Vertebrate Zoology 6 - Mammals
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Within the class of mammalia, what are the 2 subclasses?
Protheria.
Theria.
What amimals are in the order monotremata?
Platypus & 4 species of echidnas.
How are monotremes like other animals?
Warm blooded.
Hair.
Mammary glands - milk.
Single lower jaw bone.
3 middle ear bones.
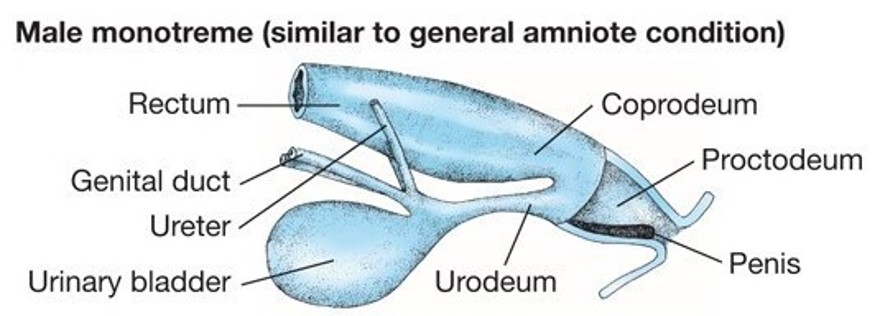
How are monotremes unlike other animals?
Oviparous.
Urinary, defecatory and reproductive systems open to single hole.
What characterisitc do infra class - methatheria have?
Pouch.

What are 6 characteristics of therian mammals?
Homethermy.
Milk production.
Give birth to live young.
Middle ear bones.
Fur and hair.
General skeletal body plan.
What does fur and hair enable mammals to do?
Enables them to be homeothermic in range of enviornments.
Homeothermic
Able to keep body temperature at same level despite any changed in temperature around it.
What are hair filaments made of?
Keratinous filaments.
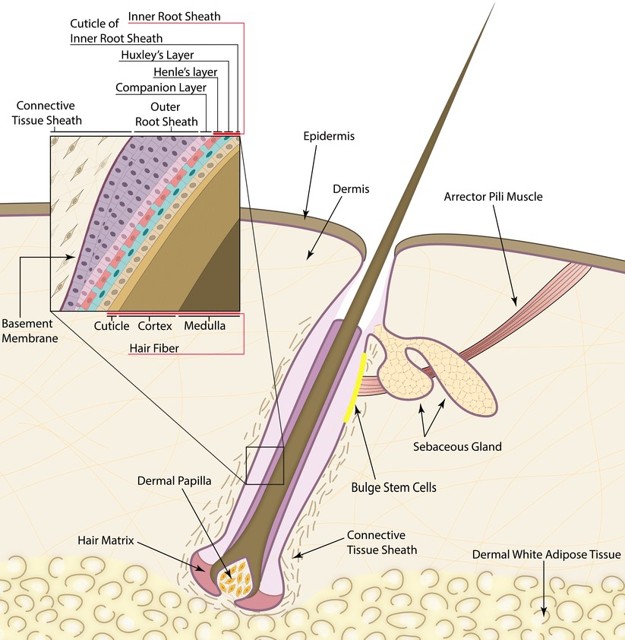
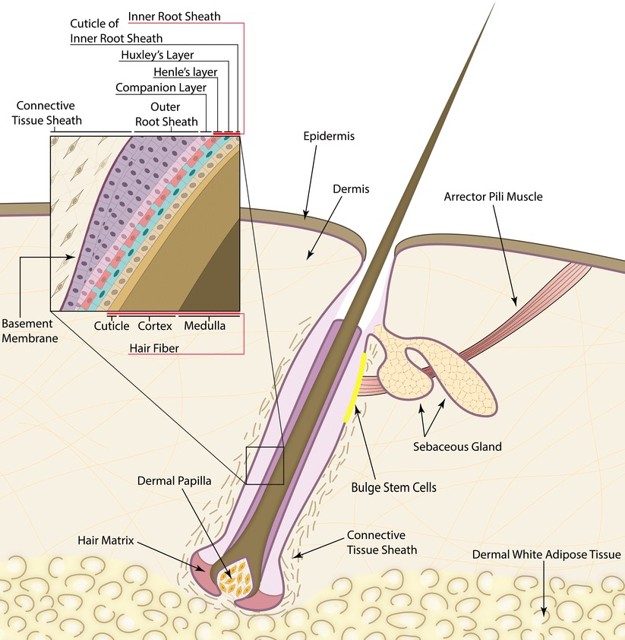
What are the layers within a hair structure?
Cortex and medulla within the cuticle.
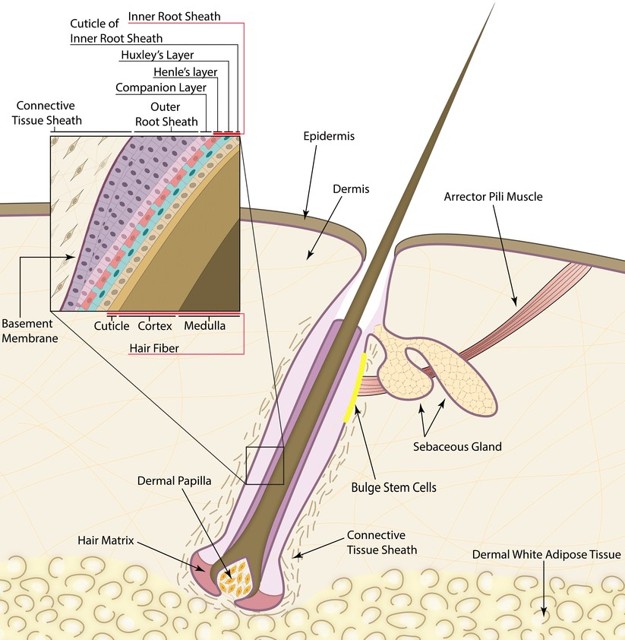
Where is hair produced?
From a hair follicle
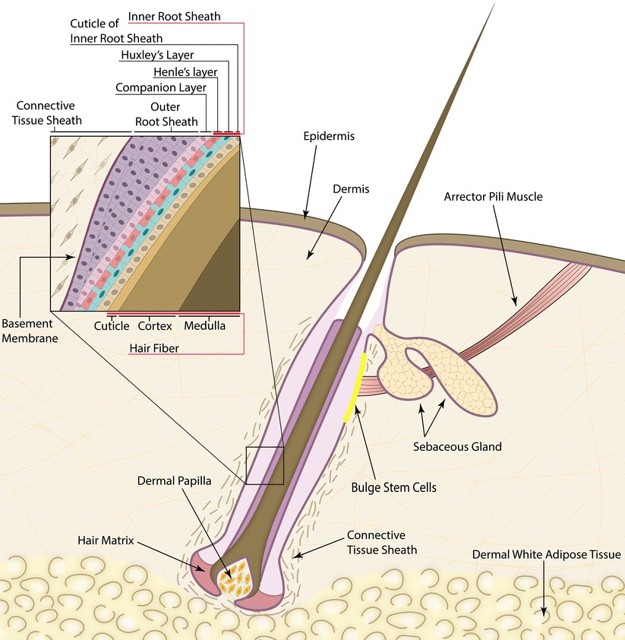
What does the matrix of a hair follicle contain?
Germinal cells.
What are the 4 phases of the hair follicle cycle?
Anagen.
Catagen.
Telogen.
Anagen
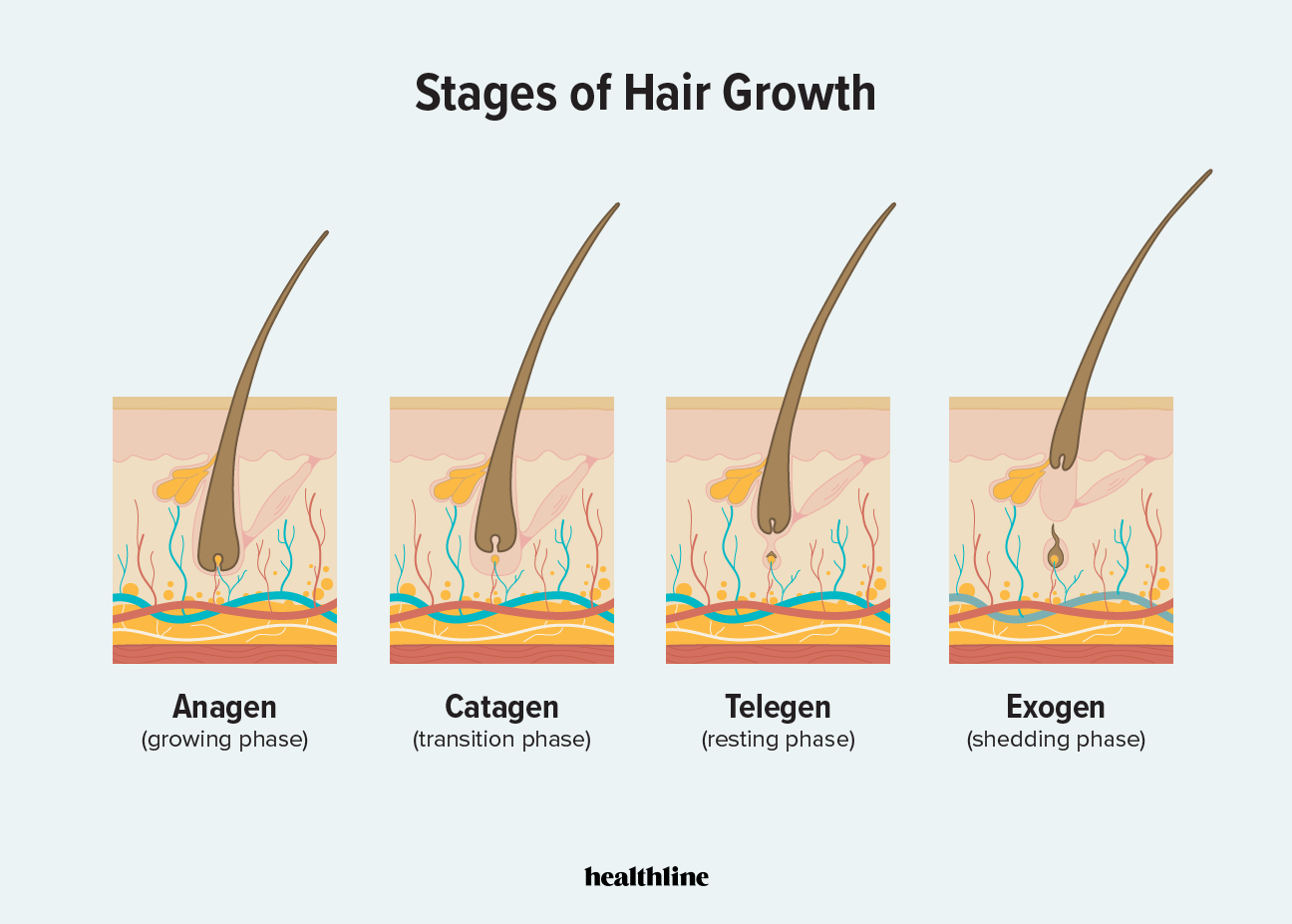
Anagen stage
Proliferation of cells in dermal papilla.
