Light and Optics Review
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Light
Form of energy
Natural Light Source
A naturally occurring light source

Artificial Light Source
Man-made light

Absorption
When light is absorbed instead of reflected or transmitted

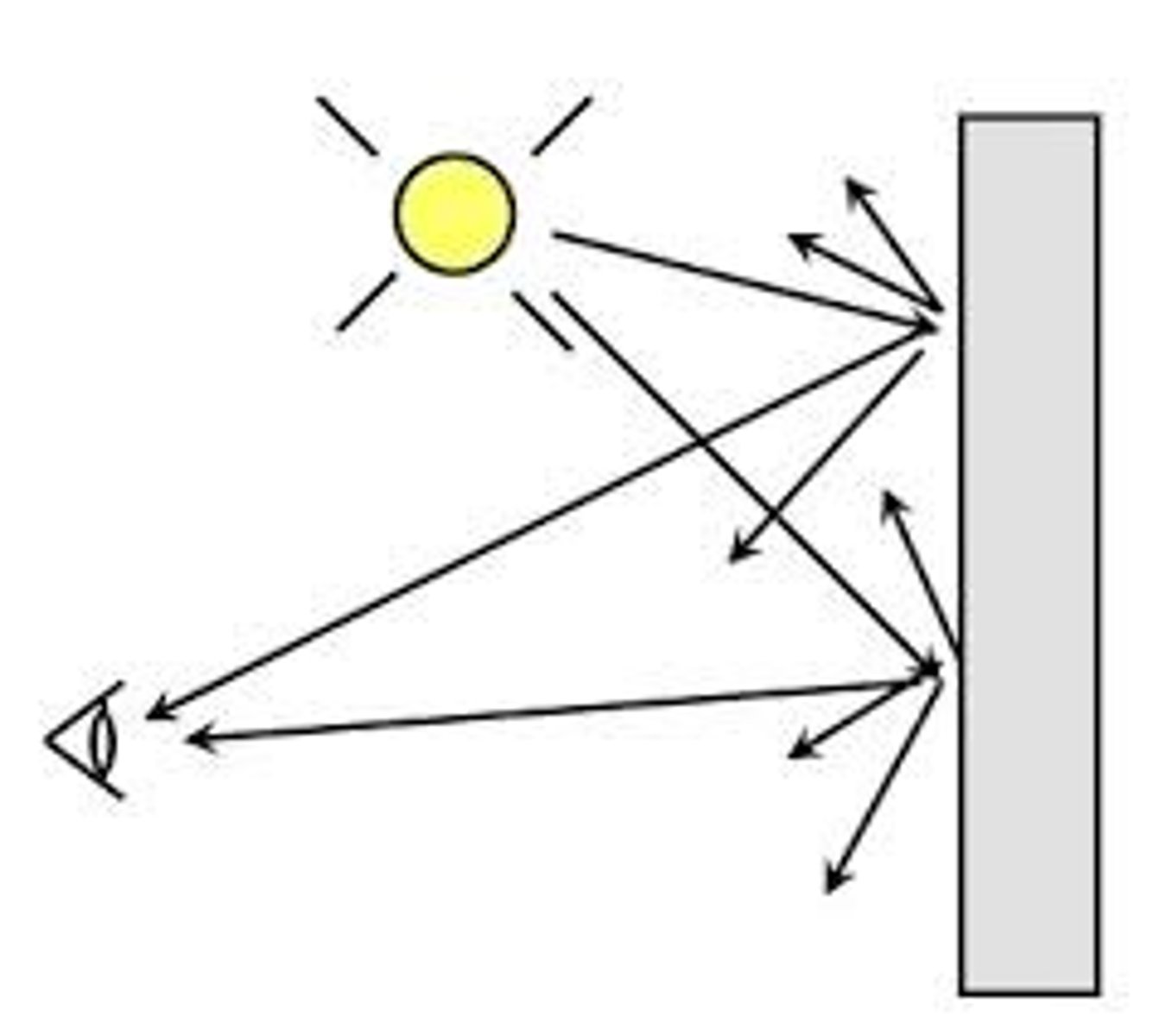
Reflection
The light reflected by a body or surface

Refraction
Bending of light when it travels from one medium to another medium of a different density

Incandescence
Emission of visible light from heat

Fluorescence
Photons are absorbed then emitted as visible light after light source is cut off

Phosphorescence
Photons are absorb and emitted as visible light immediately

Bioluminescence
Chemical reaction of an living organism that produces light
Ray diagram
Depiction of the path light takes
Transparent
Allows light to pass through

