Vertebral column,Spinal Cord, Meninges, deep and superficial back muscles
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Portion of it is Quiz #1 content!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Axial
Axis around which the rest of the body moves
Appendicular
Appendages
Name Terminology
Name Terminology
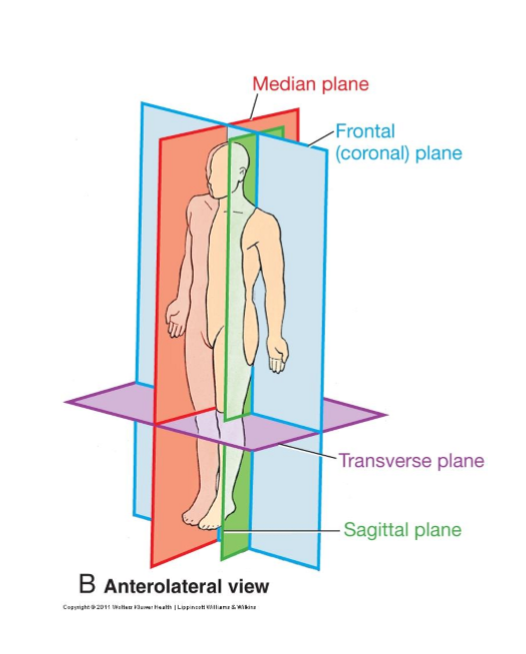
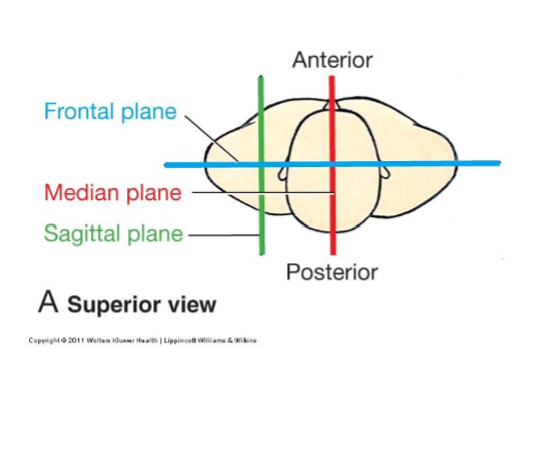
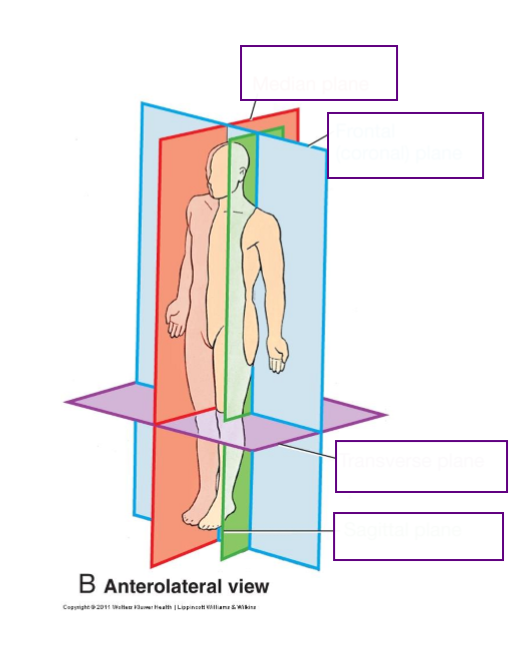
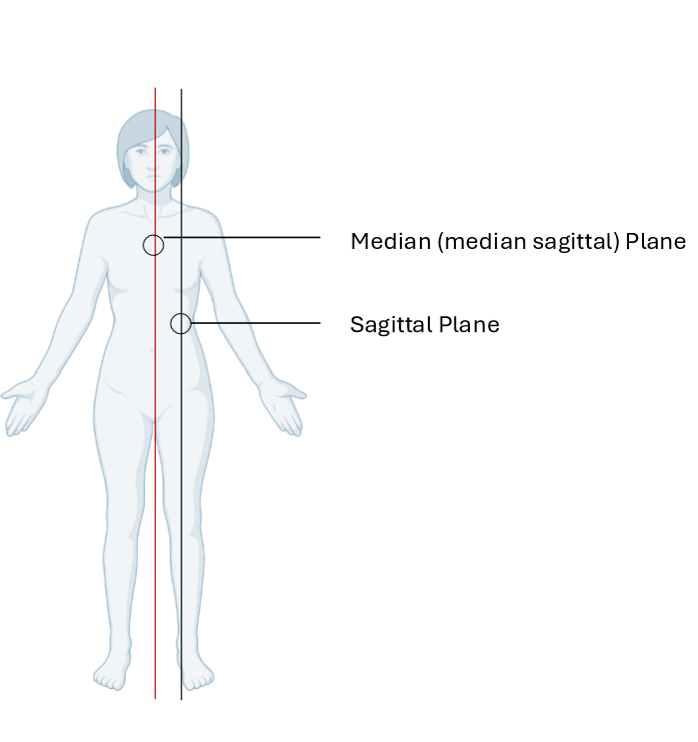
Median (Medial Sagittal) Plane
Vertical plane passing longitudinally through centre of body
Divides body into left and right halves
Sagittal planes
Vertical planes passing through body parallel to median plane
Divide body into left and right portions
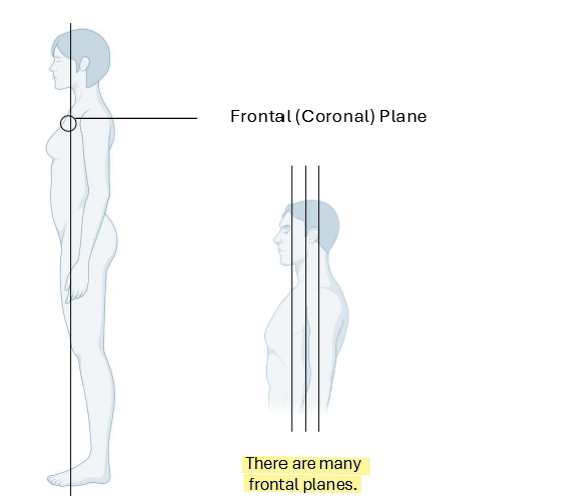