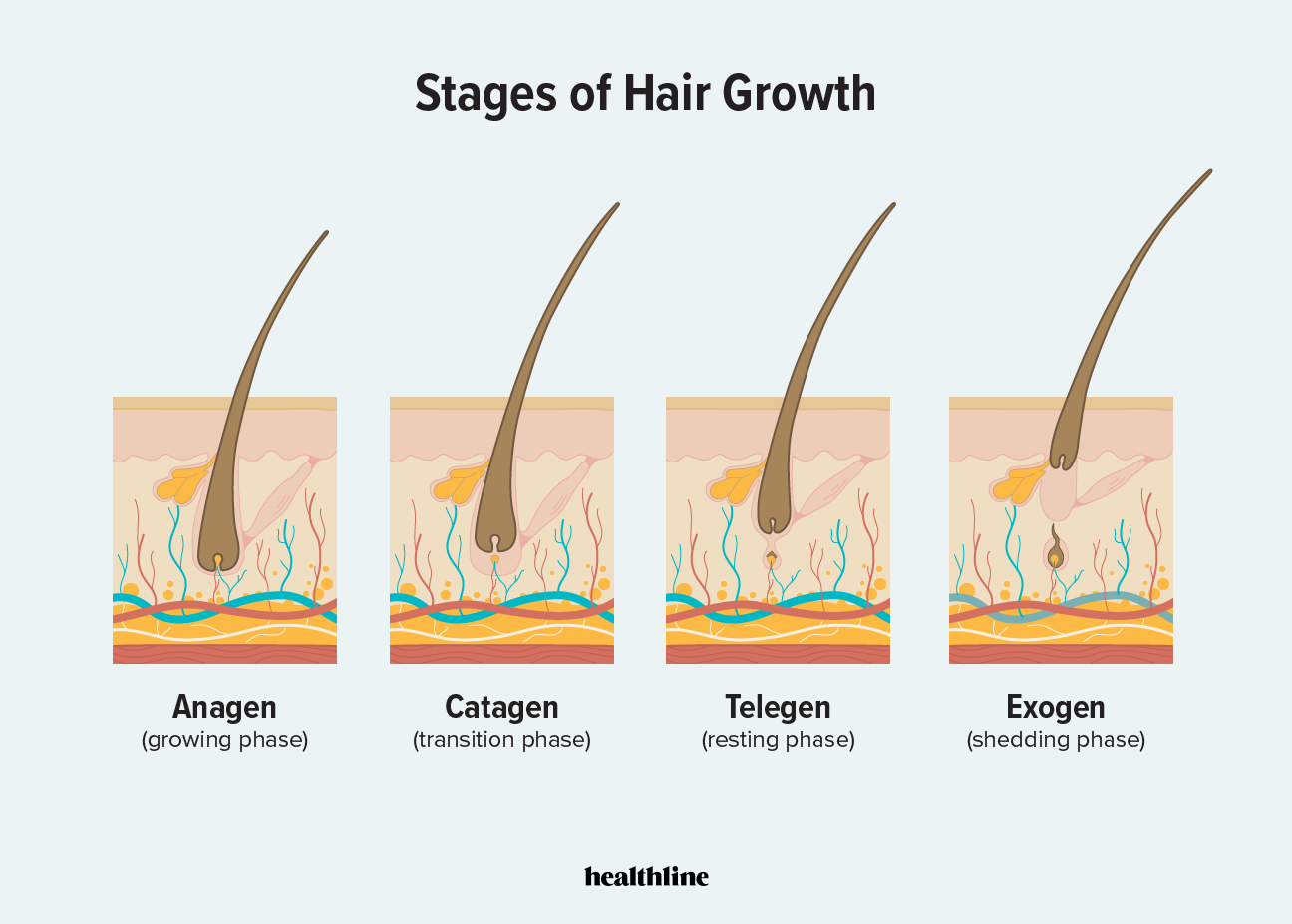
Catagen stage
Nutrients cut off, hair dies.
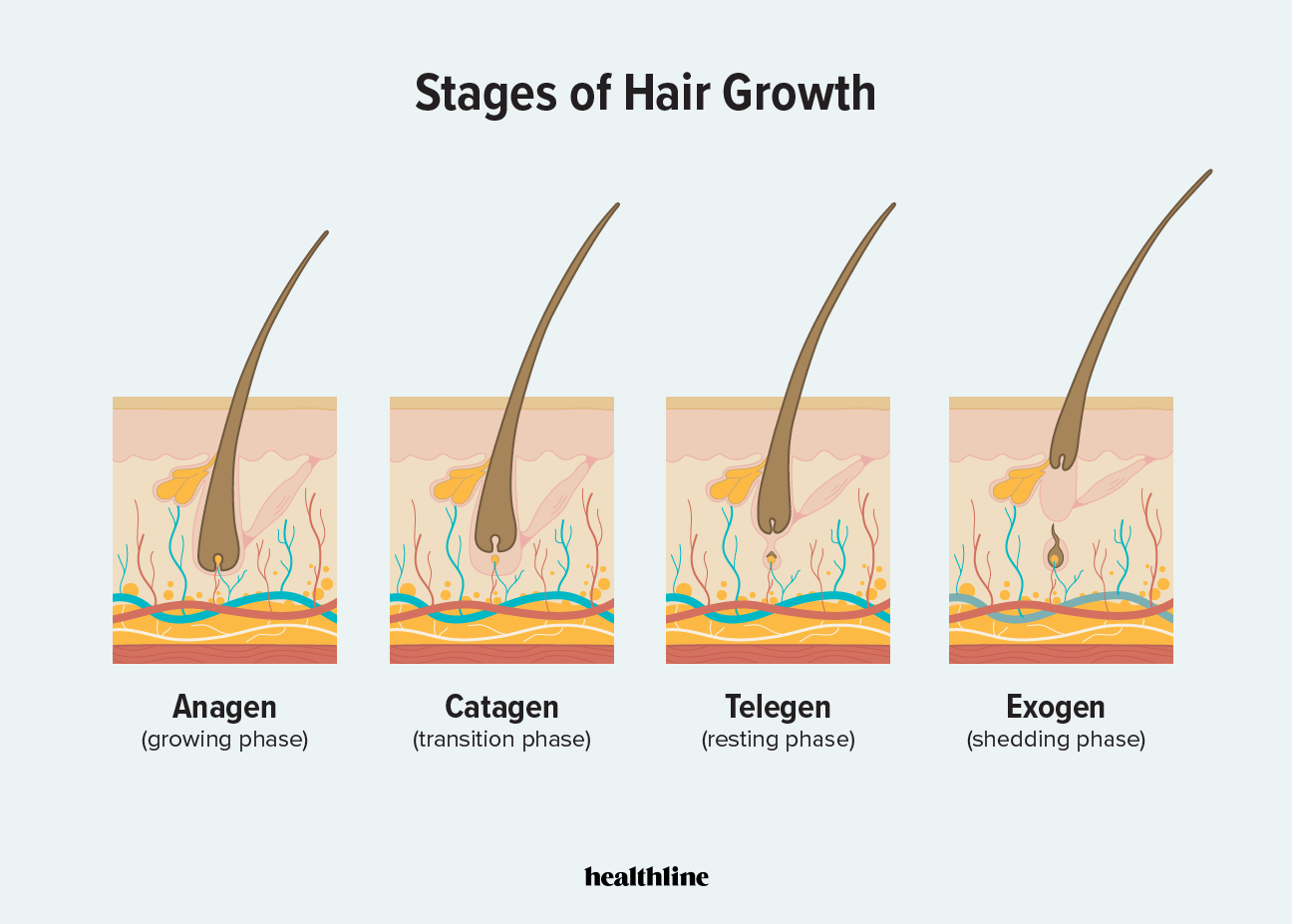
Telogen phase
Rest.
