JC + MO + SC mix
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
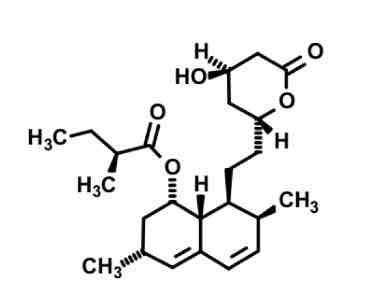
Lovastatin
cyp3A4 substrate- highly lipophilic
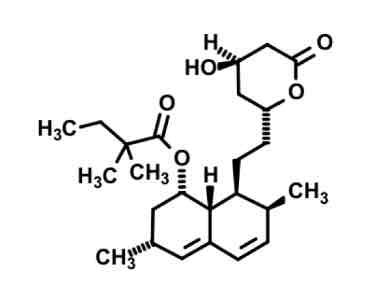
Simvastatin
cyp3A4 substrate— highly lipophilic.
Added steric bulk with two CH3 (isopropyl(?)) to lessen ester hydrolysis in gut.
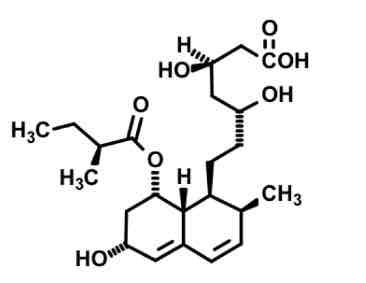
Pravastatin
more polar due to OH = less 3A4 metabolism by kidney
Less potent
Has open ring to readily bind / not a prodrug.
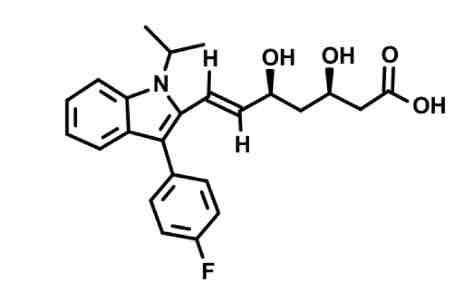
Fluvastatin synthetic
open OH chain to COOH binds mevalonate site
lipophilic anchor binds cholesterol site (stops after double bond)
Added fluorine, heterocyclic ring with isopropyl group, weird pentagon
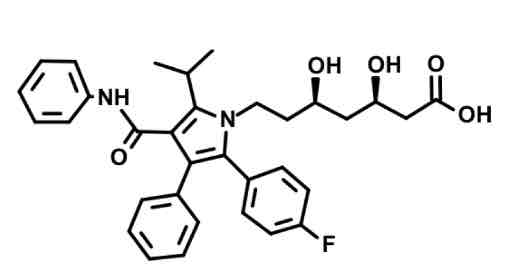
Atorvastatin
LONG t1/2 due to slow metabolism of lipophilic anchor
