AP Bio Unit 1
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
oxygen being more electronegative than hydrogen
How does the chemical structure of water result in polarity?
Water can bond with the positive and negative regions of other molecules
How does water’s polarity result in cohesion and adhesion through hydrogen bonds?
water’s heat resistance helps aquatic life maintain their internal body temperature, and ice’s ability to float on liquid water provides insulation between the air’s freezing temperatures and the water & aquatic organisms.
How do living systems depend on the chemical properties of water?
to grow, reproduce, and stay organized.
Why do living system require a constant supply of energy?
nucleic acids
What macromolecule contains carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and hydrogen?
carbon is the backbone of all organic molecules because it have 4 valence electrons, allowing it to make 4 covalent bonds.
What role does carbon play in the construction of life?
covalent bonds
What type of bond connects monomers to form polymers?
dehydration
What reaction builds polymers?
hydrolysis
What reaction breaks down polymers?
hydroxide and hydrogen
What subcomponents form the water molecule through dehydration synthesis?
amino loses hydrogen and carboxyl loses hydroxide.
What terminus loses a hydroxide and which loses a hydrogen?
in the sequence of nitrogen bases.
How do nucleotides store information?
sugar (ribose & deoxyribose), structure (single helix & double helix), and function (librarian & library)
Determine the 3 differences between DNA and RNA.
the properties of their amino acids’ R groups.
What gives different proteins different shapes?
They either bend towards water, away from water, or seek the opposite charge.
Describe how the properties of R groups shape the structure of proteins.
the presence of double bonds in unsaturated fats cause bends in the structure, which makes it less dense and liquid.
Explain why saturated fats are solid at room temperature while unsaturated fats are liquid.
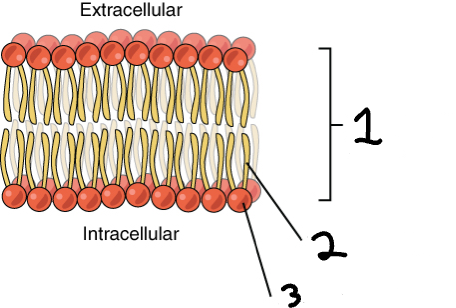
2, 3.
Identify by number the hydrophobic phospholipid tails and the hydrophilic heads.
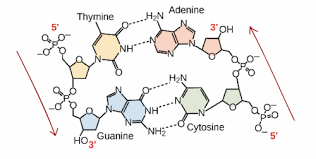
AT
Based on bonds, which nucleotides are more prone to mutation, AT or CG?
dehydration
What chemical reaction connects new nucleotides to the growing strand?
dehydration
What chemical reaction forms the peptide bond?
starch is less branched, glycogen is more branched, and celllulose is linear.
Describe the differences between starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
carboxyl
At what terminus does a new amino acid connect to the sequence?
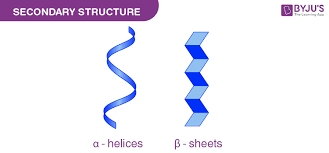
alpha-helix and beta-sheet
What are the two types of secondary structure?
the properties of amino acid’s R groups
How is tertiary structure determined?
primary, secondary, and tertiary (all)
If a change is made at the primary level, which proteins structures are affected?
linear and branched
What are the two structure types of carbohydrates?
3 terminus
At what terminus can nucleic acids be added to the greater nucleotide?
opposite directions
What direction do the nucleotide sequences run in DNA?