Oral H & E 2 exam 1
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
bone is highly vascularized, dental materials avascular
key difference between bone and dental hydroxyapatite materials (enamel, dentin, cementum)
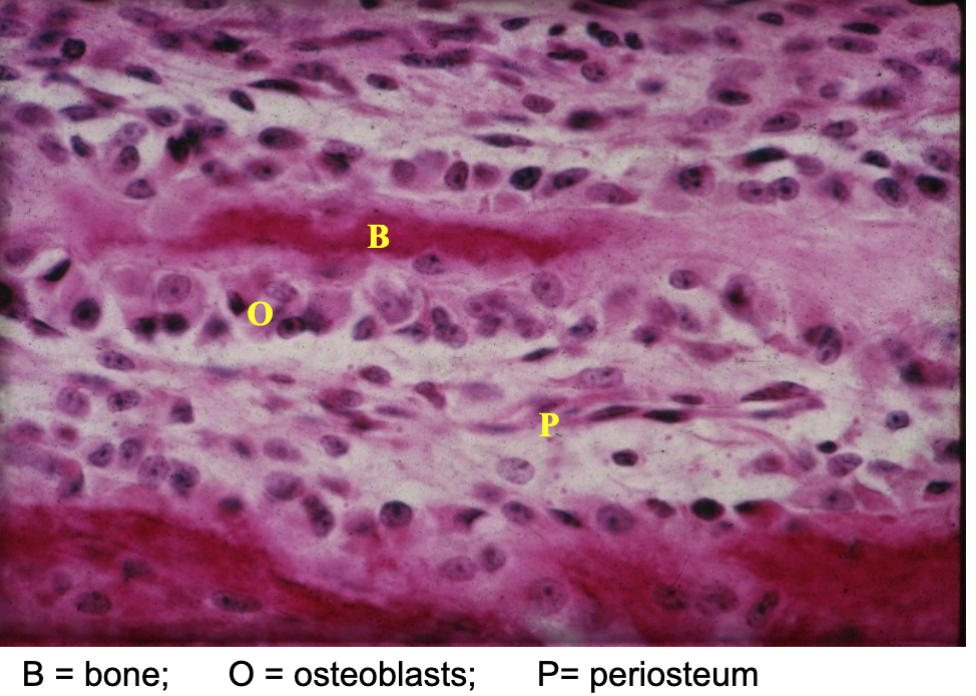
osteocyte
a bone cell embedded within the bone matrix, responsible for maintaining bone tissue
60% inorganic, 40% organic
composition of bone
sialoprotein
major protein in bone that plays a crucial role in mineralization and structural integrity.
type I
type of collagen found in bone
bone remodeling
process by which new bone is deposited and old bone is resorbed
support, protection, levers, reservoir (calcium/phosphate), blood cell production
functions of bone
compact (cortical) bone
high density of bone material tightly packed, filled wil OSTEONS and HAVERSIAN canals
spongy/cancellous/trabecular bone
lighter, less dense bone with a porous structure with low density of material to volume
lamellae
thin layers of bone matrix that form around Haversian canals in compact bone.
