CKD, ESRD, and RRT
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
100-120 mL/min/1.73 m2 (drops 1 ml per year after 30)
Normal GFR levels
Abnormal kidney function for 3+ months OR structure 3+ months with/without abnormal renal function
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is characterized by
Hematuria, proteinuria, PCDK, hydronephrosis
Examples of CKD with normal GFR (remember these gotta be present for 3+ months)
DM (then HTN)
What is the number 1 cause for CKD?
90+ (kidney damage with normal or high GFR)
GFR levels for stage 1 CKD
60-89 (Kidney damage with mildly decreased GFR)
GFR levels for stage 2 CKD
45-59 (mildly-moderately decreased GFR)
GFR levels for stage 3a CKD
30-44 (Moderately-severely decreased GFR)
GFR levels for stage 3b CKD
15-29 (severely decreased GFR)
GFR levels for stage 4 CKD
Under 15 (ESKD and its time to dialyze)
GFR levels for stage 5 CKD
glomerular disease, cystic diseases, vascular and systemic disease
Etiology for CKD
DM, HTN, CVD, HLD, smoking, salt intake, overweight, meds
Modifiable Risk factors for CKD
age, gender, race/ethnicity, FHx, chronic infections (HIV, Hep B/C), renal diseases
Non-modifiable Risk factors for CKD
loss of nephrons → hyperfiltration → fibrosis and sclerosis → lose functioning nephrons → toxins can’t be removed and urine cannot be made
Pathophysiology for CKD
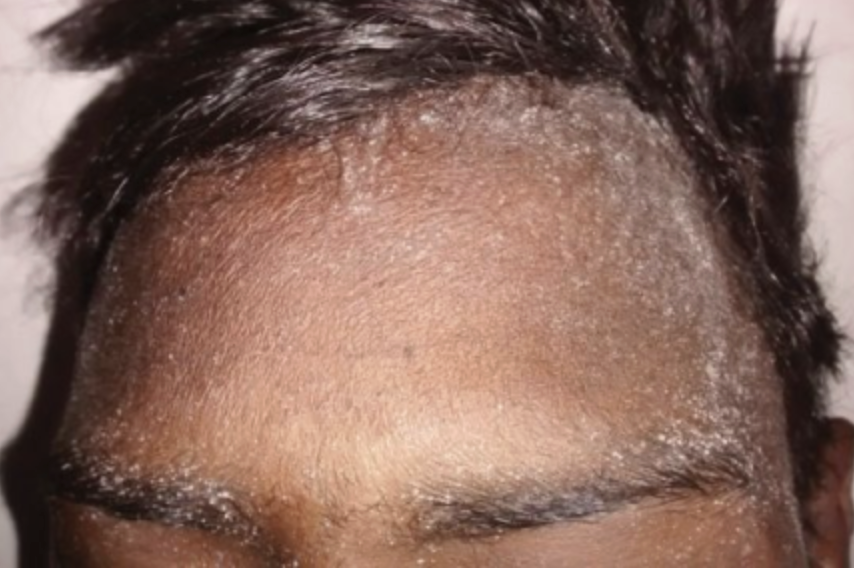
HTN (most common 🥇), edema 🥈, uremic symptoms (metallic taste, frost skin, etc) at stage 5
What are the most common physical exam findings in CKD
urine dipstick, microscopy, Albumin-Creat ratio (ACR), Protein-creat ratio (PCR), GFR, BUN/SCr, CMP, CBC (normal then anemia), ABGs (monitor for acidosis)
Lab work up for CKD
bilateral small kidneys (under 10 cm on U/S) → except in PCKD, DM, HIV, Amyloidosis, obstructive uropathy
Imaging findings for CKD
GFR!!
CKD staging is based on
GFR and albuminuria/proteinuria (the more stuff you kidneys are throwing out the worse it is)
CKD risk is based on
Anemia, HTN, CVD, DM, osteodystrophy, malnutrition, metabolic acidosis, dyslipidemia, hypothyroidism
Complications associated with CKD
Stage 3b - V
When are we referring to nephrology for CKD?
