SciRev. X102 Exam 3 wk. 8 Netwon exam with 100% correct answers
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Newton basics
-the leading mathematician of his age
-worked on mathematics, natural philosophy, mechanics, optics, alchemy, chronology, and theology
-studied in Grantham and then at Trinity College
-in 1665 Cambridge university closed bc of the plague and newton returned home where he later that winter DISCOVERED CALCULUS
The Trinity
-The truth that God, although one, is three Divine Persons: the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit.
-Newton disagree and thought it was unsupportable
-he would have refused to take the oath but the terms of the Lucasian chair exempted him
-was ordained as a priest at the college
-Newton believed in the one God
-newton recognized christ as a mediator btw God and man
-considered jesus an intermediator btw God and man who is subject to his creator (aka, Jesus and man respond to God)
-Gods messengers have intermediate roles like all creatures
Newtonian Calculus
-based on the notion that the dervicative and the integral are inverse operations
-earlier versions of several techniques of integration and differentiation existed but their inverse relation had not been fully appreicated
-adopted the "dot notation"
-also mastered infinite series and differential geometry
dot notation
a dot placed over a function's name (x) to denot the derivative of that function
What resulted in Newton being elected to the Royal Society
-invention of the reflecting telescope (using a mirror)
-relied on his discoveries of refraction and the nature of life
-later wrote a book called the OPTICKS
newton's optical discoveries
a. noticed that the light refracted by a prism formed an oblong rather than a circular spot
b. the prism refracts each color by a specific fixed angle
c. white light consists of a combination of rays w/ all the colors of the spectrum
d. while a monochromatic light ray is bent going thru a prism, its color is not changed
e. a prism or lens can also recompose white light from a multicolored collection of ray
a. noticed that the light refracted by a prism formed an oblong rather than a circular spot
-by using a larger or smaller hole in the window shut he made the circular images larger or smaller at pleasure
-the amount of light could be increased by using a narrow oblong hole rather than a circular one, keeping the ends of the spectrum image sharp
-lead him to the discovery of the other conconclusions
b. prism refracts each color by a specific fixed angle
-separation of colors is a secondary effect ofthe prism
-unerlying process is the separation of 'rays of different refrangibility.'
-light consists of rays differently refrangible
-dependent on the color and nature of the glass
-phenomenon of colors in refracted light is caused by the refrangibility of rays already present in the white beam NOT by the modification coming from the glass it passes through
c. White light consists of a combination of rays w/ all the colors of the spectrum
-a prism decomposes white light into its components
-was shown by the adding of the long, flat prism and altering the angle of a screen
-when altering the angle, the colored beams strike the screen at sufficiently separated places for a spectrum to be seen
d. While monochramatic light ray is bent going through a prism, its color is not changed
-once the colors are properly separated they were unaffected by any of his manipulations
-newton iluminataed an object w/ monochramatic light from the object to the eye thru the prism and no differences in color was shown
e. a prism or lens can also recompose white light from a multicolored collection of rays
-a prism decomposes white light into colored rays while another recomposes it from those rays
newton's experiment shows:
1. a prism decomposes white light into colored rays, while another decomposes it from those rays
2. recombining a portion of colored rays does not give white light
3. a colored ray is bent by a second prism but its color does not change
newton and gravity
-suspected that gravity on the earth's surface and the force keeping the moon in its orbit were the same
-mutual attraction of particles NOT a pull towards the center of the earth
-idea came from observing a falling apple
-started working on orbital motion after Halley's visit who posed a question
Halley's question
which force is required to keep a planet in its elliptical orbit?
answer: a force inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the focus of the ellipse, occupied by the sun
Whose finding's did Newton draw from?