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Vertical planes passing through the body at right angles to medial plane
divides body into Anterior and Posterior portions
Transverse Planes
Pass through body at right angles to median and frontal planes
divides the body into Superior and Inferior portions
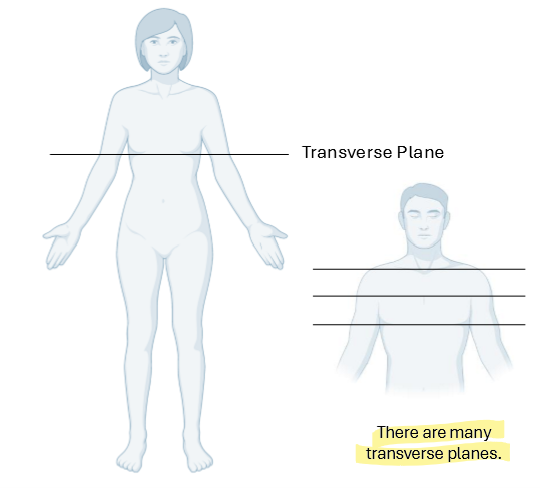
Flexion and Extension
Generally occur in Sagittal Plane
Flexion: Motion that decreases a joint angle
Extension: motion that increases joint angle
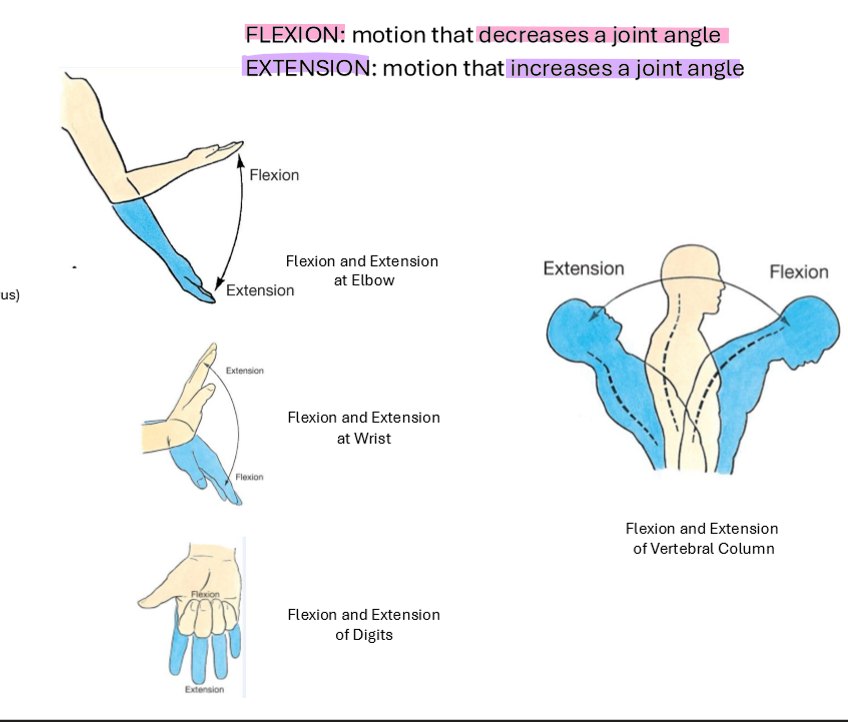
Abduction and Adduction
Abduction: Movement away from the median plane/midline
Adduction: Movement toward the median plane/mindline
*Think ADDuction - “add” to the body
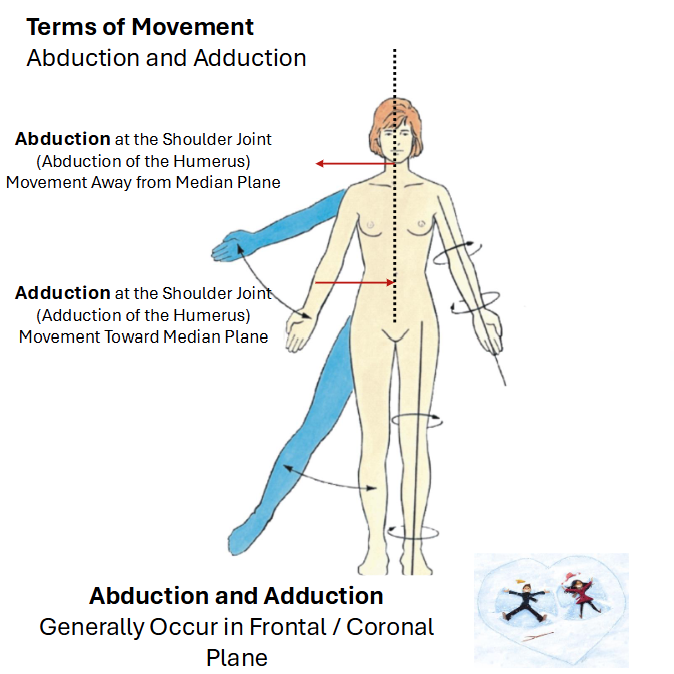
