Macro Econ final study guide
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
_______ are generally the result of price ceilings.
Excess supply
Shortages
Price equilibrium
Equilibrium quantity
Shortages
The main reason price ceilings are set is so that consumer prices
Will be higher.
Will remain at equilibrium.
Will be lower.
Never reach equilibrium
Will be lower
Refer to the figure below. If the government sets a price ceiling of $8,

There would be a shortage of 12 units.
Consumers would demand 12 units.
There would be an excess supply of 4 units.
Sellers would supply 12 units.
Consumers would demand 12 units
A price floor attempts to keep prices ________.
Lower than the equilibrium price.
At the equilibrium price.
Higher than the equilibrium price.
Constantly adjusting to quickly reach equilibrium
Higher than the equilibrium price
What is a the typical result of a price floor?
Excess supply.
Excess demand.
Quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.
Excess supply
If the government set a price ceiling of $40, there would be:

A surplus (or excess supply) of about 12 units.
A surplus (or excess demand) of about 12 units.
A surplus (or excess demand) of about 4 units.
A shortage (or excess demand) of about 8 units.
A shortage (or excess demand) of about 8 units.
Isabel experiences diminishing marginal utility when
The price of each additional hat she purchases falls when she gets volume discounts.
The value of the hats she purchased start to fall as they wear out over time.
The value to her of each additional hat she purchases start falling.
The price of hats increases overtime.
The value to her of each additional hat she purchases start falling.
Consumer surplus is best described as the extra benefit consumers receive when they ________.
pay more than they would have been willing to pay
pay exactly what they would have been willing to pay
pay less than they would have been willing to pay
pay less that what it costs to produce the items.
pay less than they would have been willing to pay
Refer to the figure below. Consumer surplus is:
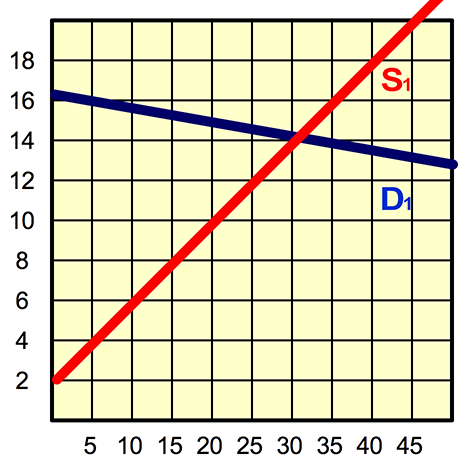
$60.
$120
$180.
$30
$30
The sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is know as ________.
consumer surplus
social surplus
producer surplus.
Super surplus
Social surplus
Making an economically rational decision requires
equal consideration for your own and others’ welfare.
considering the prospective benefits and costs to oneself.
always considering the long-run.
avoiding opportunity cost.
Considering the prospective benefits and costs to oneself
The theory of rational behavior
is an assumption that economists make to have a useful model for how decisions are made.
implies that people will always take the time to make correct decisions.
assumes that people will behave in the best interest of society as a whole.
assumes that people will always ignore others’ best interest.
is an assumption that economists make to have a useful model for how decisions are made.
Which of the following statements reflects marginal decision-making?
If we double the order to a dozen doughnuts, we will pay only 20 percent more.
The total cost of the program is equal to the total benefits.
Booking this condo in a better location is worth the extra $100.
Staying in this rental cottage longer would be nice, but the cottage next door is more attractive.
Booking this condo in a better location is worth the extra $100.
A positive statement is
can be shown to be correct or incorrect.
a value judgment.
based upon an optimistic judgment.
reflects one’s opinions.
can be shown to be correct or incorrect.
Normative statements are based upon
conjecture.
what can be demonstrated to be true.
facts
value judgments.
value judgments.
Which of the following statements is positive?
Social security benefits are not taxed.
There is a limit to the income each year to which the FICA tax applies, but that is fair, since there is a limit to social security benefits.
I am absolutely positive that there is a better way.
Social security payments to retirees should not be taxed.
Social security benefits are not taxed.
Which of the following statements is normative?
Congress gives too many tax breaks to corporations.
Tax breaks can change corporate behavior.
Congress gives certain business corporations tax breaks.
