Lecture 7: Common Diseases in Veterinary Neurology
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Idiopathic epilepsy: signalment
- Young dogs (6m-6y)
- Purebred, large breed (labs common)
Idiopathic epilepsy: signs
- Partial or generalized seizures
- Single or cluster seizures
- Normal between seizures
Idiopathic epilepsy: diagnosis
- Diagnosis of exclusion
Idiopathic epilepsy: treatment
- Goal is to decreases the frequency and severity of seizures
- Medications (not all required drugs) if seizures closer together / cluster
Old dog vestibular disease: signalment
- Geriatric dogs (10+ years)
- Large breeds
Old dog vestibular disease: signs
- Peracute onset
- IDIOPATHIC
- Peripheral vestibular signs (severe healed tilt*, ataxia, nystagmus, rolling, falling)
- NO CP deficits! No seizures.
Old dog vestibular disease: treatment
- Symptomatic and supportive (fluids, anti-emetics, +/- anti-anxiolytics)
- Brain MRI is unremarkable
- move them around slowly! they're dizzy!
what is MUE (meningoencephalitis of unknown etiology)?
- A non-infectious inflammatory process in the CNS
- Immune-mediated
- Can occur anywhere in the CNS
MUE (meningoencephalitis of unknown etiology): signalment
- Young, middle aged dogs
- Small toy and terrier breeds
- female > male
MUE: diagnosis
- Rule out infectious causes
- MRI affected area
- CSF analysis
MUE: treatment
- Corticosteroids
- Immune modulatory drugs
- Other drugs as needed
IVDD: two types?
- Type 1: chondrodystrophic dogs; acute disc extrusion (nucleus hits cord)
- Type 2: large breed dogs; chronic disc protrusion (annulus presses on cord)
IVDD: location
Anywhere you have a disc
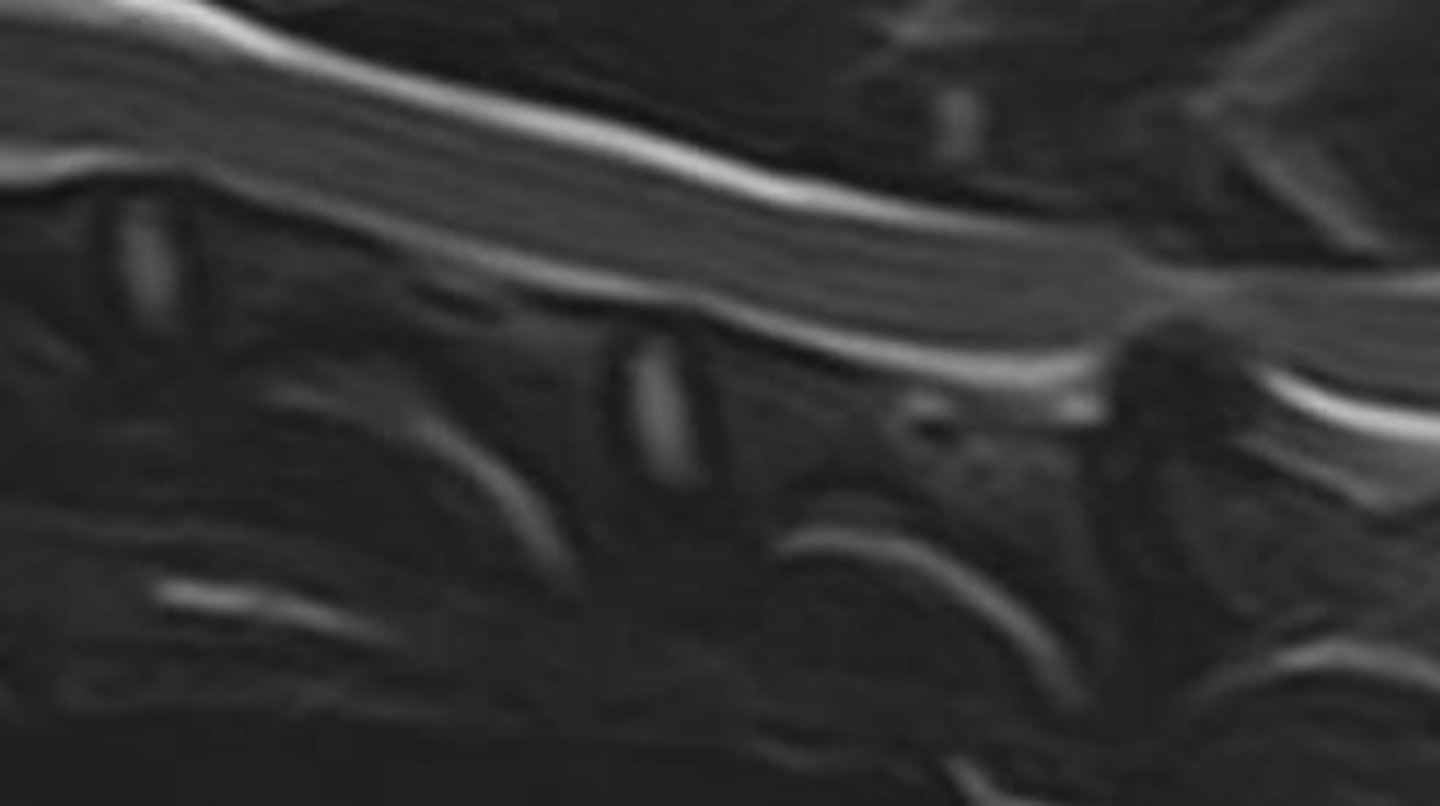

where is IVDD most common?