Describe Medial/Lateral Rotation of Humerus
Humerus Revolves Along its longitudinal Axis
Medial Rotation of Humerus:
brings anterior surface of limb closer to median plane
Lateral Rotation of Humerus:
takes anterior surface of limb farther from median plane
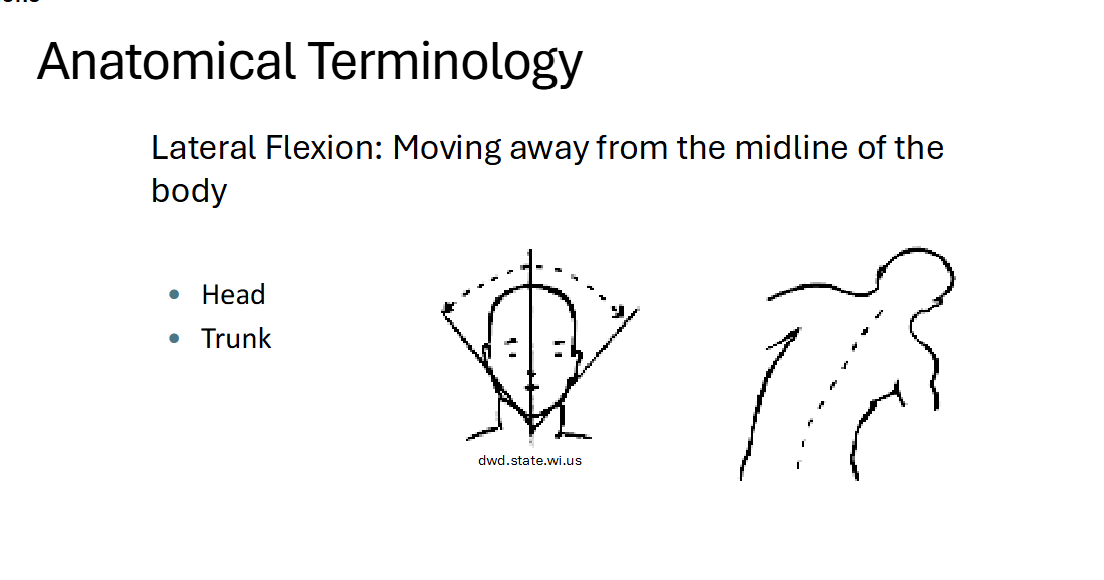
Lateral Flexion
Moving away from the midline of the body
head & trunk
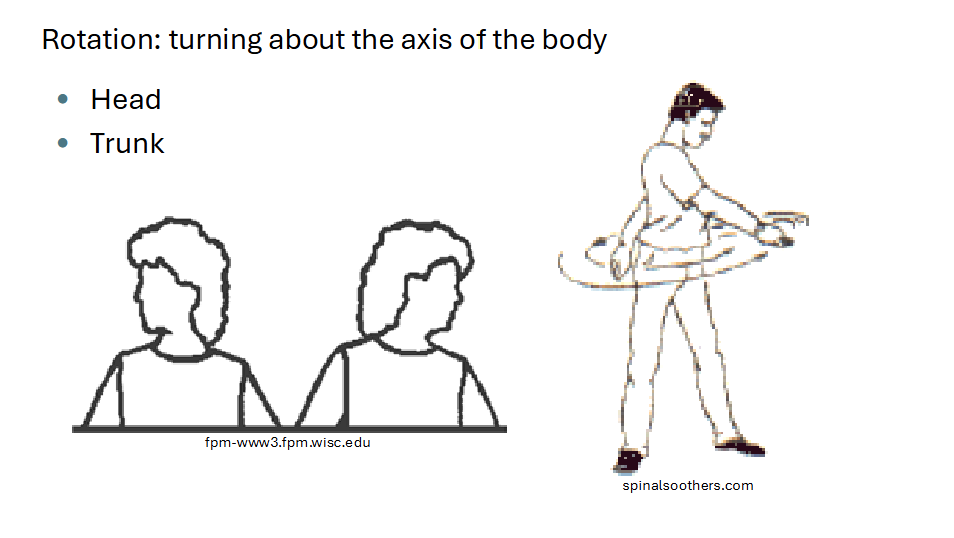
Rotation
Turning about the axis of the body
head & trunk
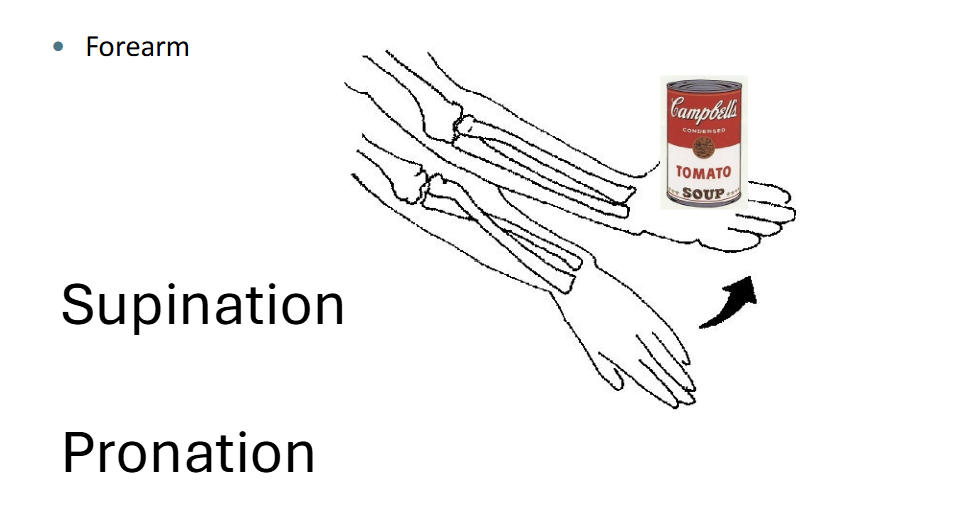
Pronation and Supination
Distal end of Radius swings around proximal aspect of radius
rotates in place
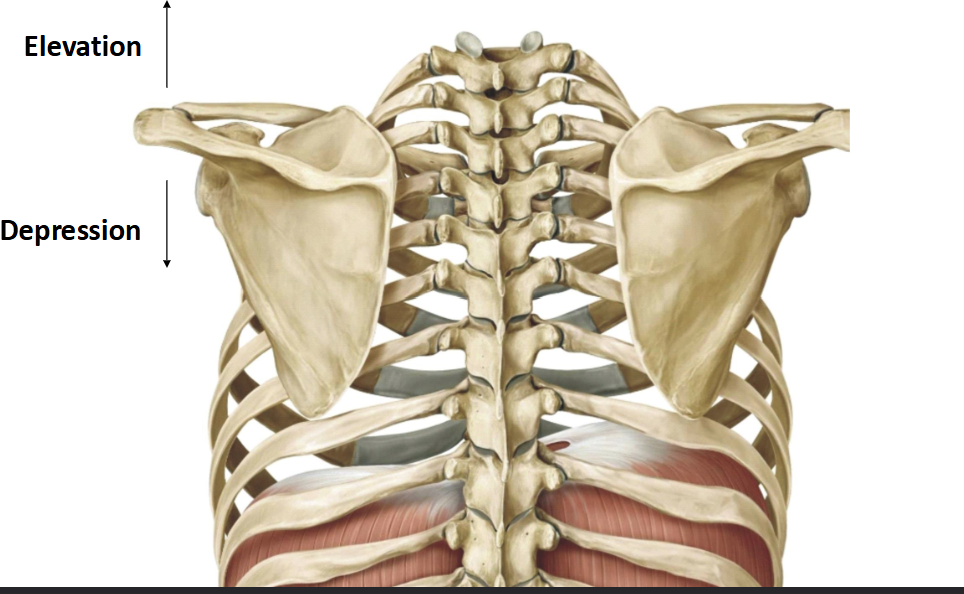
Elevation and Depression
Part of the movement of the Scapula
Retraction and Protraction
Part of the movement of the Scapula
