CS166 Network Protocols
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
studying for finalll :,)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
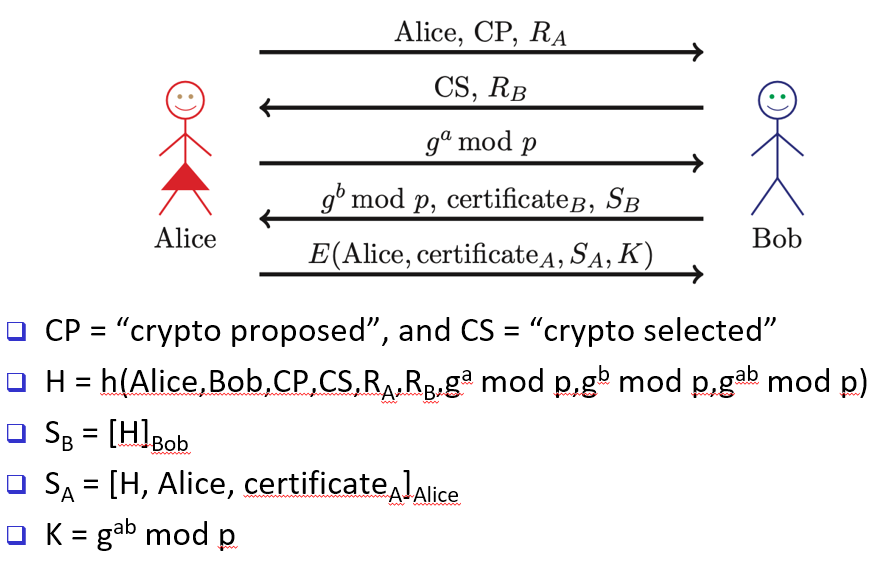
Secure Shell (SSH)
creates a secure tunnel for private info to be sent across the network
can be based on public key, digital certificate, passwords, etc.
perfect forward secrecy
protected against MiM attacks by encrypting g^(ab)modp parts
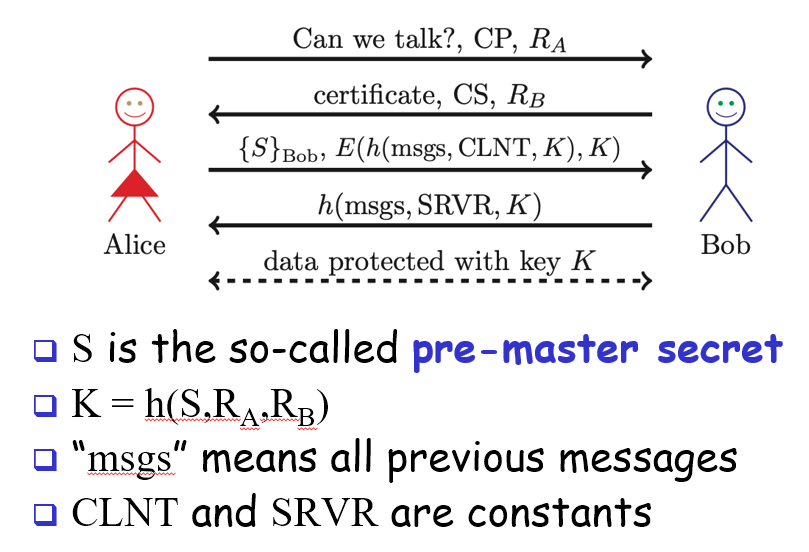
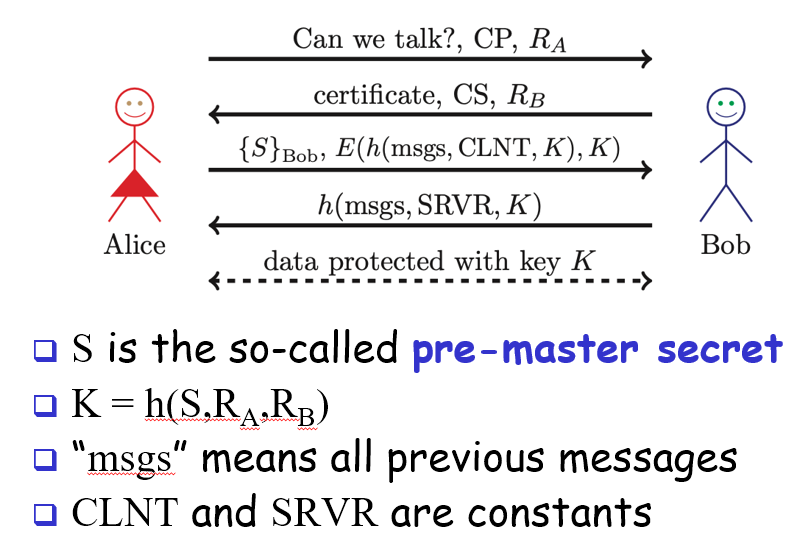
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
socket layer (part of application layer)
majority of internet transactions use this
does not need mutual authentication because clients don’t need authentication
6 keys derived from K = h(S, Ra, Rb)
2 encryption keys
2 integrity keys
2 IVs
^each for client and server
Why different keys in different directions? To prevent reflection attacks