fluorine, heterocyclic ring with N, and amine group on lipophilic anchor for cholesterol binding site
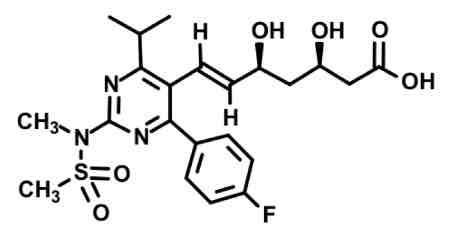
Rosuvastatin aka SUPERSTATIN
Sulfone group very lipopholic substituent
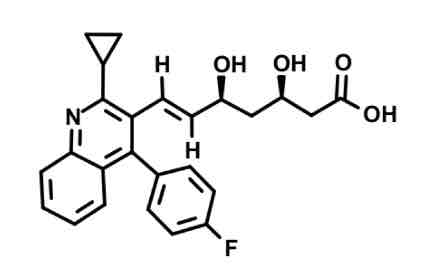
Pitavastatin
Alien triangle comes off of N-heterocycle
Weaker vs atorva/rosuva
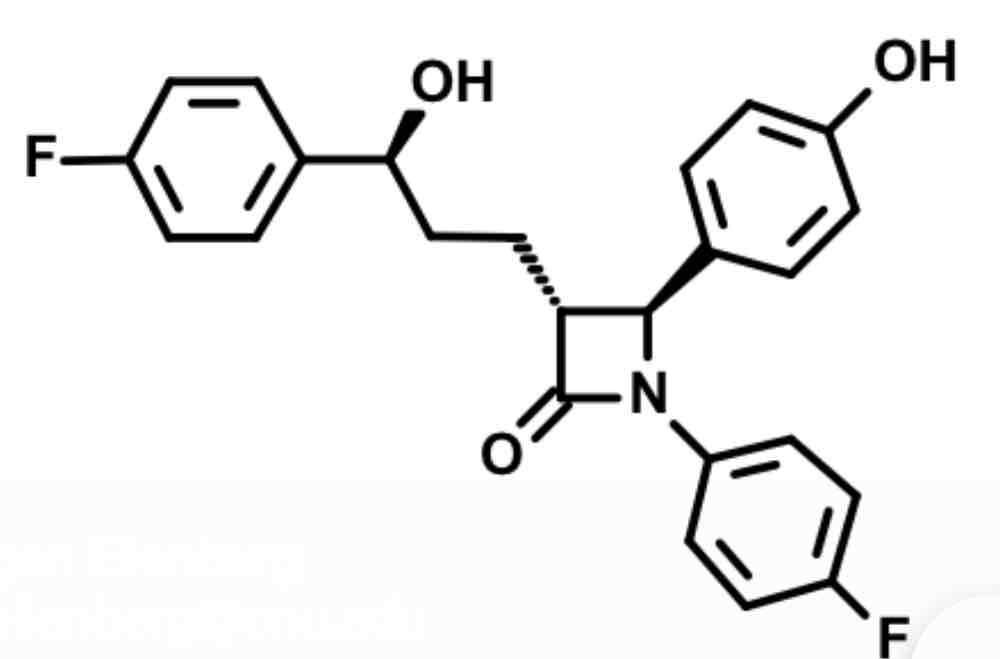
Ezetemibe- cholesterol absorption inhibitor
beta lactam square boi with =o covalently binds to target
This inhibits annexin1/caveolin1 transport protein complex in GI Which normally binds to Nieman Pick receptor.
can’t bind NPC1L1 = decrease serum cholesterol and liver cholesterol esters
Why does it make sense that statins will effectively inhibit the biosynthesis of cholesterol?
The shape of the molecule allows for the lipophilic section to anchor into the cholesterol site & the hydrophilic chain to bind the mevalonate site.