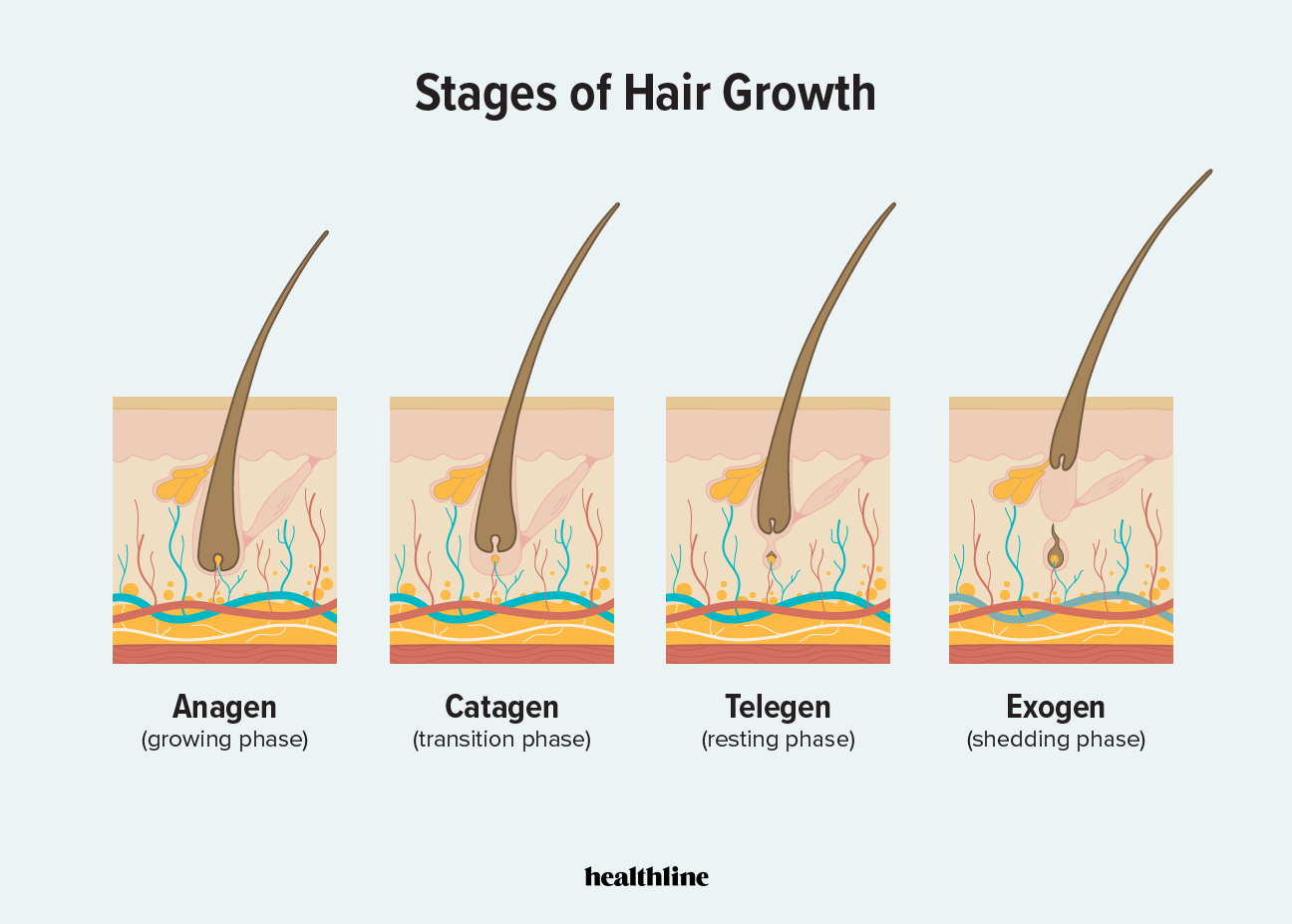
Exogen stage
Stem cells in DP produce new hair, old hair falls out.
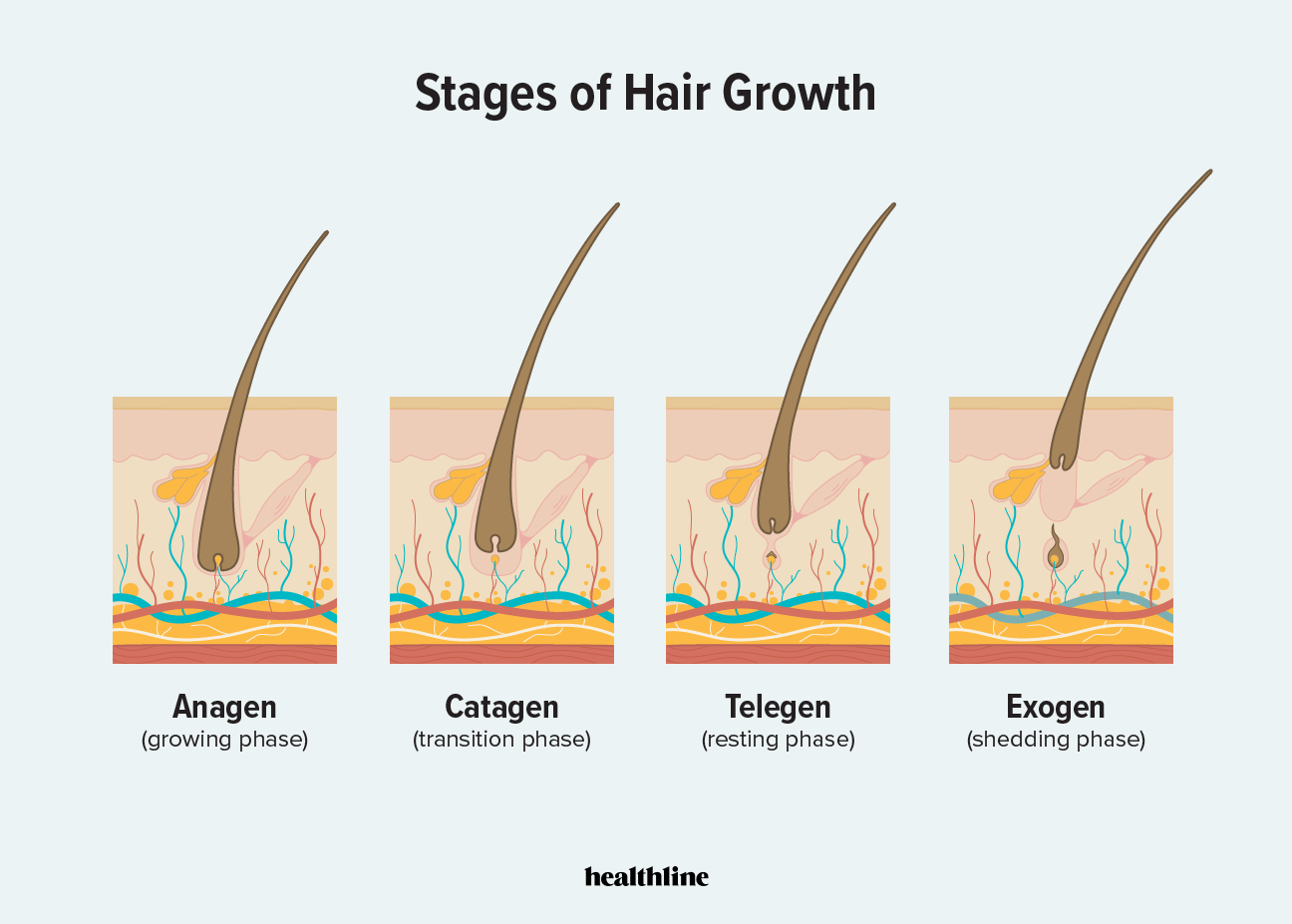
What does the anagen phase determine?
