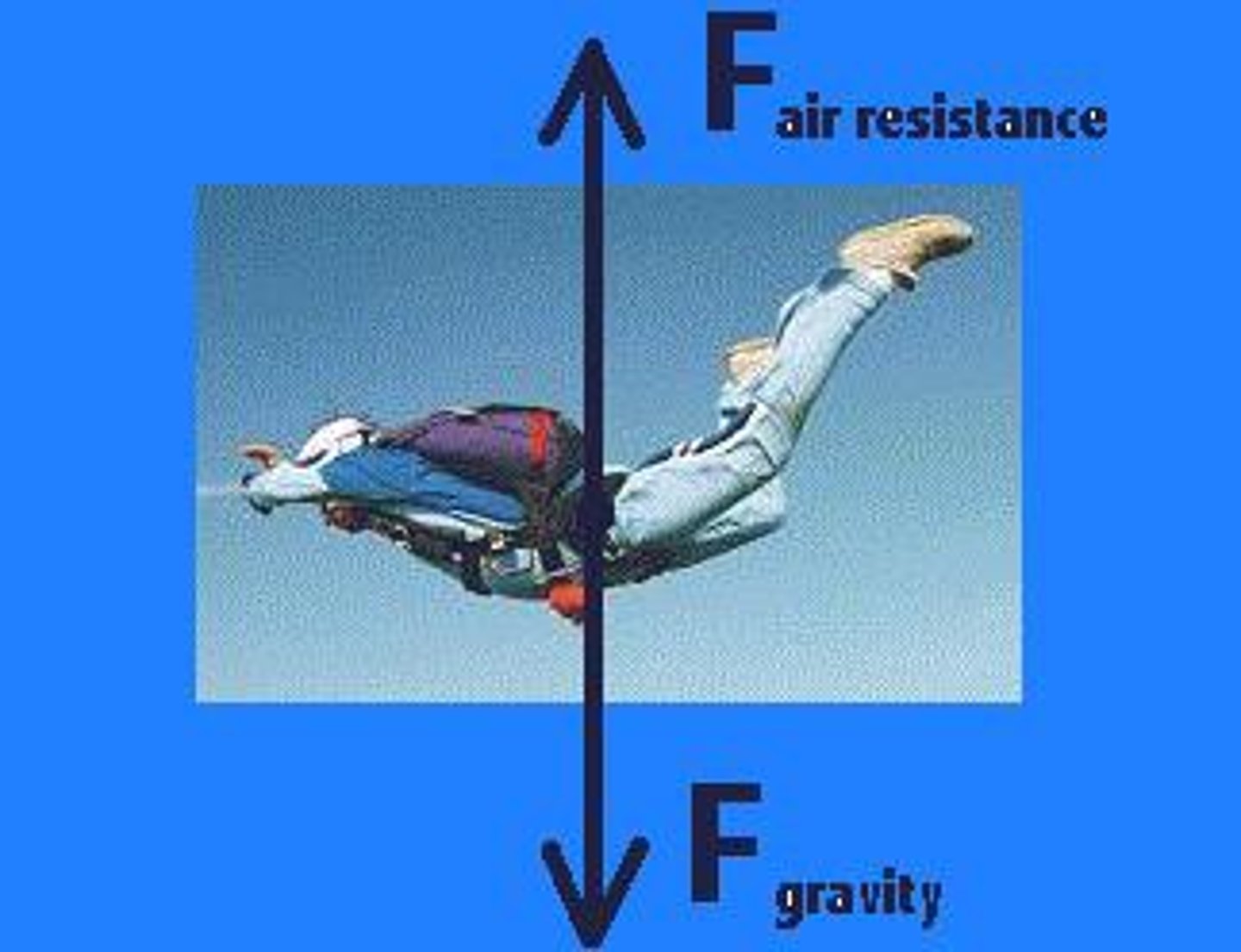
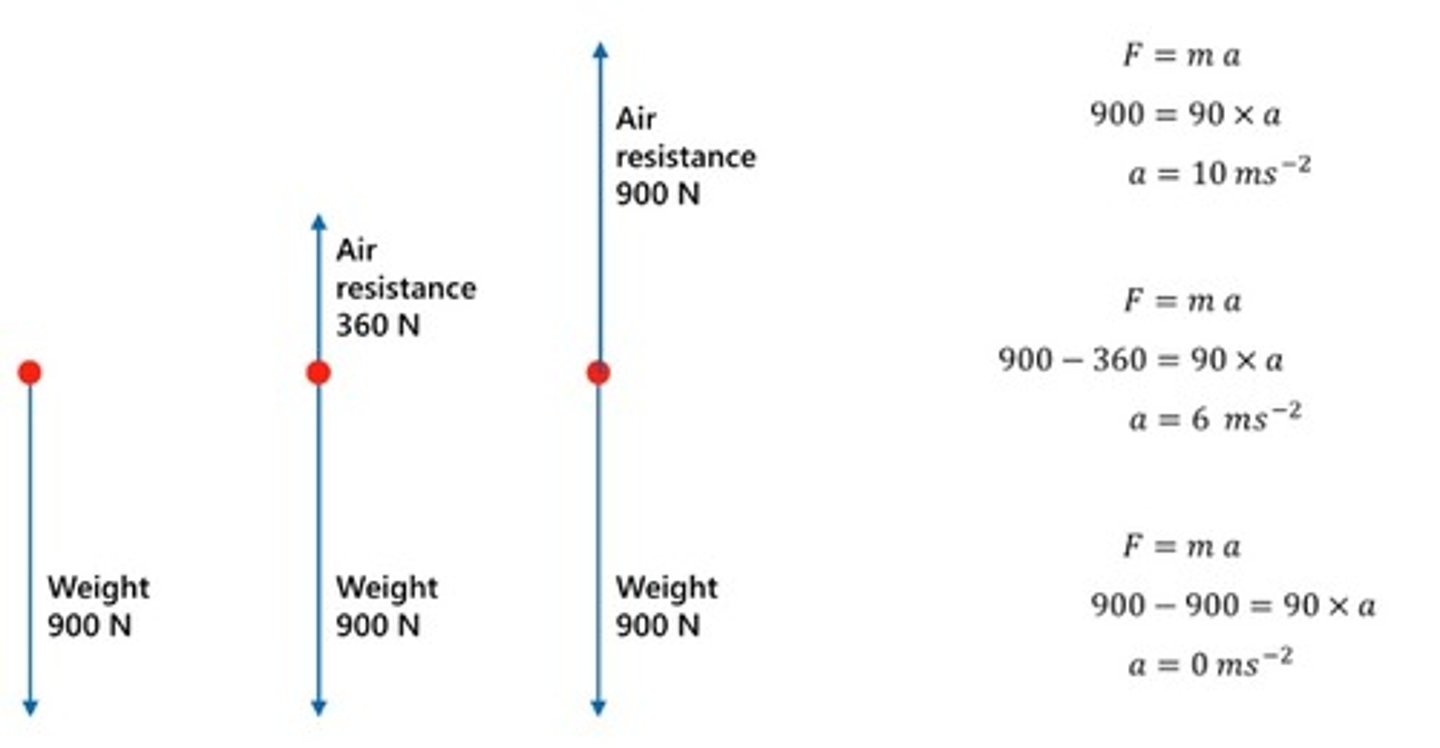
- A skydiver jumps out of a plane. The skydiver has a mass of 90 kg
- Just at the moment that they jump out of the plane, the only force acting on them is gravity
- After a few seconds, the air resistance force has increased to 360 N
- After a few more seconds the air resistance force becomes equal and opposite to the weight
1) Sketch these 3 situations as free-body diagrams