Occupation of cholesterol binding site
Cascade can’t continue
Less cholesterol biosynthesis
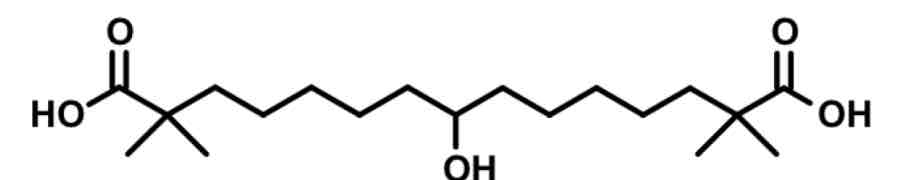
Bempedoic Acid— ATP citrate lyase inhibitor
symmetrical prodrug with methyls alpha to COOH to avoid stepwise b-oxidation metabolism
converted to active form= added acetyl coA
ACoA is long with phosphate, pentagon, then double ring with 5N
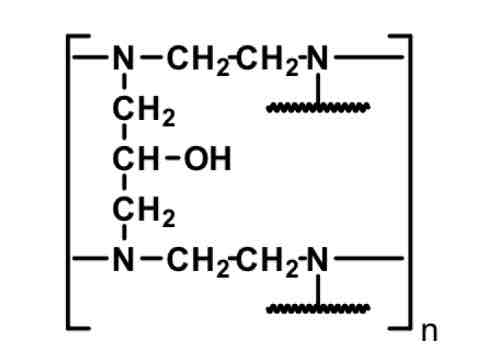
Colestipol— Bile Acid Sequestrant
polymer
N has H+ when it becomes protonated in HCl within stomach. This is why we avoid with use of PPI, H2ant, ca carb
Bile acid biosynthesis: RLS and features
Bile acid synthesis accounts for 90% cholesterol use and eventually becomes waste
RLS is cholesterol-7a hydroxylase which adds OH to B ring
Eventually becomes an ampiphilic molecule with its ability to conjugate with AA which have ionized terminuses
Ampiphilicity of bile acids
Lipid parts: grab fats
polar AA part: keep dispersed in water; usually glycine or taurine
rx target: solubilize fats in aqueous environment to eliminate more cholesterol in poo
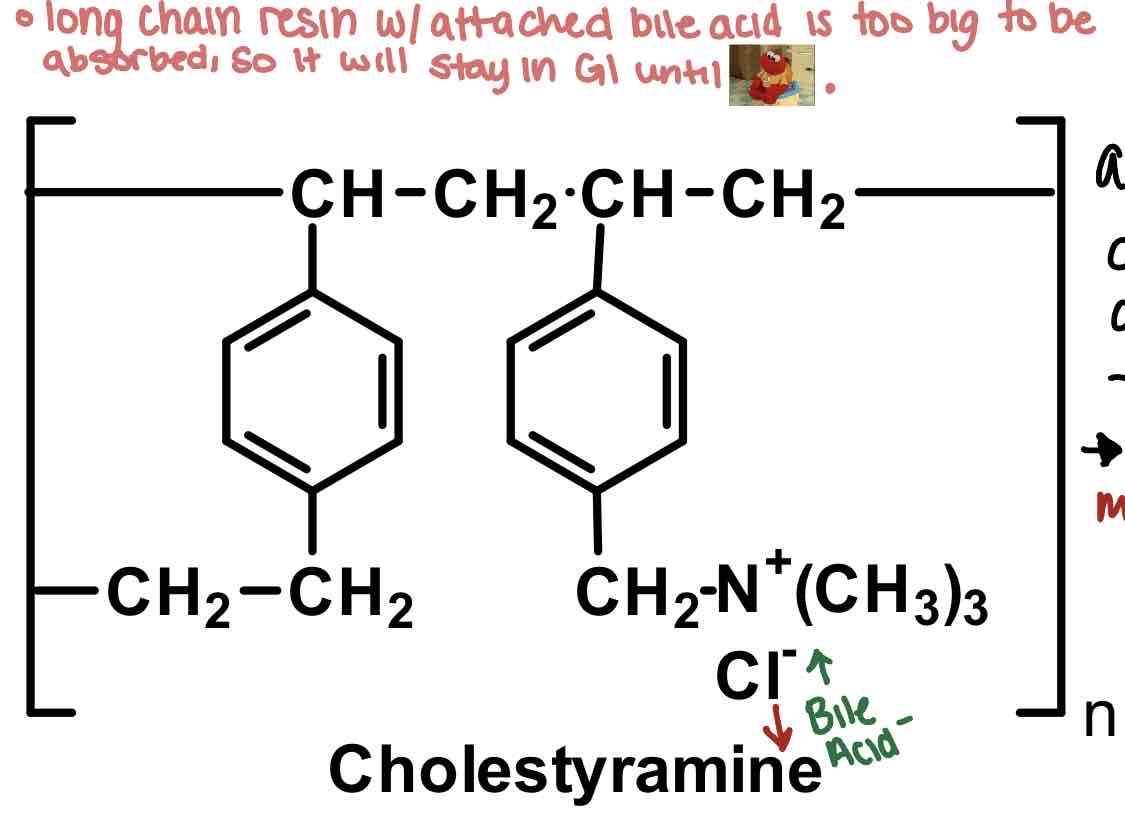
How do bile acids work: example cholestyramine
BAS like cholestyramine are LONG CHAIN ion exchange resins that are too big to be absorbed. exchange Cl- for bile acid negative terminus.