woven bone
first bone deposited, forms rapidly, poorly organizes and LESS mineralized
concentric lamellae
Identify A
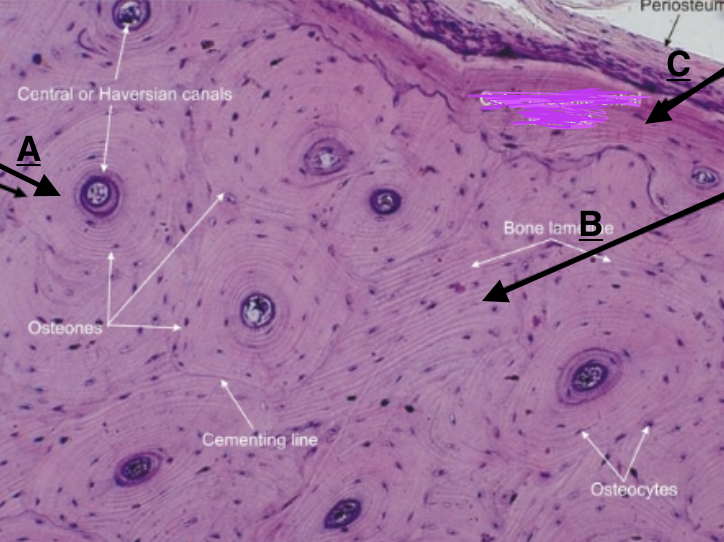
circumferential lamellae
Identify C
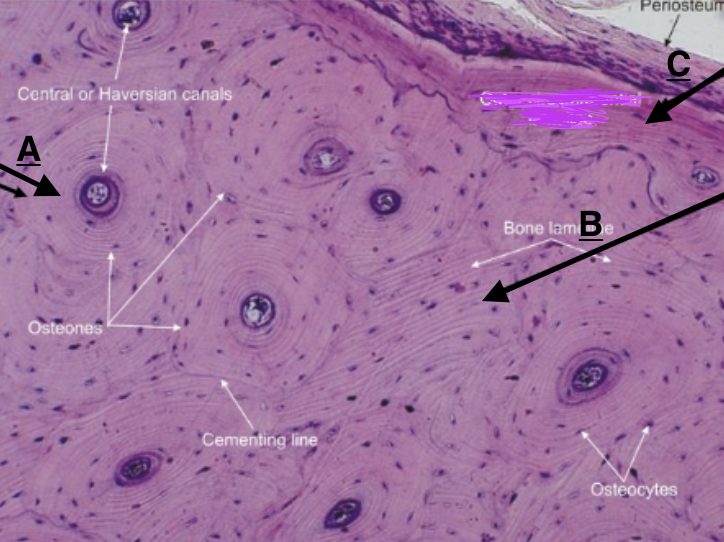
interstitial lamellae
identify B
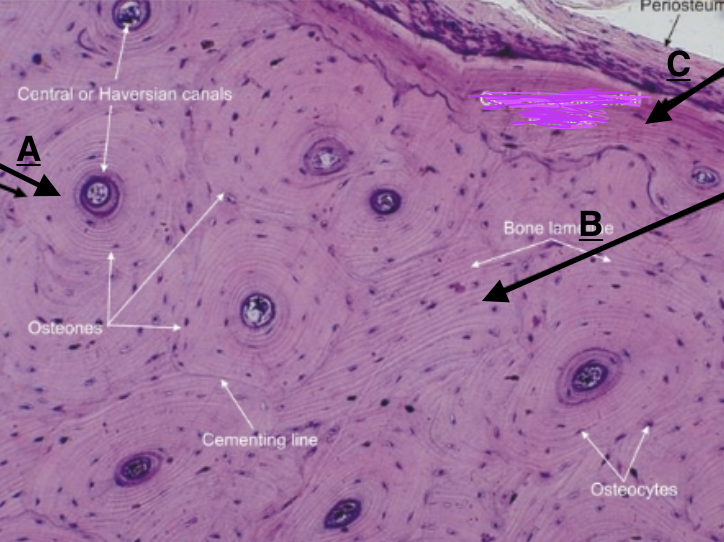
periosteum
fibrous outer layer of dense connective tissue that surrounds bones, point of attachment for tendons and ligaments
sharpey’s fibers
thick collagenous fibers that connect the periosteum to the underlying bone.
inner
which layer of the periosteum is CELL RICH
endosteum
internal lining of central cavity of bone and trabeculae
reticular fiber CT
what type of connective tissue is the endosteum
outer dense CT periosteum
layer of periosteum connected to surface of bone by SHARPEY’S FIBERS
osteoprogenitor,osteoblasts, stem-like periosteal, fibroblasts
cells found within cell rich inner periosteum
osteoblasts
Bone-forming cells responsible for synthesizing and mineralizing the bone matrix.