Translucent
Allows SOME light to pass through, others are absorbed

Opaque
Does not allow any light through

Incident Ray
The ray that strikes a reflecting or refracting surface

Reflected Ray
The light that is cast back (reflected) from a reflective surface
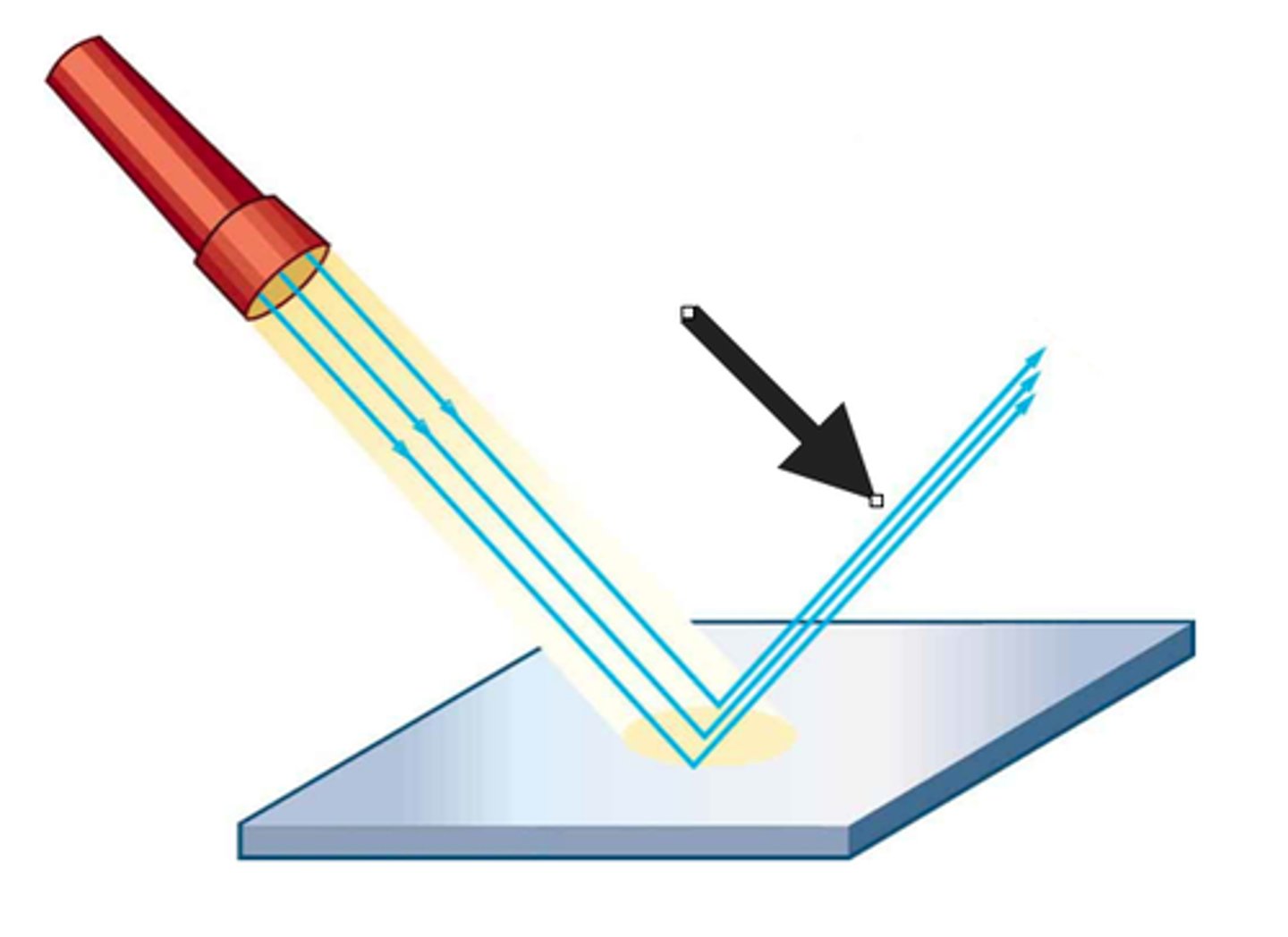
Normal Line
Perpendicular to the reflecting surface at the point where the incident ray strikes the surface
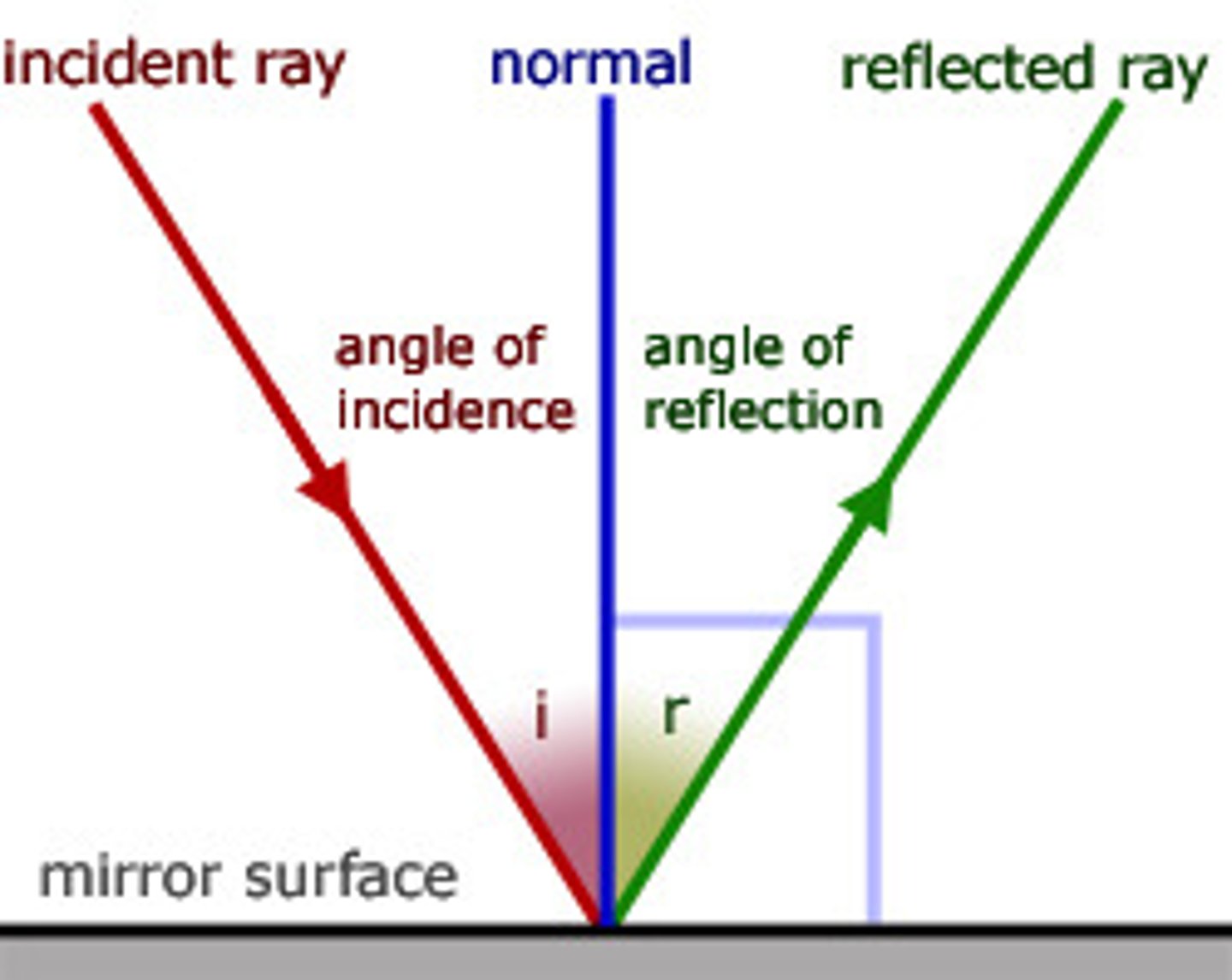
Angle of Incidence
the angle which an incident line or ray makes with a perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence.
Angle of Reflection
the angle made by a reflected ray with a perpendicular to the reflecting surface.
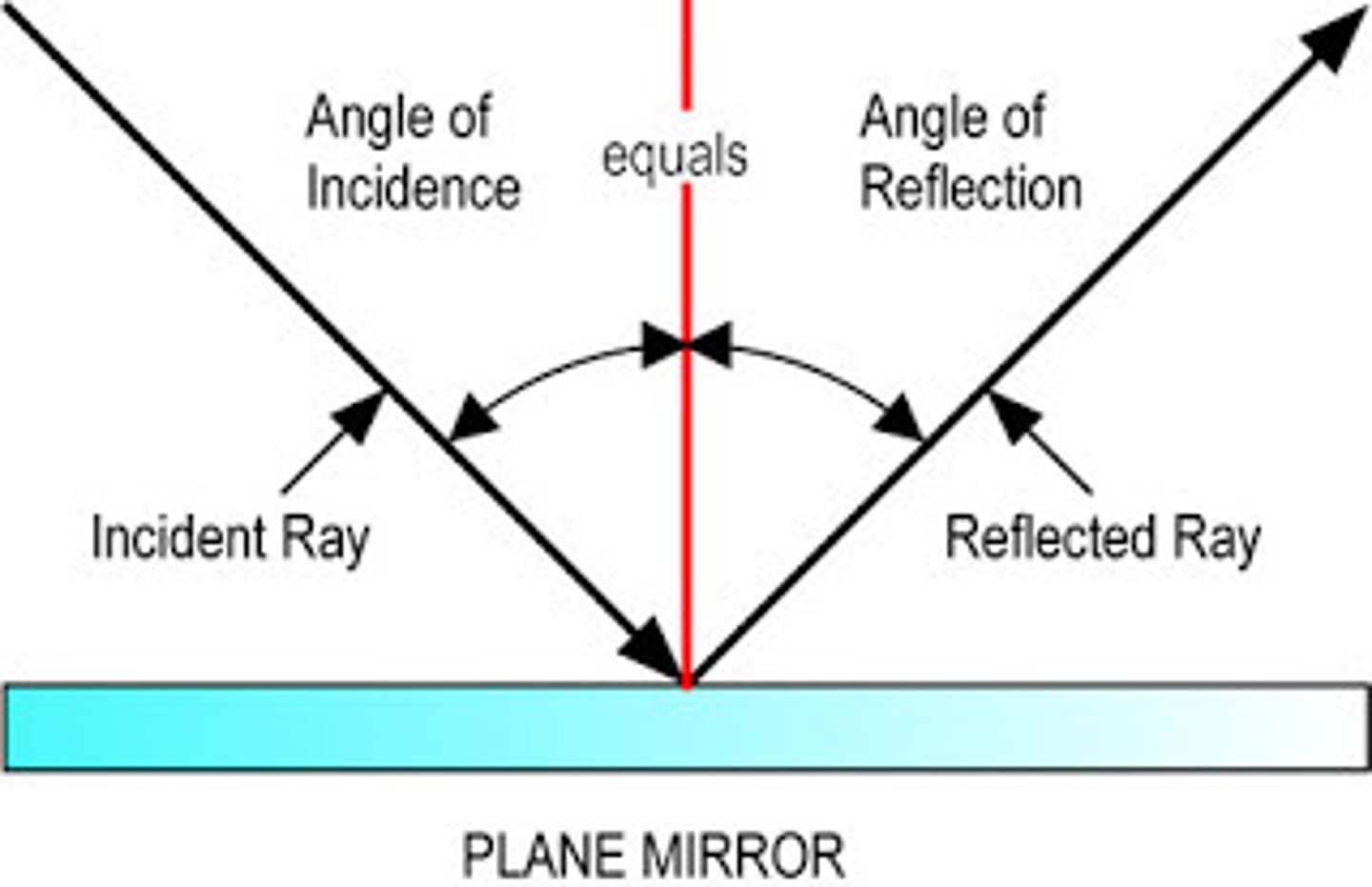
Plane Mirror
Mirror with a flat surface