yes we are exchanging negative for negative here but that is because there is a stronger attraction between bile acid- than Cl- (to drug)
always has 4* ammonium so no activation
Weird texture may deter use for patients
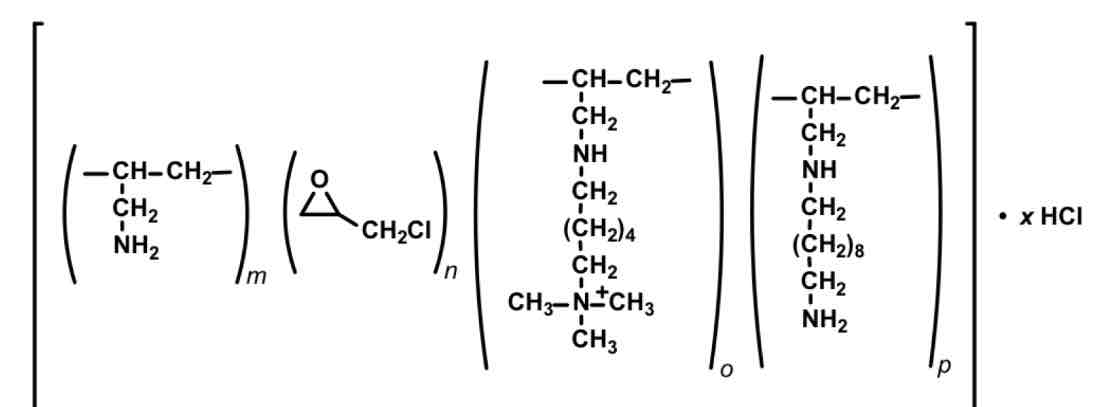
Colesevelam— bile acid sequestrant
HETEROPOLYMER
Tablet 3tab BID
Less interactions, more palatable
What is one consideration to take when giving bile acid sequestrants
ALL highly negatively charged drugs can bind by mistake (unintended consequences)
statin
warfarin, thyroid hormones
NSAID
Fat sol vitamins ADEK
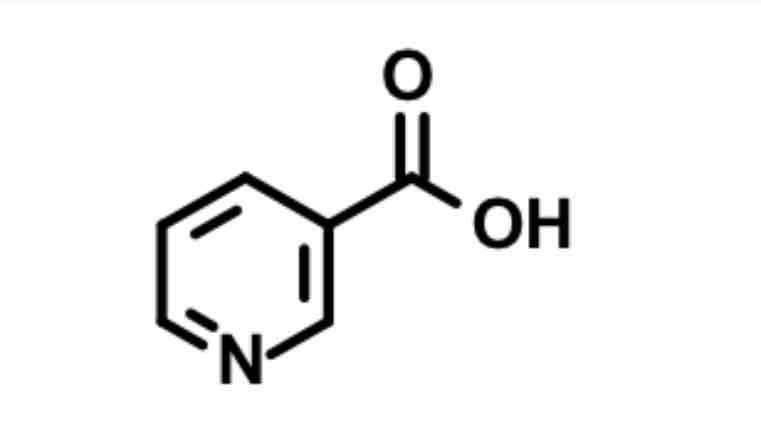
Niacin / nicotinic acid
Agonizes small Gi to inhibit cAMP & acts as PPAR activator (activate LPL for degradation)
decreased mobilization of FA
XR = less flushing, can minimize flushing with NSAID
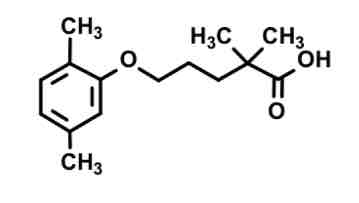
gemfibrozil— fibrate
double methyl alpha to COOH prevents beta oxidation metabolism
COOH provides binding
Chain of X length = receptor activation
Acid (?)