Retraction of Scapula
medial border of scapula moves posteromedially on thoracic wall
Protraction of Scapula
Medial Border of Scapula moves anterolaterally on thoracic wall
Describe the Upward/Downward Rotation of Scapula
Upward
Glenoid Cavity Moves up (Lateral rotation of scapula: relative to inferior angle)
Downward
Glenoid Cavity Moves down (medial rotation of scapula: relative to inferior angle)
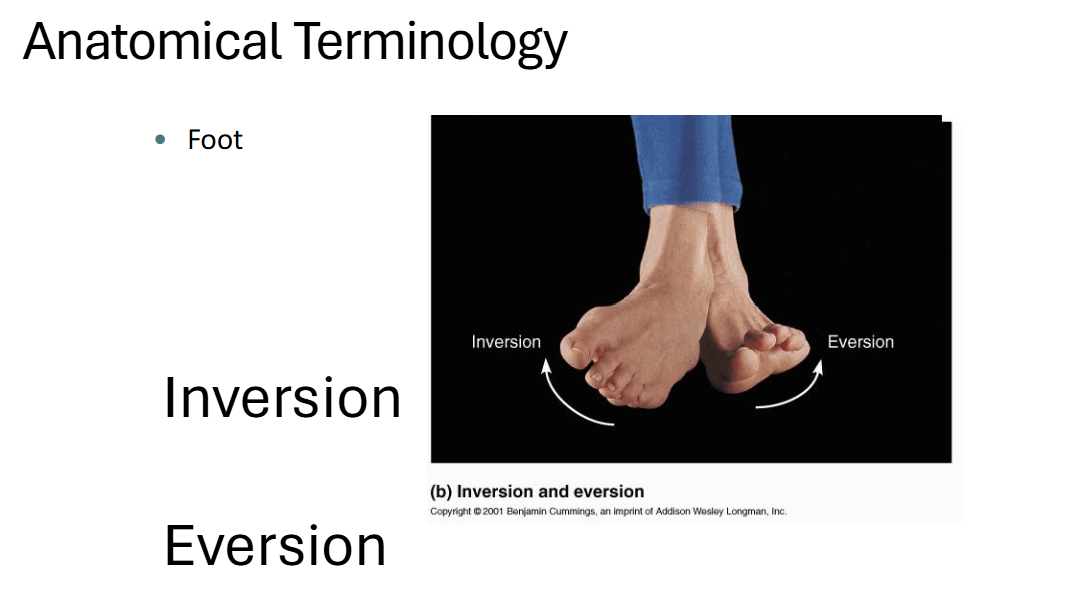
Inversion and Eversion
FEET
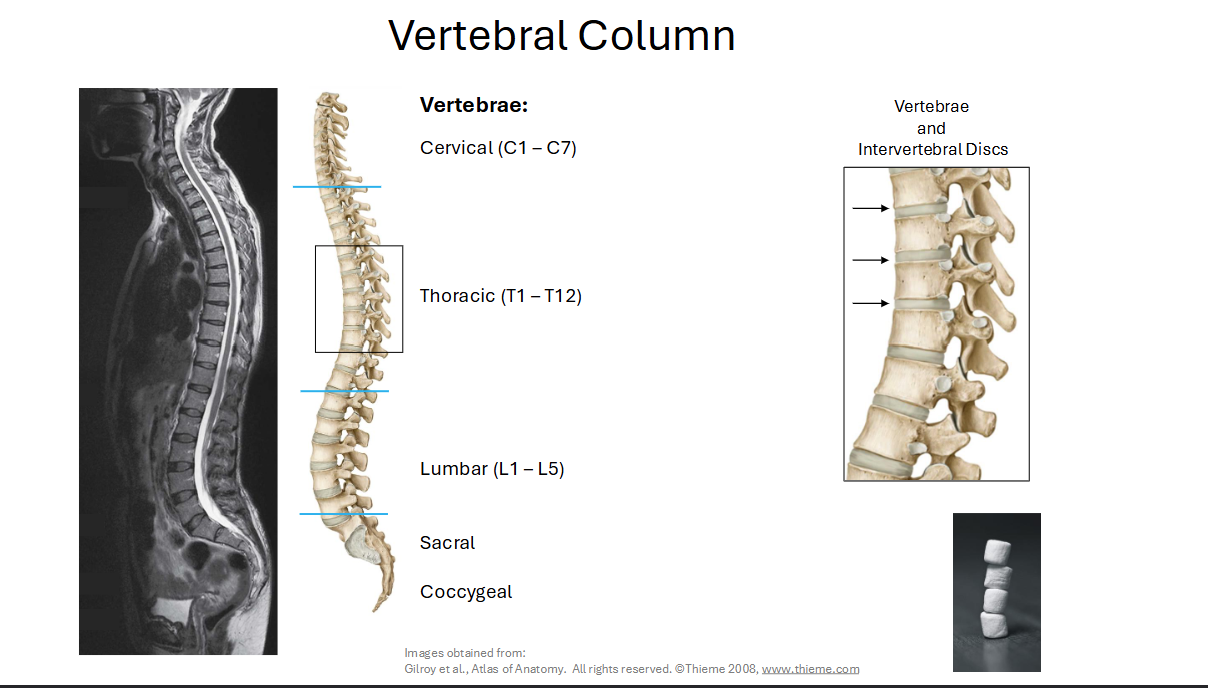
Describe the different sections of the Vertebral Column
7 Cervical Vertebrae → 12 Thoracic Vertebrae → 5 Lumbar Vertebrae → Sacrum (5 sacral Segments that are fused)→ Coccyx (4 Coccygeal Segements that are fused)
Where do Spinal Nerves exit?