Hair length
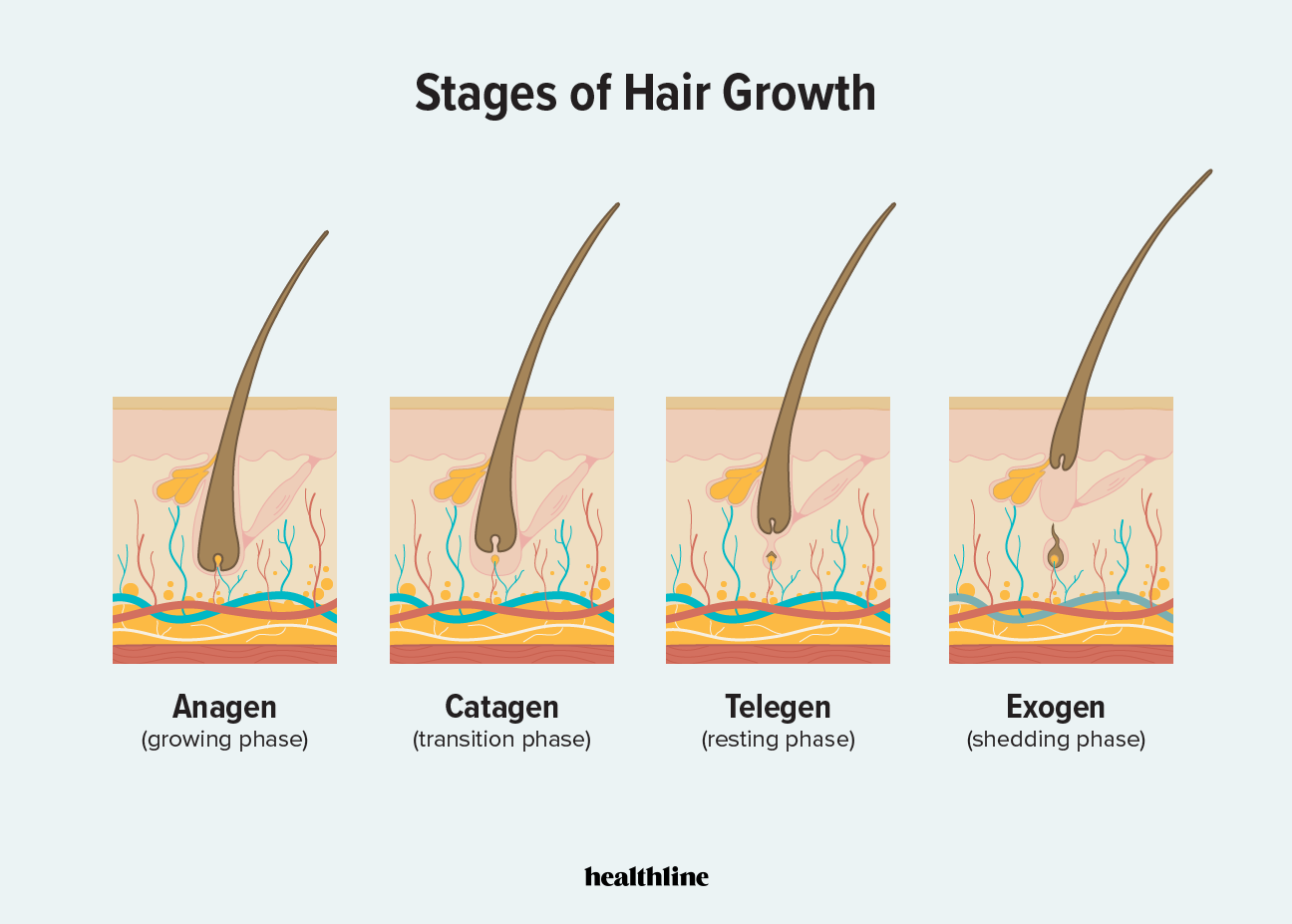
How can extreme stress affect hair development?
It can trigger rapid progression to the telogen phase.
What is alopecia areata?
An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss.
What is fur/hair phenotype influenced by?
Density of hair fibres.
Follicle shape.
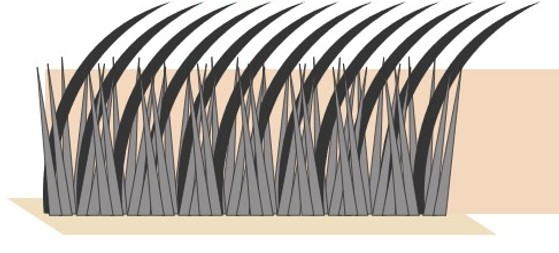
Characteristics of guard hair
Straighter, longer.
Sensing, protection, camouflage.
Characteristics of undercoat
Wavier, shorter.
Insulation function.
Advantage of hairless mammals
Streamline.
Disadvantage of hairless mammals.
Cannot maintain a stable temperature.
Advantages of pigmented hair
Camouflage.
Communication.
Thermoregulation.
What gives hair its color?
Melanocytes.
Where do melanocytes originate from?
Melanoblasts.
Why does hair turn gray or white with age?
Melanocytes die, leading to a loss of pigment.
What are the two main types of melanin in hair?
Eumelanin and pheomelanin.
What are the 5 regions on the mammalian vertebral column?
Caudal.
Sacral.
Lumbar.
Thoracic.
Cervical.
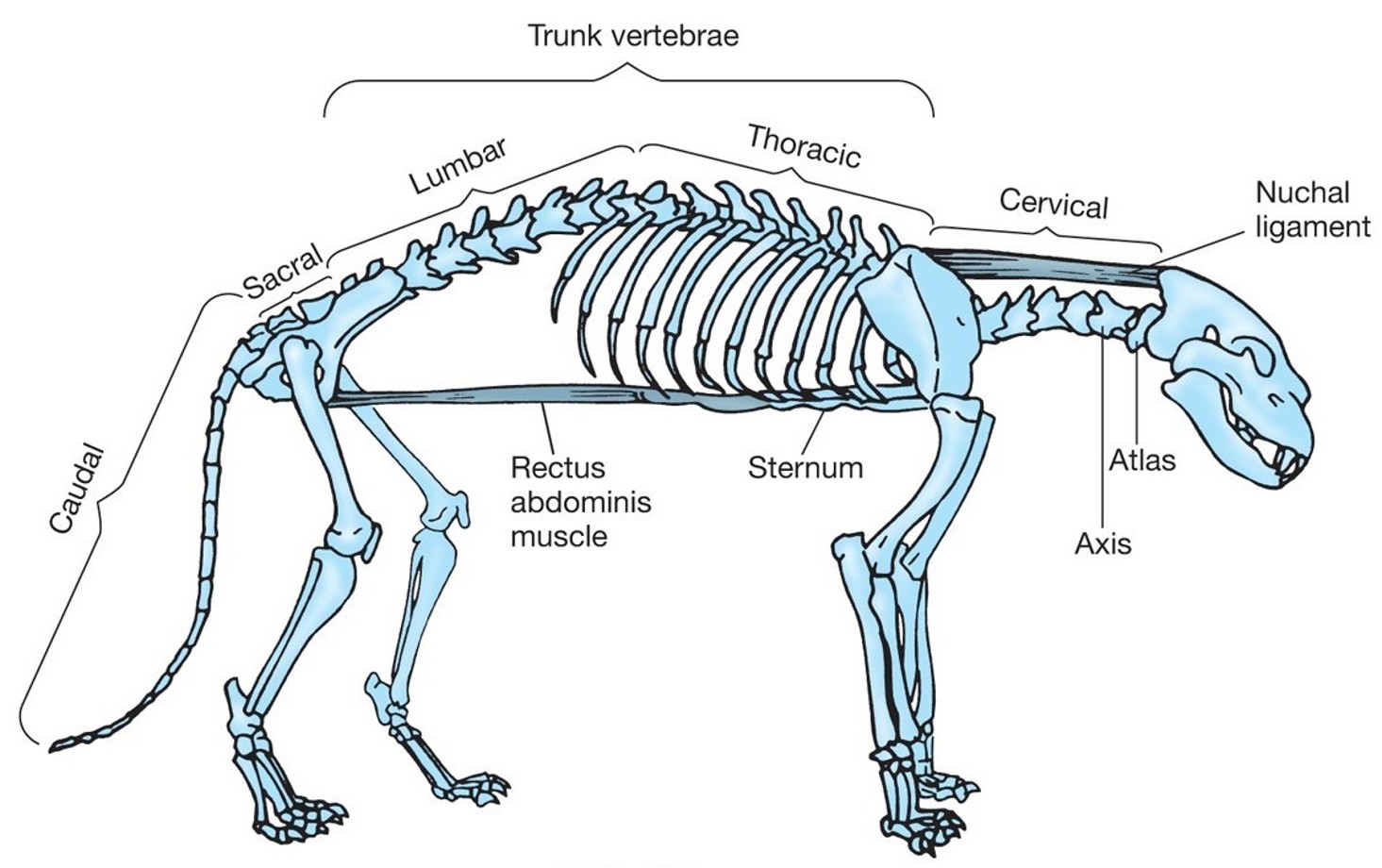
What is the main function of the caudal region?
Posture and movement.
What are the 3 anatomical adaptations for capturing food?
Skull.
Jaw shape.
Muscles.
Claws.
Elongated claws.
Elongated tongue.
Hyoid apparatus
Skeletal structure that supports the tongue, aiding in movement and function.