Medium level effectiveness at enhancing LPL
Because fibrates are PPAR activators; what other effects do they have
More lipids processed = lesser lipid conc
insulin sensitizing
Lipid homeostasis by reducing TG and mid level blood glucose lowering
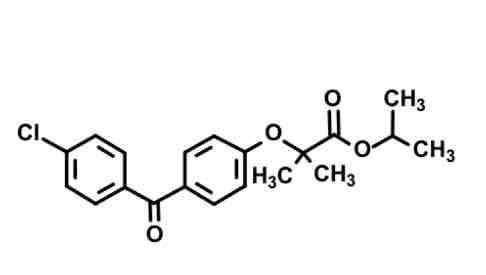
fenofibrate— fibrate (ester prodrug)
Cl, benzene, =o, benzene with ether chain to eater and isopropyl
Cleavage of isopropyl ester: yields active form with COOH terminus
Gemini twins still here (geminal dimethyl) to reduce B-oxidation metabolism.
Fibrate considerations
acid form highly lipophilic highly protein bound
Enterohepatic recycling - increase t1/2
Elimination limited: free acids or cool glucuronides in urine or bile
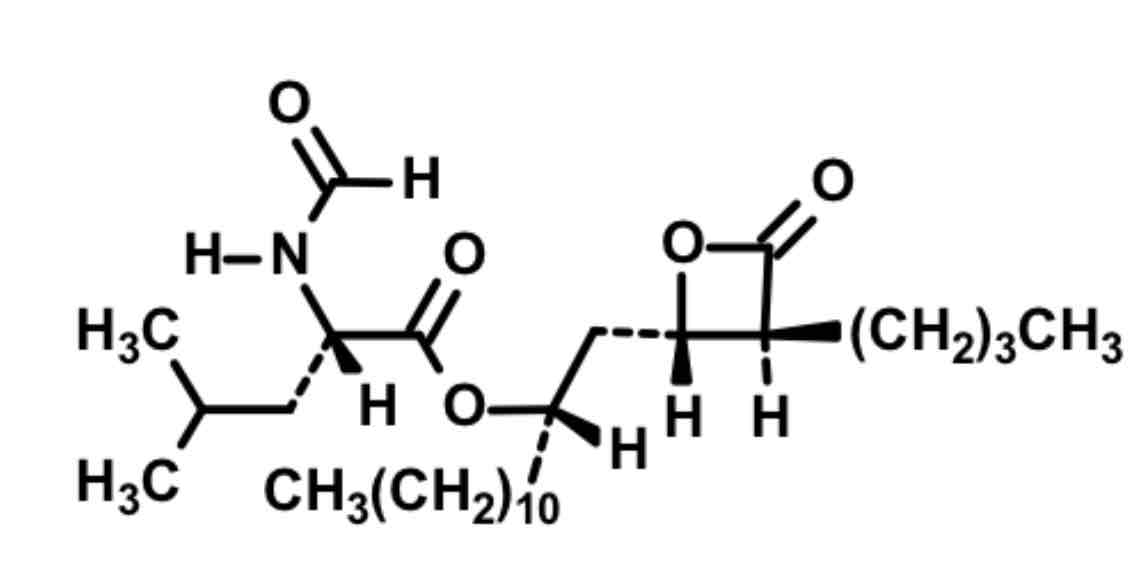
Orlistat: intestinal lipase inhibitor
Reactive Square boi with O but different from ezetimibe because there’s no F on molecule
Mimics glycerol
Ester chain
Binds and blocks as false substrate to serine on intestinal enzyme = poop out fats instead of absorb
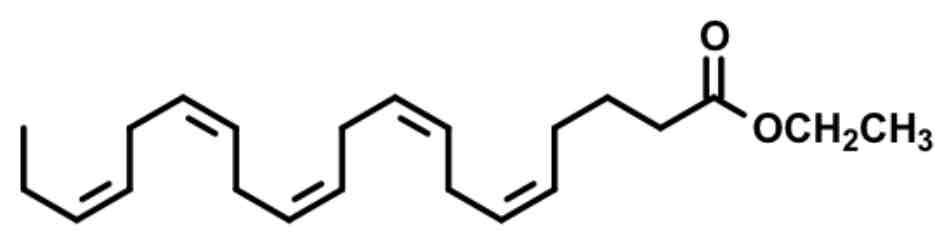
eicosapentaenoic acid 20:5 — omega 3 FA
chain linkages: eskimos had better lipid profiles eating lots of fish fats
Less sticky fats, less sticky plaques
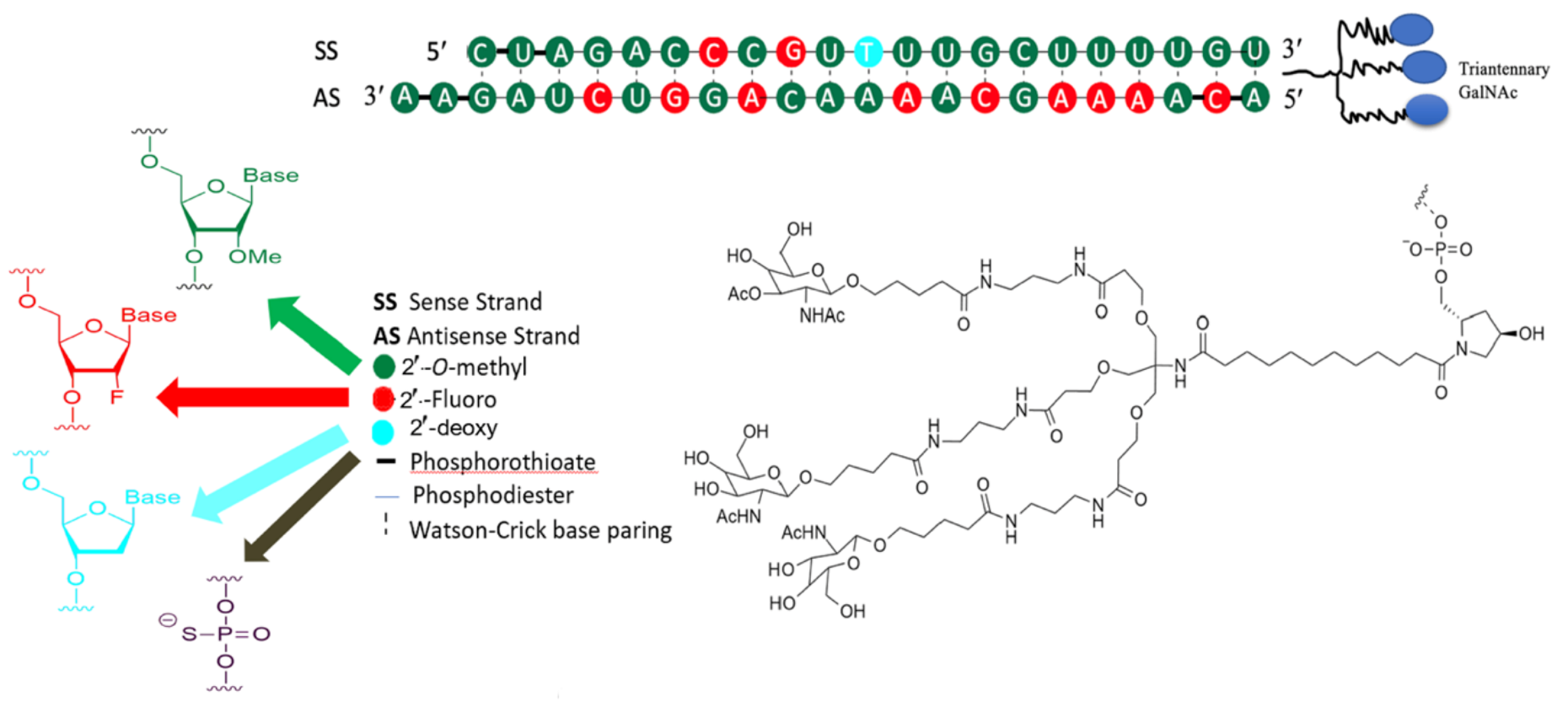
inclisiran siRNA
Modification of nucleic acids to add: fluorine or OMe
(MO) response to inhibition of chokesterol absorption by ezetimibe