MiM attack works if Trudy sends her own cert or a fake cert and Alice ignores the warning and doesn’t verify the cert
has open session protocol (to establish session key) and then subsequent connections protocol (cheaper)
IPSec
network layer
the overengineered protocol…
2 parts: IKE and ESP/AH
Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
establishes mutual authentication and session key
has 2 phases:
Phase 1 (comparable to SSL session)
Phase 2 (comparable to SSL connection)
IKE Phase 1
establishes mutual authentication and session key
has 4 key options, each with main mode and agressive mode
public key encryption (original)
public key encryption (improved)
public key signature
symmetric key
all key options have perfect forward secrecy
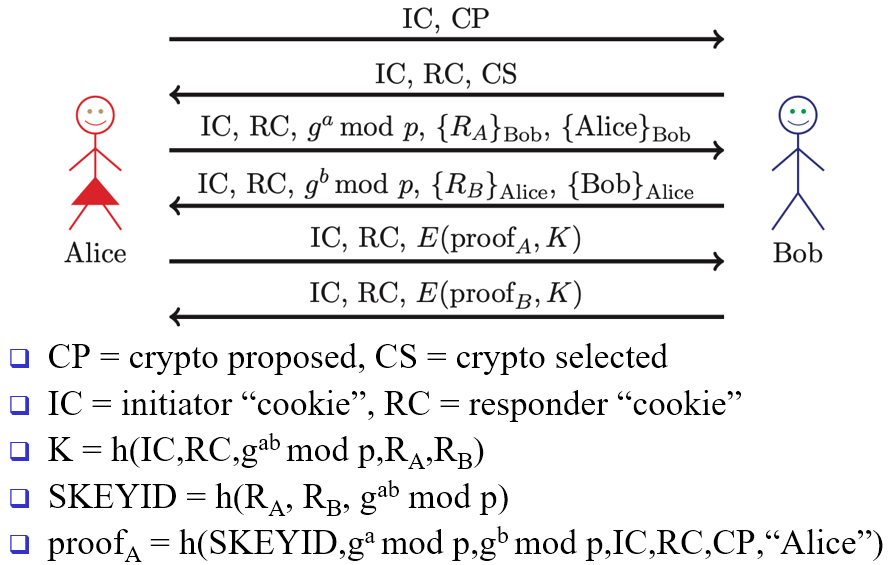
IKE Phase 1 public key encryption main mode
IKE Phase 1 public key encryption aggressive mode