Tax breaks can lead to additional production.
Congress gives too many tax breaks to corporations.
The slope of a budget constraint line is influenced by
how effectively one more of each of the two competing goods satisfies wants.
the tastes and preferences of the decision-maker.
the cost of production of the products considered
how much one product costs compared to the other.
how much one product costs compared to the other.
A budget constraint model differs from production possibilities model in that, typically
only the budget constraint depicts an inverse relationship, or a trade-off.
only the budget constraint demonstrates diminishing returns.
the budget constraint shows how scarcity applies to producers
only the production possibilities model demonstrates diminishing returns.
only the production possibilities model demonstrates diminishing returns.
If an economy was in a recession and the government decided to use a supply side policy to address it, the government would most likely
expand and increase government spending instead of enacting tax cuts.
enact stimulate aggregate demand through its policies instead of aggregate supply.
increase spending on social programs to boost demand.
institute cutting taxes rather than increasing spending by the government.
institute cutting taxes rather than increasing spending by the government.
According to the Keynesian approach to fiscal policy
The crowding out effect is a significant problem that reduces the effectiveness of expansionary fiscal policy.
The crowding out effect is quite limited as the demand for private loans is low in times of recessions.
The crowding out effect occurs only when high inflation is present.
The crowding out effect is a significant problem that reduces the aggregate demand.
The crowding out effect is quite limited as the demand for private loans is low in times of recessions.
Which of the following is likely to lead to economic growth in the long term?
interest payment on debt.
spending on printing new dollar bills.
new highways to serve new neighborhoods and business parks
new laws toward a more equitable or fair distribution of income.
new highways to serve new neighborhoods and business parks
An argument to promote capital deepening is that it will
lead to a more stable economy.
increase productivity and economic growth in the long run.
lead to a more equitable (fair) distribution of income.
increase productivity and economic growth in the long run.
If an economy moves into an inflationary period, causing that country to produce more than potential GDP, then
automatic stabilizers will cause tax revenue to decrease and government spending to increase.
tax revenue and government spending will be higher because of automatic stabilizers.
automatic stabilizers will cause tax revenue to increase and government spending to decrease.
tax revenue and government spending will be lower because of automatic stabilizers.
automatic stabilizers will cause tax revenue to increase and government spending to decrease.
If an economy moves into a recessionary period, examples of fiscal policies that act as automatic stabilizers include
an increase in tax revenues as household incomes fall.
a flat tax on households’ income.
an increase in transfer payments or social spending, such as unemployment benefits
an increase in government defense spending.
an increase in transfer payments or social spending, such as unemployment benefits
f the economy is producing less than its potential GDP, ________ will show a smaller deficit than the actual deficit.
the standardized employment deficit
discretionary fiscal policy.
the automatic stabilizers.
expansionary fiscal policy.
the standardized employment deficit
If the economy is producing more than its potential GDP, ________ will be larger than the actual budget deficit.
discretionary fiscal policy
the automatic stabilizers
the standardized employment deficit
expansionary fiscal policy
the standardized employment deficit
Expansionary fiscal policy might include which of the following?
Increase in taxes or increased government spending.
Reduction in taxes or lowered government spending.
Increase in taxes or decreased government spending.
Reduction of taxes or increased government spending
Reduction of taxes or increased government spending
An expansionary fiscal policy can increase the level of aggregate demand by all of the following EXCEPT
decreasing government purchases.
cutting tax rates to increase disposable income and spending.
reducing corporate tax rates to increase investment spending.
government policies to facilitate US exports to other nations.
decreasing government purchases.
If a government reduces tax rates in order to increase the level of aggregate demand, what type of fiscal policy is being used?
discretionary and expansionary
contractionary and automatic.
automatic and expansionary.
discretionary and contractionary.
discretionary and expansionary
Which of the following is NOT an example of an expansionary, discretionary fiscal policy?
an increase in government purchases.
a reduction in income tax rates.
an increase in federal spending on infrastructure.
an increase in tax rates.
an increase in tax rates.
When inflation begins to climb to unacceptable levels in the economy, the government should
use contractionary fiscal policy to shift aggregate demand to the right.
use contractionary fiscal policy to shift aggregate demand to the left.
use expansionary fiscal policy to shift aggregate demand to the right.
use expansionary fiscal policy to shift aggregate demand to the left.
use contractionary fiscal policy to shift aggregate demand to the left.