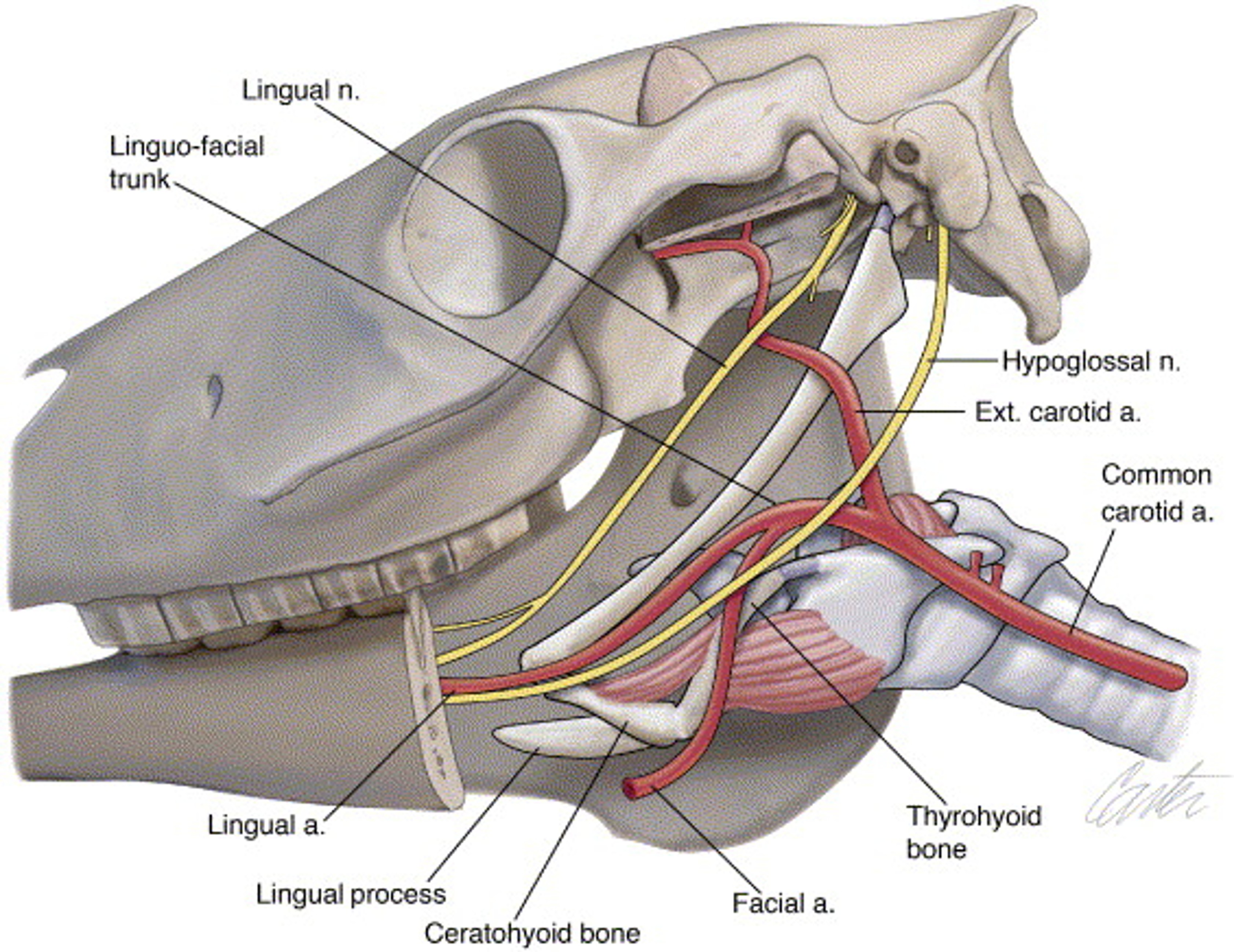
What structure on the tongue contains taste buds?
Papillae
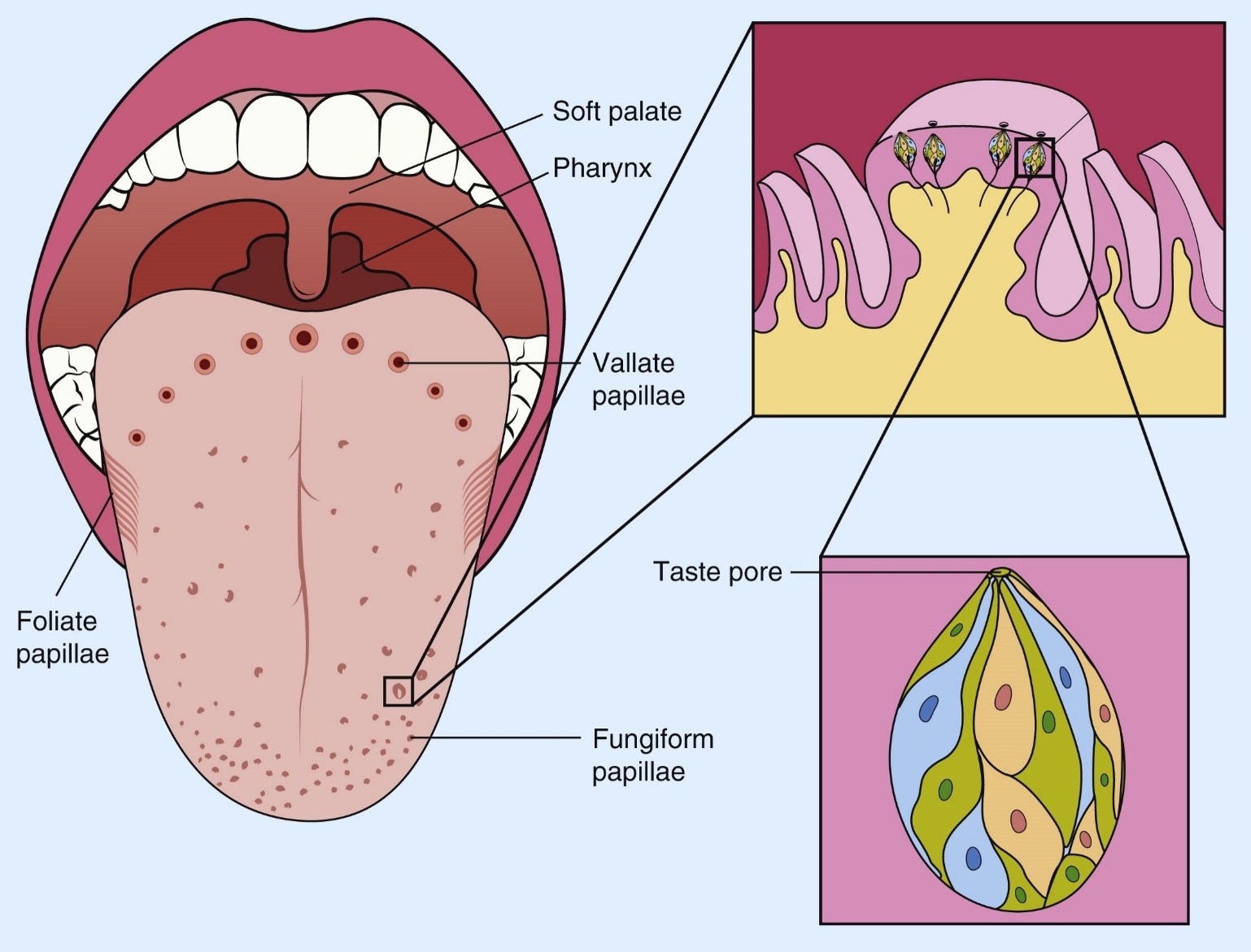
How many types of papillae are there, and how are they distributed?
Three types, each with different distributions on the tongue.
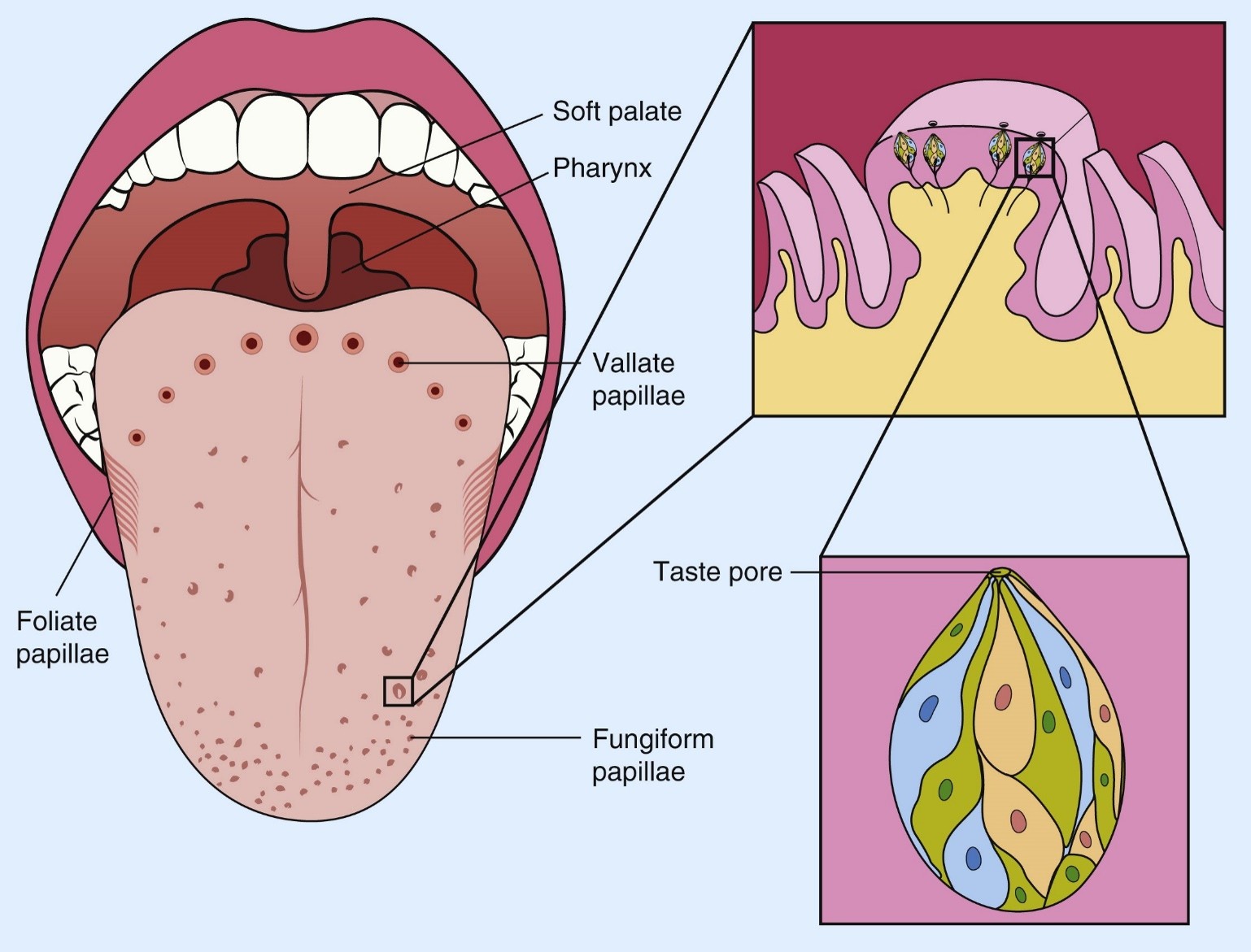
Where are taste receptor cells located?
