Biology 1.4 The Circulatory System
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the circulatory system?
Network of organs and vessels. Enables the flow of blood and transport of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and other molecules around the body.
What are the main components of blood?
Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets. Plasma.
What is the function of red blood cells?
Transport O2 from lungs to tissues. Transport CO2 from tissues to lungs.
How do red blood cells transport oxygen to body cells?
At the lungs, haemoglobin in RBCs binds reversibly with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. At the tissues, oxyhaemoglobin breaks down to form haemoglobin and oxygen, which diffuses into cells.
How are red blood cells adapted to their function?
Biconcave disk gives a large SA/V ratio, increasing diffusion rate. Lack a nucleus, allowing more space for haemoglobin molecules (increases oxygen-carrying capacity). Small and flexible so they can squeeze through capillaries.
What is the function of white blood cells?
Provide immunological protection: Phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens. Lymphocytes produce antibodies.
How are phagocytes adapted to their function?
Can change shape to engulf foreign material. Flexible membrane allows them to squeeze through pores in capillary walls and enter tissue fluid. Contain enzymes that digest pathogens.
What is the function of platelets?
Role in blood clotting.
What is plasma?
Pale-yellow liquid portion of the blood. Transports proteins, nutrients, waste products, hormones, antibodies, etc.
How is plasma adapted to its function?
It consists mainly of water, which acts as a solvent, enabling the transport of materials around the body.
Describe the double circulatory system in humans.
Blood flows through the heart twice in two circuits: Pulmonary circuit. Systemic circuit.
What is the pulmonary circuit?
Involves the right side of the heart. Deoxygenated blood is transported to the lungs. Gaseous exchange occurs between alveoli and capillaries. Oxygenated blood returns to the left side of the heart.
What is the systemic circuit?
Involves the left side of the heart. Oxygenated blood is pumped to tissues and organs around the body. Exchange of materials occurs at tissues. Deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart.
Name the four chambers of the heart.
Left atrium. Left ventricle. Right atrium. Right ventricle.
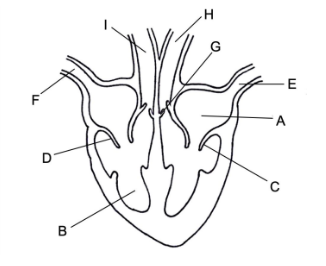
Identify the structures of the heart labelled in the diagram below.
A - left atrium
B - right ventricle
C - bicuspid valve
D - tricuspid valve
E - pulmonary vein
F - vena cava
G - semi-lunar valve
H - aorta
I - pulmonary artery
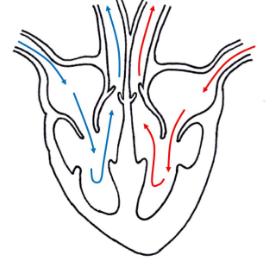
Describe the pathway of blood around the body, naming the structures of the heart.
Pulmonary vein → Left atrium → Left ventricle → Aorta → Body → Vena cava → Right atrium → Right ventricle → Pulmonary artery → Lungs.
Why is the left ventricle thicker than the right ventricle?
It pumps blood a further distance. It must generate a greater force of contraction so blood can be pumped at a higher pressure.
What are the walls of the heart made of?
Cardiac muscle.
What is the function of cardiac muscle?
Contracts to pump blood around the body.
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
Supply heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients.
What is the function of valves in the heart?
Prevent the backflow of blood.
What are the two types of valves found in the heart?
Atrioventricular valves. Semi-lunar valves.
Where are the atrioventricular valves located?
Between the atria and the ventricles.
What are the two types of atrioventricular valve?
Bicuspid valves (between left atrium and left ventricle). Tricuspid valves (between right atrium and right ventricle).
Where are the semi-lunar valves located?
Between the ventricles and the arteries.
What are the three main types of blood vessel?
Arteries. Capillaries. Veins.
Describe the pathway of blood through the blood vessels.
Heart → Arteries → Capillaries → Veins → Heart.
What is the function of the arteries?
Carry blood away from the heart under high pressure.
Describe how the arteries are adapted to their function (6).
Narrow lumen maintains high pressure. Thick wall to withstand high pressure. Thick layer of smooth muscle provides strength. Thick layer of elastic fibres allows stretch and recoil. Smooth inner lining to reduce friction. No valves.
What is the function of the veins?
Return blood to the heart under low pressure.
Describe how the veins are adapted to their function (4).
Large lumen eases blood flow. Thin wall as blood is at low pressure, allowing muscles to easily compress the vein, aiding blood flow. Relatively thin layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres. Valves prevent backflow of blood.
What is the function of the capillaries?
Allow the exchange of materials at tissues.
Describe how the capillaries are adapted to their function (4).
Form a large network, providing a greater surface area for diffusion. Walls one cell thick, giving a short diffusion distance. Walls permeable, allowing the exchange of substances. Narrow lumen decreases diffusion distance.
Why is it important that blood flows slowly through the capillaries?
Allows time for the exchange of materials.
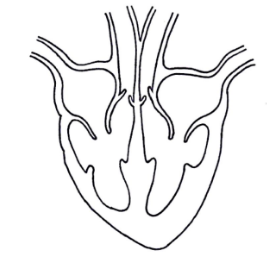
Show the direction of blood flow through the heart on the diagram below