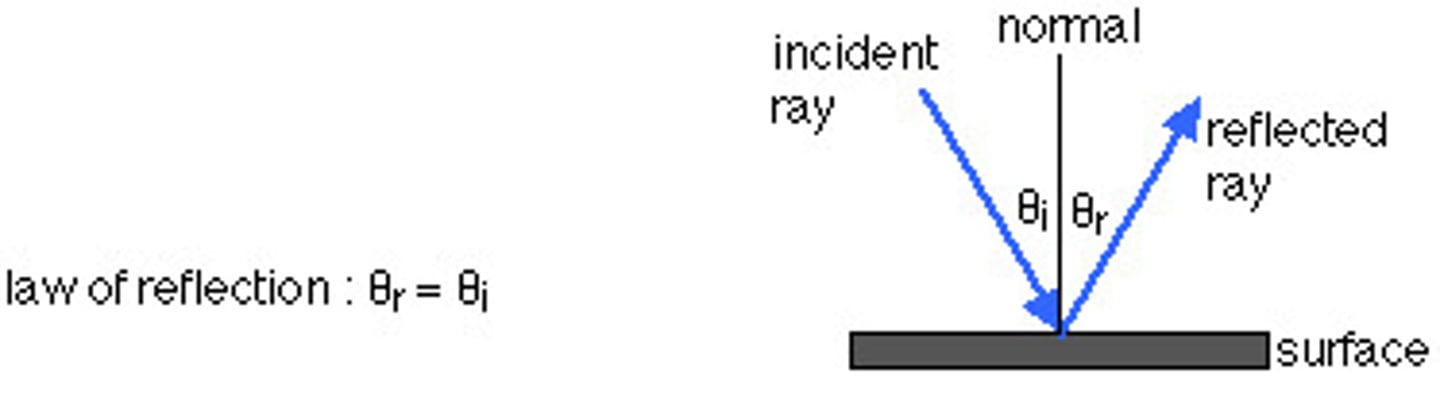
Law of Reflection
Angle of reflection=Angle of incidence
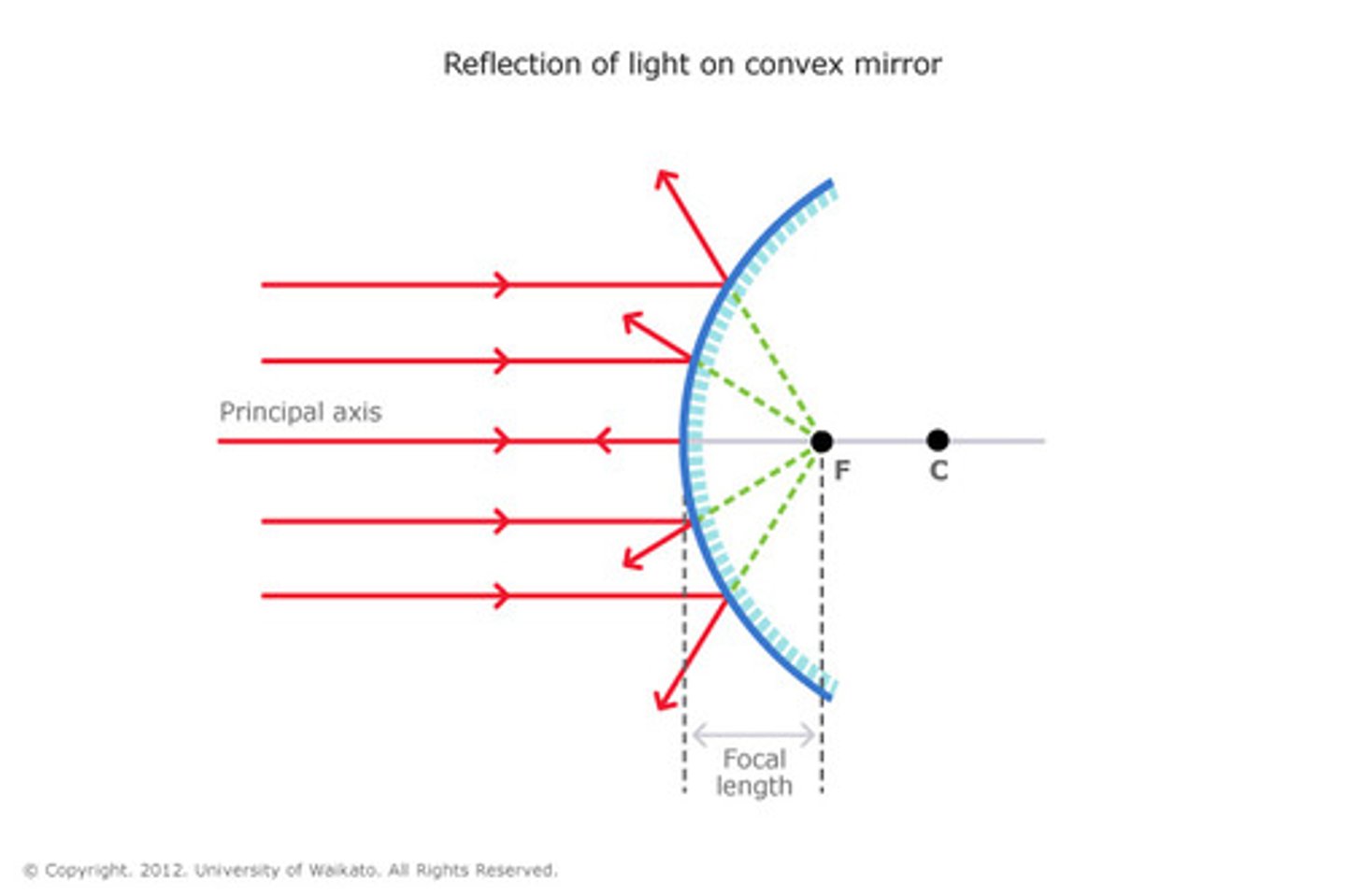
Convex Mirror
An reflecting surface in which its bulging side faces the source of light.
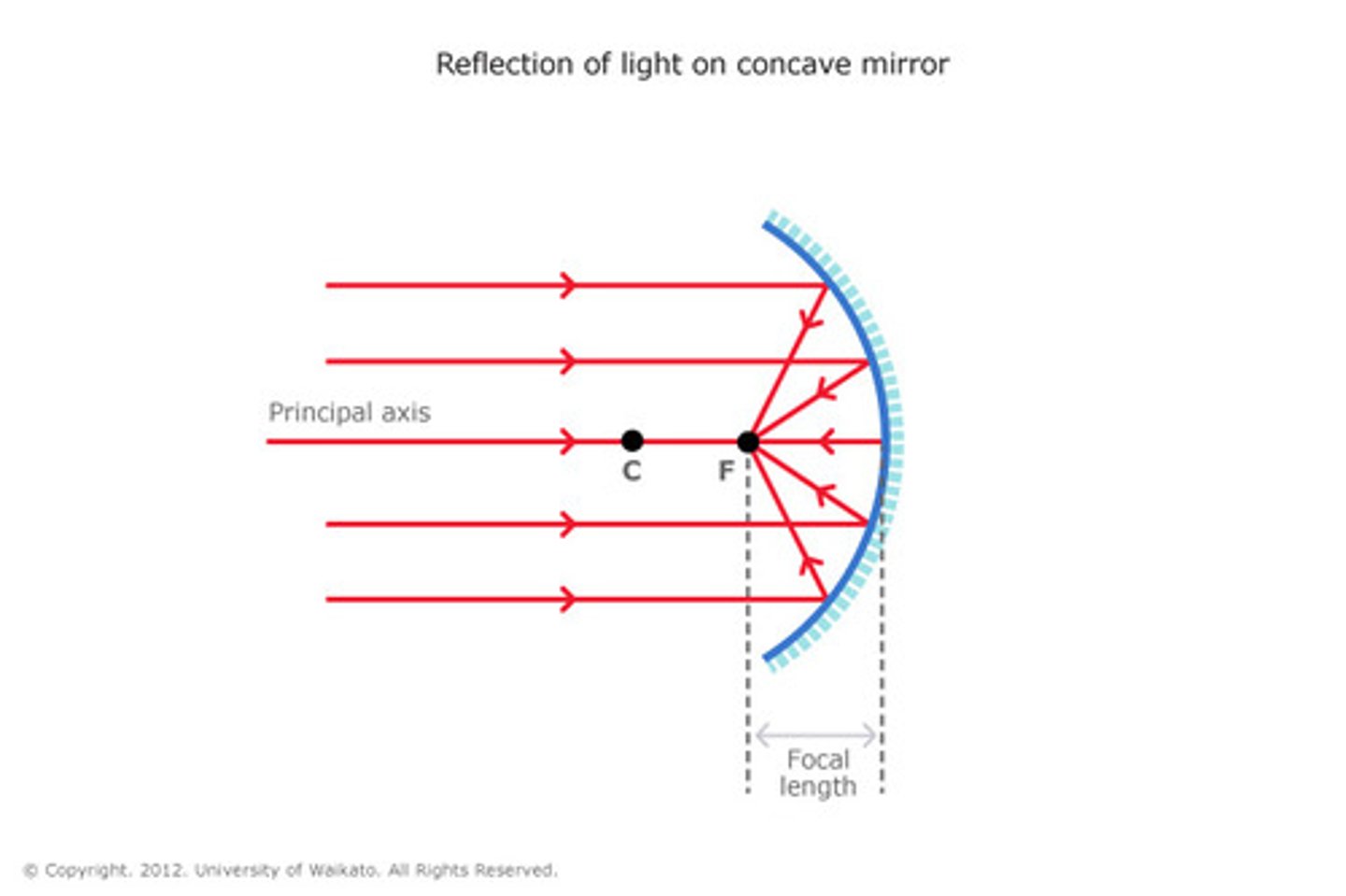
Concave Mirror
An reflecting surface in which its bulging side does not face the source of light
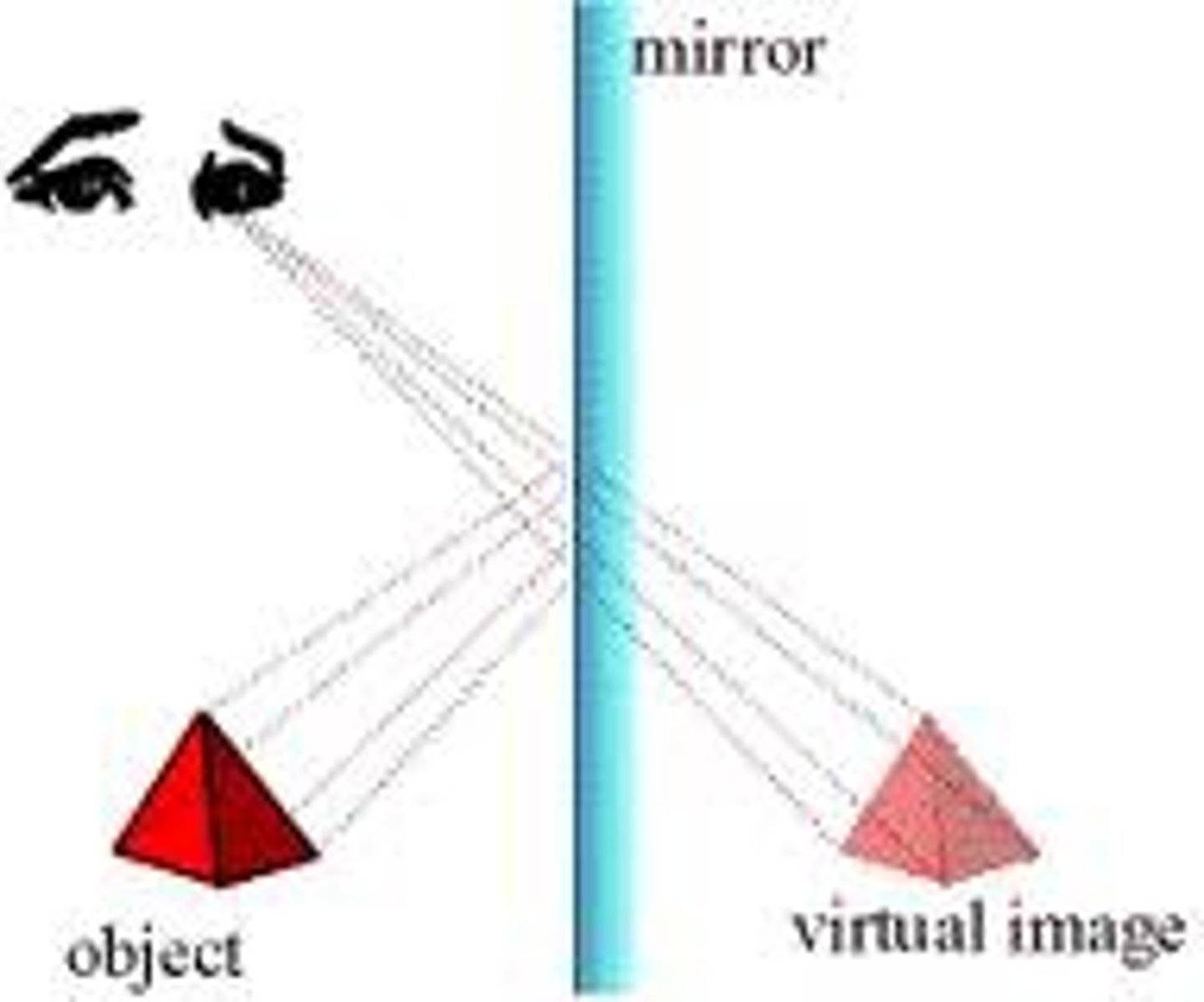
Virtual Image
Angle of Refraction
Angle between the normal and the refracted ray