Fiscal policy is concerned with which of the following?
Interest rate changes.
Money supply changes.
Price controls
Government expenditure changes.
Government expenditure changes.
A major concern of fiscal policy is
how changes to the money supply affect aggregate demand.
how changes to the budget affect the money supply.
controlling international trade balances
how federal government taxing and spending affects aggregate demand.
how federal government taxing and spending affects aggregate demand.
When the government increases its spending, it is conducting
monetary policy.
supply-side policy.
trade policy
fiscal policy.
fiscal policy.
When does a budget surplus occur?
When government spending exceeds government tax collections.
When government spending equals government tax revenues.
When the increase in the rate of government spending is smaller than the rate for government tax collections.
When government tax revenues exceed government spending.
When government tax revenues exceed government spending.
What do goods like gasoline, tobacco, and alcohol typically have in common?
A proportional tax is imposed on each of them.
A progressive tax is imposed on each of them.
They are all subject to tariff taxes
They are all subject to government excise taxes.
They are all subject to government excise taxes.
Which of the following examples describe a progressive tax?
Social Security tax rate of 6.2% on earned income below $117,000 and 0% on income earned above $117,000.
Medicare payroll tax of 2.9% of income for everyone, regardless of how much they earn.
Income tax with a 10% tax rate on low income households and 20-30% tax rates on higher income households.
State income tax with a 10% tax rate on low income households and 8% tax rates on higher income households.
Income tax with a 10% tax rate on low income households and 20-30% tax rates on higher income households.
Which of the following example(s) describe a regressive tax?
Social Security tax rate of 6.2% on earned income below $117,000 and 0% on income earned above $117,000.
Income tax with a 10% tax rate on low income households and 20-30% tax rates on higher income households.
Medicare payroll tax of 2.9% of income for everyone, regardless of how much they earn.
State income tax with a 10% tax rate on low income households and 15% tax rates on higher income households.
Social Security tax rate of 6.2% on earned income below $117,000 and 0% on income earned above $117,000.
A tax that is a flat percentage of all wages earned is a
regressive tax.
progressive tax.
proportional tax.
a lump sum tax
proportional tax.
Property taxes are
generally considered to be progressive.
generally considered to be flat.
imposed based on ownership of assets such as real estate.
imposed based on the property owner’s income.
imposed based on ownership of assets such as real estate.
Sales taxes are
imposed as a percentage of the value of the purchase
generally considered to be progressive.
a tax burden that is entirely paid by consumers.
generally considered to be proportional
imposed as a percentage of the value of the purchase
A ________ is created each time the federal government spends more than it collects in taxes in a given year.
budget surplus.
regressive tax.
lower federal debt
budget deficit
budget deficit
A ________ means that government spending and tax revenues are equal.
fiscal budget.
discretionary fiscal policy.
balanced budget
budget surplus
balanced budget
The U.S. produces strawberries in Oregon, but also imports strawberries from Chile. The production costs are lower for strawberries from Chile. Instead of a free trade environment in the U.S., the U.S. government has imposed a value quota. What will the quota on strawberries from Chile do to the U.S. market?
Lower the price of strawberries in the U.S., and lower the quantity of strawberries sold in the U.S.
Keep the price of strawberries the same in the U.S., and increase the quantity of strawberries.
Lower the quantity of strawberries in the U.S. and increase prices.
Lower the price of strawberries in the U.S., and increase the quantity of strawberries sold in the U.S.
Lower the price of strawberries in the U.S., and increase the quantity of strawberries sold in the U.S.
An example of a tariff would be ________.
rules and regulations placed on a good
a limit on the number of a good imported into a country
A free trade agreement.
a tax on an imported good
a tax on an imported good
The World Trade Organization (WTO) was established in ________.
1993
1994
1947
1995
1995
A common complaint with trade policies is the act of ________.
value chaining
marginalizing
Division of Labor
dumping
dumping
Since the change in GDP is a greater change than in the expenditure model the multiplier has a value ________.
less than one
equal to one
more than one percent
greater than one
greater than one
Why does the multiplier effect exist?
