(Prelims) Chirality and Stereoism
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Mirror image
Reflection of an object in a mirror
Superimposable mirror images
Images that coincide at all points when the images are laid upon each other
Achiral molecule
A molecule that is superimposable on its mirror image.
Nonsuperimposable mirror images
Images where not all points coincide when the images are laid upon each other.
Chiral molecule
A molecule that is not superimposable on its mirror image.
Chiral center
C atom attached to 4 different groups.
Chiral organic molecule
A molecule with a chiral center, such as bromochloroiodomethane.
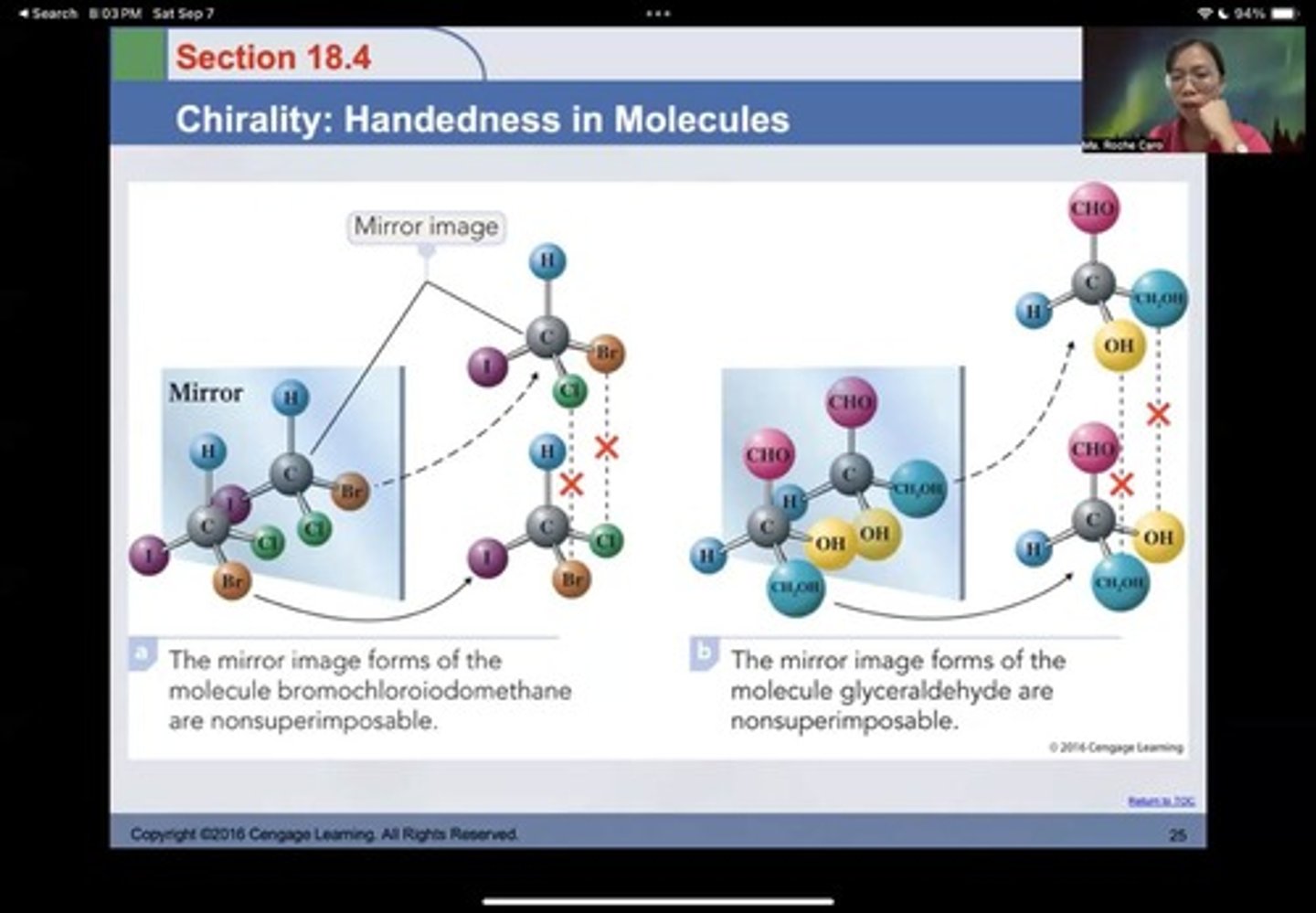
Glyceraldehyde
A molecule with nonsuperimposable mirror image forms.
