3ry Hemostasis & Coag Regulators
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
which steps require Ca2+ and phospholipid (PL) in coag cascade?
11, 9, 10, 2 (XI, IX, X, II)
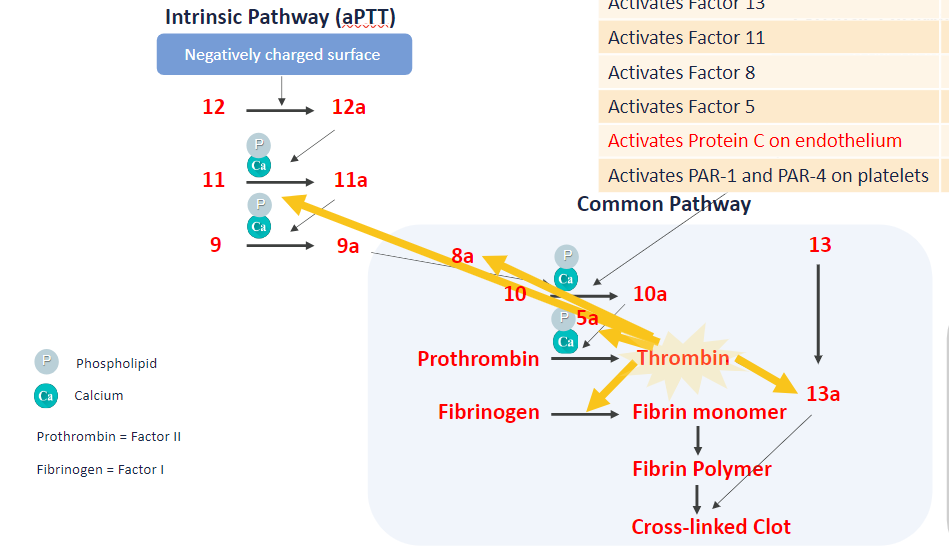
how is thrombin the MVP?
forms fibrin (Ia)
activates factor 13, 11, 8, 5 (XIII, XI, VIII, V)
activates protein C on endothelium → inhibits coag
activates PAR-1 & PAR-4 on plts → plt activation
IIa (thrombin) acts on which coag cascade factors?
VIII
V
I
XIII
XI
(1, 5, 8, 11, 13)
inhibitors of coag
protein C & S
thrombin activates thrombomodulin (on endothelial cells) → PC becomes APC (activated protein C) → APC + PS form complex inhibits factor 8 & 5
antithrombin
inhibits IIa and Xa
AT is enhanced by heparin
TFPI (tissue factor pw inhibitor)
inhibits TF:VII complex (extrinsic pw) & factor X (start of common pw)
fibrinolysis: how to remove clot?
tPA (tissue plasminogen activator) + plasminogen → plasmin degrades fibrin polymers’ covalent bonds
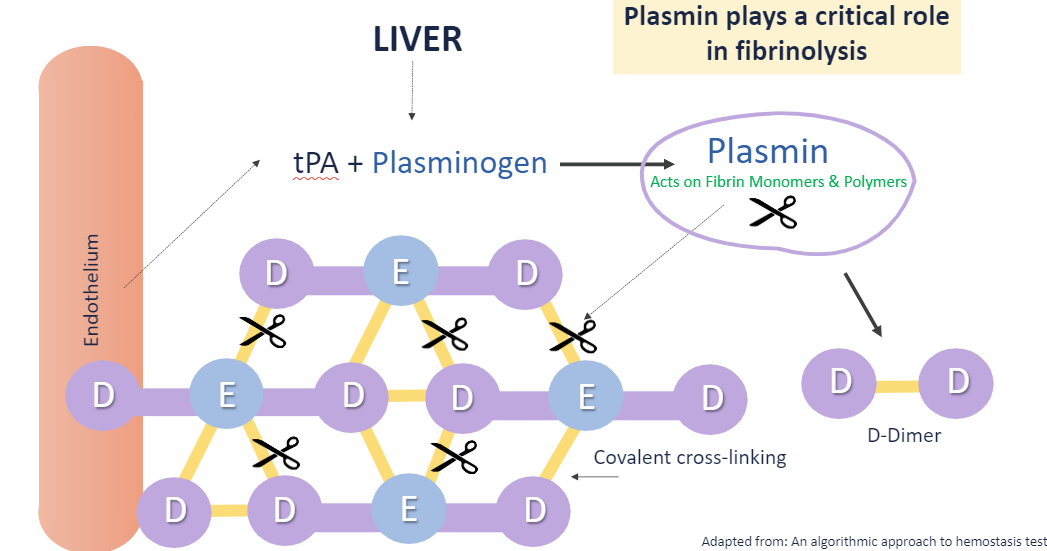
stable fibrin clots require ___
covalent crosslinking by factor XIIIa which crosslinks at outer D domains and central E domains
ie: D—E
D-dimer vs FDP (fibrinolysis degradation products)
D-dimer
latex immunoassay to assess fibrin degradation
FDP assay: also latex immunoassay
all D-dimers are FDPs, but not all FDPs are D-dimers
DIC panel results would look like:
what score is required for dx?