2) Calculate the acceleration in each case
3) Explain why the air resistance increases with time
(Take g = 10 N/kg)
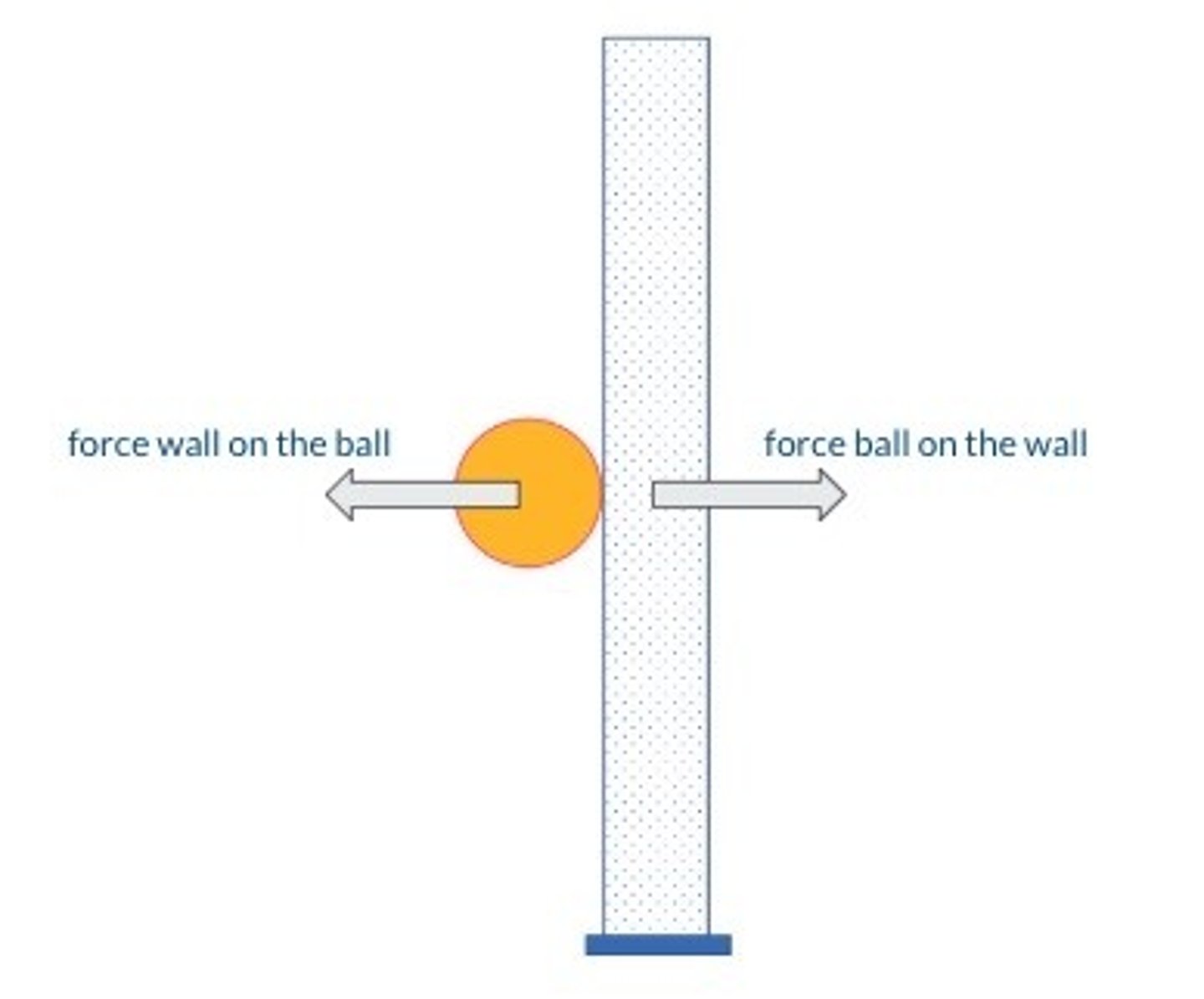
A ball of mass 0.50 kg is moving horizontally to the right at a constant speed of 10 m/s
The ball hits a wall at right angles and rebounds with the same speed
The collision time is 0.20 seconds
Sketch this scenario
Does the ball accelerate?
Is there a resultant force on the ball?

