Intro to PNS
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the two types of cells in the nervous system?
Neurons: excitable cells that are specialized for rapid communication of information
Glial: cells that provide structural and functional support for neurons
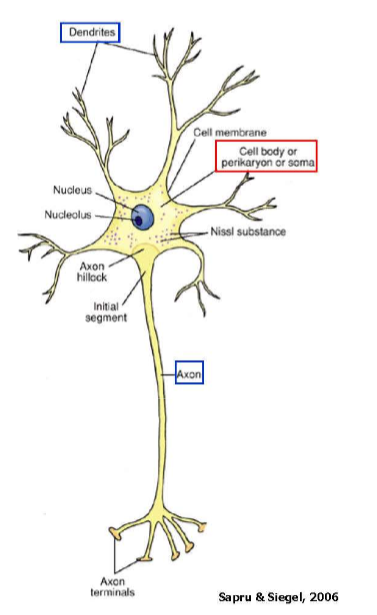
What are the components of a neuron
Cell body: an area containing the nucelus and various organelles; Maybe also be known as the soma or the perikaryon
Neurites: Numerous thin, tube-like structures projecting from the soma
Two types: Dendrites and axons
Axon terminals
What does the CNS consist of?
Brain and spinal cord
What does the PNS include?
ganglia
nerves and their branches
end organs
sensory receptors
neuromuscular junction
visceromotor endings
What are the two divisions of the Nervous system and describe them
Somatic Division:
Soma, Gr. Body
sensory and motor
innervation of skin, tendons, joints, and skeletal muscles
Visceral Division:
Viscera, Gr. Guts
Sensory/motor (autonomic)
innervation of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, organs and glands
How many pairs of cranial nerves and spinal nerves are there?
12 pairs of cranial nerves
31 pairs of spinal nerves (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal)
How are spinal nerves numbered?
In cervical:
spinal nerves are numbered according to the vertebra below
All other spinal nerves: Numbered according to vertebra above
What are spinal nerves formed by? How are they divided?
Formed by union of anterior and posterior nerve roots
Anterior (ventral) roots = contains primarily motor axons leaving the spinal cord
Posterior (dorsal) roots = contain primarily sensory axons entering the spinal cord
The spinal nerve divides into:
ventral ramus: supplies the anterolateral body wall and the extremities
Dorsal Ramus: supplies structures of the back (excluding extrinsic back musculature)
What are the two types of neurons?
Sensory (afferent neuron) (centripetally)
Motor (efferent neurons) (centrifugally)
Both have somatic and visceral divisions
What is a reflex?
An involuntary, steroeotypeed motor response to a particular sensory stimulus. Mediated by chains of neurons called reflex arc
What are the different nerve fibers a spinal nerve has?
General somatic efferent (GSE) fibers
General somatic afferent (GSA) fibers
General visceral efferent (GVE) fibers
General visceral afferent (GVA) fibers
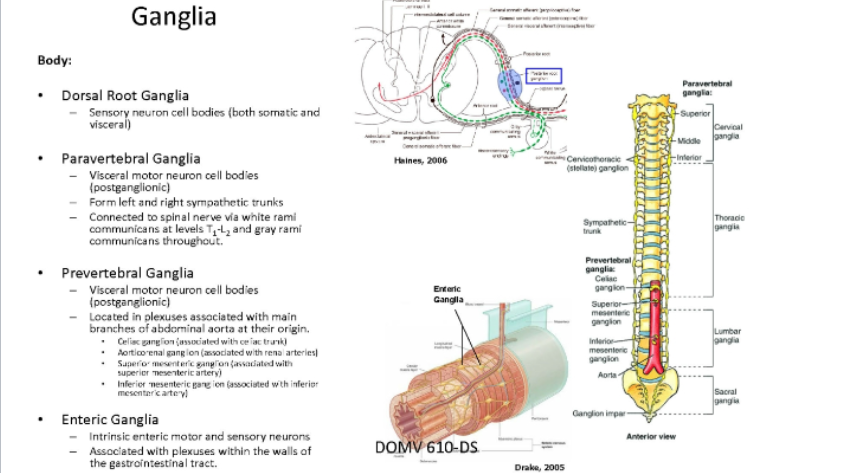
What is a ganglia? how are they classified?
A collection of neuron cell bodies within PNS;
Classified as Sensory, Autonomic, or enteric
What are the two ganglias in the head?
cranial sensory ganglia
sensory neuron cell bodies (somatic/visceral)
Cranial parasympathetic ganglia
Visceral motor neuron cell bodies (postganglionic)
What are the body ganglias?
What does the PNS-somatic division do?
innervates skin, tendons, joints, and skeletal muscles
What are somatic plexuses? What are the three major plexus?