C2 to tail
common at T11-L3
IVDD: diagnosis
- CT or MRI (can see the spinal cord being pressed on)
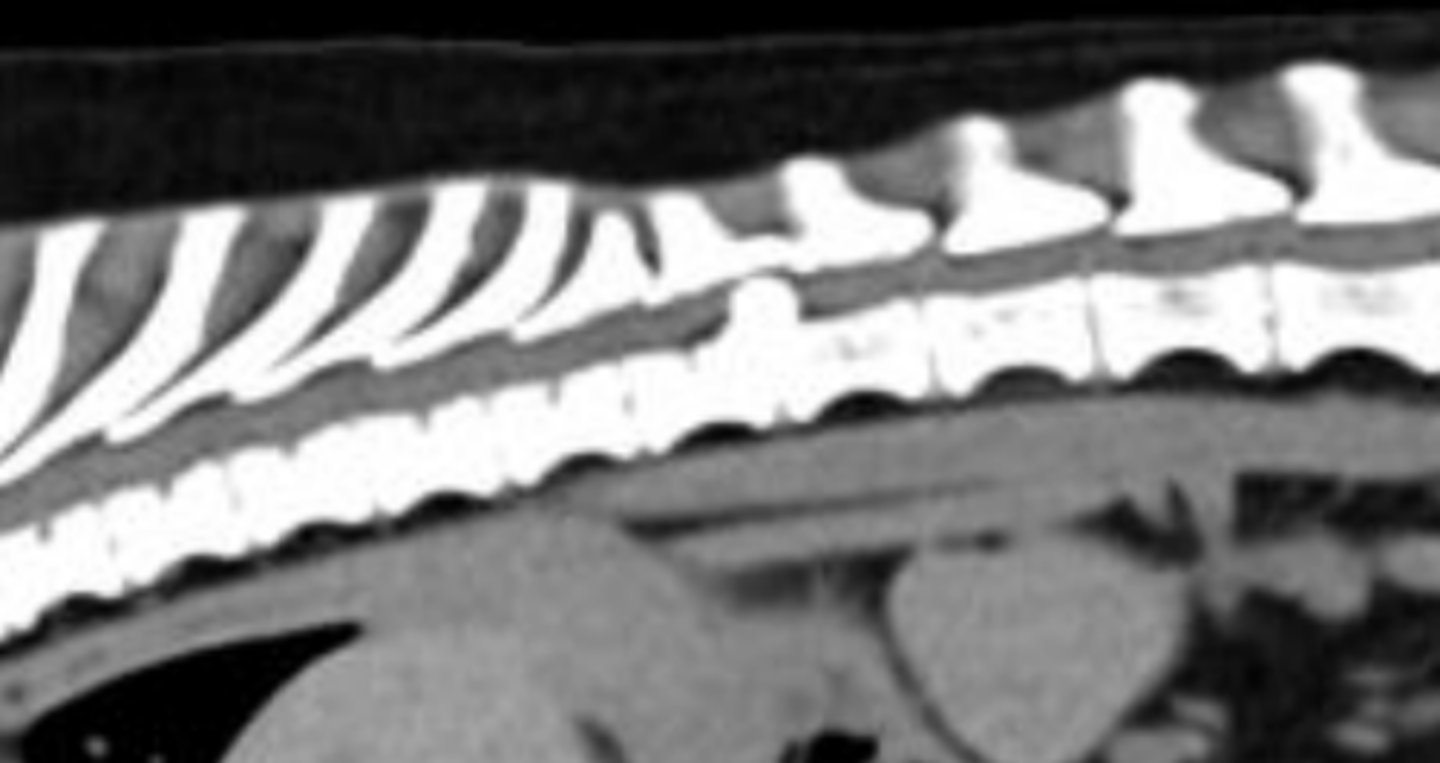
IVDD: treatment
- Medical management
- Surgery if they go down (excellent prognosis if pain perception present, 50% if paraplegic with absent pain perception)
what is fibrocartilagenous embolism?
