Cross Sectional Thorax and Abdomen Anatomy
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
what makes up the bony thorax
sternum, costal cartilage, ribs, and thoracic vertebrae
parts of sternum
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
anterior boundary of bony thorax
sternum
manubrium and what it articulates with
triangle shaped, most superior portion of sternum
articulates w/ ribs 1 and 2 and clavicles
jugular notch
concave upper border of the manubrium (T2-T3)
sternal angle
Ridge between manubrium and body at T4-T5
indentations on sternal body articulate w ribs #s
3-7
xiphoid process
attachment for rectus and transverse abdominis muscles
parts of rib
head, neck, tubercle, body
costovertebral joint
pertaining to the joint between a rib head and a vertebra
costotransverse joint
Tubercle of rib articulates with transverse process of vertebra
1st 7 pairs of ribs
true ribs (articulate directly w sternum via costal cartilage)
lower 5 pairs of ribs
false ribs, do not attach to sternum directly
the costal cartilages of ribs 8-10 attach to:
the costal cartilage of rib 7
ribs 11-12
floating ribs, attach only to t-spine vertebrae
floating ribs have no _____ or _____, only _____ and ______
neck, tubercule
sternal ends, vertebral ends
pleural cavities
contain the lungs, lined by serous membrane
pleural serosa
visceral and parietal pleura
parietal pleura is continuous with
the thoracic wall and diaphragm
parietal pleura moves during
respiration
visceral pleura attaches to lungs and continues into the
fissures (indentations of lung lobes)
visceral pleura secretes
pleural fluid to lubricate surfaces of cavity during breathing
what are lungs composed of?
Parenchyma (light, spongy, highly elastic substance)
lungs extend from
the apex (above first rib) down to the diaphragmatic dome (base)
lungs medial surface
next to mediastinum
lungs costal surface
surface that lies against the inner ribs
bronchi
two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs.
the R mainstem bronchi is
wider, shorter and more vertical than the L
where is the carina?
T5
mainstem bronchi turn into secondary, which correspond to
the lobes of each lung (2 on L, 3 on R)
bronchial tree
many divisions into small bronchi called bronchioles that terminate at alveoli
Alveoli
The functional unit of the lung.
the mediastinum extends from
superior thoracic aperture to diaphragm
inside mediastinum:
thymus gland, esophagus and trachea, lymph nodes, thoracic duct, heart and vessels, nerves
thymus gland located
bilobed lymph gland at top of mediastinum, behind manubrium
what gland is the primary lymph organ responsible for developing cellular immunity and producing thymosin?
thymus gland
thymosin hormone
promotes the maturation of T cells (lymphocytes) for the immune response
trachea is reinforced by
16-20 c-shaped rings of cartilage to maintain open airway
c-shaped cartilages close ______ by elastic ______ ______ to allow for food passage through esophagus
posteriorly, connective tissue
on a x-sectional image, the trachea will appear
the esophagus will appear
round and air filled (black)
oval shaped
the esophagus descends through the ____ and enters the abdomen through the
mediastinum
esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm
lymph vessels in the mediastinum are clustered around
vessels, esophagus, bronchi and carina
how are lymph vessels classified?
location (14 regional nodal stations)
what are lymph vessel nodal stations used for?
determining stage of lung cancer
lymph vessels are only seen if
they're inflamed/enlarged
lymph vessels carry fluid away from tissue into
venous blood circulation
thoracic duct
main vessel that receives lymph from the left side of body above diaphragm and lower extremities below diaphragm
where does the thoracic duct begin and end?
inferior to diaphragm @ L2, passes through abd. into chest through aortic hiatus of diaphragm, ascends chest and empties in R. subclavian vein
the heart is found
in the anterior thorax slightly posterior to sternum
the heart points to the
left, this is why there are only 2 lobes of L lung
apex of heart
most inferior, rests on diaphragm
4 Chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
what separates the ventricles?