prolonged PT, aPTT
dec fibrinogen
dec plt
inc D-dimer and FDPs (inc bc in DIC both xs coag and fibrinolysis are occuring)
each of the above contribute to DIC score
DIC score >=5 = compatible w overt DIC
Protein C system
what is required of PS?
thrombin activates thrombomodulin (on endothelial cells) → PC becomes APC (activated protein C) → APC + PS form complex inhibits factor 8 & 5
free PS is required for PC to work!
lab measures free PS first
PS in dynamic equilibrium w protein C4b binding protein
PS+C4b binding protein = inactive PS → cannot bind to APC
antithrombin (ATIII) function?
how does heparin affect it?
inhibits IIa (thrombin) and Xa (Stuart Prower factor)
heparin binds ATIII via pentasaccharide sequence → accelerates inhibition of IIa & Xa
AT is enhanced by heparin → why thrombin time (TT) is sensitive to heparin → TT prolonged
thrombophilia: venous vs arterial
tendency towards recurrent thromboembolism (pathogenic blood clots)
venous: deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolus (PE)
arterial: myocardial infarction (MI), cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
factors that predispose pts to thrombosis
factor gene mutations
factor V Leiden
prothrombin variatn 20210A
defic of naturally found inhibitor
ATIII
protein C or S
presence of acquired inhibitor (anti-PL Ab)
Lupus anticoagulant
anti-cardiolipin Ab
Factor V Leiden leads to _?
how is it tested?
abnormal factor V → resistant to APC inhibition
(m/c in Caucasians, Netherlands hence name)
tests:
function assay (APC resistance)
PCR for mutation
Prothrombin Variant 20210A leads to __?
inc levels (2-3X) prothrombin (II) in plasma → inc risk of thrombosis
1-2% in Caucasians
tested via PCR
ATIII deficiency
how is it acquired?
can lead to?
what test is used?
can be acquired or inherited (auto dominant)
acquired: DIC, acute thrombosis, liver dz, nephrotic syndrome, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), asparaginase therapy, heparin therapy
→ thromboembolism, reduced efficacy of heparin
tests: chromogenic assay
measures ability to inhibit factor IIa & Xa
more color → less ATIII, more factor Xa cleaving chromogenic substrate
protein C defic
homo vs heterozygous risks?
test?
homozygous → severe thrombosis w necrosis at birth (purpura fulminans)
heterozygous → inc risk of thrombosis
test: chromogenic assay
protein S defic
inc risk of __
how to test?
inc risk of thrombosis
in severe cases → infants get purpura fulminans soon after birth
test: free protein S assay
Lupus anticoagulant (LA)
what is it? why is it a misnomer?
what dz states are assoc’d w/it?
LA = antiphospholipid → inc thrombosis
misnomer bc it’s Ab interfere w coag in vitro (prolong PTT), but activates coag in vivo (→ thrombosis)
found in pt w/ or w/o SLE
assoc’d w APS
APS: antiphospholipid syndrome
autoimmune disorder char by xs blood clot formation, organ failure, pregnancy complications 2ry to anti-PL Ab
SLE: systemic lupus erythrematosus
systemic autoimmune dz which may accompany APS
what steps does LA interfere w/in the coag cascade?