nerve fibers from different spinal nerves (levels) intermingling within plexuses; Give rise to individaul NAMED PERIPHERAL NERVES that contains axons from more than one spinal nerve
Cervical: C1-C4
for neck region and posterior scalp
Brachial Plexus (C5-T1)
for upper extremities
Lumbosacral plexus (L1-S4)
for lower extremeties
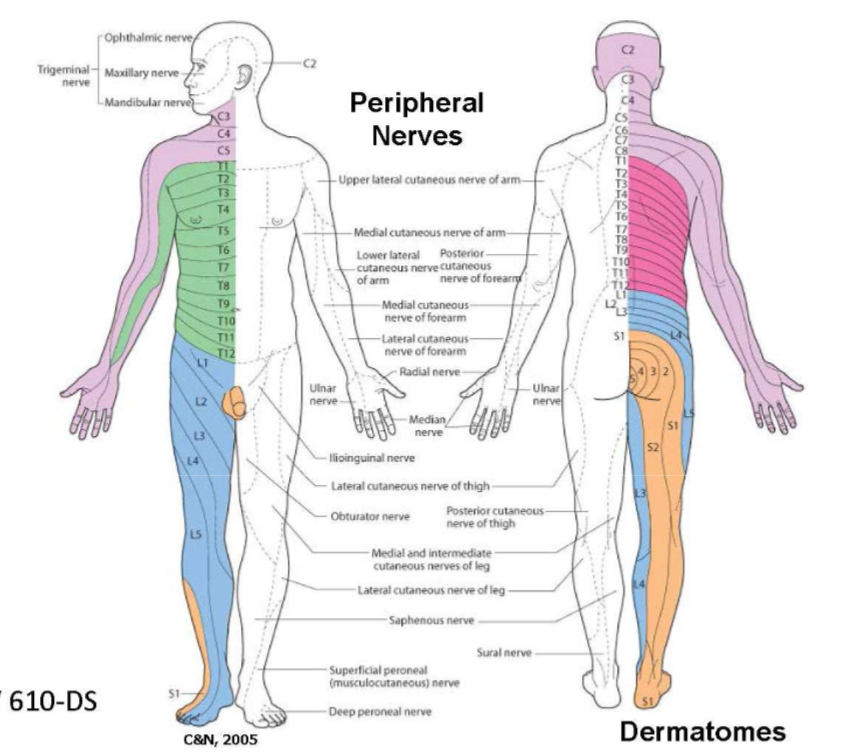
What is a dermatone? What is the paradox here?
where Sensory neurons within a single spinal nerve innervate a specific area of skin;
The dermatomal pattern DOES NOT CORRESPOND with the cutaneous distribution of named peripheral nerves
What is a myotome?
muscle mass innervated by somatic motor fibers from one spinal nerve (Muscles are commonly innervated by motor neurons from more than one spinal nerve; however certain levels may play a more primary role)
What does the PNS’s visceral division do?
Innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, organs, and glands
List out the visceral plexuses; describe their similarities
Includes:
esophagel plexus
cardiac plexus
pulmonary plexus
prevertebral plexus (assocaited with abdominal aorta and lateral wall of pelvis)
Contains visceral sensroy and visceromotor (autonomic) fibers;
Visceromotor fibers exit the paravertebral ganglia or anterior spinal rami and travel through splanchnic nerves to reach visceral plexus
What are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic:
controls energy expending processes
short preganglionic fibers, long postganglionic fibers
Parasympathetic:
controls energy conserving processes
long preganglionic fibers, short postganglionic fibers
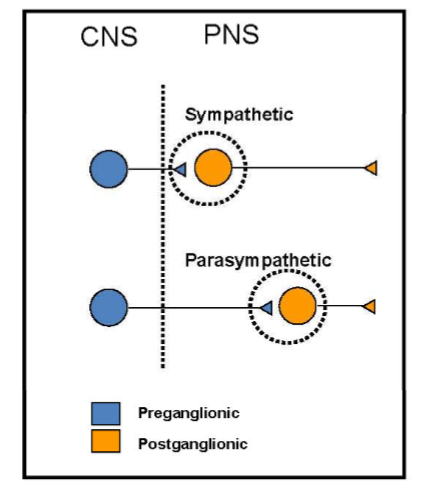
Where does the SNS preganglionic neurons originate? Where are the postgang. found?
Pre: originates in the thoracic and upper lumbar spinal cord (T1-L2)
Post: located in paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia
Where does the PNS preganglionic neurons originate? Where are the postgang. found?
PRe: brain stem and sacral (S2-S4) spinal cord
Post: cranial parasympathetic ganglia and in walls of organs
Describe the visceral sensory pathways and a consequence in their organization
The visceral sensory pathways use the same pathway as the visceromotor fibers run in the opposite direction;
Visceral Afferents of the SNS may carry pain related information. The CNS can misinterpret this information as coming from somatic structures = refered pain
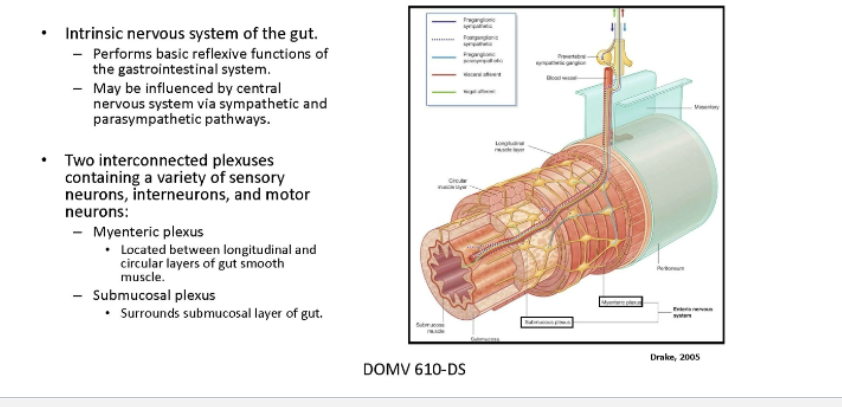
Describe the ENteric Nervous system and its plexus