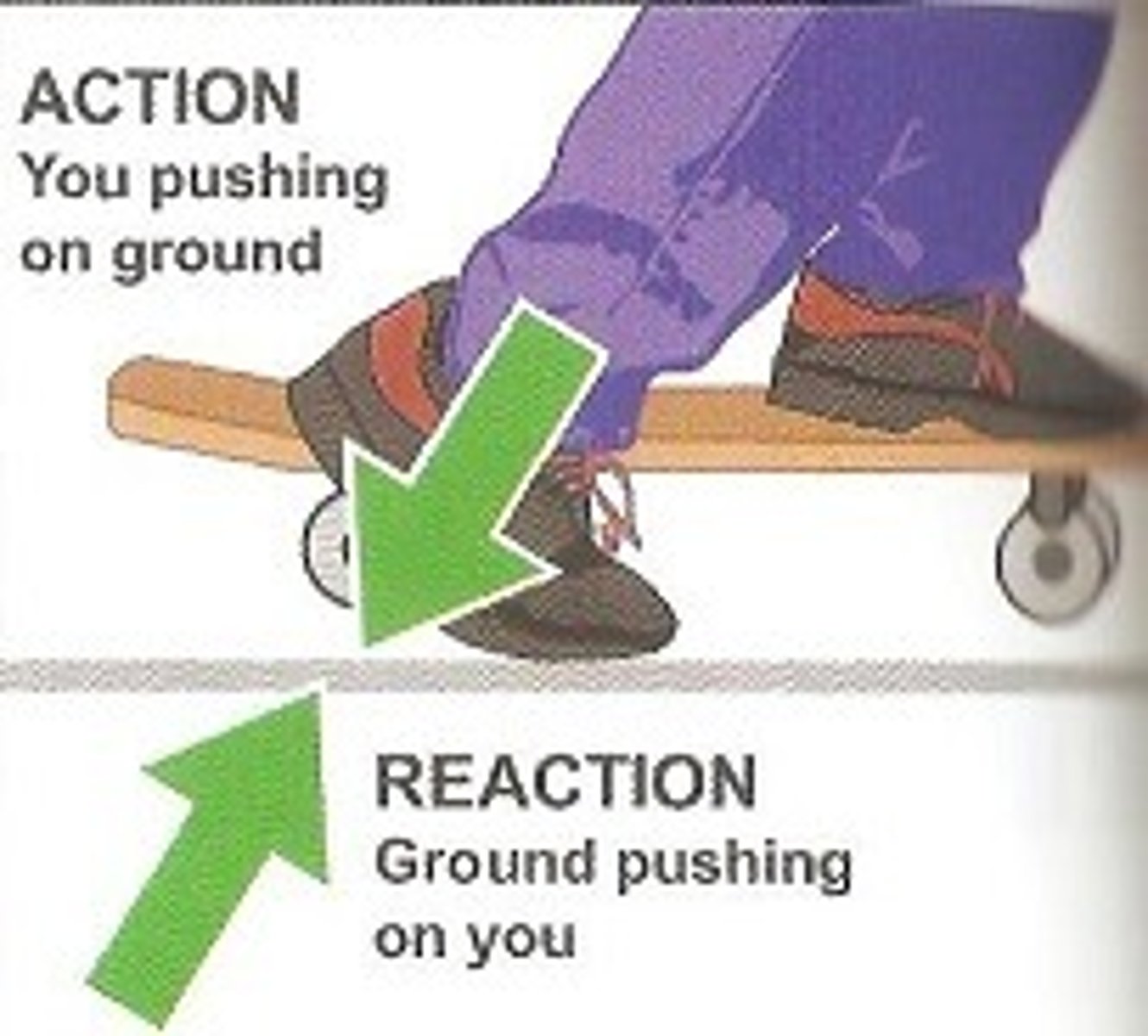
Newton's Third Law
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
An interaction between two objects can be replaced by two forces, one acting on each object. These forces are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.
SUVAT equations
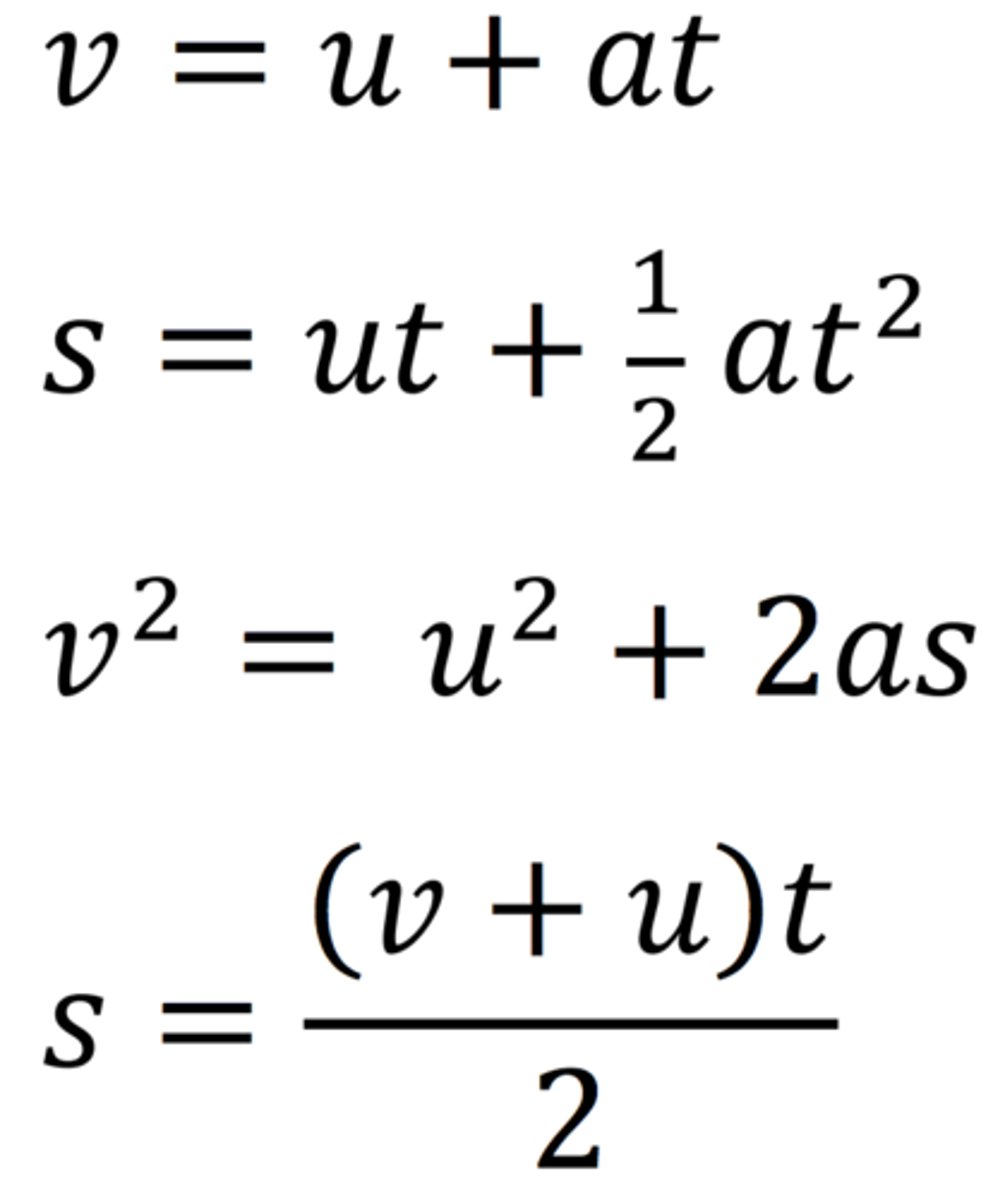
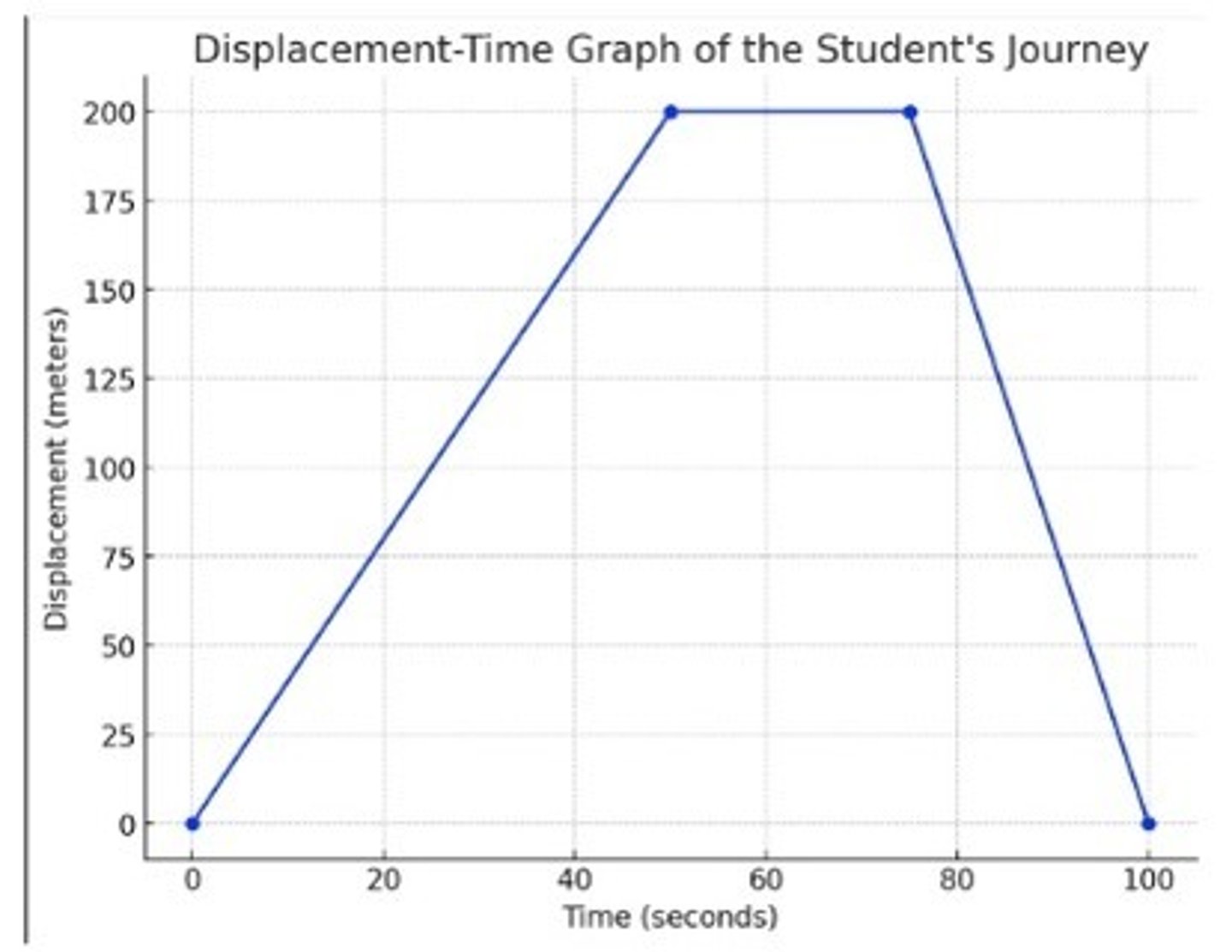
A student walks 200 m to a shop in a time of 50 seconds. They stop for 25 seconds then they return at a speed of 8 m/s back to the start along the same route
Plot this journey onto a displacement time graph
How far have they travelled?
What is their velocity in the first section?
What is their average velocity for the whole journey?