Kepler; law of gravitation fit w/ kepler's laws
Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy
-principia
-3 books
-answered Halley's question
-newton
book 1 (principia)
-motion under central forces
-says nothing about universal gravitation
-applies the law of motion to point masses orbiting attracting center (centripetal forces)
-states the three laws of motion
-idealized problem of point masses moving w/out friction
centripetal force
-force that seeks the center
-in contrast to Hyugen's centrifugal force (outward motion)
book 2 (principia)
-motion in a resisting medium
-demolishes the cartesian system
-considered bodies moving through resisting fluids and the movement of such fluids themselves
-turned to the examination of Descartes vortices
-demonstrated that a vortices can never yield a system of planets moving accroding to Kepler's three laws
-proved a vortex can't be self-sustaining
book 3 (principia)
-the world system
-application of his dysnamics to the system of the world
-the law of universal gravitation depends on the correlation of the centripetal acceleration of the moon w/ the acceleration of gravity on the surface of the earth
-concluded that the inverse square forces in operation must be identical in nature (apple being similar to satellites in orbit)
newton's laws
1. law of inertia
2. F = ma
3. the law of action and reaction
law of inertia
-similar to Descartes' first two laws
-Descartes 1st law: each thing always remains in the same state and continues to move
-2nd: all movement of itself, along straight lines
-object in motion stays in motion
F = ma
- force = mass x acceleration
-introduce the concept of force into rational mechanics
-when an object is close to earth's surface, like an apple in a tree, gravity makes it accelerate
-mass is mass of the earth (the bigger the object, the greater pull)
law of action and reaction
-was original w/ Newton
-can be seen as an extension, in terms of dynamics, of the changes of motion in impact (which Hyugens had demonstrated earlier)
-an action must have an equal and opposite reaction
The inverse-square law applies to all point-like particles of matter: what happens if you have a large mass like the Earth?
-if the large mass is exactly spherical, the inverse-square law holds on its surface
-however, the earth isn't exactly spherical and this creates complications w/ its interaction w/ the moon
-a sphere attracts as though its entire mass were concentrated at its central point
what is the earth's shape?
-the earth is squashed at the poles and has a bulge at the equator
-cited pendulum measurements as support, given they were slower at the equator
-points on the equator are farther from the center than points in France and therefore force of gravitation was weaker
-also due to how fast the earth is moving
How can one explain tides in relation to universal gravity? Are they related to the moon?
-was a huge theoretical and empirical work involving extended records over many different locations on the Earth's surface
-stronger gravitational pull towards the moon creating higher tides at the equator and low tides at the poles
how do you calculate the motion of comets?
-newton showed that comets move along conic sections (ellipses, parabolas, hyperbolas)
one of newton's greatest achievements of the Principia
-study of comets
-most previously thought that there were two comets
-newton's reconstruction of the trajectory relied on graphic methods
-beforehand they were uncertain and seen as omens
How do you explain the motion of the moon, which presents major irregularities?
-this made his head ache the most
-three-body problem
-earth, moon, and sun
how can one account for the precession of the equinoxes?
-newton's understanding of the mechanics was insufficient in this case
-he needed conservation of angular momentum
precession of the equinoxes
-a wobble of the earth's axis due to the action of the Moon and sun on a non-spherical earth
-can be studied both through astronomical observations over a long period of time, and theoretically w/ universal gravity, as newton tried to do
newton challenged descarte's vortices
-argued that the heavens are empty of matter
-bc planetary motions are very regular and follow Kepler's laws
What caused gravity? (descartes and newton)
-gravity on the heavens or on earth was caused by a vortex
-many scholars refected newton's system bc it didn't provide physical/mechanical explanation of gravity
newton's opinion on what caused gravity?