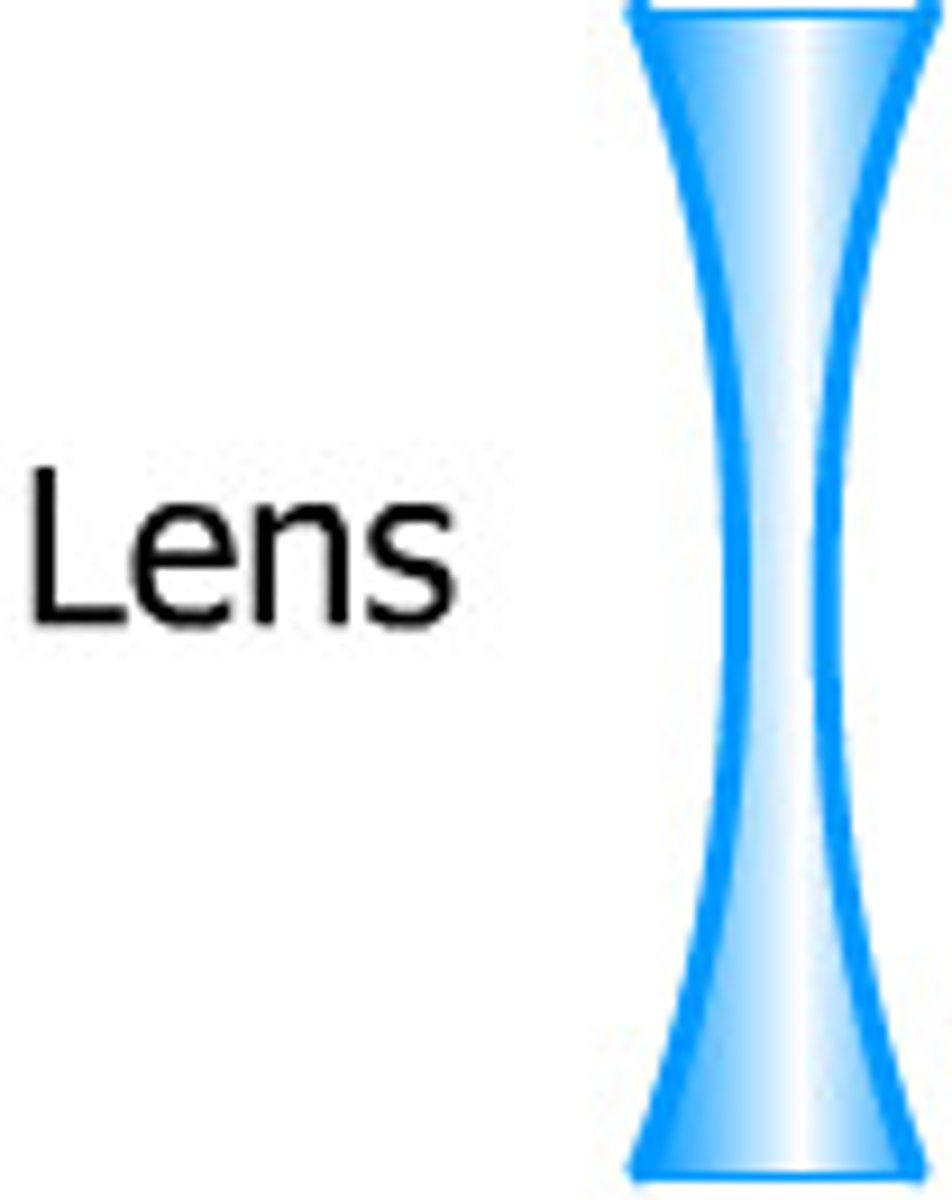
Concave Lens
Image result for concave lens definition
A concave lens is a lens that possesses at least one surface that curves inwards
Convex
Curving outwards

Concave
Curving inwards
Real image
Appears in front of a mirror, like a movie screen