What is their average speed?
Total distance travelled:
400 meters (200 m to the shop and 200 m back).
Velocity in the first section:
4.0 m/s (they walked 200 meters in 50 seconds).
Average velocity for the whole journey:
0.0 m/s (since the displacement at the start and end is the same, the overall displacement is 0).
Average speed for the whole journey:
4.0 m/s (total distance of 400 meters divided by the total time taken for the journey).
Velocity-time graphs
On a velocity-time graph the area between the line and the x-axis is the displacement, the gradient is the acceleration
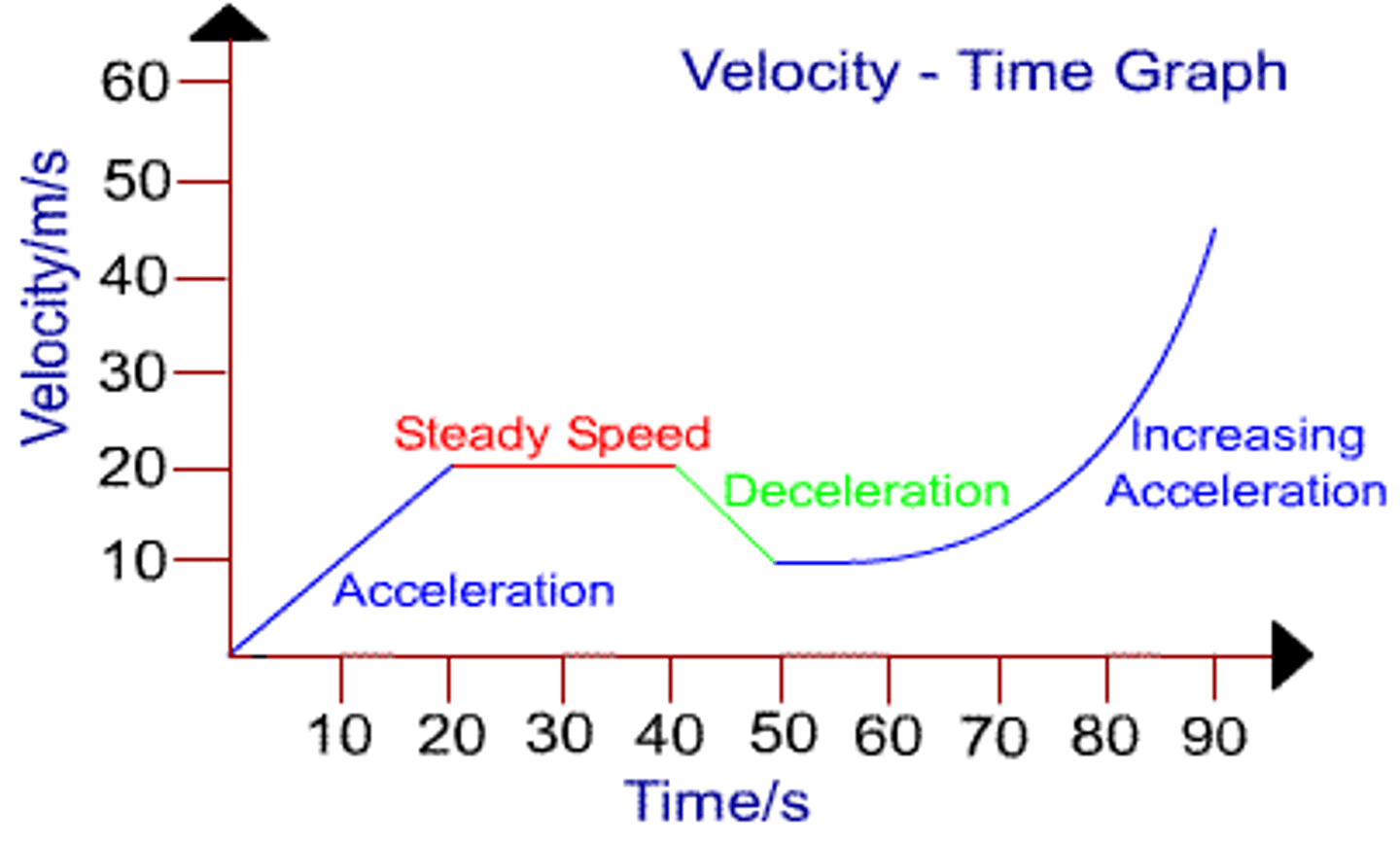
A rock, initially at rest, is dropped from a height of 2.0 m. At what time does the rock reach the ground?