Because a change in expenditures induces households to save.
Because a change in expenditures induces the country to export.
Because a change in the consumer price index causes consumption.
Because a change in expenditures leads to changes in income, which generates further spending.
Because a change in expenditures leads to changes in income, which generates further spending.
If government spending increases by $4 billion and real GDP increases by $8 billion, the expenditure multiplier must be ________.
1.5
3.0
1.0
2.0
2.0
If the MPC is 75%, what is the spending multiplier?
.75
1.33
1.0
4
4
If the expenditure multiplier is 2.5 and the government spending increases by $4 billion, what would be the increase in the real GDP?
$8 billion
$6.5 billion
$1.6 billion
$10 billion
$10 billion
When the economy experiences an inflationary boom, the GDP gap is:
Positive.
zero.
one.
negative.
Negative
Keynesian economists believe that the economy needs to be influenced in order to correct itself from the effects of unemployment and inflation. This can be done through ________ policies.
monetary
accounting
financial
fiscal
fiscal
Keynesians believe the economy is characterized by recessions and inflationary booms which can cause unemployment and inflationary concerns. The solutions to a recession causing unemployment is expansionary fiscal policy in the form of ________.
tax increases and decreased government spending
increasing the discount rate to influence the fed fund rate
increased debt instruments
tax cuts and increased government spending
tax cuts and increased government spending
The Keynesian approach focuses on aggregate demand and sticky prices has proven useful in understanding how the economy fluctuates in the ________-run and why recessions and cyclical unemployment occur.
long
gap
intermediate
short
short
Keynes believed that economies are ________ driven in the ________ .
demand; long-run
supply; long-run.
supply; short-run.
demand; short-run.
demand; short-run.
Keynes understood that in the short-run wages and prices are ________ and therefore encourage the use of ________ to return an economy to equilibrium.
rigid; monetary policy
flexible; monetary policy
sticky; monetary
rigid; fiscal policy
rigid; fiscal policy
What is the best explanation for the slope of the neoclassical zone of the aggregate supply curve?
A small increase in aggregate demand when the economy is operating below its potential output will not have much effect on the price level.
An increase in aggregate demand causes both real output and the price level to increase.
A decrease in the consumer price index would cause the slope to increase over time.
A small an increase in aggregate demand when the economy is operating at potential output causes the price level to rise, with little or no effect on real output.
A small an increase in aggregate demand when the economy is operating at potential output causes the price level to rise, with little or no effect on real output.
Neoclassical economists argue that
the long run aggregate supply curve is below the level of potential GDP.
the long run aggregate supply curve moves gradually to the left as potential GDP grows.
the long run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
stocks and bonds will increase the GDP to appropriate levels.
the long run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
A rightwards shift of the AD curve along the Neoclassical portion of the aggregate supply curve will result in
no effect on the price level.
a decrease in the price level.
the GDP deflator moving.
an increase in the price level.
an increase in the price level.
Aggregate demand is more likely than aggregate supply to ________ in the short run.
remain unchanged
increase slightly
shift substantially
remain at zero
shift substantially
If you are explaining the theory of rational expectations to a friend, you would say that the change in an agents’ expectations is ________ and therefore ________ the effectiveness of monetary or fiscal policy.
slow; increases
based on historic information; always improves
based on future information; does not improve
immediate; precludes
immediate; precludes
Which of the following scenarios would most likely be viewed from a neoclassical perspective as an undermining element of the long-run productivity growth in an economy?
stimulus spending by the government
unemployment that is cyclical
tax cuts by the government
business capital investment tax cuts
business capital investment tax cuts
Keynes argued that the ________ was unable to keep the economy at full employment. As a result, the ________ should take an active role in managing the economy.
public sector; government
private sector; corporations
public; corporations.
private sector; government
private sector; government
Which one of the following statements best represents the Keynesian Perspective?
Build it and they will come.
Build things so long as the supply is there.
Demand is not as important as supply.
People’s demand determines what is built.
People’s demand determines what is built.
What are the components included in aggregate demand?
Consumption, private sector spending, and net imports
Consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
Production, investment, private spending, and net imports
Output, investment, government spending, and net exports
Consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
According to the Keynesian perspective, reasons for an increase in aggregate demand include
decrease in foreign demand for net exports.
relative price increase of U.S. goods.
the GDP deflator moving.
increase in foreign demand for net exports.
increase in foreign demand for net exports.
