ALCOHOLS
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
How do you name alcohols?
have the -ol ending
if there are other functional groups they could have the hydroxy- prefix
What is the shape of alcohols?
tetrahedral between the H-C-H bonds and the C-C-O bonds
bond angles are 109.5
bent between the H-O-C
bond anglea are 104.5
What’re the boiling points of alcohols?
they have a low volatility and high boiling points due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds between alcohol molecules
Why can smaller alcohols dissolve in water?
they can form hydrogen bonds to water molecules
What is a primary alcohol?
where only 1 carbon is attached to the carbon adjoining the oxygen
What is a secondary alcohol?
where 2 carbons are attached to the carbon adjoining the oxygen
What is a tertiary alcohol?
where 3 carbons are attached to the carbon adjoining the oxygen
What oxidising agent causes alcohols to oxidise?
potassium dichromate
What occurs in the partial oxidation of primary alcohols?
forms an aldehyde
reagent- potassium dichromate solution and dilute sulfuric acid
conditions - use a limited amount of dichromate, warm gently, distill out the aldehyde as it forms
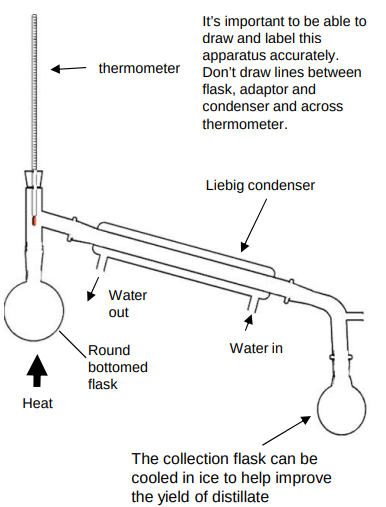
What is distillation used for?
separation technique
separates an organic product from its reacting mixture
only collect the distillate at the approximate boiliing point
Where should the bulb of the thermometer be during distillation?
at the T junction connecting to the condenser to measure the correct boiling point
Why does water go into the bottom of the condenser during distillation?
allows more efficient cooling and prevents back flow of water
Why are electric heaters often used rather than bunsen burners during distillation of organic chemicals?
organic chemicals are often highly flammable and could set on fire with a naked flame
Draw a diagram of distillation?
What occurs during the full oxidation of primary alcohols?
forms a carboxylic acid
reagent - potassium dichromate solution and dilute sulfuric acid
conditions - use an excess of dichromate, heat under reflux
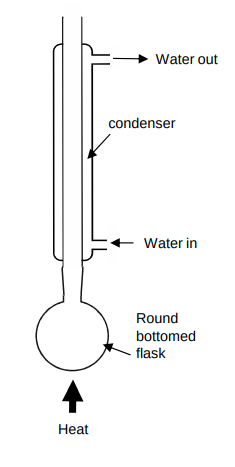
When is reflux used?
when heating organic reaction mixtures for long periods as the condenser prevents organic vapours from escaping by condensing them back to liquids
Why should you never seal the end of the condenser during reflux?
the build up of gas pressure could cause the apparatus to explode
Why are anti-bumping granules added to the flask in distillation and reflux?
prevents vigorous, uneven boiling by making small bubbles
Draw a diagram of a refluxer
What happens in the oxidation of secondary alcohols?
forms a ketone
reagent - potassium dichromate and dilute sulfuric acid
conditions - heat under reflux
Why can tertiary alcohols not be oxidised?
there is no hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon with the -OH group
What is tollens reagent?
formed by mixing aqueous ammonia and silver nitrate
What happens when you use tollens reagent to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones?
heat gently
aldehydes are oxidised by tollens reagent so a silver mirror forms coating on the inside of the test tube
What happens when you use fehlings solution to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones?
heat gently
aldehydes are oxidised by fehlings solution into carboxylic acids and the blue ions turn to a red precipitate
How can you test for the presence of a carboxylic acid?
add sodium carbonate which will fizz and produce carbon dioxide
What occurs when an alcohol is dehydrated?
an alkene forms
reagents - concentrated sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid
conditions - warm, under reflux
acid catalysed elimintation
What is the mechanism for an acid catalysed elimation?
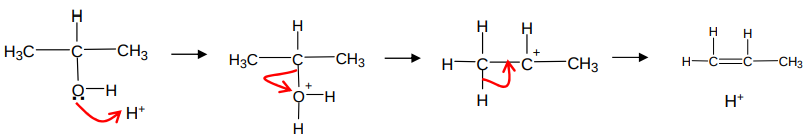
Where does the H+ come from in the acid catalysed elimination mechanism?
from the conc H2SO4 or conc H3PO4
What’re the 2 ways to form ethanol?
fermentation
from ethene
What occurs in fermentation?
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
conditions: yeast, no air, warm (30-40)
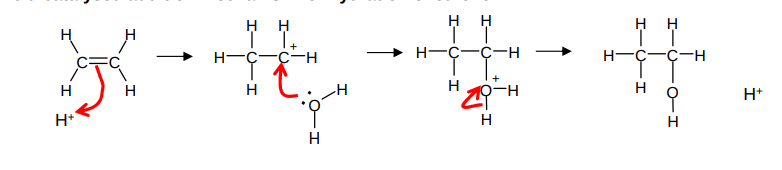
What occurs when using ethene to get ethanol?
ethene from cracking of fractions from distilled crude oil
hydration/ addition
conditions: high temp (300), high pressure (70atm) strong acid catalyst
What is the optimum temperature for fermentation?
38 degrees
lower temperatures means the reaction is too slow
higher temperatures means the yeast dies and enzymes denature
What’re advantages to using fermentation?
sugar is a renewable resource
production uses low level technology
cheap equipment
What’re advantages to using ethene to make ethanol?
faster reaction
purer product
continuous process
What’re disadvantages to fermentation?
batch process which is slow and gives high production costs
ethanol needs to be purified by fractional distillation
depletes land used for growing food crops
What’re disadvantages to using ethene to make ethanol?
high technology equipment needed
ethene is non-renewable
high energy costs for pumping to produce high pressures
What is the mechanism for the acid catalysed addition mechanism for the hydration of ethene?
What is biofuel?
a fuel produced from plants
What does carbon neutral mean?
an activity which has no net annual carbon emissions to the atmosphere