decreased chylomicron synthesis & remnant transport to liver
INCREASED LDL RECEPTOR EXPRESSION
INCREASED CHOLESTEROL SYNTHESIS (hmg coa REDUCTASE increase)
Blocks apical NPC1L1
MO ezetimibe rat
Inhibits absorption of cholesterol when bound to apical NPC1L1
usually acts to package ApoB100 into chylomicrons
When inhibited with ezetimibe: decreased cholesterol transport to liver & upreg of LDL-r
(MO rat) Statin pleiotropy
Inhibit statins =
decrease cholesterol biosynthesis
reduced FA molecules that are used in the prenylation of small G protein ATPases so they cant get to location or function right
Equals helpful CV effects- disruption of VSMC proliferation and migration
ACLi: Bempedoic Acid MOA
Prodrug
activation by ACS
works upstream of HMG CoA reductase but only act in liver and fat
no skeletal muscle action means no myopathy
(MO rat) Bile Acid Sequestrant MOA
Nonsystemic Inhibition of the reabsorption of cholesterol by
keeping them in the GI tract (JC ion exchange resin AA- in exchange for Cl-)
Increase LDL-r expression
Fibrates: PPAR activators interaction
Statins especially gen fibrosis cause myopathy in combo
Which decrease enterohepatic recycling
Bile acid sequestrants
Niacin MOA / SE
Increase HDL via increased ApoA-I
causes flushing bc prostaglandin release and niacin GPCR
Can minimize with aspirin/nsaids