Chiral C
A carbon atom that must have four different groups attached to it in order to be a chiral center.
2-Butanol
A molecule that contains a chiral center.
1-Chloro-1-iodoethane
A molecule that contains a chiral center.
3-Methylhexane
A molecule that contains a chiral center.
Responses of Left and Right Handed Forms of a Molecule in a Human Body
Both forms may be active, one may be more active, or one may be active and other non-active.
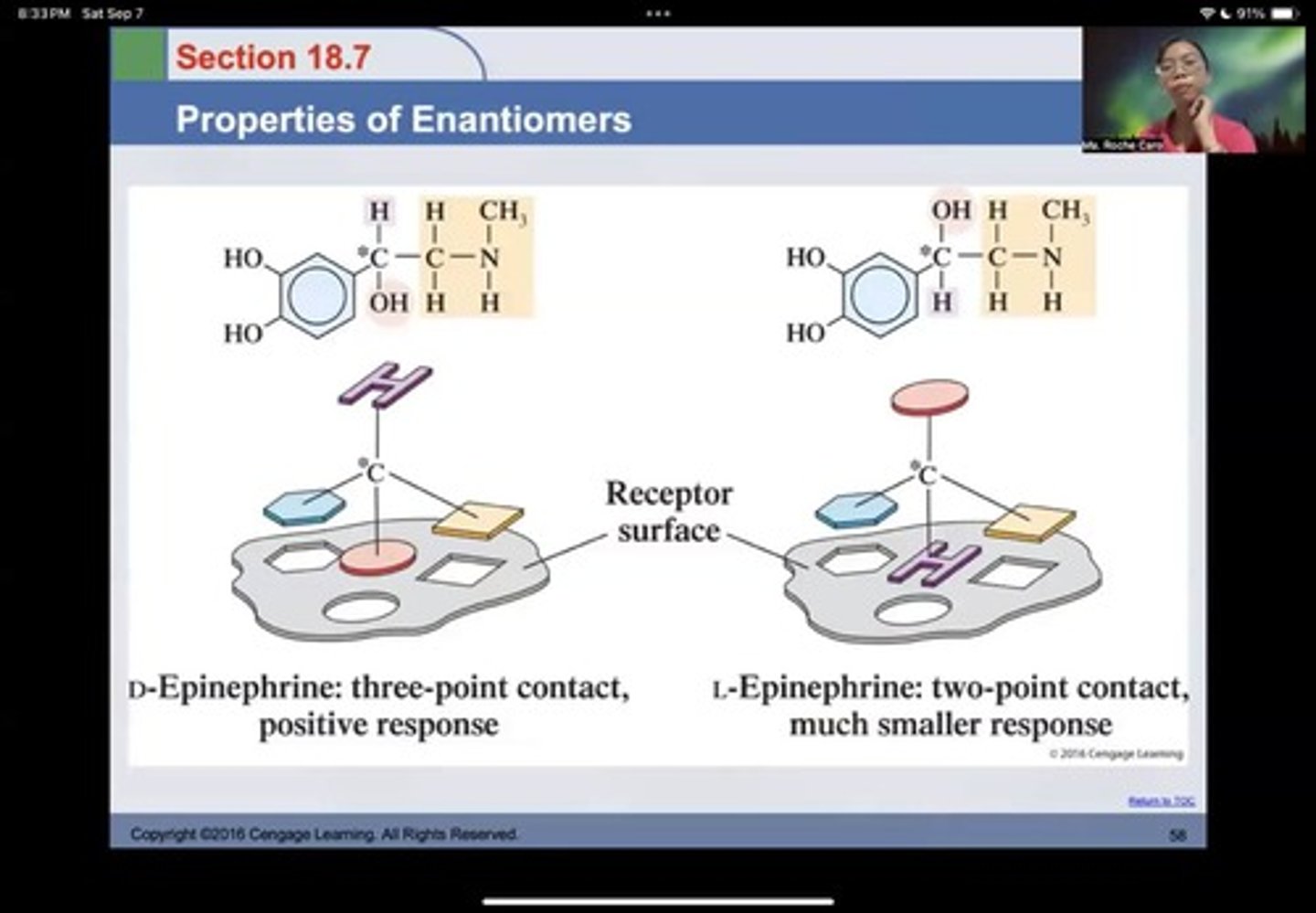
Epinephrine
The response of the body to the right-handed hormone is 20 times greater than responses to the left-handed form.
Monosaccharides
Almost all monosaccharides are right handed.
Amino acids
Amino acids are always left handed.
Chiral center identification
Indicate whether the circled carbon atom in each of the following molecules is a chiral center.
Not a chiral center
A carbon atom that does not have four different groups attached.
Achiral molecule (ring)
A molecule where two 'halves' of the ring are the same.
Chiral molecule (ring)
A molecule where two 'halves' of the ring are different.
Carbon atom identifications
This carbon is not chiral, because the three groups shaded are identical.
Stereoisomers
Isomers that have the same molecular and structural formulas but differ in the orientation of atoms in space.
Enantiomers
Stereoisomers whose molecules are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Diastereomers
Stereoisomers whose molecules are not mirror images of each other.
Cis-trans isomers
A type of diastereomer where the orientation of groups differs around a double bond or ring.
Constitutional isomers
Isomers that have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms.
Fischer Projection Formula
A two-dimensional structural notation for showing the spatial arrangement of groups about chiral centers in molecules.
Tetrahedral geometry
The arrangement of four groups around a chiral center, where vertical lines represent bonds directed into the page and horizontal lines represent bonds directed out of the page.