Exit the Vertebral Canal at each vertebral level via the intervebral foramina
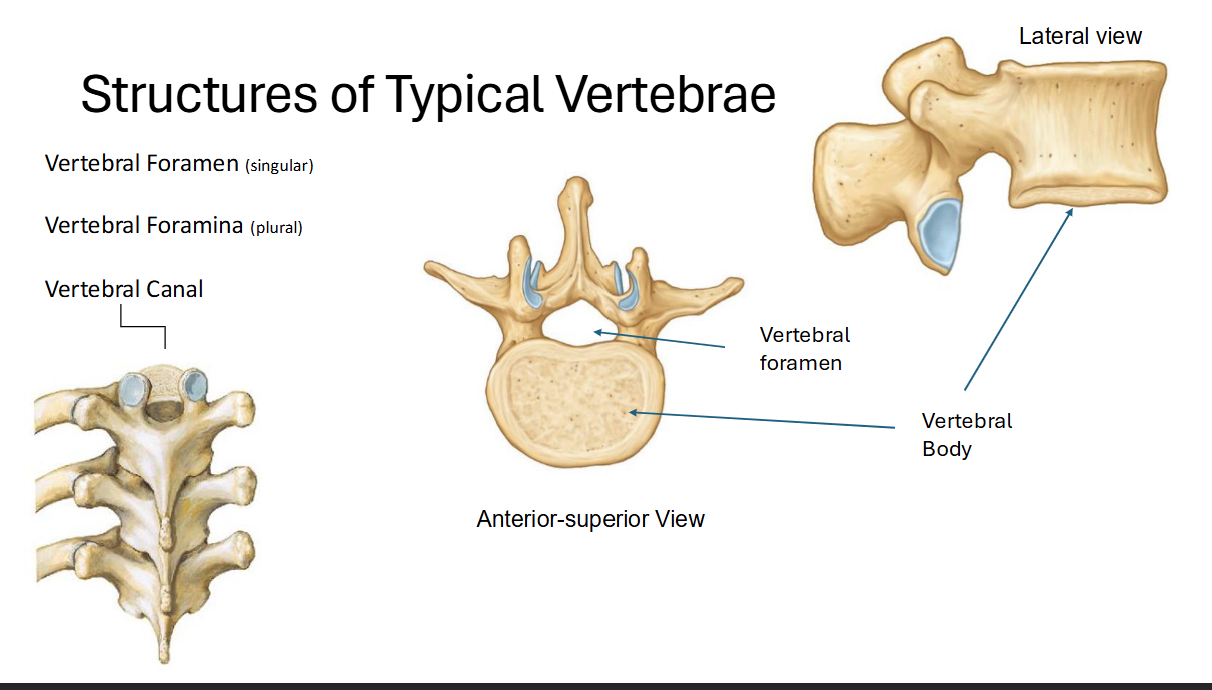
Describe the Vertebral Foramen and Vertebral Body
Foramen is the “hole” in the vertebrae → where nerves travel through
body is basically the main body (self explanatory)