-issue was related to God acting across space
-believed that the mathematical relationships inherent in the universe's structure was willed by God (extra info)
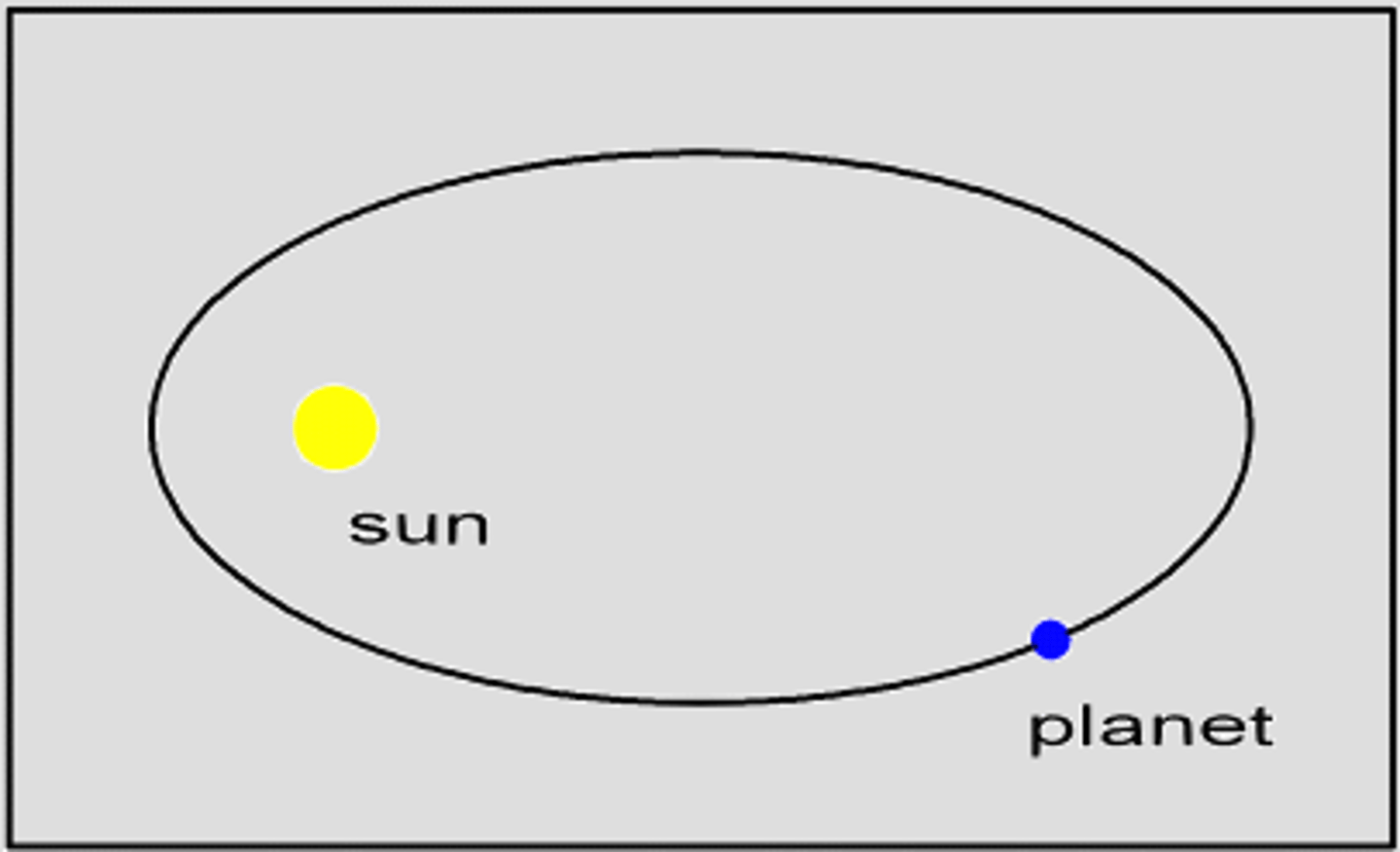
kepler's first law
(Kepler obesrved Mars)
-The orbit of each planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
-every planet has an elliptical orbit w/ the sun at one of the two focii of the ellipse (not the center)
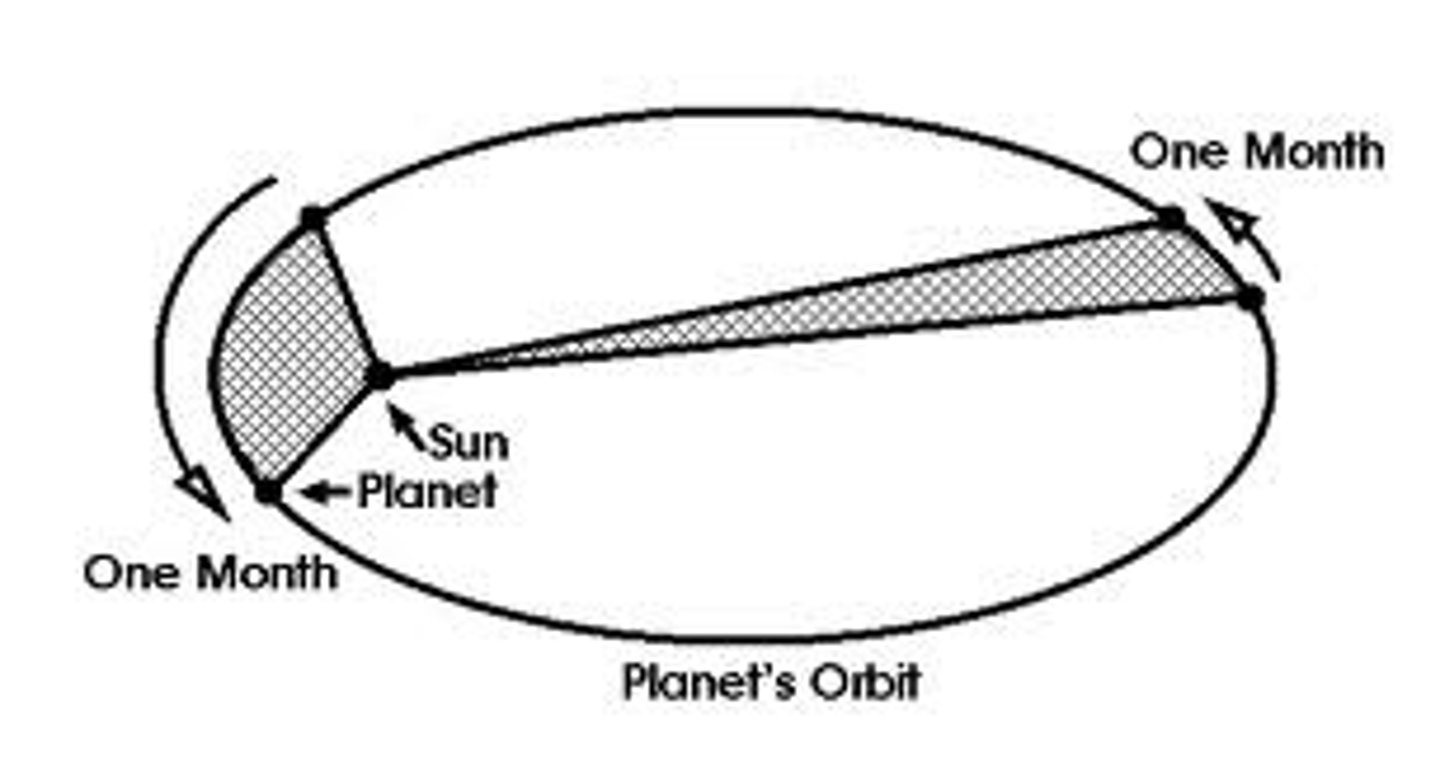
kepler's second law
A line joining a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time
(even though the speed differs as the planet gets closer and further from the sun)
kepler's third law
States that the square of the ratio of the periods of any two planets is equal to the cube of the ratio of their average distances from the Sun.
-planets that are farther away from the sun have longer periods (move slower) than those close to the sun

Descartes' vortex theory
-universe is filled w/ sublte fluids responsible for the motion of planets and comets
-no void
-gravity is caused by rotating vortices pushing heavy bodies toward the center