osteoid
the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix secreted by osteoblasts that REGULATE CALCIUM and PHOSPHATE
bone lining cells
osteoblast that flatten and line the surface of bones; regulate passage of minerals and assist in maintenance
alkaline phosphatase (AlPase)
enzyme secreted by OSTEOBLAST that cleave phosphate for HYDROXYAPATITE FORMATION
where cells are NOT secreting
where can alkaline phosphatase be found
sialoprotein, osteopontin, osteosialoprotein
mineralization promoters (loci) that regulate CaPO4
osteocytes
osteoblasts that have been trapped in mineralized matrix
rate of bone formation
what affects the conversion rate of osteoblast to osteocyte
osteocytic lacunae
small cavities in bone housing osteocytes.
canaliculi
Enclosed channels around osteocyte processes that connect osteocytic lacunae
canaliculi
what allows for osteocyte regulation of bone repair, formation, and removal
gap junctions
how do osteocyte contact adjacent cell processes
sclerostin
marker of mature osteocyte, NEGATIVE REGULATOR of bone FORMATION
osteoclasts
multinucleated cells responsible for bone RESORPTION and remodeling.
monocytes
what cells do osteoclast arise from
osteoblasts
what cells must be present for osteoclast formation
RANKL
a protein necessary for osteoCLAST differentiation and activation
IL-1a
stimulates osteoCLASTS to RESORB bone
hormones
what mediates osteoclast driven bone resorption
cathepsin
COLLAGENASE involved in the degradation of the bone matrix and activation of osteoclasts.
MMP9
gelatinase and recruiter of osteoclasts
activation, resorption, formation
phases of bone remodeling
cutting cone
structure of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, that facilitates the removal of old bone and the deposition of new bone.
type H cells (HECs)
cells that induce formation of new blood vessels in bone
noggin
secreted by HECs, sustains osteoblasts
VEGF
molecule secreted by OSTEOBLASTS that supports angiogenesis
stimulates OPCs to release SCF leading to increased immune response
how does exercise affect bone
SCF (stem cell factor)
stimulates common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs) to differentiate into various types of blood cells.
bone modeling
process of establishing bone size and shape
cartilage growth/endochondral ossification and intramembranous ossification
modes of ossification
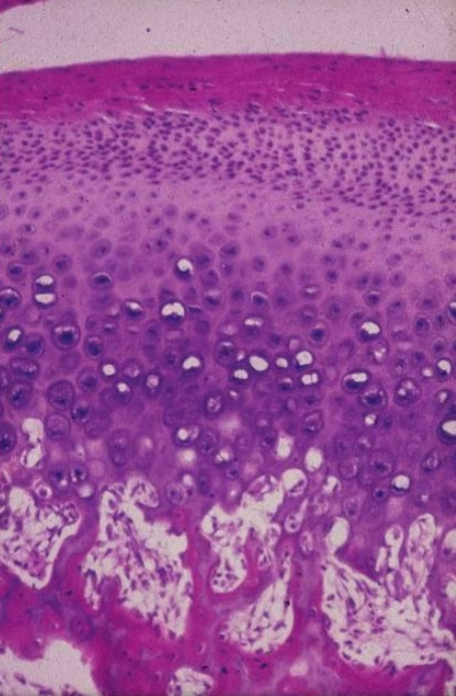
endochondral ossification
ossification in which osteoblasts produce osteid on pre-existing hyaline cartilage
long bones
where does ENDOCHONDRAL ossification occur
intramembranous ossification
bone formation in which osteoblasts differentiate directly from mesenchyme and secrete osteoid
flat bones (skull, jaw, clavicle, bone repair)
where does intramembranous ossification occur
woven
what kind of bone is formed from endochondral and intramembranous ossification
ossification
process of new bone formation on organic matrix
proliferation (1), hypertrophy/maturation(2), mineralization (3)
zones in endochondral bone formation
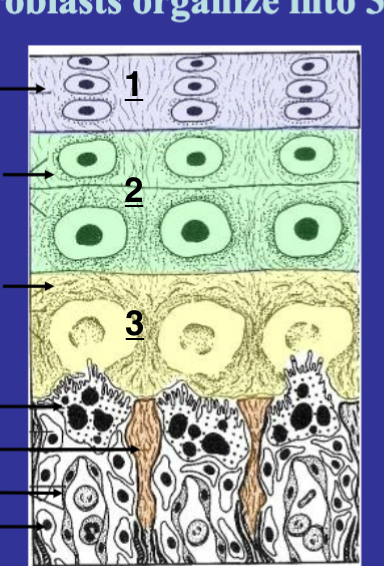
chondroblasts
cells that produce cartilage matrix, key in formation of cartilage during endochondral ossification.