Functional groups of high priority
Groups that are written at the top in Fischer projections.
Molecular formula
A representation that shows the number and type of atoms in a molecule.
Same molecular formula
When two or more compounds have identical chemical formulas.
Not isomers
Molecules that do not share the same molecular formula.
Isomers
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in structure or arrangement.
Non-superimposable mirror images
Molecules that cannot be aligned to match their mirror images.
Presence of a chiral center
A feature that generates stereoisomerism in carbohydrates.
Presence of structural rigidity
A characteristic that may influence molecular behavior but does not directly generate stereoisomerism.
Presence of three or more carbon atoms
A condition that can lead to the formation of stereoisomers.
Presence of an achiral center
A condition that does not contribute to stereoisomerism.
Molecules are constitutional isomers
When they have the same molecular formula but different IUPAC names or numbering.
Molecules are stereoisomers
When they have the same molecular formula and connectivity but differ in spatial arrangement.
Molecules are enantiomers
When they are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Molecules are diastereomers
When they are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other.
Fischer Projection
A formula used to show the two-dimensional structure of groups around chiral centers in a molecule.
L-Glyceraldehyde
A form of glyceraldehyde where the -OH group on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl group is on the left side.
D-Glyceraldehyde
A form of glyceraldehyde where the -OH group on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl group is on the right side.
D,L System
A system used to designate the handedness of glyceraldehyde enantiomers, which can be extended to other monosaccharides with more than one chiral center.
Epimers
Diastereomers whose molecules differ only in the configuration at one chiral center.