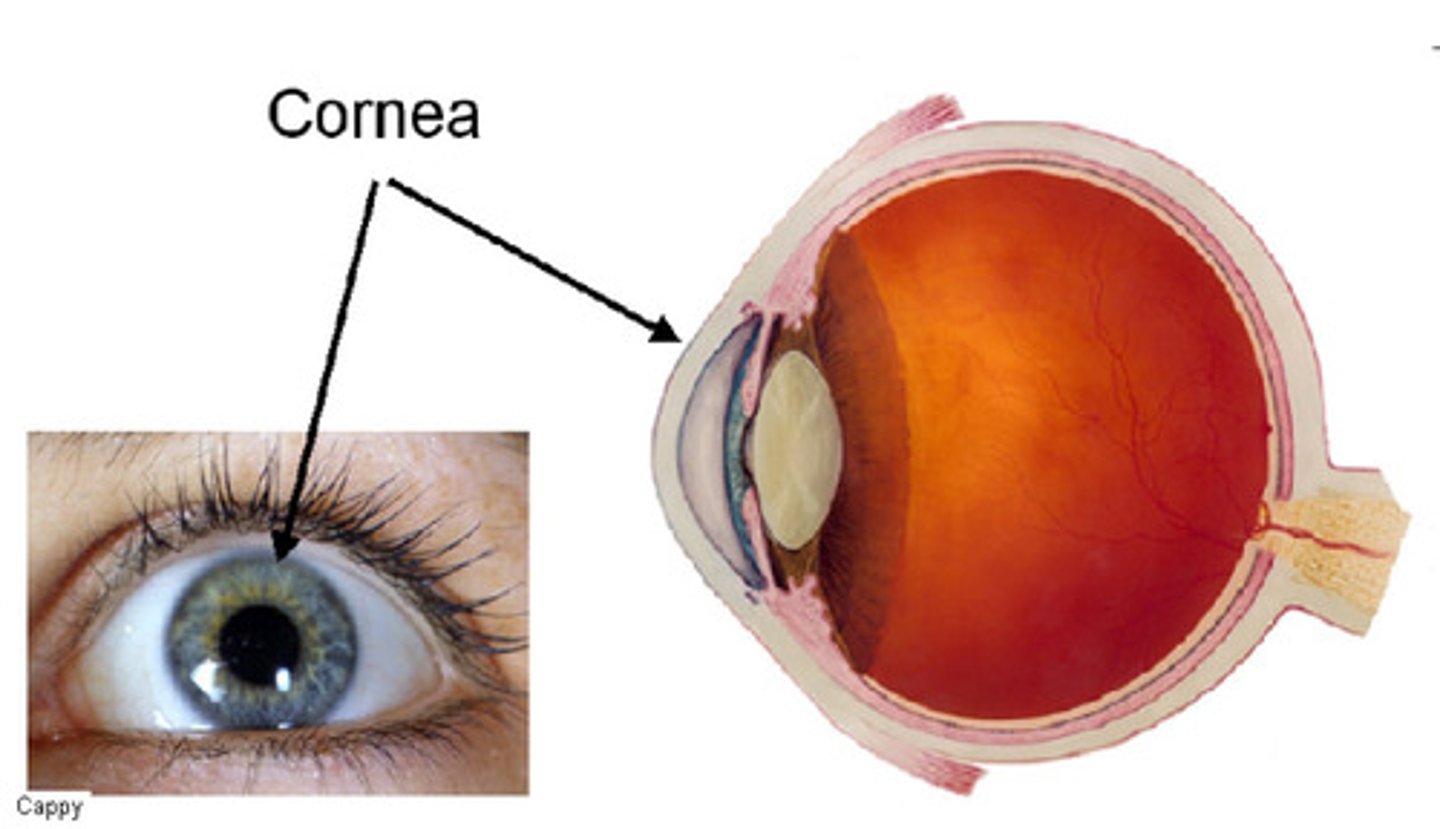
Cornea
Transparent lens forming the front of the eye
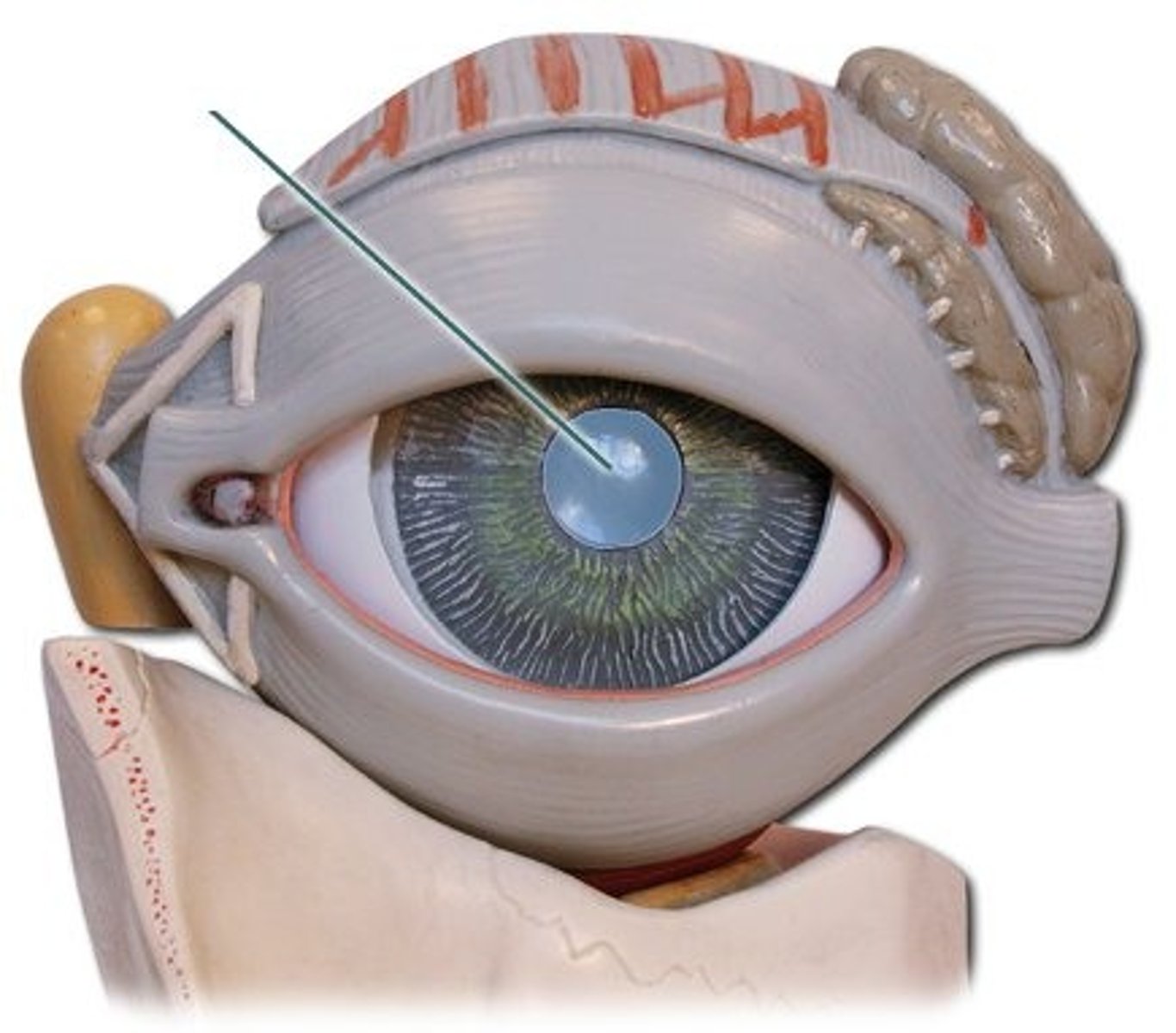
Blind spot
small area in your vision where you can’t see anything
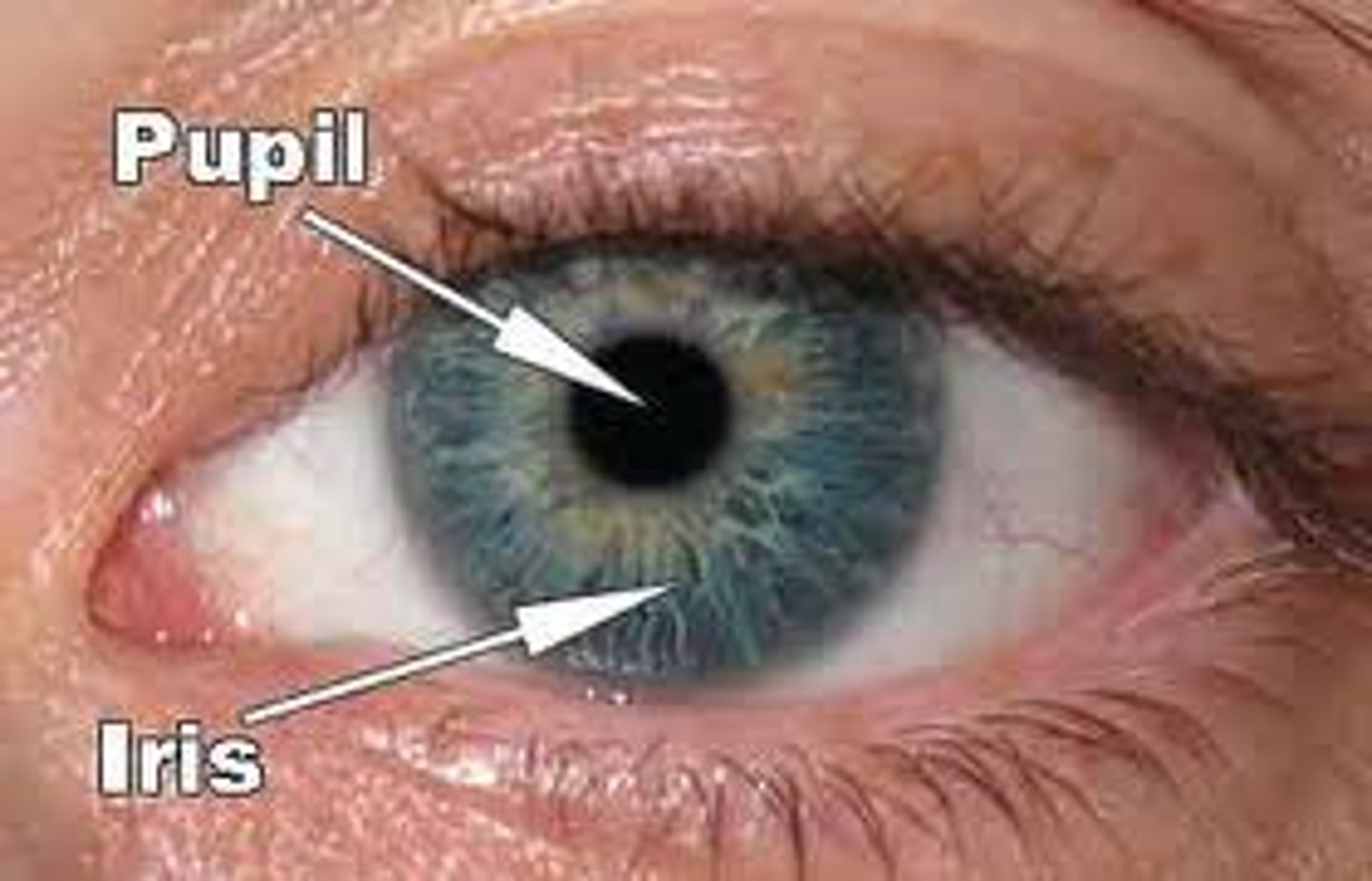
Pupil
Allows light into the eye
Iris
Controls the size of the pupil
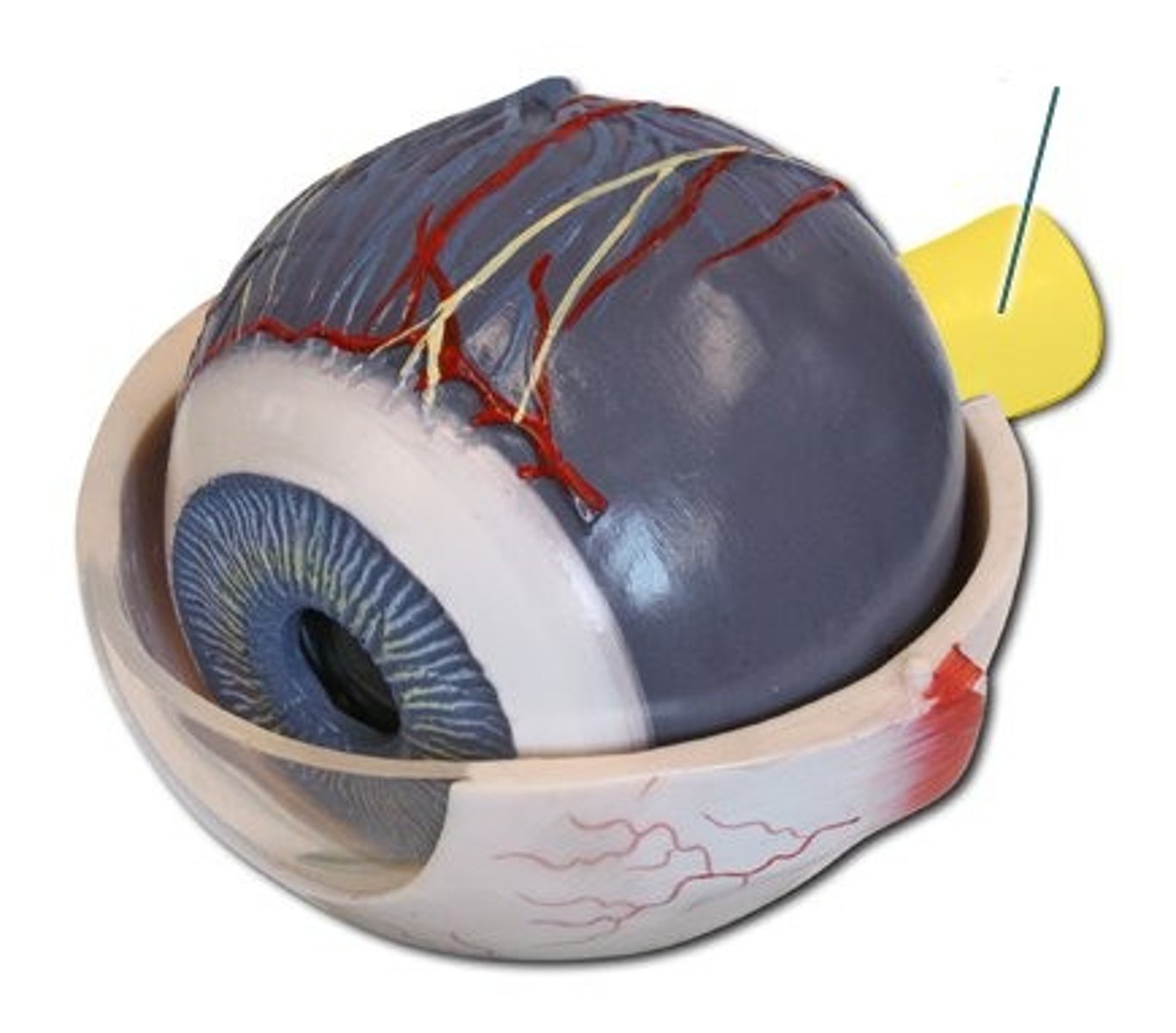
Optic Nerve
Only nerve in the body that is not in the spinal cord
Transports the image to the brain
Iris
Muscle surrounding the pupil controlling how much light enters the eye
Pupil
Opening in the eye to allow light in
Lens
bends and focus light to create a sharp image
Retina
Forms the image
Diaphragm (camera)
Controls the amount of light entering the camera