**Vertebral Canal runs right through the middle of the spine! (collection of foramen assembled)
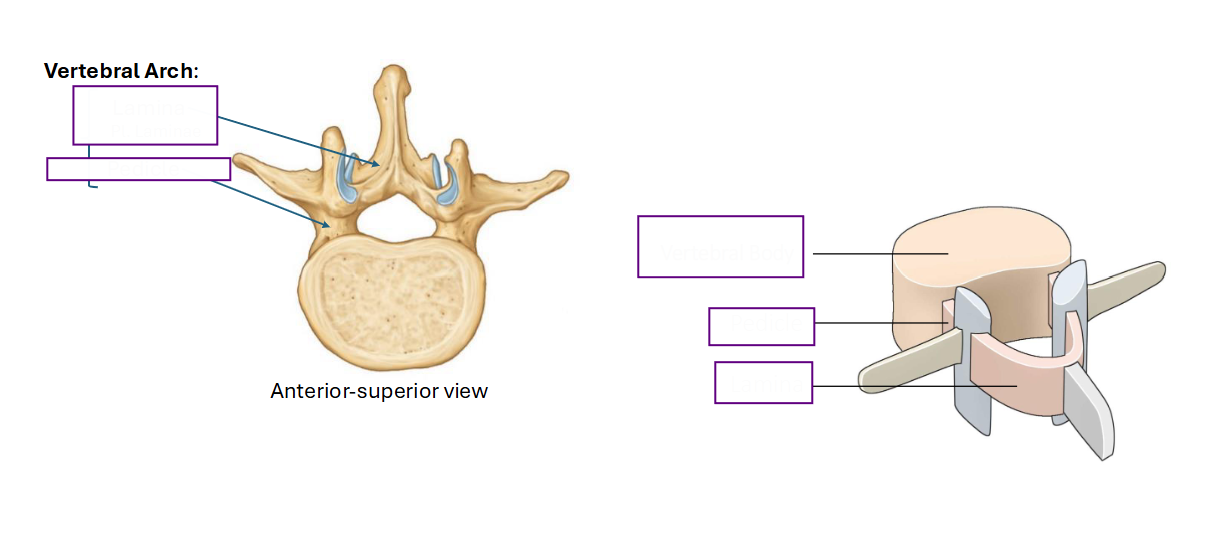
Name the connecting structures of the vertebrae
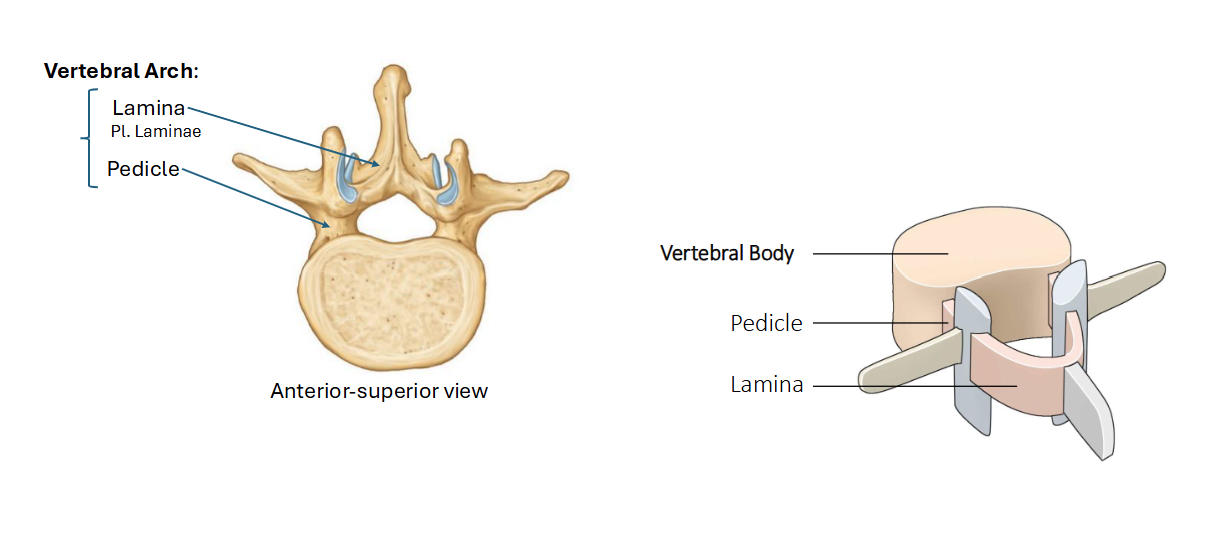
Describe this structure and where it meets
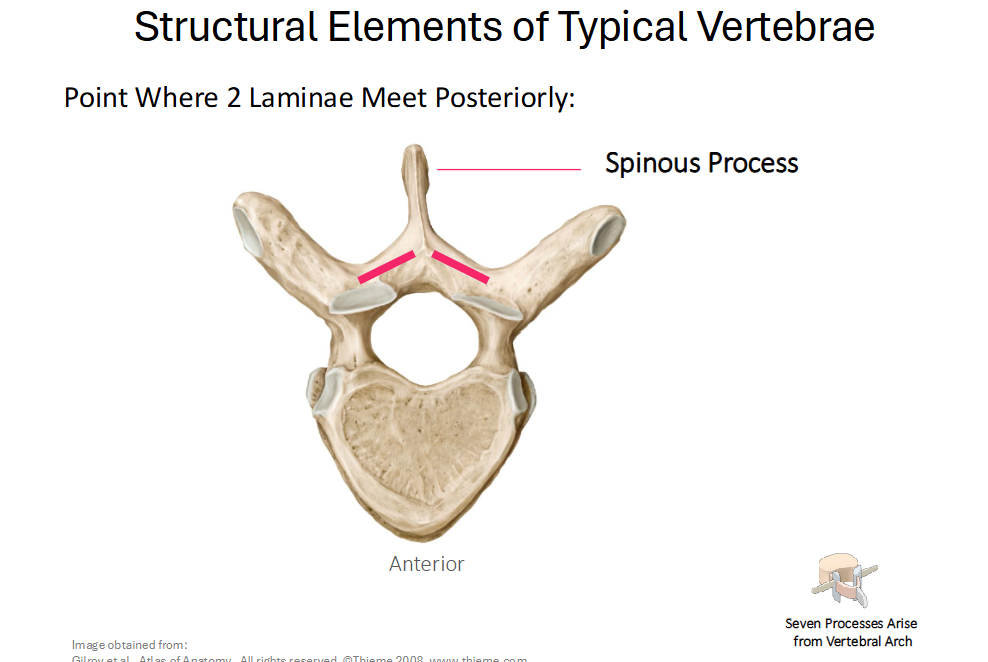
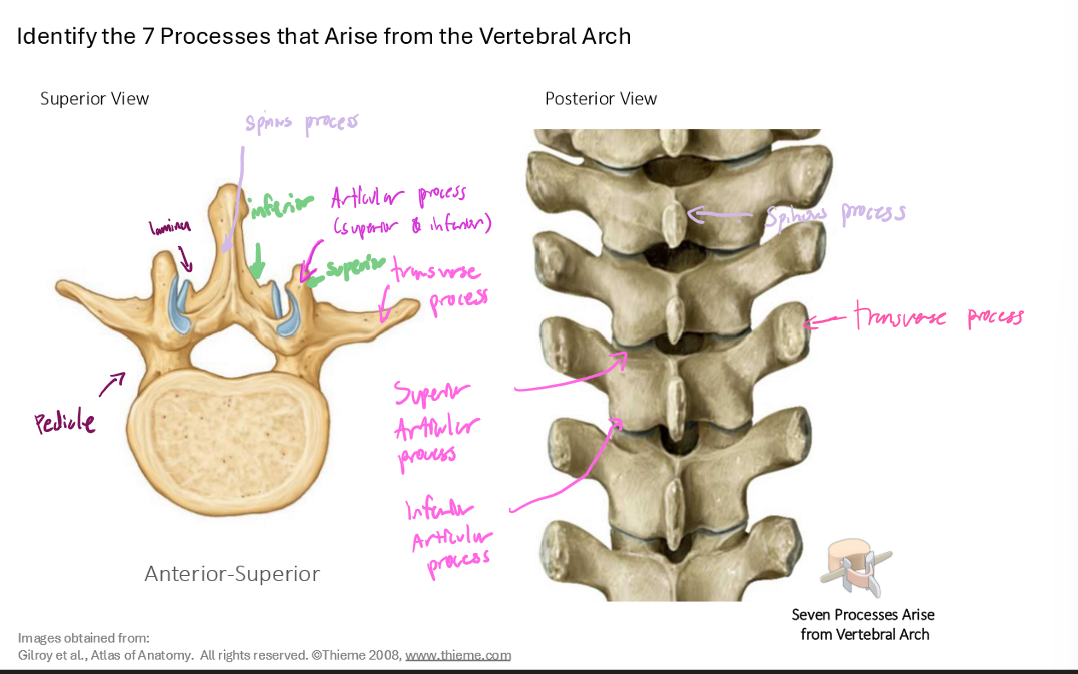
Spinous Process