In the epithelia of taste buds within papillae.
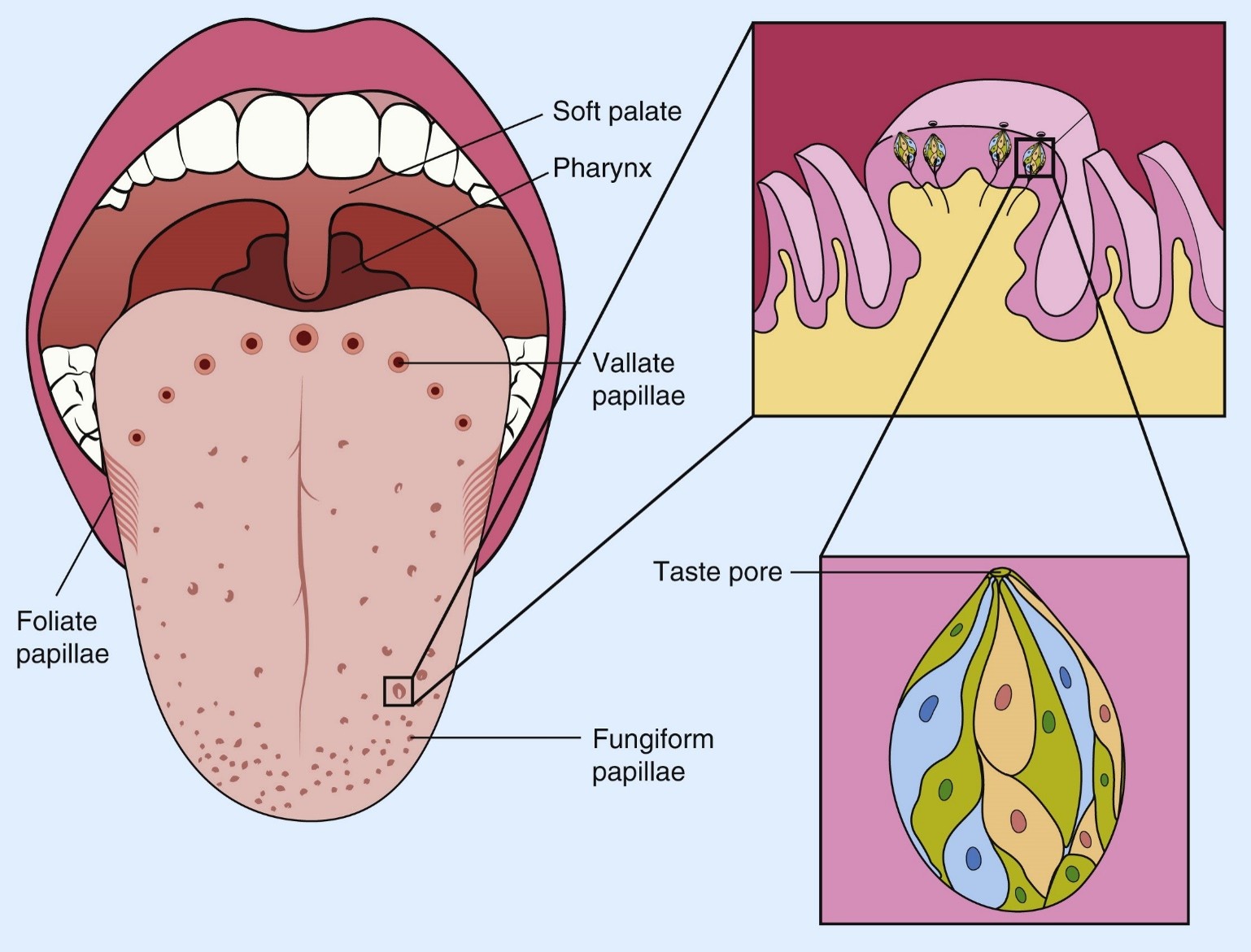
What is the function of taste receptor cells?
They detect and transmit taste signals.
How do receptors for the five basic tastes vary among mammals?
Some mammals experience a loss or increase in specific taste receptors based on their diet and environment.
What are the 5 basic tastes ?
Bitter.
Sweet.
Sour.
Umami.
Salty.
What are the 4 types of teeth?
Incisors.
Canines.
Premolars.
Molars.
Monophyodont
Only one set of teeth throughout life.
Diphyodont
Only 2 successive sets of teeth.
Almost all mammals.
Polyphyodonts
Several sets of teeth.
Kangaroos, elephants etc.
What are the 3 main types of teeth growth?
Brachydont.
Hypsodont.
Hyselodont.
What are the characteristics of brachydont teeth, and which animals have them?
Low-crowned teeth that grow and then stop; found in primates.

What are the characteristics of hypsodont teeth, and which animals have them?
High-crowned teeth with alternating layers of dentine and enamel to maintain occlusal surface functionality; found in cows and horses.
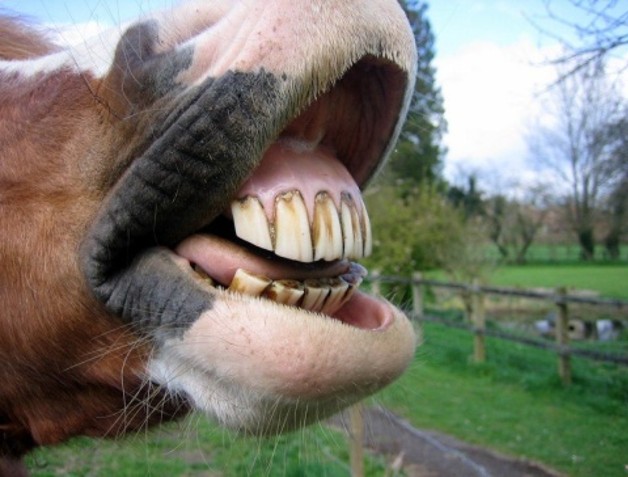

What are the characteristics of hyselodont teeth, and which animals have them?
Teeth that continuously grow via stem cells; found in rodents and lagomorphs (e.g., rabbits).
Which types of teeth do aardvarks lack?
Incisors and canines.
What is missing from aardvark teeth that is usually found in other mammals?
Enamel—aardvark teeth are composed of rounded structures of dentine instead.
What are the key characteristics of aardvark teeth?
They are ever-growing, unrooted, and diphyodont (having two sets of teeth in a lifetime)
What happens to an aardvark’s milk teeth?
Small milk teeth are lost before birth.
What are the three main types of molar cusp shapes?
Bunodont, lophodont, and selenodont.
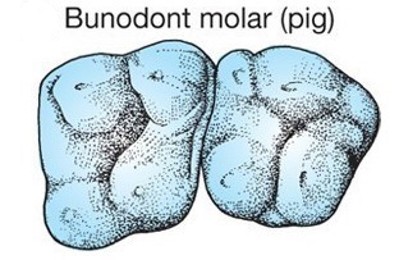
What are the characteristics of bunodont molars, and which animals have them?
Bunodont molars have rounded peaks and are found in omnivores.
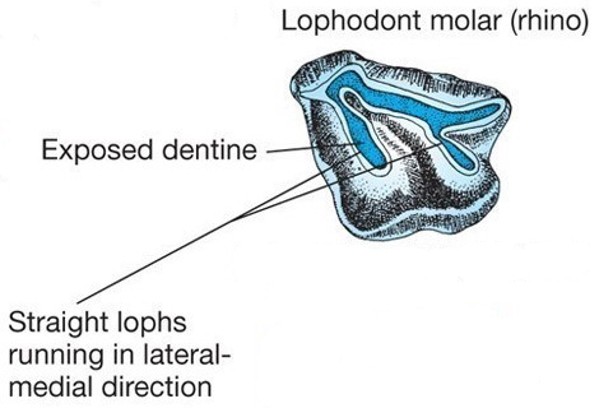
What are the characteristics of lophodont molars, and which animals have them?
Lophodont molars have cusps drawn into straight ridges and are found in perissodactyls (horses, rhinos) and rodents.
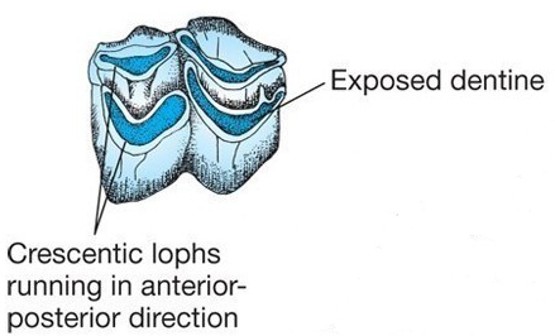
What are the characteristics of selenodont molars, and which animals have them?
Selenodont molars have crescent-shaped cusps and are found in artiodactyls (deer, cows).
Do baleen whales have teeth?
They have teeth only in utero but no adult teeth.
What replaces teeth in adult baleen whales?