PLAUSIBLE DENIABILITY: Anyone can deny a conversation ever took place, because Trudy can use other people’s public keys to impersonate a conversation between 2 people (using her own a, b, Ra, Rb)
has anonymity despite being aggressive
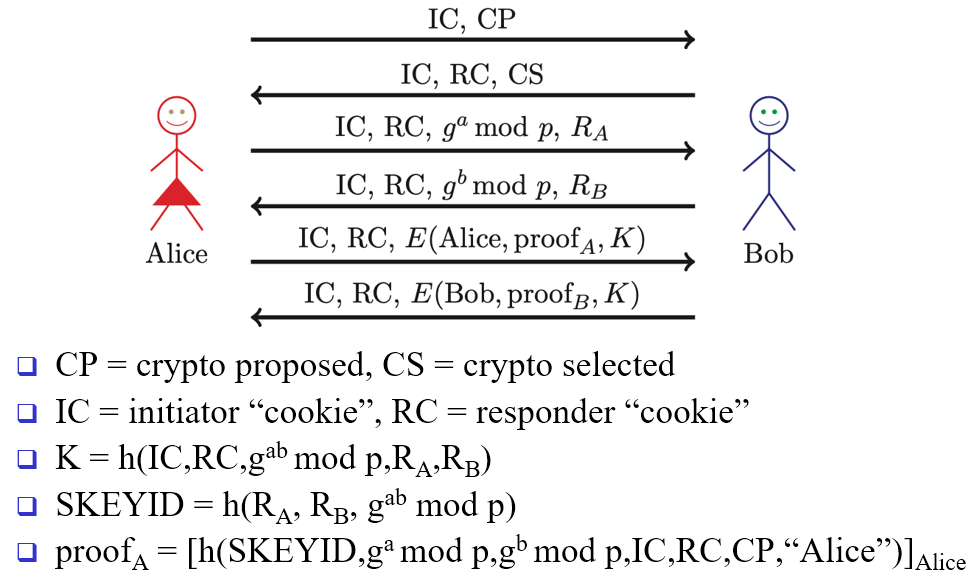
IKE Phase 1 digital signature main mode

IKE Phase 1 digital signature aggressive mode
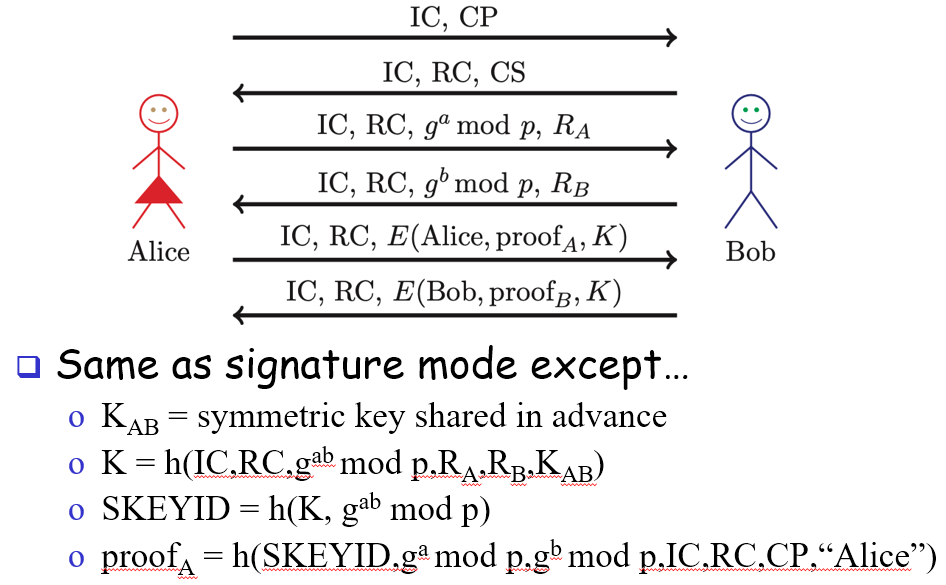
IKE Phase 1 symmetric key main mode
CATCH-22: Bob must know to use K_ab to decrypt Alice’s 5th message (which contains Alice’s encrypted identity), but Bob can have shared keys with multiple people and thus not know which to use.
Solution: Alice’s IP address used as ID
However, this does not protect anonymity because it would need a static IP address to work
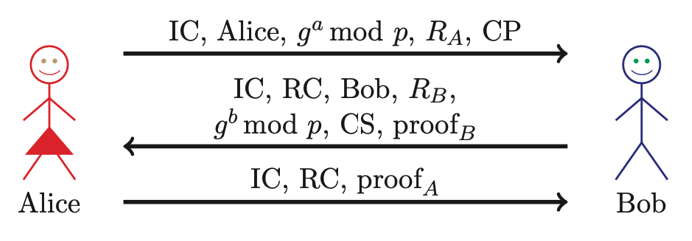
IKE Phase 1 symmetric key aggressive mode
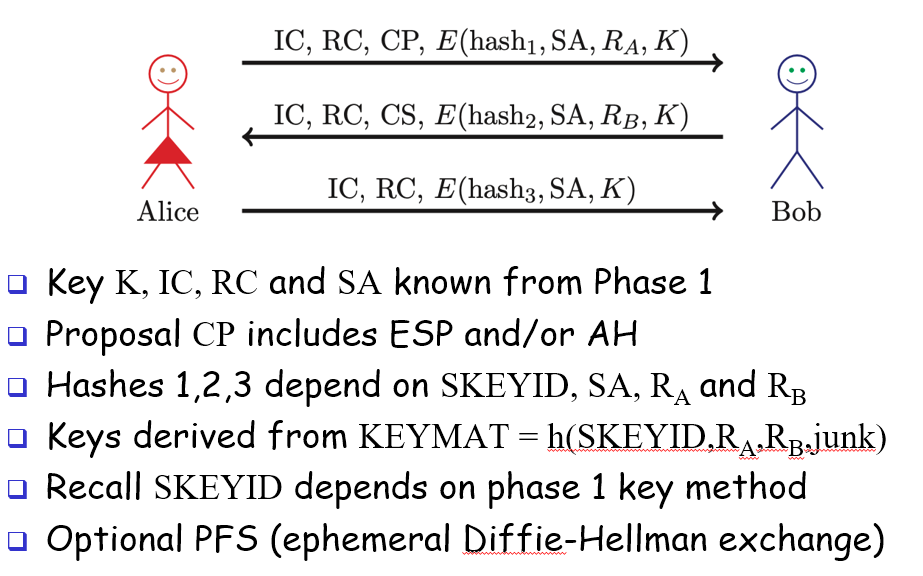
IKE Phase 2
cheaper than Phase 1, assumes session key is already established
IPSec Transport Mode
designed for host-to-host