2,3,4-Trihydroxybutanal
A monosaccharide with four carbons and two chiral centers, which has four stereoisomers and two pairs of enantiomers.
Carbon Chain Numbering
The carbon chain is numbered starting at the carbonyl group end of the molecule.
Farthest Number of Chain
The basis for determining the D or L configuration in the D,L system.
D Isomer Identification
The -OH group on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl group is pointing to the right.
L Isomer Identification
The -OH group on the chiral carbon farthest from the carbonyl group is pointing to the left.
Haworth Projection
A formula used to represent cyclic forms of monosaccharides.
Line Angle
A simplified way of drawing organic molecules where lines represent bonds.
Expanded Formula
A formula that shows all atoms and bonds in a molecule explicitly.
Carbonyl Group
A functional group consisting of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
Monosaccharide
The simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of a single sugar molecule.
Chiral Carbon
A carbon atom that is attached to four different substituents.
Stereoisomer Count
There are four stereoisomers for the compound 2,3,4-trihydroxybutanal.
Configuration Determination
The highest-numbered chiral center is used to determine D or L configuration.
Plane Polarized Light
Light waves that vibrate only in one direction.
Dextrorotatory Compound
Chiral compound that rotates light towards right (clockwise; +).
Levorotatory Compound
Chiral compound that rotates light towards left (counterclockwise; -).
Polarimeter
An instrument used to determine the + and - rotation of light.
Chiral
Molecules that cannot be superimposed on their mirror images.
Achiral
Molecules that can be superimposed on their mirror images.
Solubility in Achiral Solvents
Enantiomeric pairs have the same solubility in achiral solvents like ethanol.
Solubility in Chiral Solvents
Enantiomeric pairs have different solubility in chiral solvents like D-2-butanol.
Boiling Points