Baleen plates on the maxilla (jaw).

What are baleen plates made of?
Keratin, meaning they are not true teeth.
What structure are baleen plates homologous to in other mammals?
Ridges on the roof of the mammalian mouth.
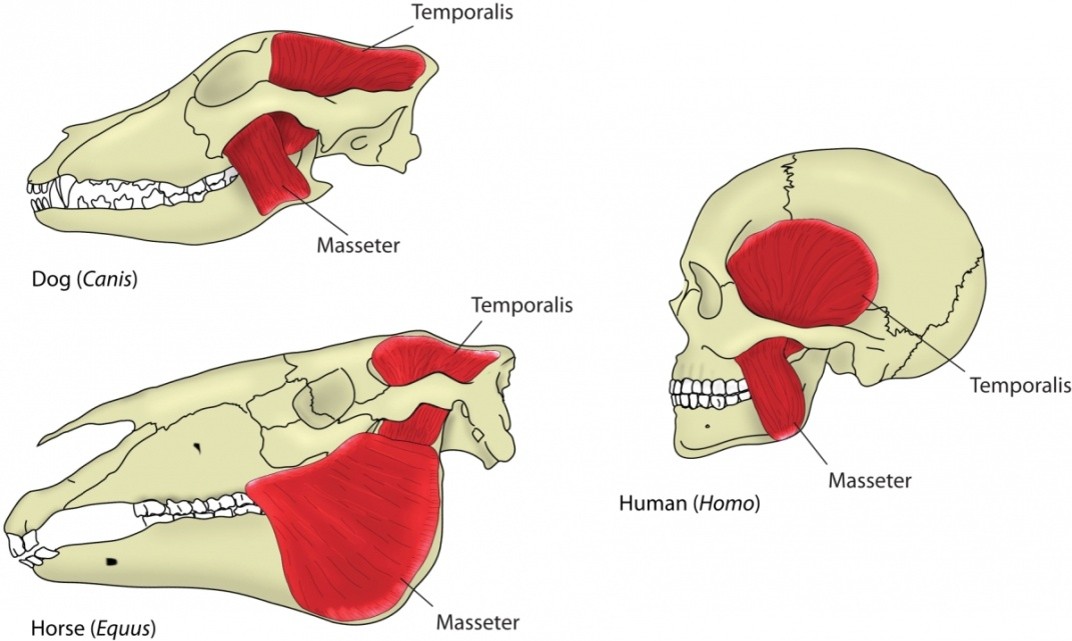
How do the jaw muscles of carnivores and herbivores differ?
Carnivores have a large temporalis muscle, while herbivores have large masseter and pterygoid muscles.
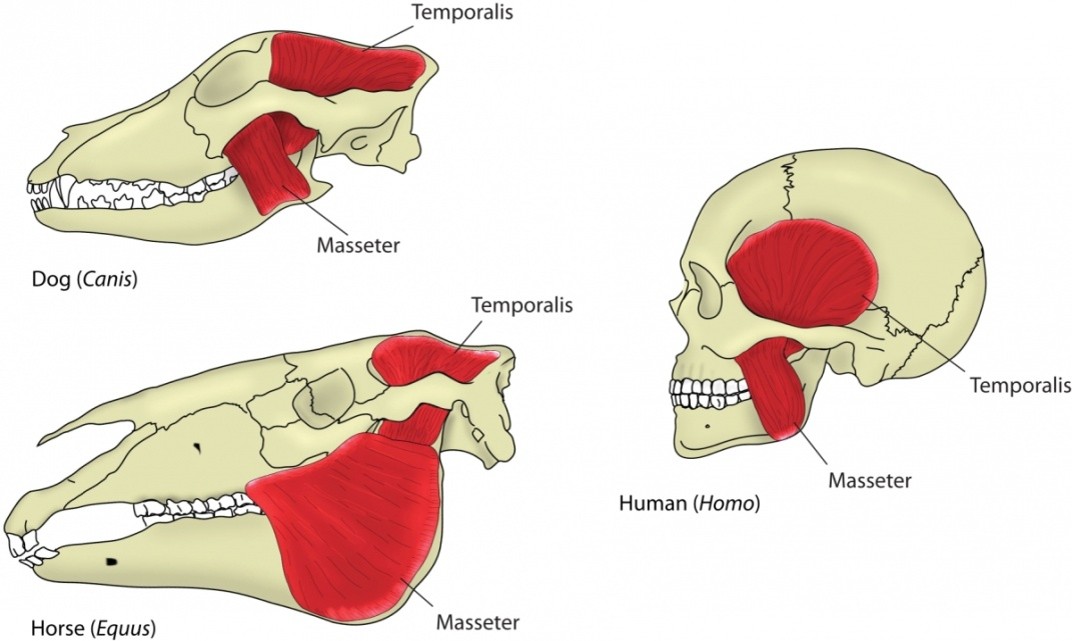
Which jaw muscle is largest in carnivores, and what is its function?
The temporalis muscle is largest, helping to snap the jaw shut (e.g., in dogs).
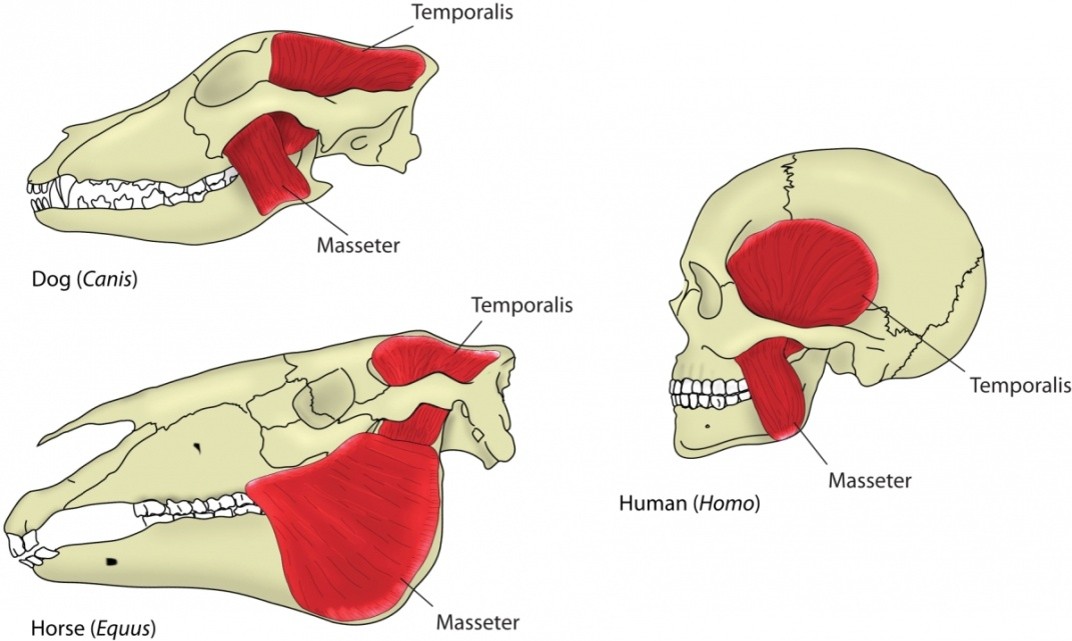
Which jaw muscles are smaller in carnivores?
The masseter and pterygoid muscles.
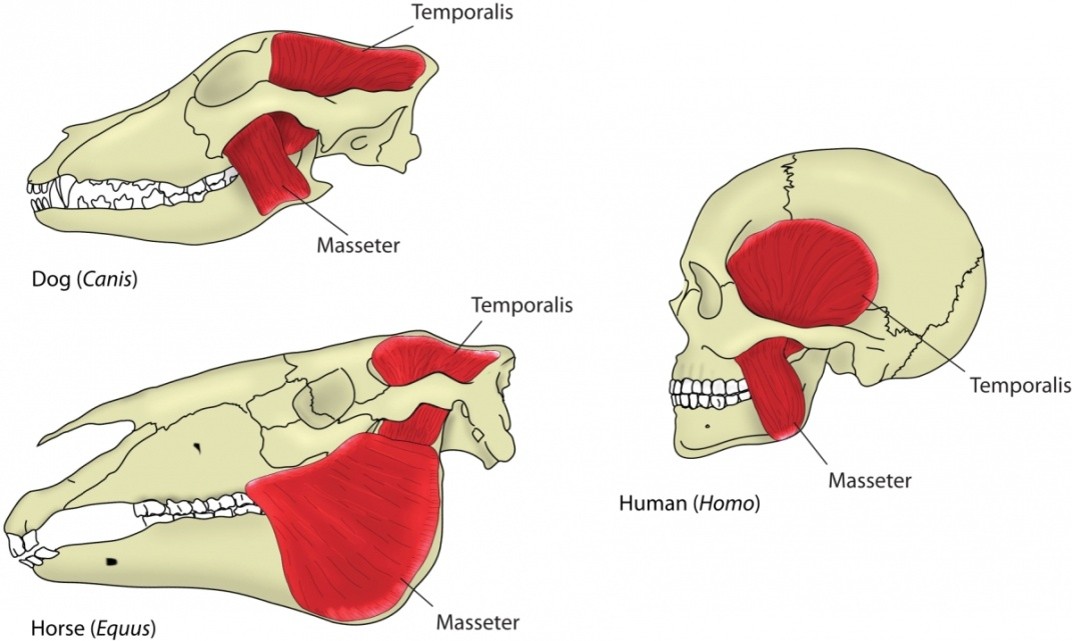
Which jaw muscles are largest in herbivores, and what is their function?