Shutter (camera)
Opens the aperature to allow light reach the film

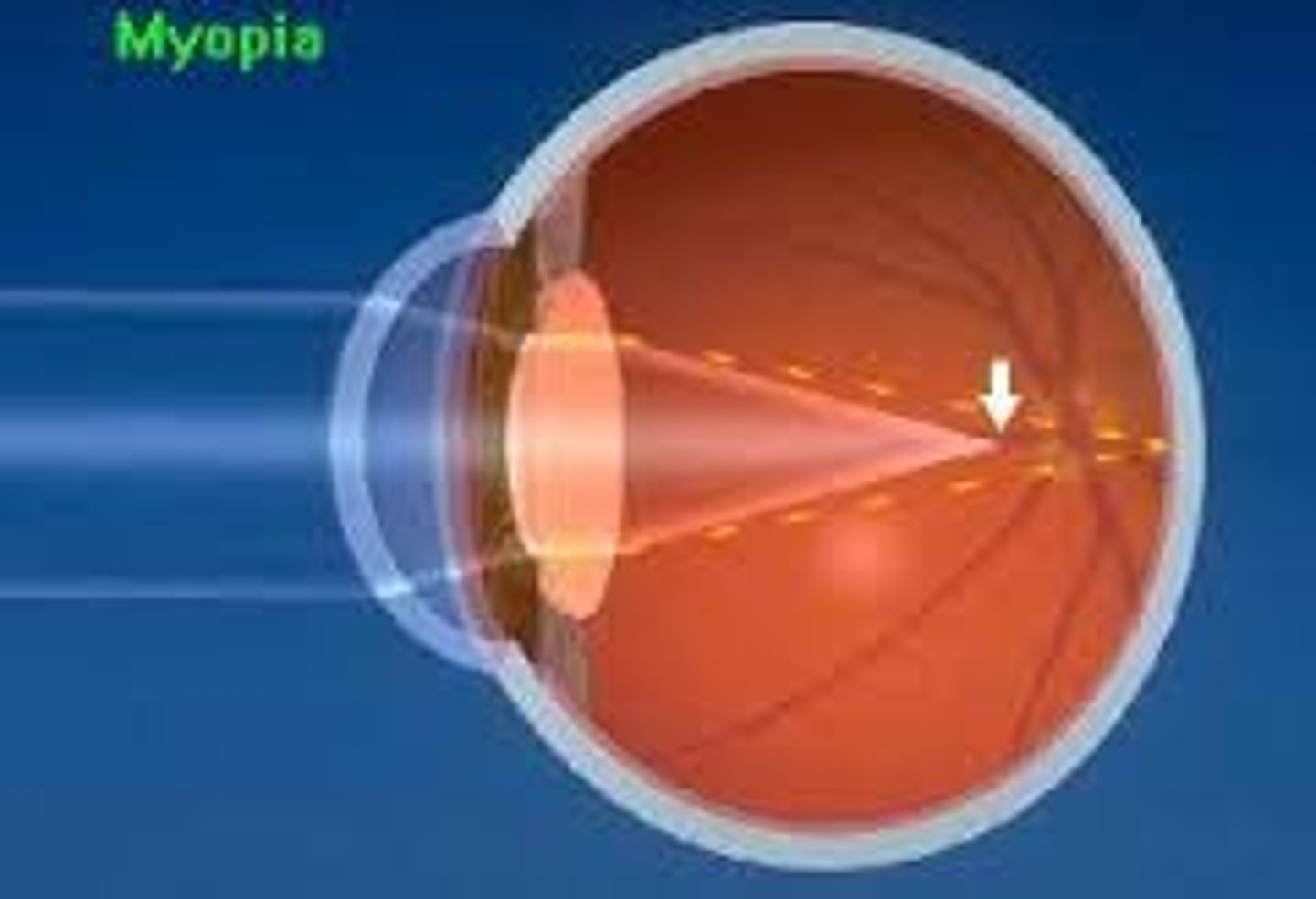
Myopia
Unable to see far objects clearly (Near-sightedness)
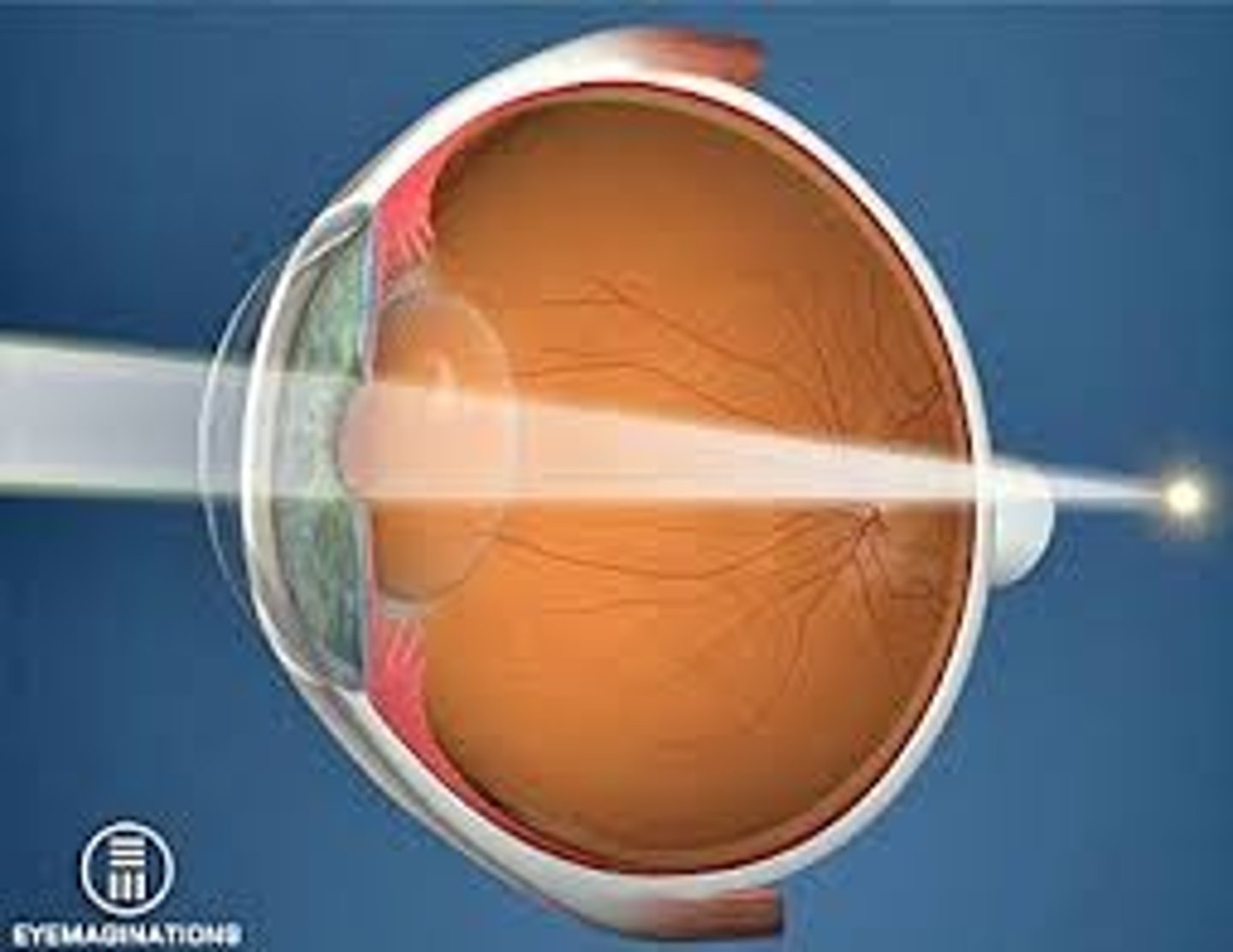
Hyperopia
Unable to see near objects clearly (Far-sightedness)