A car accelerates in a straight line from 10 m/s to 30 m/s in a distance of 80 m. What is the acceleration of the car?

A motorcycle accelerates from 5 m/s for 6 seconds with an acceleration of 3 m/s^2
a) How far has the motorcycle travelled?
b) What is the final velocity of the motorcycle?

A plane goes from a velocity of 20 m/s to 80 m/s with an acceleration of 4 m/s^2 . How far has the plane travelled?
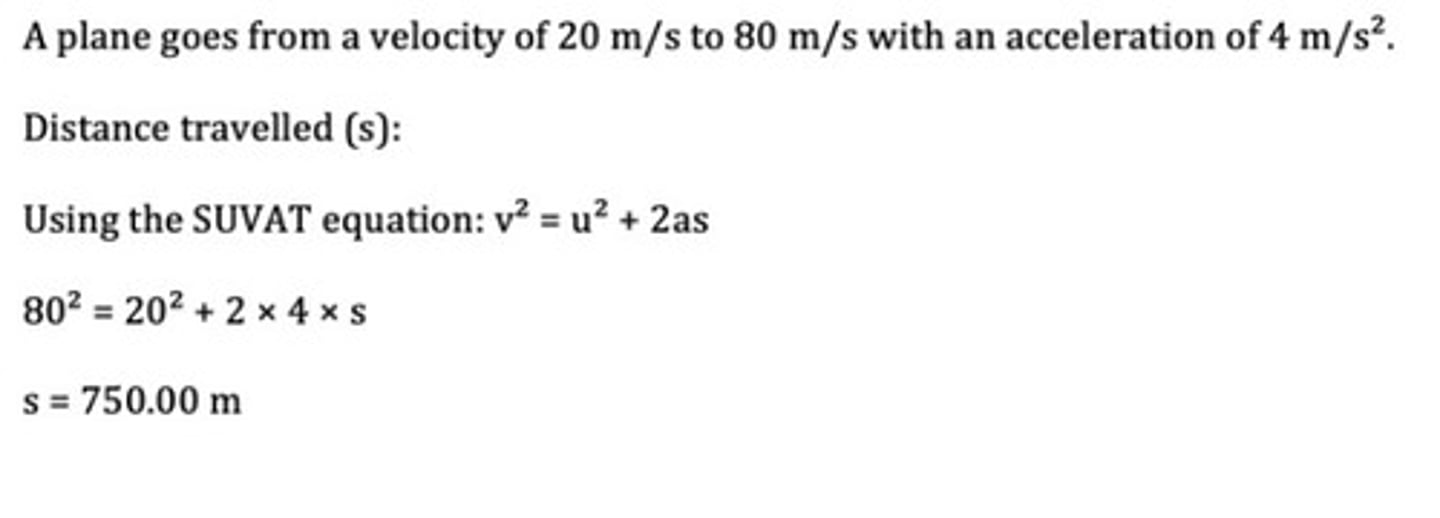
A 1 kg rock and a 2 kg rock are both dropped from a height of 10 m. Which one reaches the ground first?

A bullet is fired vertically up with a velocity of 200 m/s.
How high does the bullet get?
How high would it get on the Moon (g = -1.6 ms^-2)

Movement energy
Kinetic
Light
Thermal
Sound
stored energy
Gravitational
Elastic
Chemical
Nuclear
Magnetic
Electrical
energy