The masseter and pterygoid muscles are large, aiding in extensive chewing (e.g., in deer).
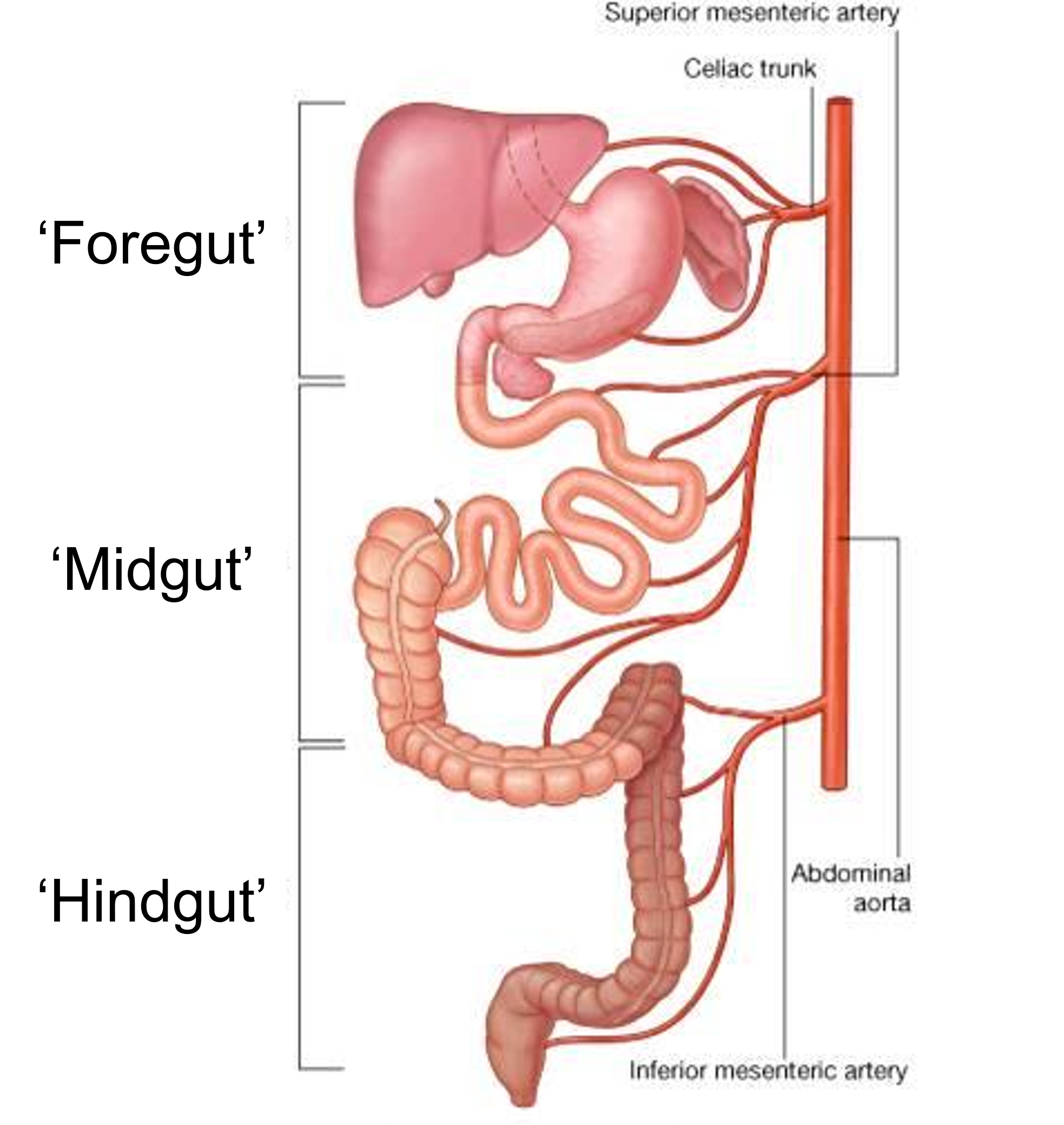
What are the 3 digestive system parts?
Foregut.
Midgut.
Hindgut.
What type of stomach do most carnivorous mammals have?
A simple stomach with a relatively short and simple digestive tract.
What is an exception to the typical carnivore stomach structure?
Cetaceans (whales, dolphins), which have a large multi-compartment stomach inherited from herbivore ancestors.
How does the digestive tract of most carnivores compare to that of herbivores?
It is relatively short and simple, designed for digesting meat efficiently.
What digestive structure is absent in some carnivorous mammals?
A distinct hindgut.
What type of stomach do omnivores have?
A simple stomach.
What structure aids in digesta retention in omnivores?
The caecum in the hindgut.
What are haustrations, and where are they found in some omnivores?
Haustrations are pouch-like structures in the caecum and colon that help with digestion.
Which omnivores have a colon that is haustrated (Segmented) throughout its entire length?
Pigs, humans, some monkeys, and chimpanzees.
How do most mammalian herbivores obtain a substantial part of their nutrients?
Through microbial fermentation of plant material.
What type of stomach do ruminants have?
A four-chambered stomach with specialized bacteria.
Where does nearly all digestion occur in ruminants?
In the rumen.
What is the purpose of rumination in ruminants?
It allows the animal to regurgitate and re-chew food for better digestion (can ruminate up to 40 times).
Where does absorption primarily take place?
In the intestines.
What is the function of the small intestine?
Continued digestion and absorption.
What enzymes help with carbohydrate digestion?
Amylases (from the pancreas) and lactase.
What enzymes help with protein digestion?
Trypsin (from the pancreas) and aminopeptidase.
What enzyme helps with fat digestion?
Lipase (from the pancreas).
What is the function of the large intestine?
Water and final nutrient absorption.
What is coprophagy?
The act of consuming feces.
Which animals commonly practice caecotrophy?
Guinea pigs, chinchillas and rabbits.
What are the four types of bones in mammals?
Long.
Short.
Flat.
Irregular bones.
What are the function of long bones?
Act as a lever for movement.
What is the function of short bones?
Aid in complex movements and help reduce concussion.
What is the function of flat bones?
Protect soft organs and provide muscle attachment sites.
What is the function of irregular bones?
Provide structural support and flexibility as seen in vertebrae.
What are the 3 primary regions of the skeleton?
Axial skeleton.
Appendicular skeleton.
Splanchnic skeleton.
What are key design considerations for bipeds?
Postural control.
Proprioception.
Pelvic orientation.
Balance
What are key design considerations for quadrupeds?
Pectoral girdle.
Clavicle.
Scapula.
Thoracic sling.
Humerus.
Pelvic girdle.
Rigidity of spine.
Stride sequence.
What is proprioception?
The bodys ability to sense its position and movement, aided by stretch receptors in muscles.
How do running mammals scapulae differ from ambulatory mammals?
Longer and more narrow.
Positioned vertically to increase stride length.
How are digging mammals adapted for movement?
Triangular scapulae.
Strong forelimbs.
How are swimming mammals adapted for movement?
Elongated hands.
Shortened femur.
Long lower leg.
Paddle like feet.
What are the 3 types of foot posture in mammals?
Plantigrade.
Digitigrade.
Unguligrade.
Plantigrade posture
Entire foot on the ground.
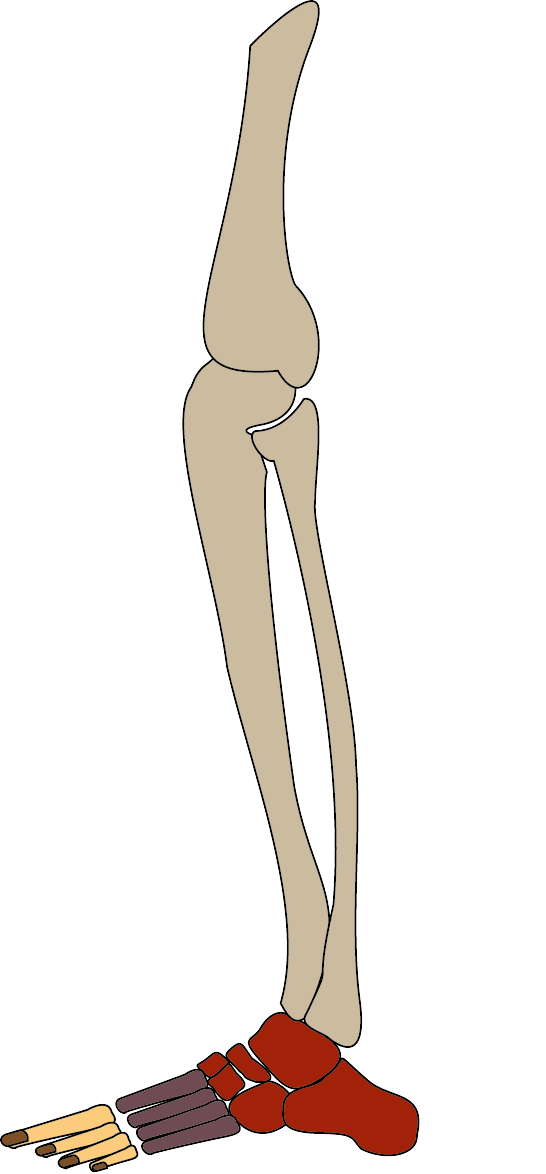
Digitigrade posture
Only digits touch ground, ankle raised.