interventricular septum
pericardium
membranous sac enclosing the heart
walls of the heart (3 layers)
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
epicardium
outermost layer of the heart (thin)
myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart (thickest)
endocardium
inner lining of the heart (thin)
tricuspid valve
between right atrium and right ventricle
bicuspid valve
between left atrium and left ventricle, also called mitral valve
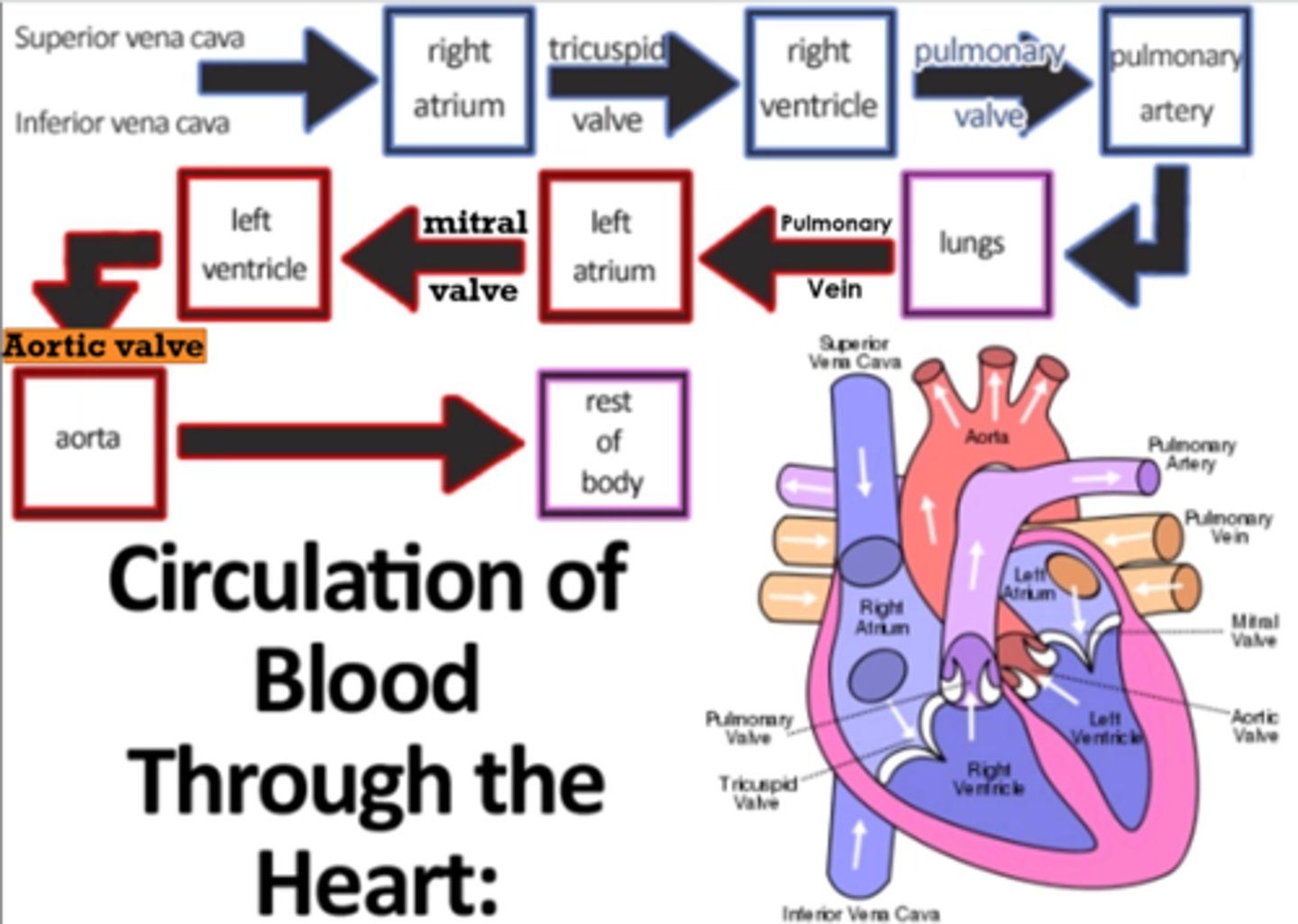
List how blood flows through the heart
SVC / IVC
r atrium
tricuspid valve
r ventricle
pulmonary valve
pulmonary artery
LUNGS
pulmonary vein
L atrium
mitral valve
L ventricle
aortic valve
aorta
BODY
abdominal cavity
between diaphragm and sacral prominatory
abdominal cavity contents
liver, gallbladder, biliary system, pancreas, spleen, adrenal glands, kidneys, ureters, stomach, small intestine, most of large intestine, vascular structures
abdominal division
above diaphragm to top of iliac crest
pelvic division
above crests to pubic symphysis
peritoneum
serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity
visceral peritoneum
covers organs
parietal peritoneum
lines the abdominal cavity
what separates the visceral and parietal peritoneum?