osteoblast produce new bone in spicules radiating from ossification center
how does intramembranous ossification occur
intramembranous ossification
what process is occur in this picture
endochondral ossification
what process is occuring in this picture
osseous drift
process where bone tissue is reshaped due to mechanical stress and growth.
scurvy
vitamin C deficiency that impairs collagen and osteoid secretion
rickets
calcium/phosphate or Vitamin D deficiency in children that leads to improper bone mineralization and bone deformities
osteomalacia
phosphate/vitamin D deficiency in adults that leads to decrease mineral content of bone
osteoporosis
bone resorption is greater than bone deposition
osteopenia
lower mineral density/ pre osteoporosis
osteopetrosis
impaired osteoclast function leading to more mineralized brittle bone
bisphosphonates
a class of drugs that inhibit bone resorption by preventing osteoclast activity, commonly used to treat osteoporosis.
osteoclast ruffled border
site of secretion of acid and protenases
BRONJ
a serious condition characterized by the presence of exposed bone in the maxillofacial region, associated with bisphosphonate therapy.
W9
inhibits osteoclast differentiation via blocking RANKL signaling
stimulate osteogenesis and formation of osteoblasts
what is the effect of W9
mesenchymal stem cells
what are OSTEOBLASTS derived from
paraxial mesoderm
forms POSTERIOR parts of vault and cranial base
paraxial mesoderm and neural crest
what is the developmental origin of cells that form the cranioskeleton
mesenchyme
what type of cells do neural crest cells and paraxial mesoderm cells develop into
both neural crest and paraxial mesoderm
mesenchymal cells from what origin form cartilage, bone, and tendon
interstitial, fast growth, no remodeling
features of growth in cartilage
appositional, continuous remodeling
growth features of bone
hormone
what is the regulation mechanism of cartilage
mechanical
what is the regulation mechanism of bone
cartilage
tolerant of compression, higher compressive load slows elongation
bone
grows in direction of tension, resorbed under direct compression
fibroblasts, chondroblasts, or osteoblasts
cells that originate from mesenchyme cells
chondrocranium
forms cranial base
sensory capsules, body of sphenoid, occipital bone
centers of chondrification of chondrocranium
chondrocranium, pharyngeal skeleton/arch, secondary cartilages (coronoid, symphyseal, condylar)
what bones are preformed in cartilage
middle ear, base of great wing (sphenoid), lingula, styloid, hyoid
parts of pharyngeal skeleton
coronoid, symphyseal, and condylar
secondary cartilages
spheno-occipital synchondrosis, nasal septum, mandibular condyle
sites where cartilage persists throughout growth period, important for postnatal growth
controls on growth are different and affects growth potential
why is important to know how bones ossify
secondary cartilages
what contributes of growth of the mandibular symphysis (symphyseal)
intramembranous
type of ossification of desmocranium
facial bones
ossifications of facial dermis
apposition and resorption (NO INTERSTITIAL)
method of growth of bone
functional matrix hypothesis
the idea that soft tissue growth, spaces, and muscle contraction influence the growth of bone and skeletal structures.
surrounding tissues and mechanical loading
what controls bone growth
growth at spheno-occipital synchondrosis
leads to elongation of skull (A-P) and dispaces frontal bones and viscerocranium forward