HHP 1100 Exam 2
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
skeletal system
dynamic and changing organ system with tissues that grow and change throughout life
functions: framework, support body weight, attach for muscle, storage reservoir (Ca++, P)
cartilage
supporting connective tissue; semi rigid extracellular matrix that is weaker than bone, but more flexible and resilient
functions: gliding surface at joints, precursor model for bone growth
chondroblasts
produce new cartilage
chondrocytes
basic mature cartilage cells; occupy small spaces called lacunae; mature cartilage is avascular (no blood vessels)
hyaline cartilage
found at the end of long bone
fibrocartilage
more rigid and stronger than hyaline; found in between vertebral discs
elastic cartilage
found in the ears; very mobile
interstitial growth pattern
growth of cartilage from deep in the tissue
appositional growth pattern
growth of cartilage from the outside of the tissue or surface
bone
contain all four tissue types; extracellular matrix is sturdy and rigid due to deposition of minerals
functions: structural support, movement, protect organs, hemopoiesis (blood cell production in red bone marrow); storage of minerals (Ca++, P, lipids in yellow bone marrow)
long bones
longer than they are wide; bones of the appendages
highly vascularized, nutrient foramen and innervation
short bones
cubed in shape; tarsals and carpals
flat bone
broad & thin; cranial (frontal bone)
irregular bone
bone of complex shape; protects internal organs from compressive forces (vertebrae)
diaphysis
shaft of the long bone; most of bone length
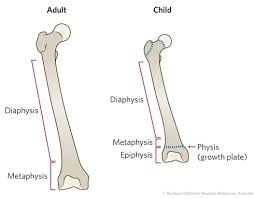
epiphysis
two ends of long bone (proximal and distal)
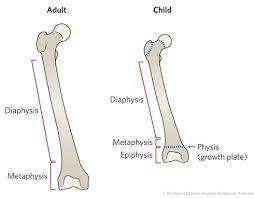
metaphysis
where diaphysis and epiphysis meet on long bone; where growth plate is
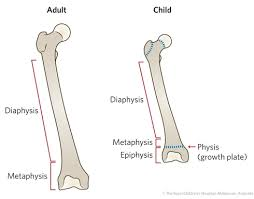
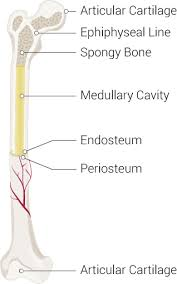
articular cartilage
end of long bones, forms joints and is covered by hyaline cartilage
medullary cartilage
open area deep in long bone; where yellow bone marrow is found
spongy bone
contains red bone marrow; spaces in between
lack osteon (no cylindrical arrangement), parallel lamellae
endosteum
membrane lining the medullary cavity (internal surface) of a bone

periosteum
a dense layer of vascular connective tissue enveloping the bones except at the surfaces of the joints; lining outer surface
osteoprogenitor cells
undifferentiated bone cells
osteoblasts
secrete osteoid (that hardens into bone tissue), forming bone matrix
osteocytes
mature bone cells; once trapped in bony matrix by osteoids
osteoclasts
break down bone tissue; if blood Ca++ levels are low
compact bone
hard and dense, but not solid, bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
ossification
formation of bone connective tissue
intramembraneous ossification
the bone development process where membrane bones develop from a membrane
forms flat bones
- cluster of osteoblasts at the ossification center, the calcification entraps the osteoblasts within the lacunae in the bone matrix
endochondral ossification
process in which bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage;
forms long bones
- cartilage calcifies and periosteal bone collar forms around the diaphysis and starves the deep tissue to it, which kills it and brings in osteoblasts
- bone replaces cartilage, except the articular cartilage and epiphyseal plates
interstitial growth
growth in length (hyperplasia)
appositional growth
growth in width
simple fracture
bone breaks but doesn't pierce the skin
compound fracture
bone breaks and pierces the skin
comminuted fracture
bone shatters into small pieces
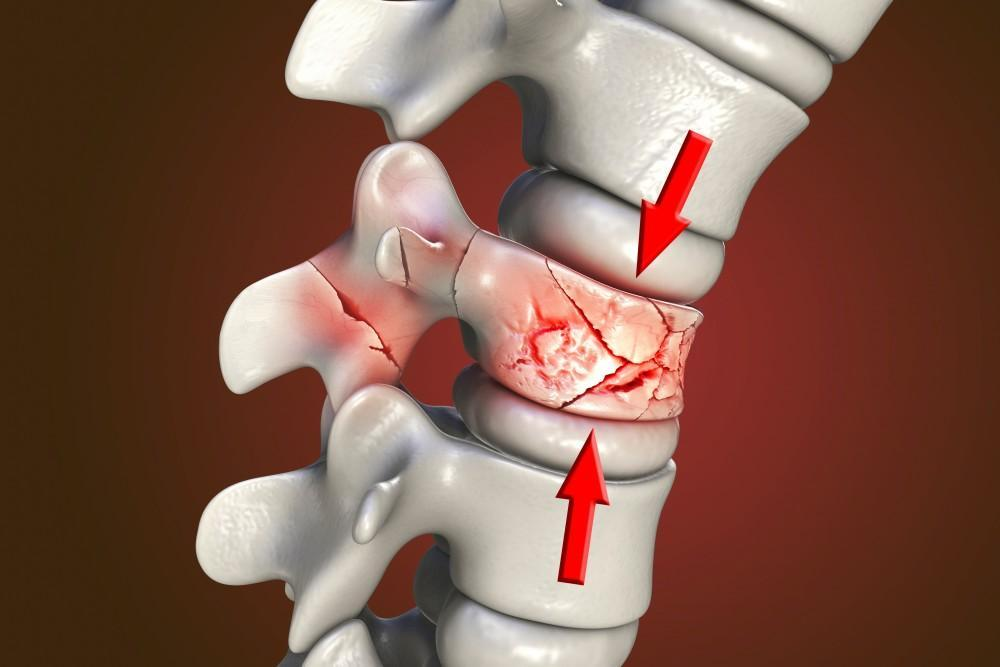
compression fracture
the bone is crushed
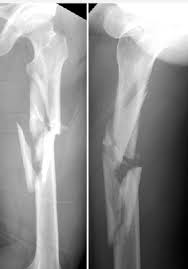
spiral fracture
caused by twisting; break at an angle
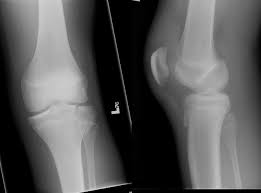
epiphyseal fracture
break at the growth plate; epiphysis separates from diaphysis