disk --> blood supply --> ischemic injury
Fibrocartilagenous embolism: location
Anywhere along spinal cord (but usually T3-L3)
Fibrocartilagenous embolism: signs
- Peracute
- Asymmetric signs
- Non-painful on exam
Fibrocartilagenous embolism: diagnosis
- Cross-sectional imaging (MRI) —> look for focal area of ischemia
(NOT CT)
Fibrocartilagenous embolism: treatment
- PT
- Pain management
Degenerative myelopathy: signalment
- German shepherds*, corgis, boxers
- ~7 years old
- Progressive over 6-18 months
Degenerative myelopathy (DM): location
- Starts at T3-L3 non-painful
- Can descend to L4-S3 and cause fecal/urinary incontinence
- Can then ascend to affect the TLs
Degenerative myelopathy: diagnosis
- MRI T3-L3 spine
- SOD-1 test: look for mutation (Homozygous mutation means at risk/affected)
Degenerative myelopathy: treatment
- No definitive treatment
- PT prolongs functional time
Most common cause of inflammatory disease in cat CNS.
FIP (Coronavirus mutation)
FIP: diagnosis
- MRI
- CSF analysis (high neutrophils and protein)
CNS FIP is a ? form
dry
- No effusion, +/- ↑globulins
FIP: treatment
New drug (nucleoside analog)?
poor prognosis
T/F: it is easy to clear toxoplasma gondii.
False — once infected, almost impossible to clear (recurrent episodes), it's in the environment (protozoal organism)
Toxoplasmosis: diagnosis
4-fold rise in serum antibody titer
Can affect the CNS anywhere
Toxoplasmosis: treatment
Clindamycin
Meningioma: signalment
Geriatric cat (12+ years old)
Meningioma: signs
Slowly progressive forebrain signs (behavior changes*, circling)
Meningioma: diagnosis
MRI >> CT
Meningioma: treatment
Surgery (>2 years to return of signs)
Most common cause of spinal disease in dogs.
IVDD
describe equine wobblers syndrome
- osseous associated
- Abnormal gait and cervical hyperesthesia
- many names

wobblers diagnosis
imaging (difficult)
Most common cause of spinal disease in horses.
Equine protozoal myelitis
EPM most common organism?
Sarcocystis neurona
EPM: signs
- Asymmetrical proprioceptive ataxia
- LMN involvement —> lameness and asymmetrical muscle atrophy ****
EPM: treatment
- Folic acid inhibition
- Ponazuril (antiprotozoal)
what is EEE/WEE/VEE?
Regional mosquito-borne viruses that still occur despite effective vaccines
EEE/WEE/VEE: signs
Forebrain signs, very high mortality
EEE/WEE/VEE: diagnosis
IgM ELISA
what is WNV (west nile virus)?
Encephalomyelitis due to a mosquito borne flavivirus
WNV signs?
Subclinical to fulminating -- Fever, paresis, ataxia, vestibular, cerebellar, behavior changes
WNV: diagnosis
IgM ELISA
regional and seasonal
WNV: treatment
supportive
equine herpes myelopathy from EHV1?
- Mostly respiratory, can cause neurologic signs
- Urinary bladder paralysis & urine dribbling!!
- Fever, paresis and ataxia. Decreased tail and anal tone, fecal retention
EHV1: diagnosis
PCR of respiratory secretions
Temperohyoid osteoarthropathy: signalment
Adult horses w/ ankylosis of the temporohyoid joint
Temperohyoid osteoarthropathy: signs
- Vestibular
- Ataxia
- Facial nerve paralysis (—> corneal ulcers)
- Fractures cause acute deteriorations
Temperohyoid osteoarthropathy: diagnosis
- Radiographs
- Endoscopy
- CT
Temperohyoid osteoarthropathy: treatment
Ceratohyoidectomy
what is listeriosis?
- Listeria monocytogenes --> microabscesses
- ruminants!!
- Rhombencephalitis
listeriosis: signs
progressive, multifocal!
Ataxia Tetraparesis Opisthotonus Tremors, hyperexcitability Compulsive movements Convulsions Stupor Vestibular signs Cranial nerve deficits
Listeriosis: diagnsois
CSF —> monocytic pleocytosis
what is horners syndrome?
Loss of sympathetic innervation in face and eye
Horner's syndrome: signs
- Ptosis
- Prolapsed 3rd eyelid
- Miosis
- Enophthalmos
cause of horners in dog
Idiopathic - Golden retrievers
Horner's syndrome: signs (horses)
- Ptosis (eyelashes point down)
- Unilateral sweating
- Increase temperature face/neck/shoulder
cause of horners in cat
Otitis media
No other signs!
thiamine deficiency in ruminants?
- Polioencephalomalacia
- Cerebrocortical necrosis --> forebrain signs
- Sulfur toxicity?
thiamine deficiency in carnivores?
- Seizures & blindness
- Focal areas of hemorrhage in the brain
- Cats fed solely cold water fish