Omega 3 FA MOA
Decrease triglycerides
Decrease VLDL synthesis
Increase b-oxidation of FA
increase LPL activity
PCSK9i: Moab MOA
AKA PCSK9 degraders:
Attach to PCSK9 antigen on the surface of LDL receptors to inhibit degradation by lysosomes
indirect PCSK9i: inclisiran MOA
modify nucleic acids of sugar phosphate backbone by adding fluorine or OMe group to disguise it from enzyme bounty hunters which mark for degradation. Because the antisense strand can not bind to the enzyme bounty hunters, it will combine with RISC instead. RISC-RNA inducing silencing complex— will then inhibit translation of PCSK9. Thus there will be more LDL-receptor recycling and more LDL-c uptake.
(SC RAT) atherogenesis
LDL enters intimal layer of blood vessel & oxidizes to become trapped & promote a good environment for adhesion molecules
O-LDL becomes ligand for scavenger molecules expressed by macrophages (used to be monocytes)
Phagocytize to foam cells
T cells secrete cytokines & macrophages
cytokines make EC become proinflammatory and activate more macrophages
SMC migrates to become part of plaque
(SC RAT) NO made by eNOS
Atheroprotective
vasodilation
Inhibition of platelet aggregation
Inhibition of monocyte adhesion
Inhibits SMC migration + proliferation
Inhibits oxidized LDL
(SC RAT) ABI to test for PAD
Good: 1.1-1.25
Bad: over 1.4, under 0.9