Enantiomers have the same boiling points.
Melting Points
Enantiomers have the same melting points.
Densities
Enantiomers have the same densities.
Intermolecular Forces
Boiling points, melting points, and densities are dependent upon intermolecular forces.
Body Response to Enantiomers
The body responds differently to different enantiomers.
Epinephrine Isomers
The body response to D isomer of hormone epinephrine is 20 times greater than its response to L isomer.
Ordinary Light Waves
Light waves that vibrate in all directions.
Clockwise Rotation
The direction of rotation of light by a dextrorotatory compound.
Counterclockwise Rotation
The direction of rotation of light by a levorotatory compound.
Chiral Molecules
Molecules that have non-superimposable mirror images.
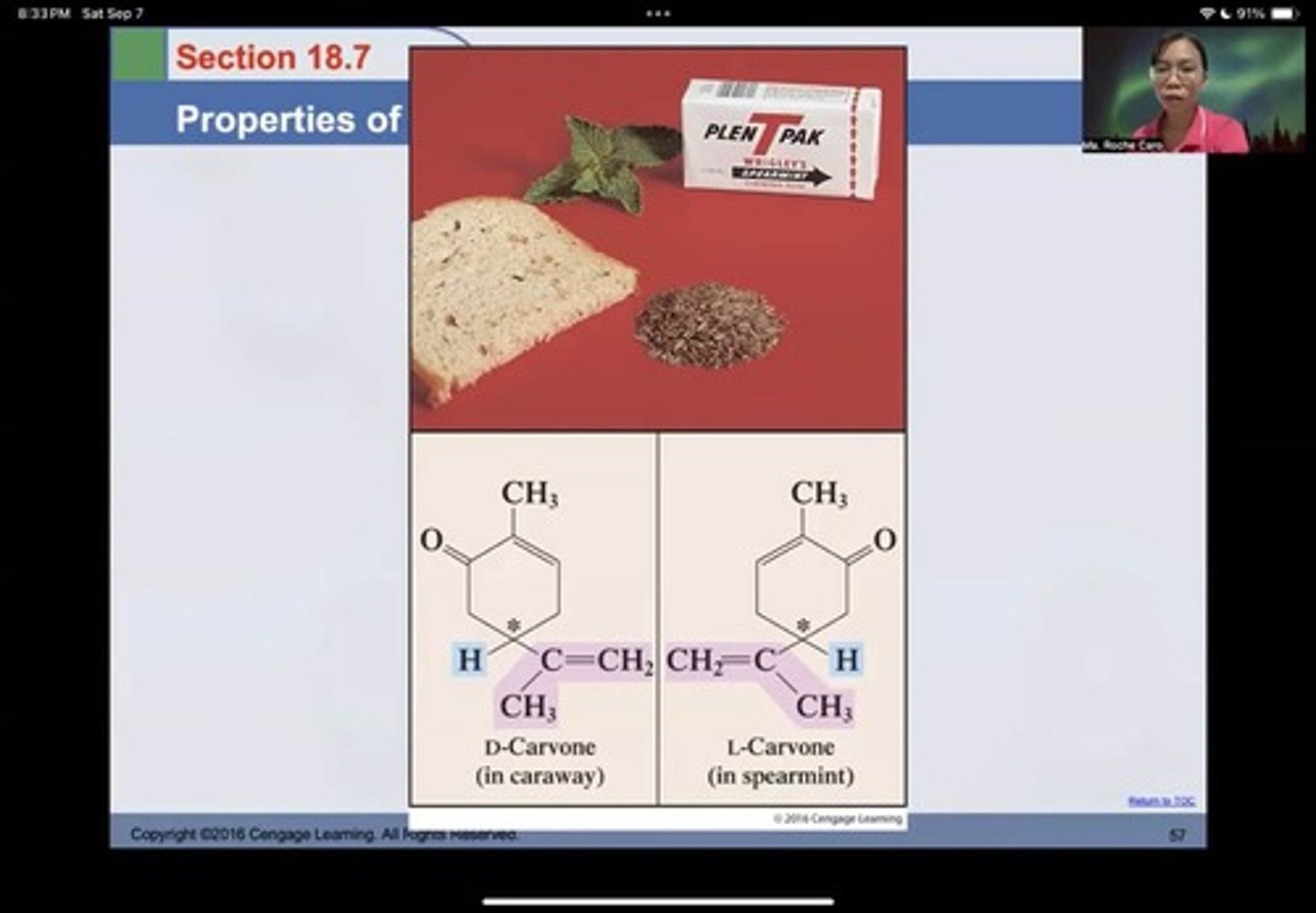
Example of Enantiomers
D-Carvone (in caraway) and L-Carvone (in spearmint) are examples of enantiomers.
Interaction with Chiral Substances
Enantiomers react differently with other chiral molecules.
Concentration of Enantiomer
The direction and extent of rotation of plane-polarized light depends upon the concentration of the enantiomer.
D-Epinephrine
three-point contact, positive response
L-Epinephrine
two-point contact, much smaller response
Optically active compounds
A solution of carbohydrate will rotate the plane of polarized light.
Triose
3 carbon atoms
Tetrose
4 carbon atoms
Pentoses
5 carbon atoms
Hexoses
6 carbon atoms
Aldoses
Monosaccharides with one aldehyde group
Ketoses
Monosaccharides with one ketone group
Aldohexose
Monosaccharide with aldehyde group and 6 C atoms
Ketopentose
Monosaccharide with ketone group and 5 C atoms
Dihydroxyacetone
Monosaccharide with a ketone group and 3 carbon atoms
D-Erythrose
A tetrose with an aldehyde group
D-Threose
A tetrose with an aldehyde group
D-Ribose
A pentose with an aldehyde group
D-Arabinose
A pentose with an aldehyde group
D-Xylose
A pentose with an aldehyde group
D-Lyxose
A pentose with an aldehyde group
D-Allose
A hexose with an aldehyde group