original header remains, attacker can see who’s talking
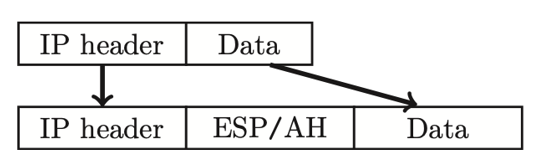
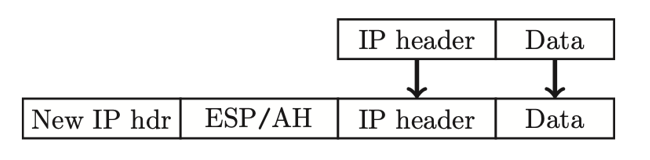
IPSec Tunnel Mode
designed for firewall-to-firewall
new IP header from firewall to firewall, attacker cannot see who’s talking
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
provides confidentiality and integrity for everything beyond IP header
exception is when you use ESP with NULL encryption
Authentication Header (AH)
provides integrity only for everything beyond IP header and some fields of header
Kerberos
authentication protocol that uses symmetric keys and timestamps
statelessness and efficiency are top priorities
uses Trusted Third Party (TTP) caled Key Distribution Center (KDC) to make N keys for N users (so, security depends on TTP)
master key K_kdc
Uses tickets system, with Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) to obtain tickets