The ability to do work or cause change - the work done is the energy transferred
Gravitational Potential Energy
the work done when an object moves up (against the force of gravity) or down (with the force of gravity) is called gravitational potential energy
The GPE depends on the
change in height, h
gravitational field strength, g
mass, m
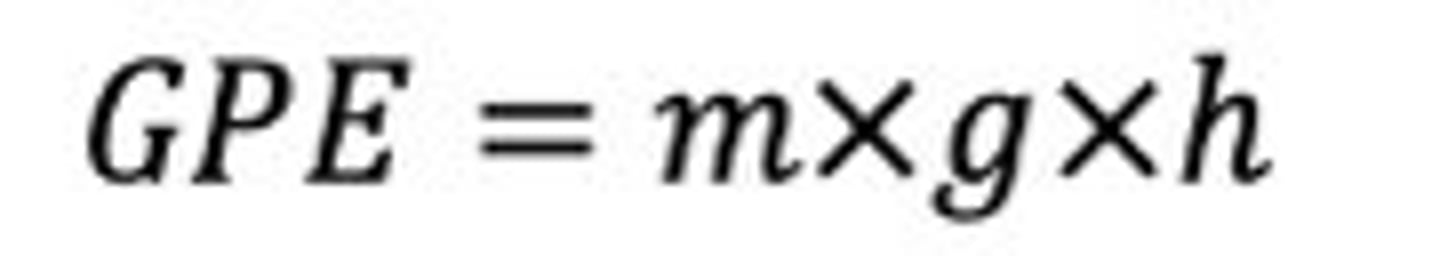
Kinetic Energy
Work needs to be done in order to get an object to a certain speed
The work done is called the kinetic energy and it depends on the
mass (in kg)
speed (in m/s)
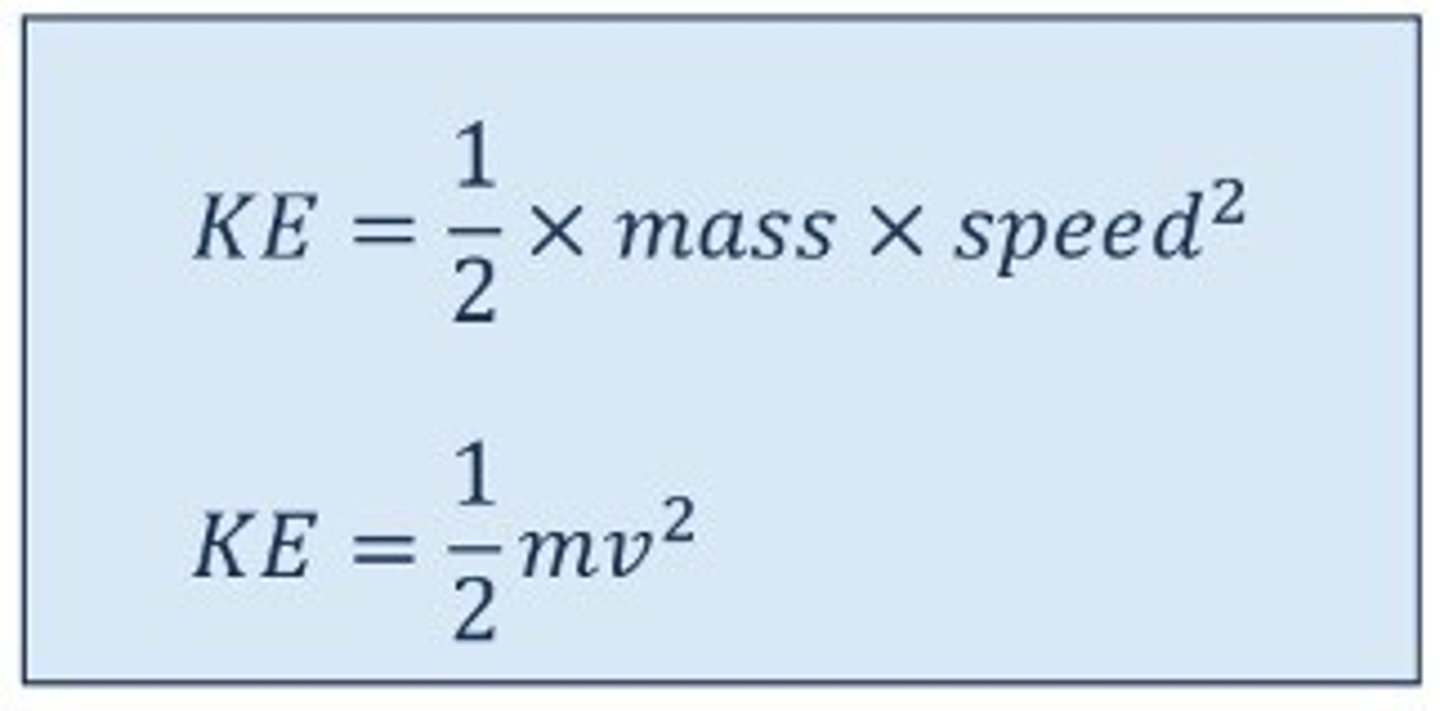
Hooke's Law
Extension is directly proportional to force until the spring reaches it's elastic limit (Where k is the spring constant, which has units of N/m)
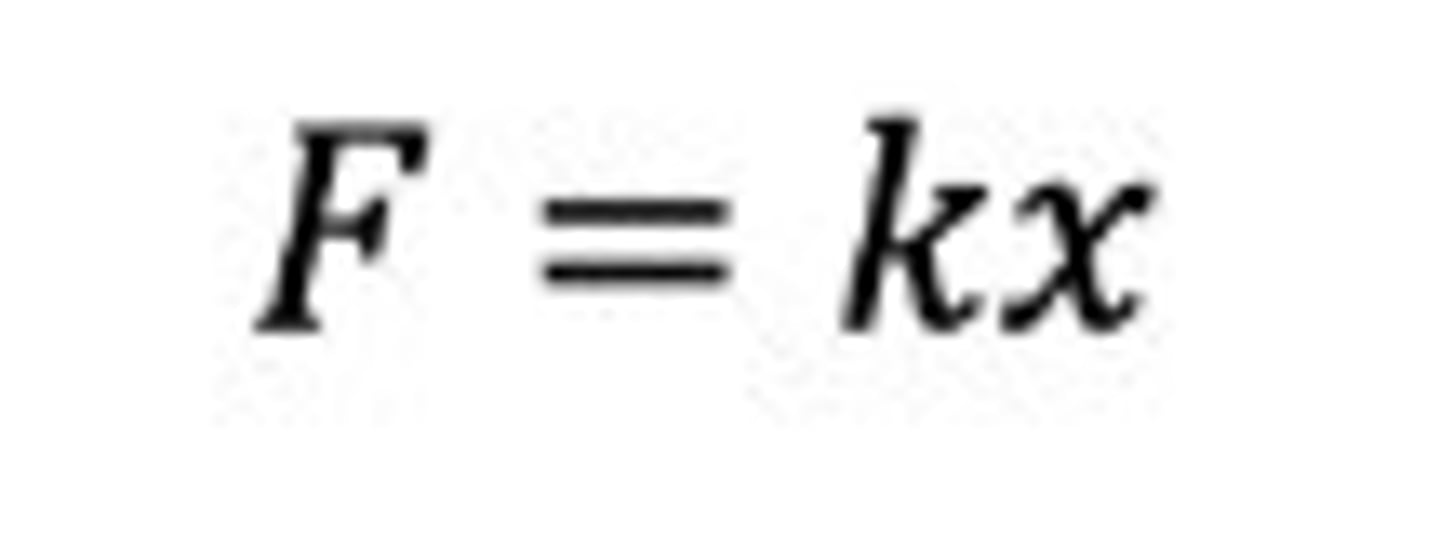
What is the unit for energy?
