Practical applications of molecular biology 2
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Analysing RNA and proteins
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Reverse transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
Total mRNA purified from cells.
Use PCR to get cDNA clone of a gene
First primer added to mRNAs, reverse transcriptase used to make cDNA strand specific to the RNA sequence of interest.
Second primer added, and the DNA molecule is amplified through many cycles of PCR.
Quantitative RT-PCR
Expression of individual genes can be measured using this.
Dyes added to the PCR fluoresce when bound to the dsDNA (Used to track the progress of the mRNA amplification)
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
Reverse transcriptase is used to copy all RNAs into cDNAs, which are fragmented and sequenced by next-gen sequencing methods (NGS).
Identifies and provides information about their relative abundance.
Global analysis of mRNAs by RNA- seq provides a snapshot of gene expression.
Purifying proteins
Proteins can be released from bacteria by lysis and precipitation with ammonium sulphate.
Analysing proteins:
Western blotting
Mass Spectrometry
X-ray diffraction/ nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
Proteins can be further separated by:
chromatography (types can be used in succession)
immunoprecipitation
SDS polyacrylamide- gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (isoelectric point)
Column chromatography
Sample components travel at different rates through the column and are fractionated into different tubes.
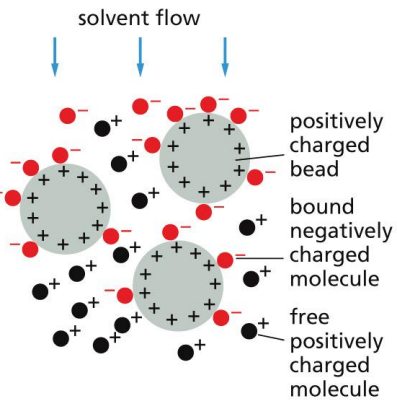
Ion- exchange chromatography
slows the movement of molecules of opposite charge
Matrices used include diethylaminoethylcellulose (DEAE-cellulose) = +vely charged or carboxymethylcellulose (CM-cellulose)= -vely charged.
Strength of association depends on ionic strength and pH of the solution.
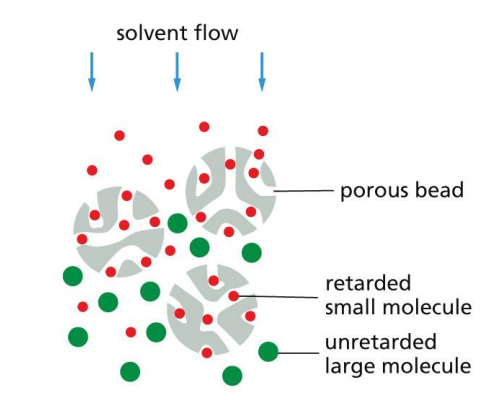
Gel-filtration chromatography
Inert porous beads form the matrix.
Beads of cross-linked polysaccharide (dextran, agarose, or acrylamide) are available commercially in a wide range of pore sizes.
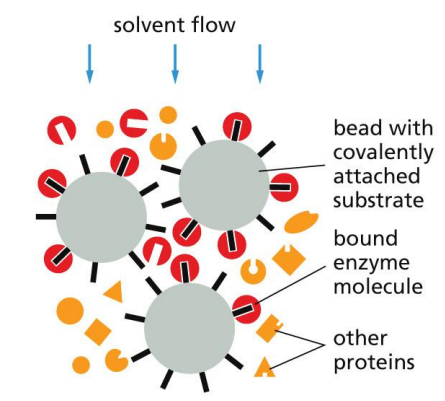
Affinity chromatography
Matrix covalently linked to a specific ligand (e.g. antibody or enzyme substrate) that will bind a specific protein.
Molecules that are binded can be removed with concentrated salt solution or solutions of high or low pH.
Immunoprecipitation
A rapid affinity purification method.
Small agarose beads that has specific antibody for the protein.
In a suspension for a period of time.
Beads collected at low speed centrifugation, unbound proteins discarded.
What detergent and reducing agent is used to solubilise the proteins in SDS-PAGE?
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and ß-mercaptoethanol.
SDS-PAGE
SDS-protein complex (-ve) migrates, smaller are faster.
What can give an incorrect mass estimate in SDS-PAGE?
Modifications e.g phosphorylation or carbohydrates can change migration.
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
Protein —> proteome
provides greater protein separation than 1 dimensional SDS-PAGE
At low pH= proteins is +ve, at high pH= proteins is -ve, between the extreme pH there is mixture of charges.
When fixed pH gradient is subjected in the appropriate direction, each species migrates until it forms sharp band at isoelectric point (no net charge).
Western blotting
Small amounts of single rare protein can be detected in a complex mixture of other proteins.
Separated in gel, stained with Coomassie blue, proteins transferred to membrane and exposed to antibodies for specific protein, unbound antibodies washed away and antibodies bound detected by fluorescent label.
MS
Highly sensitive method to identify unknown proteins
Gaseous peptides in condition where most molecules are positively charged
Ions accelerated and separates based on mass and charge.