If U.S. goods are relatively cheaper compared with goods of foreign places, then U.S. exports are likely to rise. This would make the aggregate demand curve ________.
shift to the left
remain the same
move along the line
shift to the right
shift to the right
According to macroeconomic theory, evidence that high unemployment may be accompanied by low inflation, and low unemployment may be accompanied by high inflation is illustrated by the
neoclassical aggregate demand-aggregate supply model.
Keynesian cross diagram.
Neoclassical Phillips curve tradeoff.
Keynesian Phillips curve tradeoff.
Keynesian Phillips curve tradeoff.
The Keynesian economic framework is based on an assumption that
an increase in government spending will cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left.
people can afford a high level of government services.
aggregate supply is the primary determinant of economic output.
prices and wages are sticky and do not adjust rapidly to changes in aggregate demand.
prices and wages are sticky and do not adjust rapidly to changes in aggregate demand.
During recessionary times it can be hard to coordinate lower wages for workers because of the ________.
discoordination argument
relative wage theory
shoe leather costs
coordination argument
coordination argument
If inflation occurs in a given year,
the change in the real measurement (GDP) would be greater than the change in the nominal one.
the change in the real measurement (GDP) would be equal to the change in the nominal one.
the change in the real measurement (GDP) would be greater than the change in the nominal one only if there is inflation.
the change in the real measurement (GDP) would be smaller than the change in the nominal one.
the change in the real measurement (GDP) would be smaller than the change in the nominal one.
Which of the following best defines real GDP?
Real GDP is defined as the total dollar value of final goods and services produced within a country in one year before adjustment for inflation.
Real GDP is defined as the current total dollar value of final goods and services produced within a country.
Real GDP is defined as the total dollar value of final goods and services produced within a country in one year divided by the real quantity produced.
Real GDP is defined as the total dollar value of final goods and services produced within a country in one year after adjustment for inflation.
Real GDP is defined as the total dollar value of final goods and services produced within a country in one year after adjustment for inflation.
With a Real GDP of $100 billion in 2016 and of $140 billion in 2017, the real growth would be
14%
71%
7.1%
40%
40%
The fictional small country of Dansbert has had a robust GDP the last few years. Dansbert produces just two products: TVs and Computers. The following chart shows product quantities and prices from 2016 to 2018. With 2016 as the base year calculate the real GDP using 2018 prices. What is the real yearly growth in 2017 & 2018?
TVs | Computers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Quantity | Price/unit | Quantity | Price/unit | |
Year 2016 (base year) | 1 million | $20 | 2 million | $40 |
Year 2017 | 3 million | $40 | 3 million | $65 |
Year 2018 | 5 million | $70 | 6 million | $80 |
80% for 2017 : 89% for 2018
250% for 2017 : 100% for 2018
215% for 2017 : 730% for 2018
180% for 2017 : 240% for 2018
80% for 2017 : 89% for 2018
Which of the following describes the macroeconomy?
The oil and gas sector in Texas has seen the largest job gains in 2017.
The online retail business has been growing at the expense of traditional retail stores.
Consumers in Arizona are spending more on electricity due to a very hot summer
The US inflation rate has been under 2% annually over the last 7 years.
The US inflation rate has been under 2% annually over the last 7 years.
A macroeconomist would study
the impact of regulations in the banking sector in Florida.
household spending patterns in lower income groups.
The impact of new tariffs on the agricultural sector in Iowa.
economic policies designed to stimulate the country’s economy out of a recession.
economic policies designed to stimulate the country’s economy out of a recession.
The macroeconomy
focuses on firms and the production of goods and services.
primarily studies government economic policies.
Focuses on trade with other countries
regroups the activity of all households, firms and government in a country.
regroups the activity of all households, firms and government in a country.
An economic indicator is:
one of a series of laws that was passed in the 1990s to help reduce the trade deficit.
a variable that describes how the economy fluctuates every four years due to presidential elections.