Joules (J)
Elastic potential energy
the energy of stretched or compressed objects
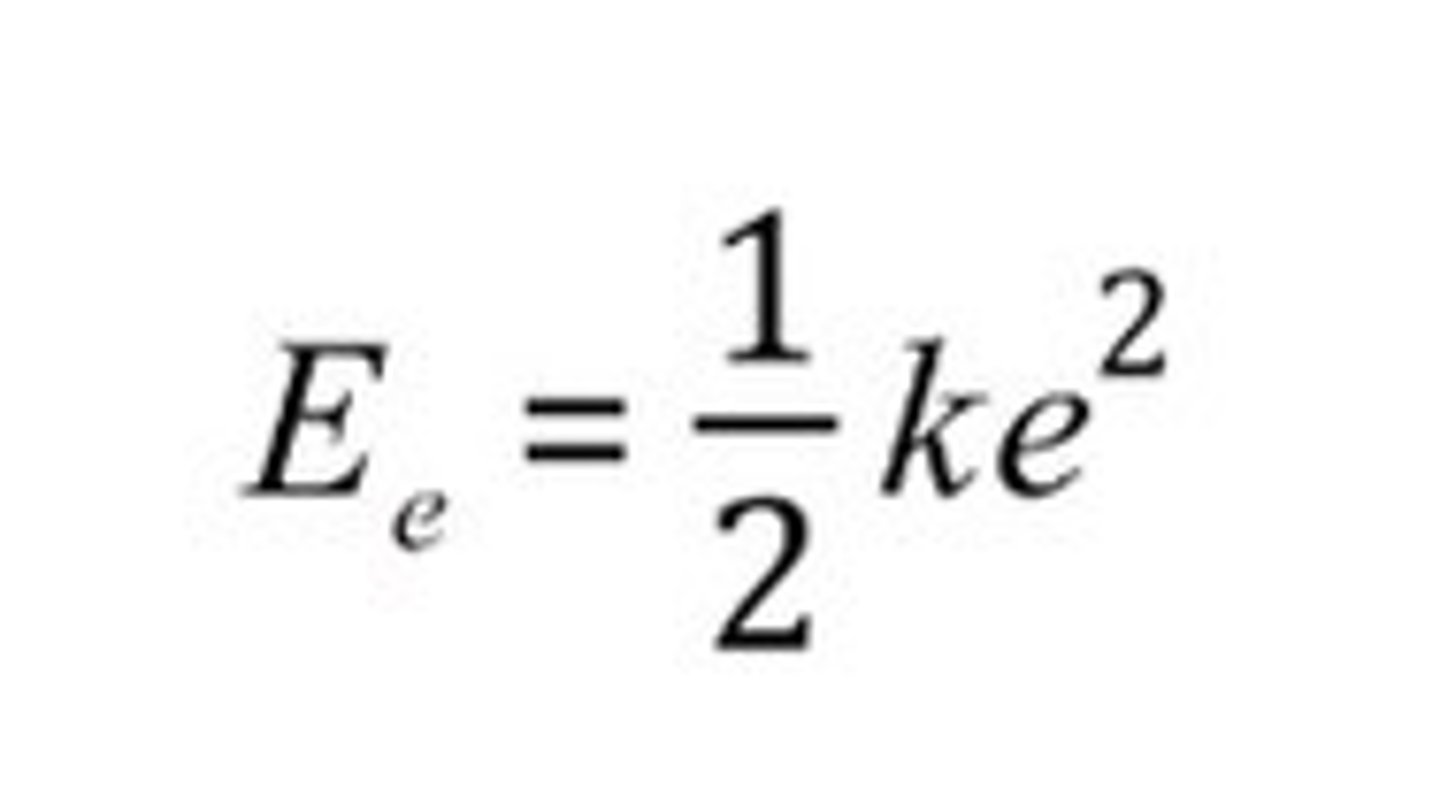
A student of mass 50 kg runs at 6 m/s
What is their kinetic energy?
900J
A car has a mass of 1200 kg and a speed of 30 m/s
A constant braking force of 5000 N is applied until the car stops
What is the stopping distance of the car?
What is the gravitational potential energy (GPE) of a 60 kg person if they are 100 m in the air? (take g=10 ms-2)
Give your answer in kilo-joules
What would the GPE be for the same height on the Moon? (g = 1.6 N/kg)