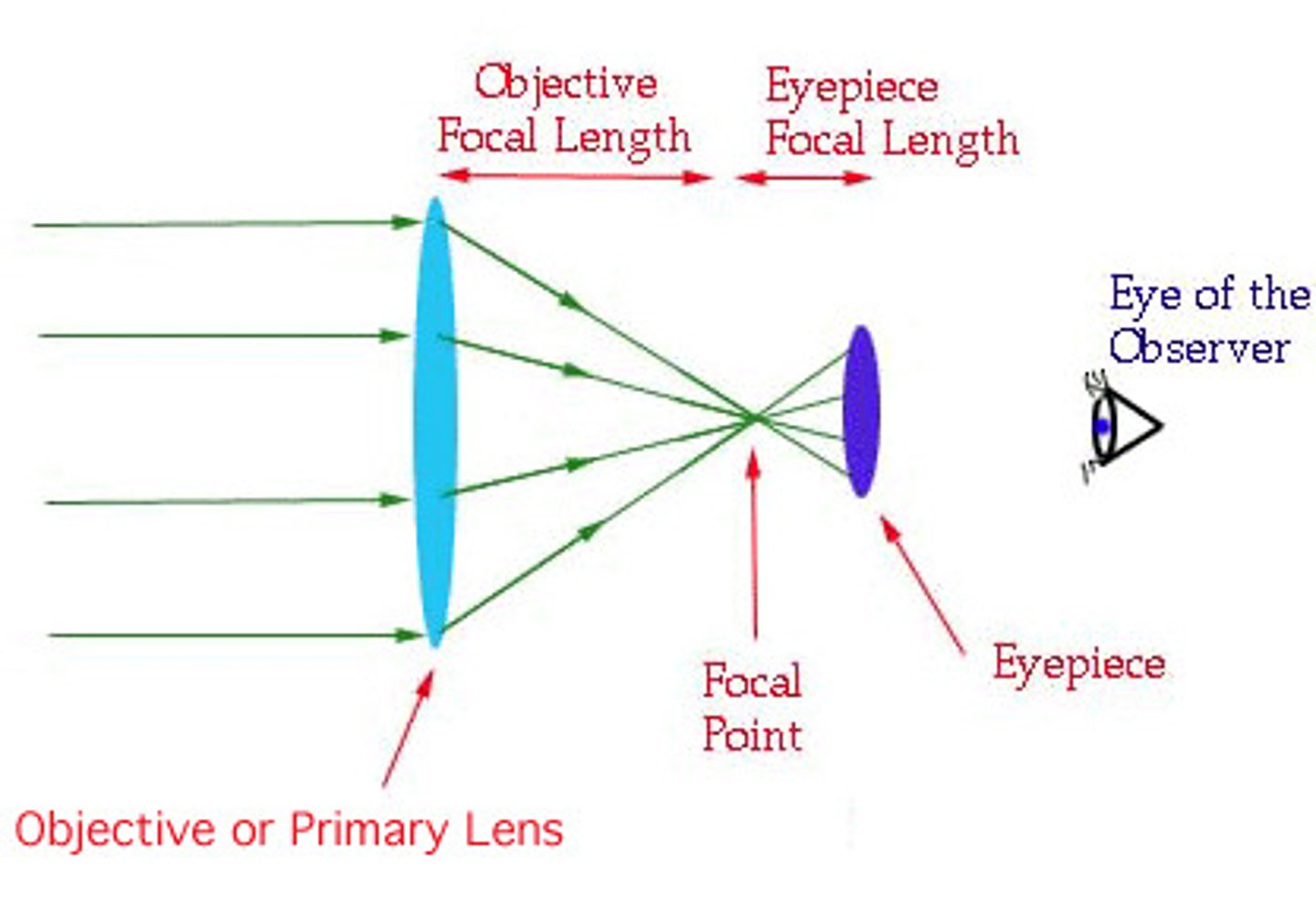
Eyepiece lens (Refracting Telescope)
Works like magnifying glass to enlarge objects
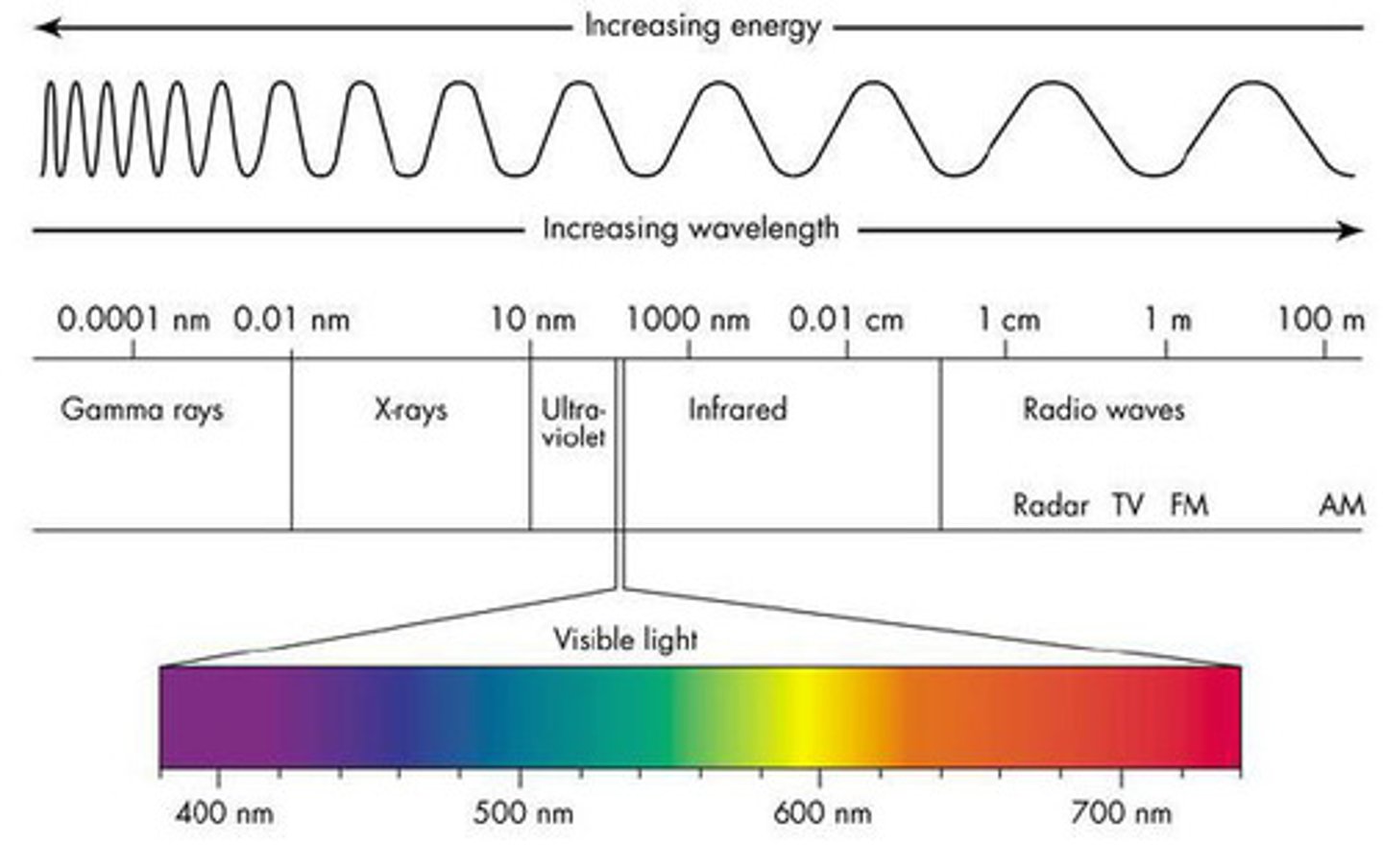
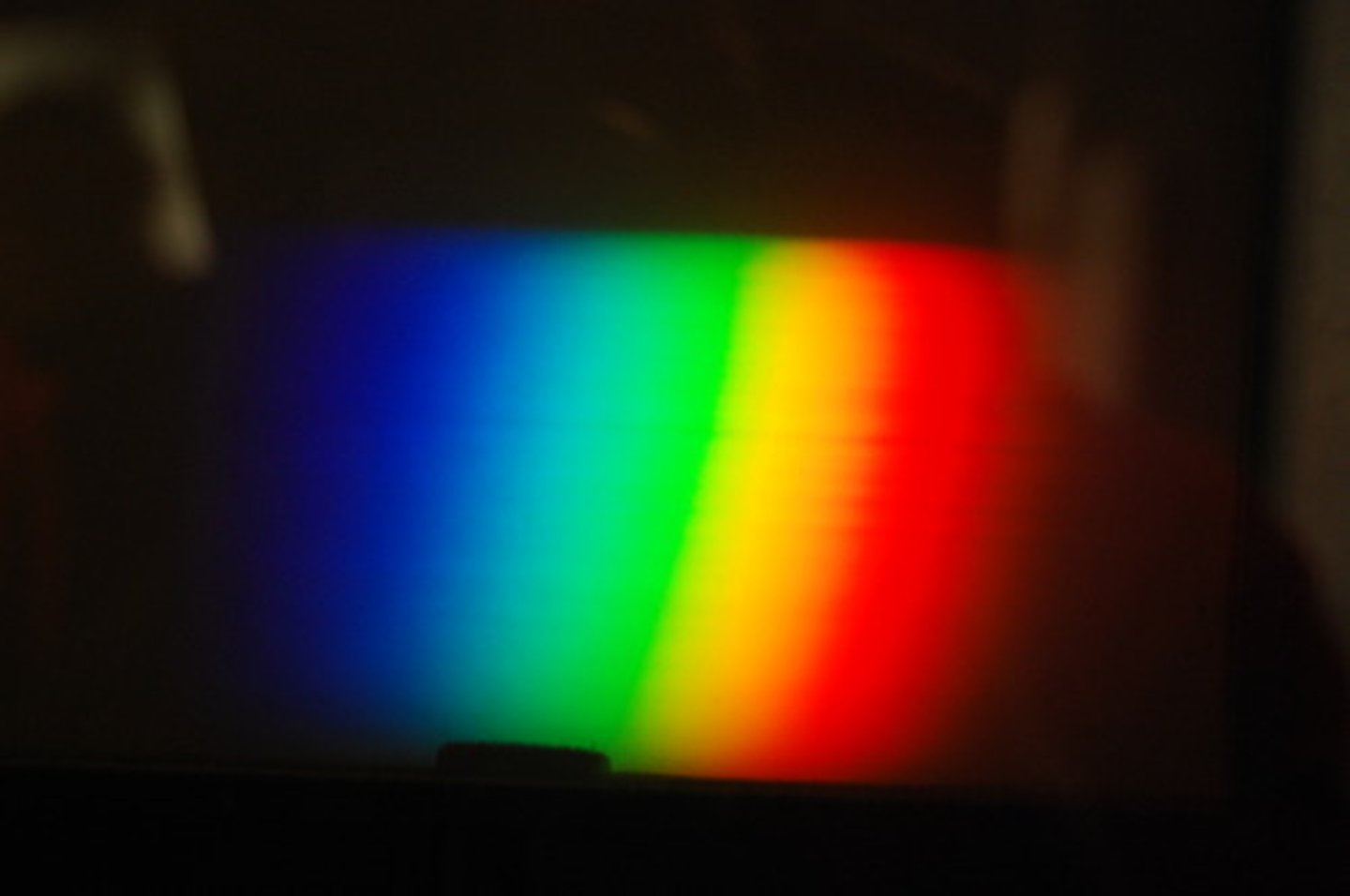
Spectrum
Series of coloured bands, produced when white light separates into its components of wavelengths