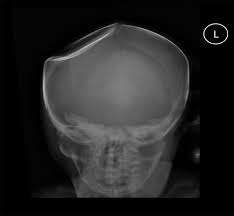
depressed fracture
dent in skull
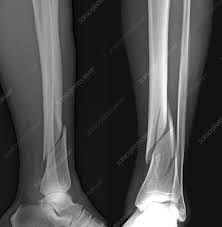
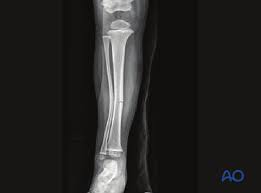
greenstick/buckle fracture
bone doesnt shatter all the way thru
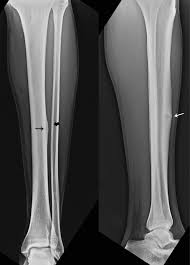
stress fracture
caused by overuse injury; tiny fracture lines
bone repair process
1. hematoma formation
2. callus formation
3. callus ossification
4. bone remodeling
osteopenia
abnormal reduction of bone mass; bone demineralizes
osteoporosis
a condition in which the bones become fragile and break easily; compact bone gets thinner, spongy bone has fewer trabeculae
number of adult bones
206
axial bones
skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
appendicular bones
upper and lower extremities, shoulder and hip bones
osteon
functional unit of compact bone (each cylinder); run parallel to the diaphysis
central canal
where the blood vessels and nerves travel in compact bone
concentric lamellae
layers of osteon with with bone cells in between (compact bone)
canaliculi
hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
perforating canals
lie at right angles to the central canal
flexion
decrease angle of joint
extension
increase the angle of a joint
hyperextension
extension beyond anatomical position (180)
lateral flexion
trunk moves away from the midline; between the cervical and lumbar region
abduction
movement away from the midline
adduction
movement toward the midline
radial deviation
abduction of the wrist
ulnar deviation
adduction of the wrist
circumduction
proximal end is stationary, distal ends move in circular motion
lateral rotation
move limb laterally
medial rotation
move limb toward the midline
depression
lowering a body part
elevation
raising a body part
protraction
moving a body part forward
retraction
moving a part backward
inversion
sole of foot facing inward
eversion
sole of foot laterally
plantar flexion
point toes
dorsiflexion
flex toes
TMJ joint
modified hinge joint; articulates with the head of the mandible and the temporal bone
AC joint
articulates with the acromial end of the clavicle, acromion of the scapula
- supporting ligaments: AC ligament, and coracoclavicular
glenohumoral joint
head of humerus in glenoid cavity
- glenoid labrum, coracoacromial ligament, glenohumeral ligament
separation
acromion and the acromial end of the clavicle separate
dislocation
head of humerus moves down out of the glenoid cavity
elbow joint
hinge joint formed by humerus, ulna, and radius
- tricep and bicep brachii
radial collateral ligament
connects the lateral epicondyle of the humerus to the radius
ulnar collateral ligament
connects the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the ulna
annular
ring around the head of the radius
hip joint
articulate with the acetabulum and head of femur
- acetabular labrum
iliofemoral ligament
strongest ligament in the body; ilium to the femur
ischiofemoral ligament
connects ischium to femur
pubofemoral ligament
pubis to femur
medial meniscus
cartilage in the knee between the femoral condyle and the medial tibial plateau
lateral meniscus
cartilage in the knee between the lateral femoral condyle and the lateral tibial plateau
prepatellar bursae
between patella and skin
lateral collateral ligamant
runs from the femur to the fibula
medial collateral ligament
attaches the femur to the tibia
anterior cruciate ligament
ligament in the knee that attaches to the anterior tibial and connects to the posterior femur
posterior cruciate ligament
attaches posterior tibia and attaches to the anterior femur
sprains
injuries to the ligaments around a joint
bursitis
inflammation of a bursa
tendonitis
inflammation of a tendon
arthritis
inflammation of a joint
osteoarthritis
inflammation of the bones and joints; cartilage thins to result in bone on bone
rheumatoid arthritis
a chronic autoimmune disorder in which the joints and some organs of other body systems are attacked