serous fluid, allows organs to move against one another w/o friction
Retropertioneum
behind peritoneum, SADPUCKER
SADPUCKER
S- suprarenal glands
A- abdominal aorta/IVC
D- duodenum (2nd and 3rd segment)
P- pancreas (except tail)
U- ureters
C- colon (ascending and descending)
K- kidneys
E- esophagus
R- rectum
liver
metabolic and hematologic organ, produces bile, largest abdominal organ
where is the liver located?
right hypochondriac and epigastric regions, but can extend to the left hypochondriac and umbilical regions
gallbladder/biliary system
drains the liver and attains bile for storage until going to duodenum for digestive aid
where is the gallbladder located?
the gallbladder fossa on the anteroinferior portion of the r lobe of the liver
what fissure is the gallbladder associated with?
interlobular fissure
pancreas location
found posterior to stomach extending transversely at an oblique angle between duodenum and splenic hilum
parts of pancreas
head, tail, uncinate process, neck and body
body of pancreas goes where
largest and most anterior part, extends transversely to left
Body of the pancreas is anterior to
and superior to
aorta
mesenteric artery
the body tapers superiorly and posteriorly into the
tail of the pancreas
tail of pancreas extends where
extends to L anterior pararenal space (in front of L kidney) at the end of splenic hilum
spleen
lymph organ made of vascular and lymphoid tissue
red and white pulp
tissues of the spleen made of vascular spongy parenchyma
red pulp
site where old blood cells and bloodborne pathogens are destroyed
white pulp
contains lymphocytes
the spleen is posterior to
and is protected by
the stomach
ribs 9-11
what is the medial spleen bordered by?
left kidney, splenic flexure, and pancreatic tail
what does the spleen do?
produce WBC, filters blood, stores iron from RBC and stimulates immune response
adrenal (suprarenal) glands
superior to kidneys, separated from kidney surface by perirenal fat
the adrenal glands are enclosed in
Gerota's fascia
the right kidney is _____ and more medial than the left bc of the
lower, liver
what does the r. adrenal gland look like on a x-sectional image?
inverted V
the left adrenal is ______ to the upper pole of the left kidney and is located in a triangle made up of the _____ ,______ and _____
anteromedial, aorta, pancreatic tail, left kidney
urinary system
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
where do the kidneys lie?
posterior wall of abdominal cavity, on either side of the spine
the kidneys are said to have an ______ orientation bc the upper poles are more _______ and ______ than the lower poles
oblique, medial, posterior
what level are the kidneys located?
between T12 and L4
perirenal fat
fatty tissue surrounding the renal capsule
stomach functions
-Acts as storage space for food
-Site of mechanical food breakdown
-Chemical breakdown of protein begins via enzymes and stomach acid
-produces intrinsic factor for B12 absorption