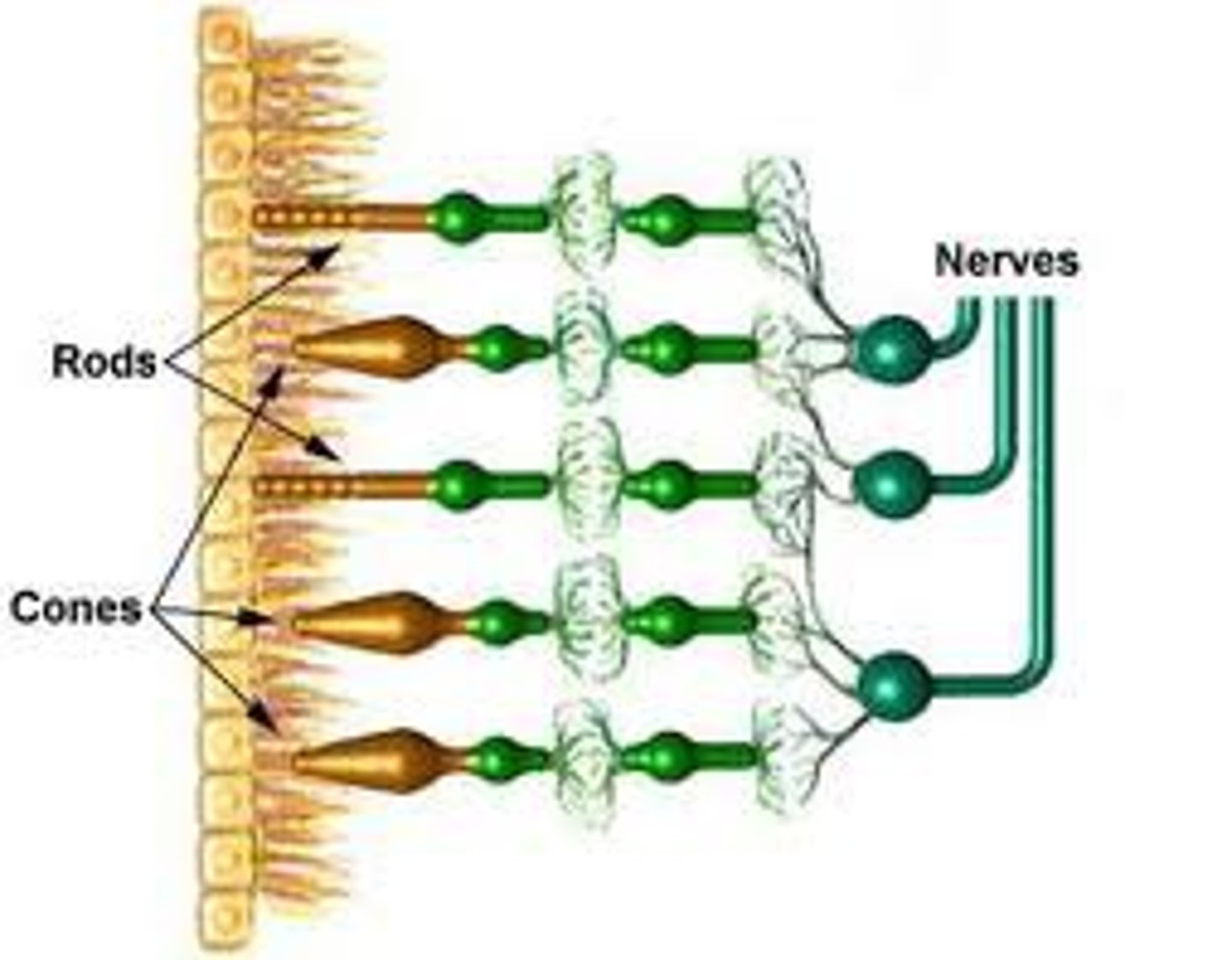
Rods
A cylinder like cell that detects the presence of light
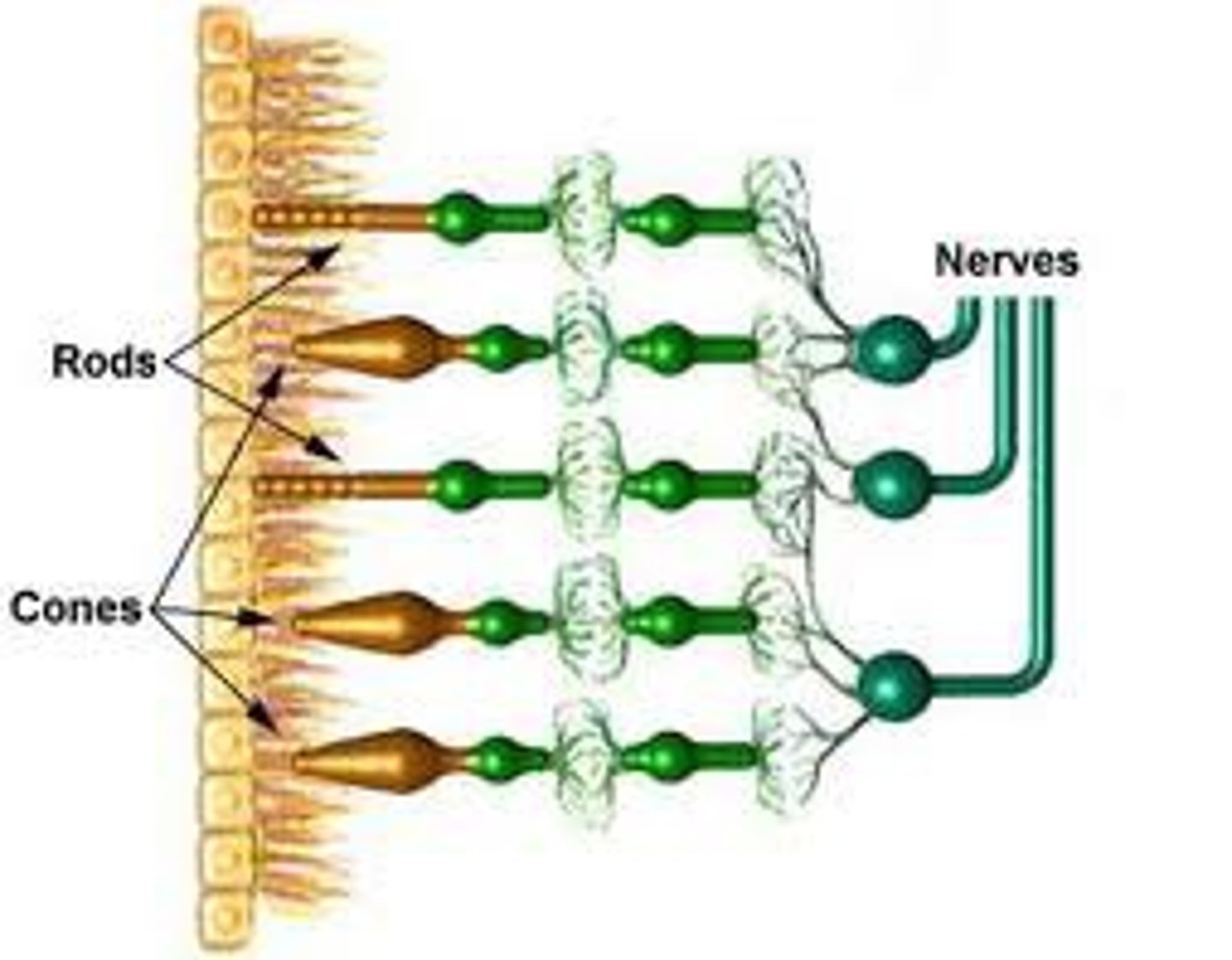
Cones
A cone shaped cell at the back of the eye that detects colour