11, 9, 10, 2 (XI, IX, X, II)
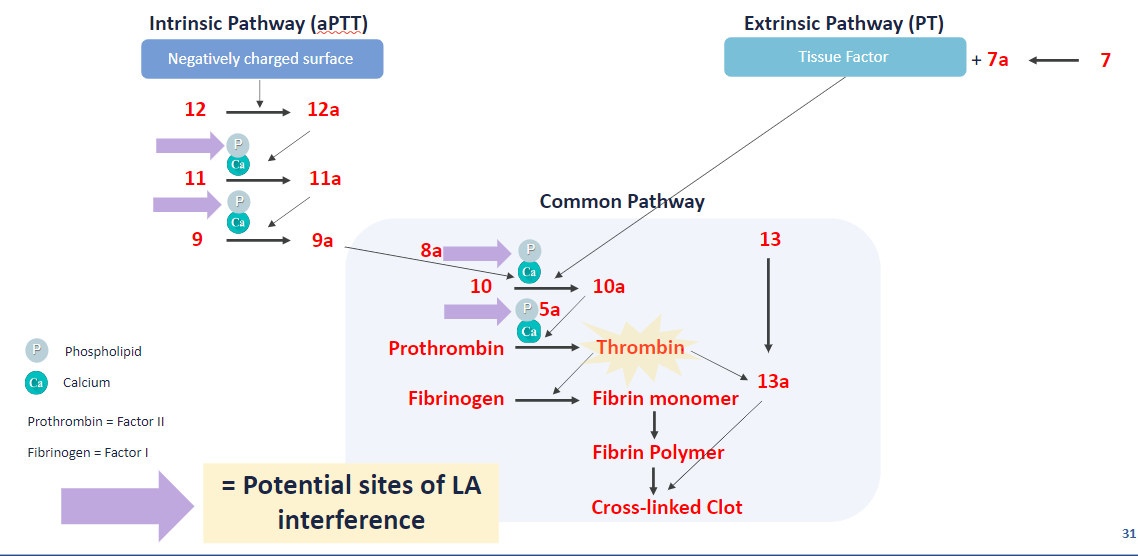
how to screen for Lupus anticoagulant?
Lupus Anticoagulant
Beta-2 GP1 Ab (IgG/IgM > IgA)
Cardiolipin Ab (IgG/IgM > IgA)
must be medium or high titer
how to confirm/dx Lupus anticoag? 3 tests:
what do they have in common?
dilute russell viper venom time (DRVVT)
silica clotting time (SCT)
Lupus anticoagulant sensitive aPTT method (hexagonal phase)
all have a screen and confirmation, where the confirmation has added PL to neutralize LA if present → expect corrected

dilute russell viper venom time (DRVVT)
what is the function of the venom?
how is the screen performed?
how is the confirmation done?
LA will prolong clot time
venom + Ca2+ → activates factor X
→ triggers coag cascade, thus don’t need upstream factors
not affected by contact factor anomalies or factor VIII & IX defic or inhibitors
screen: DRVVT performed at low conc of PL
if LA present, clot time prolonged
confirm: DRVVT performed at high conc of PL → neutralize the LA present in plasma (trying to bind all free LA’s)
clot time is shorter than screen bc neutralized all free LA → should get normal clot time
positive result = % correction above cutoff
silica clotting time (SCT)
what test is this identical to?
how is the screen done?
confirmation?
LA will prolong clot time
identical to PTT assay
silica = activator of factor XII (intrinsic pw)
more sensitive to effects of LA vs regular PTT rgts
screen: use low conc of PL
if LA, clot time prolonged
confirm: use high conc of PL → neutralize LA in plasma
clot time normalized, shorter than screen
positive result: ratio above cutoff
Lupus sensitive-PTT w hexagonal phase
what test is this based on?
screen?
confirmation?
LA will prolong clot time
aPTT based, PL-dependent coag assay (ie activates intrinsic pw)
screen: run aPTT-based, PL-dep test on plasma
confirm: adding rgt that contains xs PL (hexagonal phase PL), w/1:1 mix correcting for factor defic
pos result: time difference b/t screen & confirm (usually >8 sec)
why is glass avoided for coag testing?
glass is neg charged → can activate contact pw (intrinsic pw) → inaccurate results
to avoid false pos/neg for pt care, what has been recommended for dx’ing APS?
incorporate mixing studies into screen/confirm steps
beware anticoag medication: heparin, DOACs, warfarin
at least 2 LA assays (eg DRVVT + SCT)
anti-cardiolipin & beta2 GPI IgM alone → can no longer dx
UCI thrombophilia panel testing
protein C activity
free protein S Ag
antithrombin III (ATIII)
Lupus anticoagulant assays
DRVVT
SCT
PTT-LA/hexagonal phase = sendout
anti-B2 GP and anti-cardiolipin Ab
factor V Leiden (molecular)
prothrombin 20210A (molecular)
caveats of thrombophilia testing
most adults will test neg or mildly dec
acquired causes > > inherited causes
following acute thrombosis, PC/PS and ATIII levels may dec
1 lab tests is not enough to dx defic or thrombophilia → must RPT testing at least 12 weeks