A way to describe the main economic concepts.
a statistic that helps us understand how the economy is doing.
a statistic that helps us understand how the economy is doing.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is designed to measure:
a nation’s total consumption of final goods and services by households.
a nation’s total imports of final goods and services
a nation’s total investment level
a nation’s total production of final goods and services.
a nation’s total production of final goods and services.
GDP includes
intermediate and final goods to count all goods and services produced.
final goods and inventories of imported intermediate goods.
Cars produced by Ford in Mexico
only final goods to avoid double counting when including intermediate goods.
only final goods to avoid double counting when including intermediate goods.
Which of the following would fall in the Investment component of GDP?
The amount spent on stocks and bonds.
The amount spent on consumer durable goods.
The amount households save
The amount spent on new factories
The amount spent on new factories
Investment, when calculating GDP, refers to the:
purchase of stocks and bonds and trading financial assets.
purchase of new capital goods like real estate, equipment, and inventories.
amount of new capital goods purchased by the government.
Amount of savings from households
purchase of new capital goods like real estate, equipment, and inventories.
In calculating GDP, which component of spending must be subtracted from total spending?
Depreciation
Export
Change in inventory
import
import
Economic growth is supported by
laws restricting trade between nations.
laws limiting access to private property.
laws restricting immigration.
laws that build trust between parties.
laws that build trust between parties.
Fluctuations in real GDP are called ________?
Depressions
Recessions
Inflation
business cycles
business cycles
An economy is considered to be in a recession if
real GDP has increased for two consecutive quarters.
it is moving from the trough to the peak of the business cycle.
it is moving from one peak of the business cycle to the next.
it is moving from the peak toward the trough of the business cycle.
it is moving from the peak toward the trough of the business cycle.
Which of the following best describes a business cycle?
The cyclical movement in interest rates.
Regular fluctuations of prices.
How firms grow and eventually go out of business.
Periods of increasing and decreasing real GDP.
Periods of increasing and decreasing real GDP.
If a country’s Gross Domestic Product increased slower than its population increase, the country’s GDP per capita would
Rise.
not change significantly.
Remain the same
fall.
fall.
Gross Domestic Product is a ________measurement of standard of living because ________.
perfect; all important determinants of standard of living are incorporated
imperfect; all important determinants of standard of living are incorporated
perfect; not all important determinants of standard of living are incorporate
imperfect; not all important determinants of standard of living are incorporated
imperfect; not all important determinants of standard of living are incorporated
What factors are left out of the Gross Domestic Product calculation but are still necessary in determining and reflecting our standard of living?
The value of our imports, the improvements in product quality.
The value of our imports and exports, the value of leisure.
Improvements in product quality, profit for shareholders ad business owners
The value of leisure, the quality of our environment, improvements in products quality.
The value of leisure, the quality of our environment, improvements in products quality.
Labor productivity is
the value of the production or output per worker.
the production or output per hour.
The value of the production per hour
the production or output per worker per hour.
the production or output per worker per hour.
Which of the following is unlikely to affect labor productivity?
The quality and quantity of available capital resources.
Technological change.
Education levels
The frequency of business cycles.
The frequency of business cycles.
Which is a factor that drives economic growth?
Government spending.
Decreased unemployment.
Low prices
Increased human capital.
Increased human capital.
Which factors contribute to economic growth?
A decrease in the quantity of labor due to emigration.
A decline in the stock of physical capital.
A decrease in the number of government funded research programs
An increase in university graduates.
An increase in university graduates.
If the total number of hours worked per year increases, then automatically
the value of the production per hour worked will also increase.
the production or output per worker will also increase.
hourly wages will rise
the value of the production will increase.
the value of the production will increase.
Compound growth in an economy can increase people’s standard of living for country Z. If the economy for country Z starts with a GDP of 150 and a growth rate of 2% per year, what will its GDP be after 15 years?
2,295
230
300
202
202
The country of Wachovia has an economy that will double in 144 years. From what you’ve learned of the power of compound growth what does this mean for Wachovia?
Wachovia has a thriving and rapidly growing economy growing over 1% per year.
Wachovia has a somewhat stalled economic growth of over 1% per year.
Wachovia has a thriving and rapidly growing economy growing over 2% per year.
Wachovia has a slow growing economy at a growth rate of .5% per year.
Wachovia has a slow growing economy at a growth rate of .5% per year.