CVD (worse with proteinuria)
What is the #1 cause of death for CKD and ESKD patients
Low salt diet, diuretic for edema (thiazide, loop/K+ sparing if severe), ACEI/ARB/Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist
Gameplan for HTN associated with CKD
treat HTN aggressively, lifestyle changes
Gameplan for Coronary Artery Disease associated with CKD
loop diuretics, ACEI/ARB/Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, lifestyle
Gameplan for HF with CKD
low dose statins (we want it under 100 or 70 if they have proteinuria)
Gameplan for lipidemia with CKD (usually pops up in stage 3)
DOACs (eliquis, pradaxa, xarelto)
Gameplan for A.fib with CKD (there’s an increased risk with dialysis peeps)
prolactin elevated contributes to gynecomastia and sexual dysfunction, low T contributes to ED and osteoporosis
Mechanism behind male hypogonadism associated with CKD
Elevated LH → irregular cycles, amenorrhea, infertility (can carry baby to term if SCr is under 1.4 and CKD is not advanced)
Mechanism behind female hypogonadism associated with CKD
SGLT2s (NOT metformin especially if GFR is under 30)
What meds should be used in a diabetic patient with CKD?
Get a TFT, B12, retic count, ferritin, hepcidin → try oral iron → start erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (epoetin/darberpoetin when Hgb under 10, BP under 160/100, and everything else is ruled out)
Game plan for anemia associated with CKD
desmopressin, dialysis (uremia)
Game plan for coagulopathy associated with CKD (stage 4-5) - bleeding occurs due to platelet dysfunction or severe anemia
infection (get those vaccines)
What is the 2nd most common cause of death in patients with CKD?
We cannot get rid of phosphorus → bones release FGF-23; We cannot make vitamin D, so less calcium is absorbed, less calcium in the blood, more PTH is released
Describe the mechanism behind renal osteodystrophy (usually stage 3 to ESKD)
osteitis fibrosa cystica, adynamic bone disease, osteomalacia
Types of renal osteodystrophy
Osteitis fibrosa cystica
Which type of renal osteodystrophy is characterized by HIGH BONE TURNOVER with bones being broken too fast to release calcium (overactive parathyroid glands)
Adynamic bone disease
Which type of renal osteodystrophy is characterized by low bone turnover due to too little PTH, low osteoblast and clast activity so bones become brittle
Osteomalacia
Which type of renal osteodystrophy is characterized by soft bones due to the lack of bone mineralization (most commonly caused by vitamin D deficiency)
Phosphate binders (Calcium carbonate, acetate), Sevelamer, lanthanum, cinacalcet, aluminum hydroxide, vitamin D supplements (once phosphate is normal)
Treatment plan for renal osteodystrophy
Change medication dosing based on CrCl, low protein, salt and water restrictions, K and phosphorus restrictions, low cholesterol; exercise and weight loss, reduce EtOH, stop tobacco, Avoid NSAIDs/Contrast dyes; treat any anxiety and depression
Additional treatments for CKD
5-10 yrs (up to like 30 though)
What is the life expectancy on dialysis?
GFR under 10 (with or without uremic symptoms)
When should RRT be initiated
remove waste products and excess fluid, maintain electrolyte balance, regulate bp
What is the role of dialysis (usually done 3 days a week)?
Acid base issues, electrolyte problems, intoxications, fluid overload, uremic issues
What are the 5 signs that a patient need to be dialyzed in any CKD stage?
Hemodialysis
Which type of dialysis am I describing - a dialyzer is used to remove waste and extra fluid from the blood, and return the filtered blood back into the vascular system?
Subcutaneous arteriovenous fistula (AVF - most common and lowest complications), Polytetrafluoroethylene graft (PTFE - matures in 2 weeks, higher infection risk), Tunneled catheter (inserted into a large vein, high infection risk)
Types of Hemodialysis Vascular access
S. aureus
Most common infection associated with hemodialysis
Hypotension 🥇, disequilibrium, HA, febrile reaction, restlessness, tremor, fatigue, N/V, cramps, palpitations, dizziness, syncope, allergic reactions, clotting, bleedings
Complications of hemodialysis
Peritoneal dialysis
Which type of dialysis am I describing - the lining of your abdomen acts as a filter, dialysis fluid is put into the abdomen, waste products move into the solution (occurs at the capillary level), then the fluid is drained?
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (self-exchange 4-6x a day for 30-40 min), Continuous cycler (assisted peritoneal dialysis - machine does it while you sleep)
Types of peritoneal dialysis
Peritonitis (presents with fever, chills, abd pain, N/V/D, cloudy dialysate)
Complications of peritoneal dialysis
Staph A, E.Coli
Most common infectious orgs in peritoneal dialysis complications
Vanc (gram +), AMG (gram -), replace the catheter
Treatment plan for peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis
DM
What is the most common cause of a kidney transplant (makes up 25% in the US)
95% (1 yr - living donor), 89% (1 yr - cadaver), 80% (5 yr - living), 66% (5 yr - cadaver)
Prognosis for kidney transplant
Palliative care
For homies not a candidate of RRT, what are we doing?