TGT contains session key, user’s ID, and expiration date
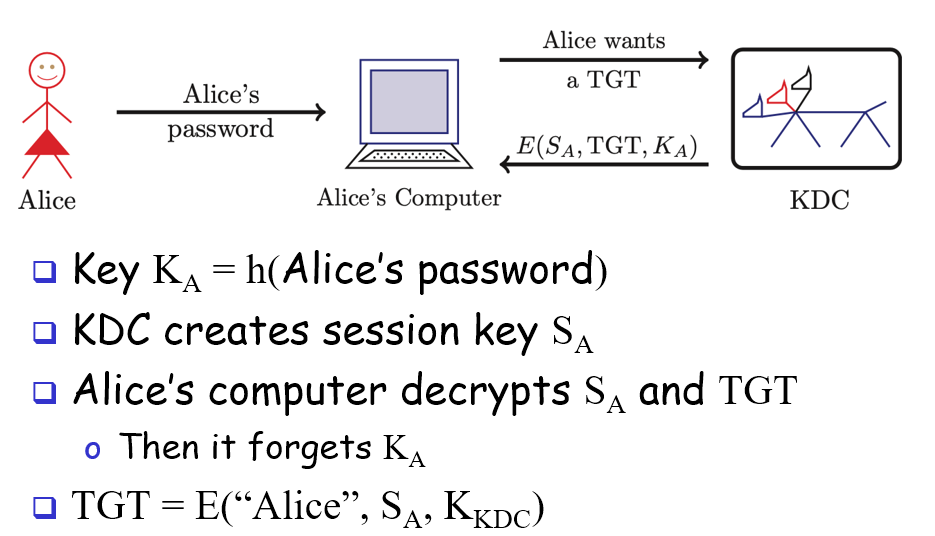
Kerberized Login
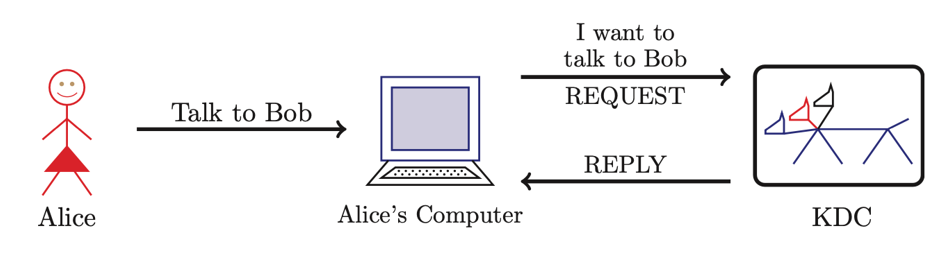
(Kerberos) Alice requests “Ticket to Bob”
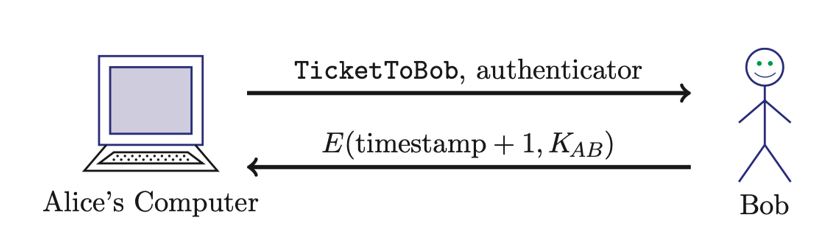
(Kerberos) Alice uses “Ticket to Bob”
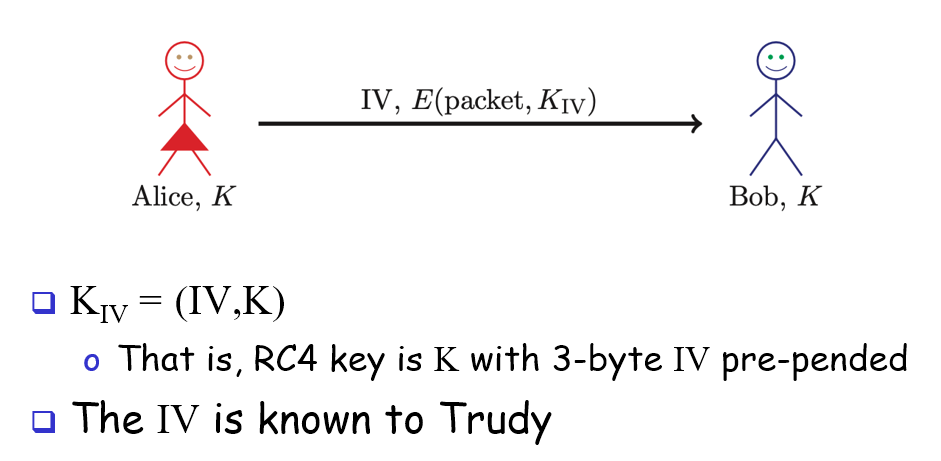
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
goal is to make wireless LAN as secure as wired LAN (not that secure)
uses one symmetrical key shared with all users and access port
uses RC4 for confidentiality
uses CRC for “integrity” —> CRC is for error detection tho…
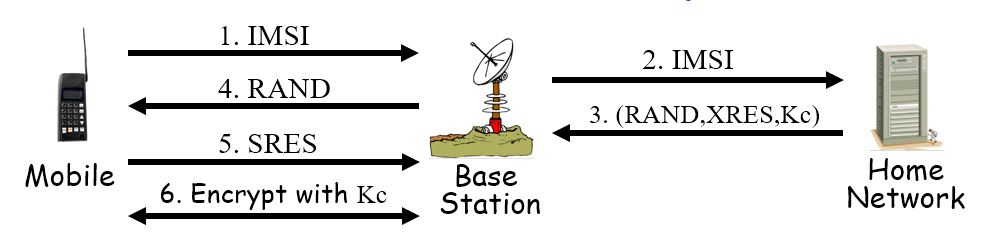
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
goal is to make cellphones as secure as landlines (not that secure), and to prevent cloning
authentication is not mutual because base station is not authenticated
Ki is ONLY known to mobile and home network and never leaves those spots (if Trudy gets it, she can clone!)