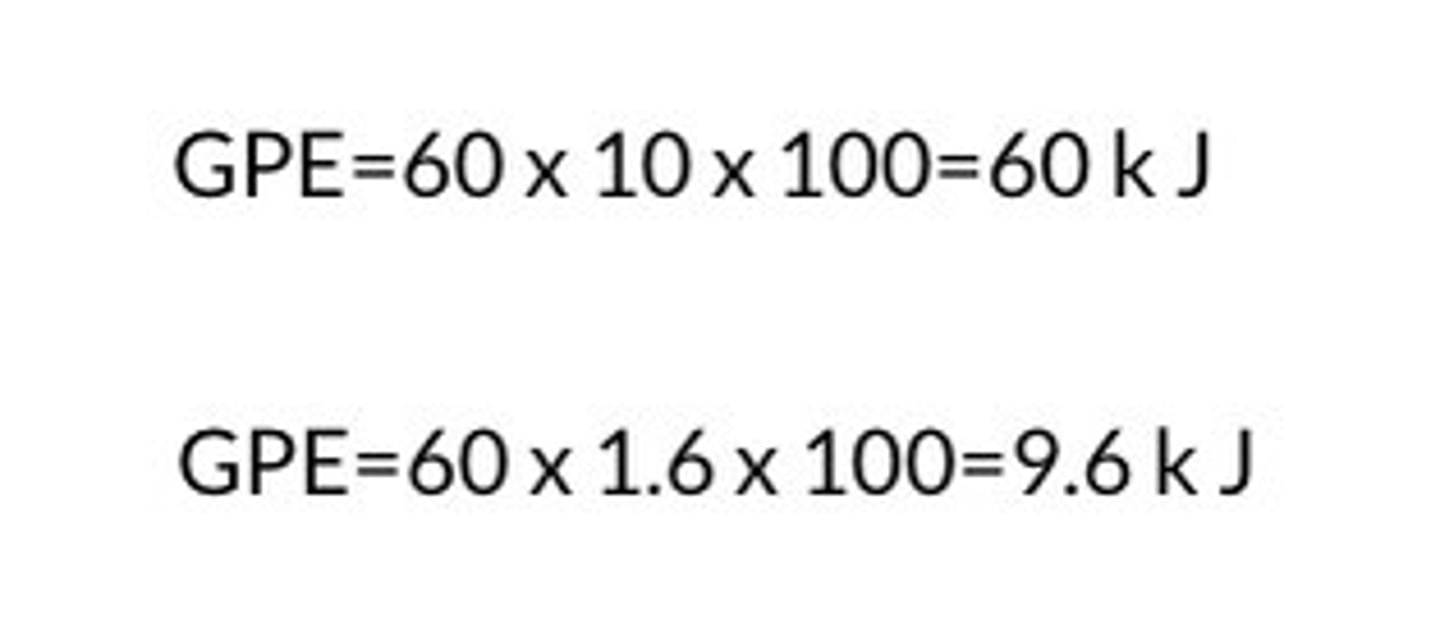
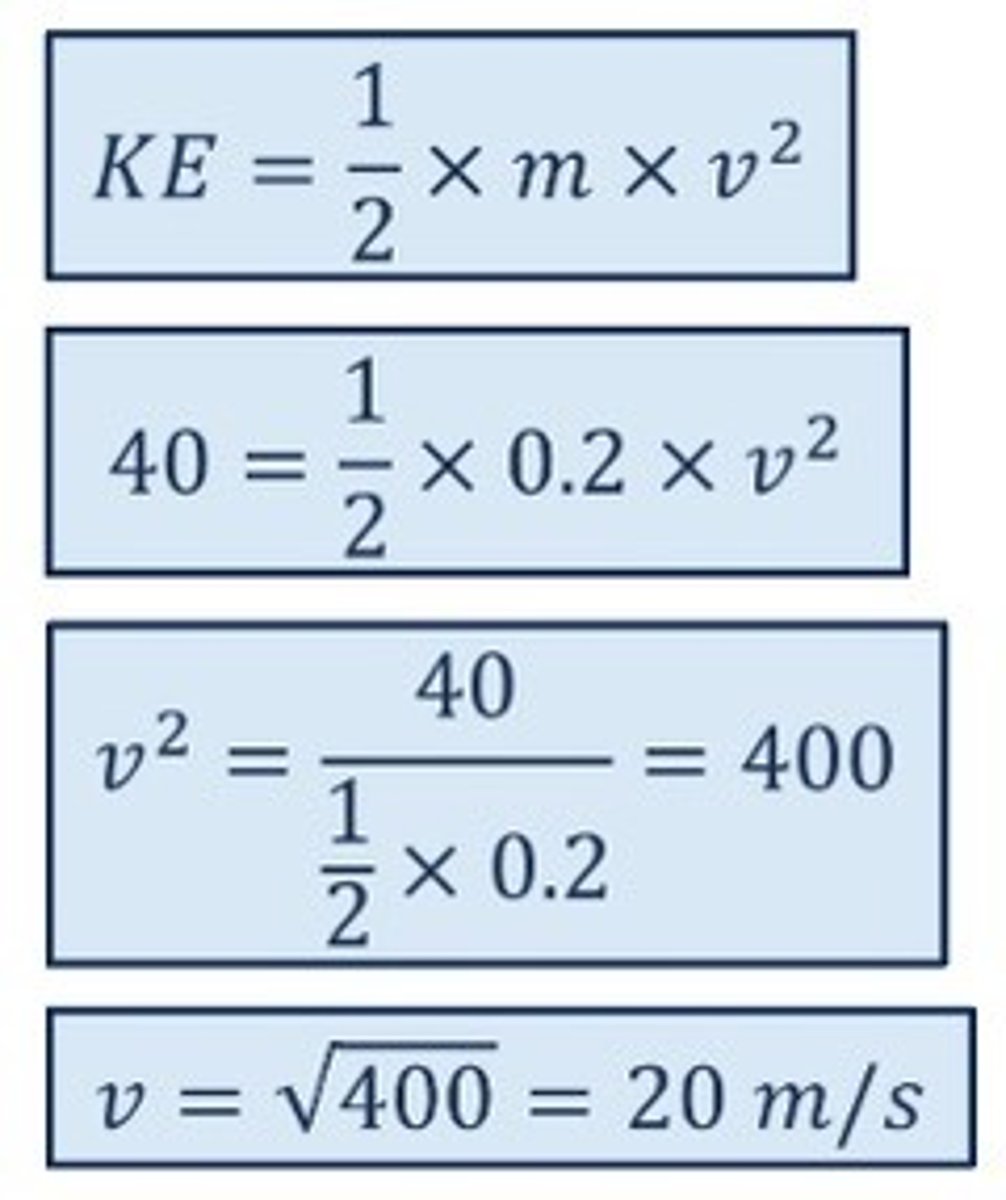
A car has a mass of 800 kg and a kinetic energy of 40 kJ
What is the speed of the car?
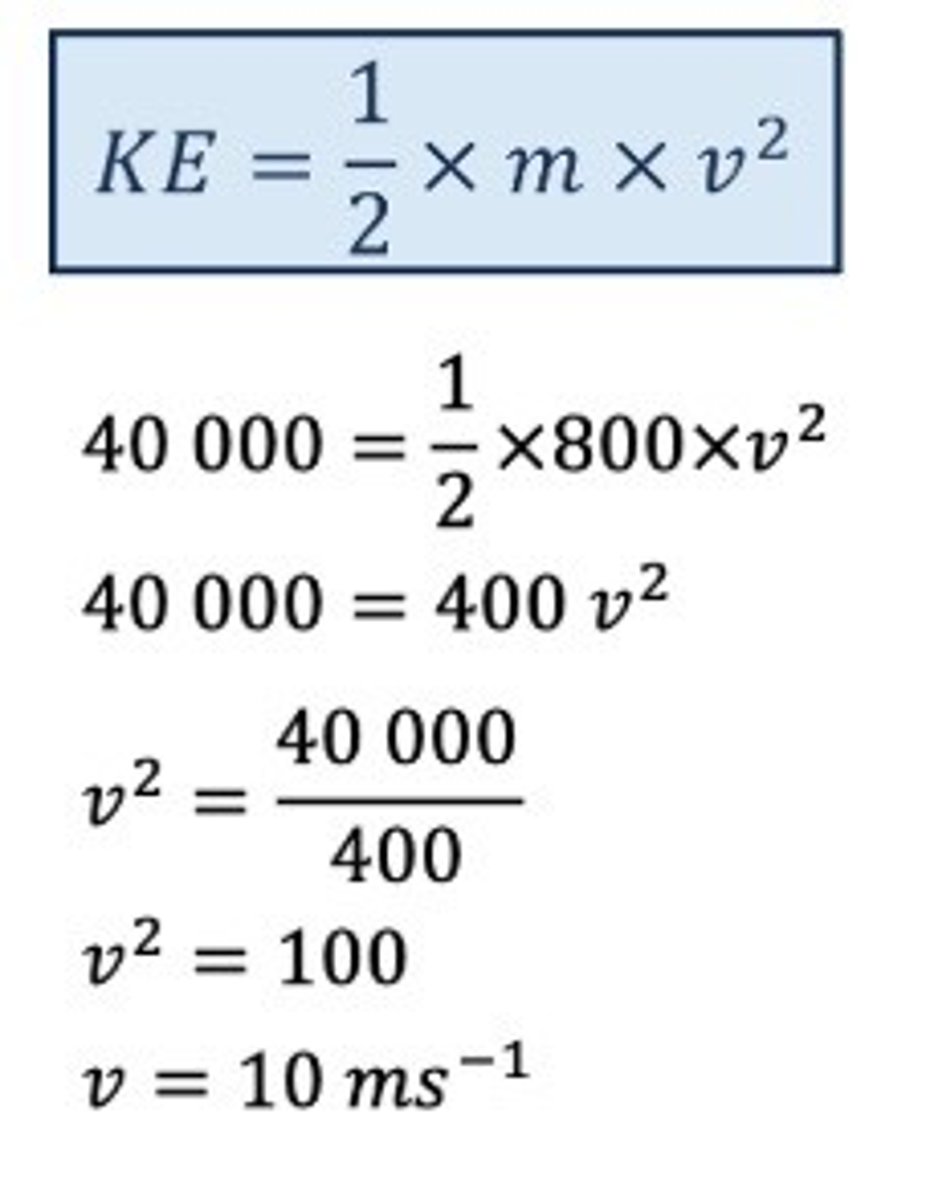
The car in the last question had a mass of 800 kg and a speed of 10 m/s
The speed of the car doubles
What happens to their kinetic energy? How many times bigger is it?

A skateboarder has a speed of 10 m/s and a kinetic energy of 2 kJ
What is the mass of the skateboarder (including the skateboard)?

A stone of mass 0.2 kg has 40 J of kinetic energy
What is the speed of the stone?