Point where 2 Laminae meet posteriorly
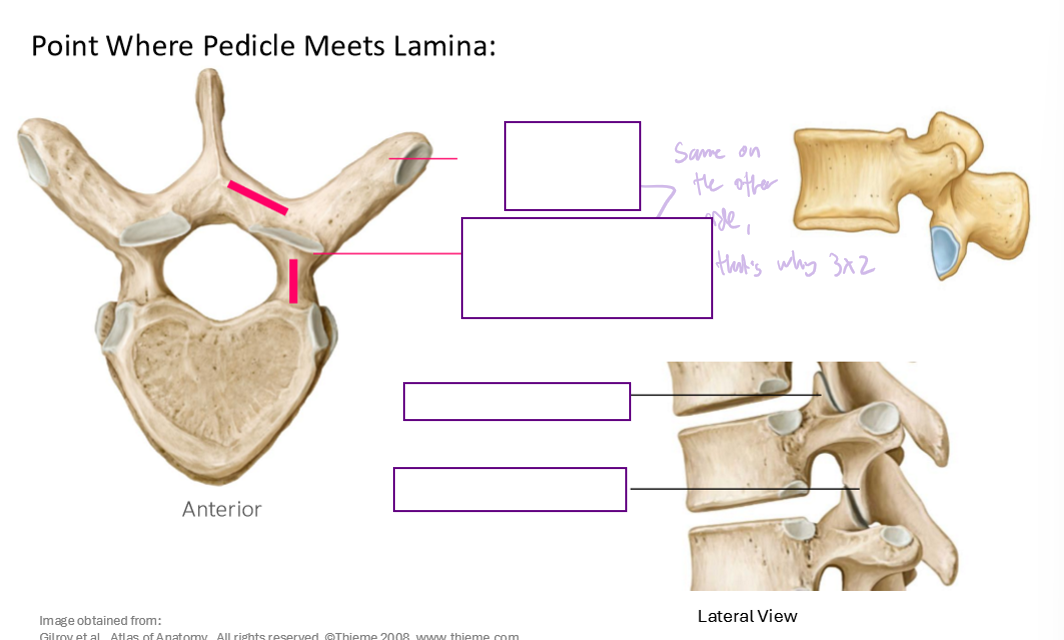
Describe this structure and where it meets
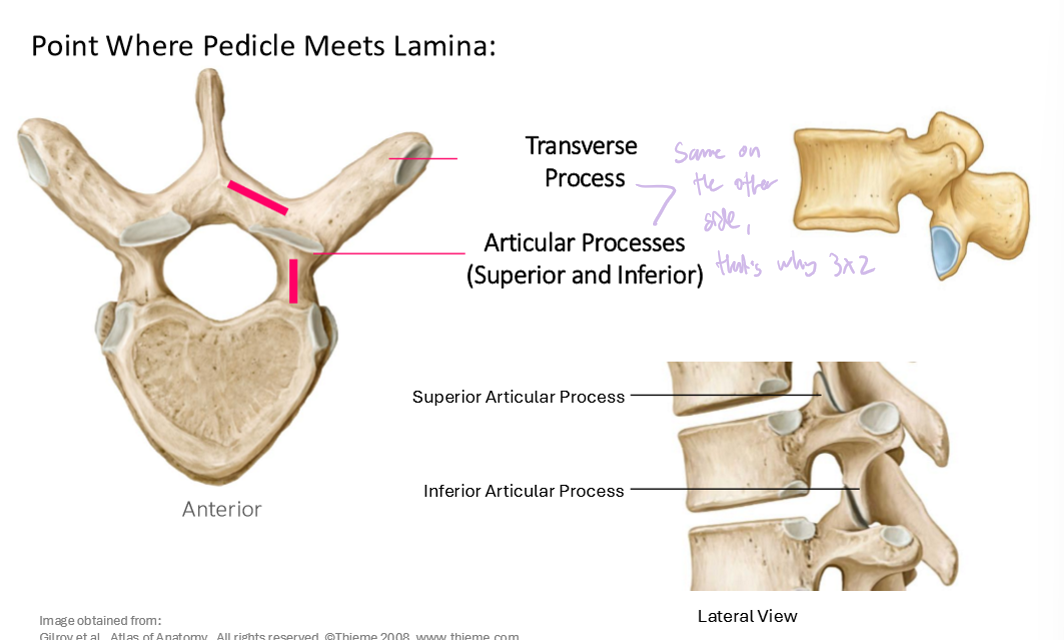
Transverse Process and Articular Process (Superior and Inferior)
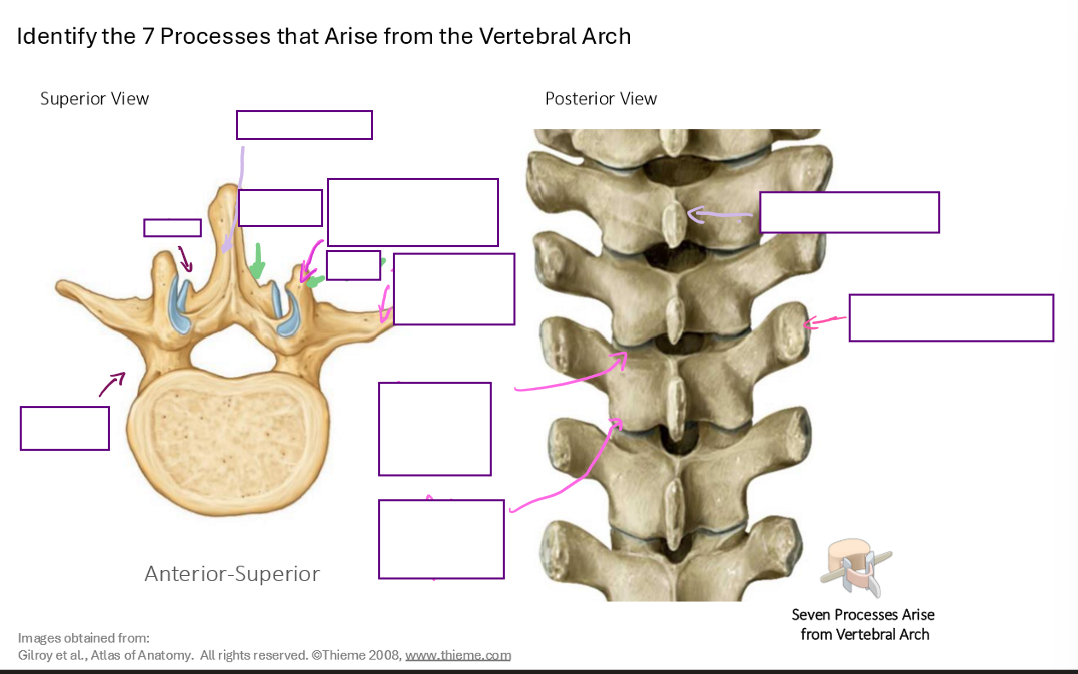
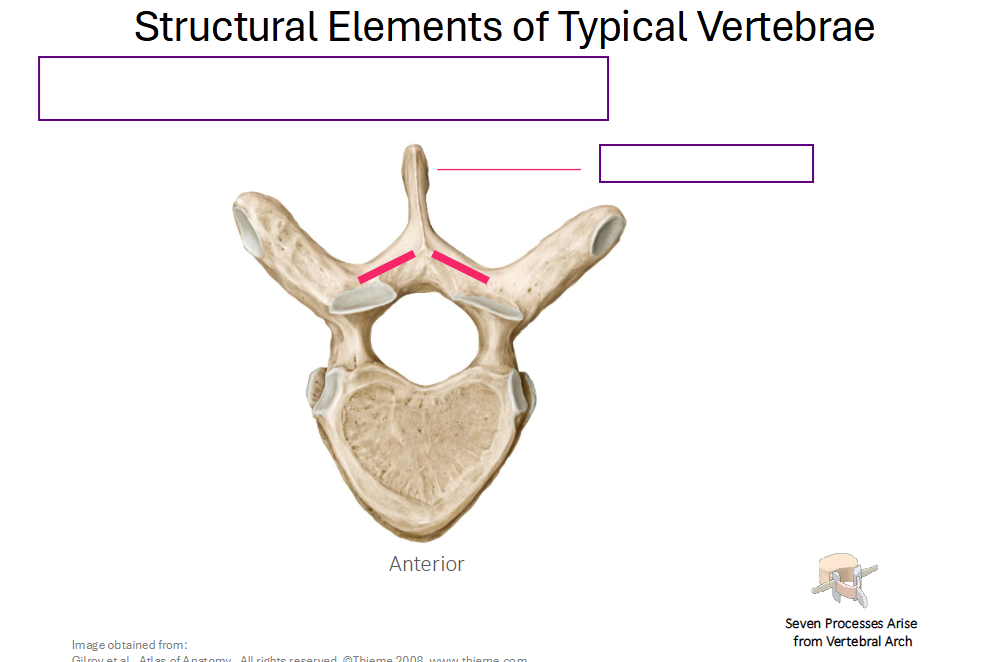
Identify the 7 processes that arise from the vertebral arch (name structures that are being pointed at)
What are the point (s) where the lamina meets pedicle?
Transverse Process (2)
Superior Articular Process (2)
Inferior Articular Process (2)
What are the point (s) where the Laminae meet?
Spinous Process
Describe the Intervertebral Foramen
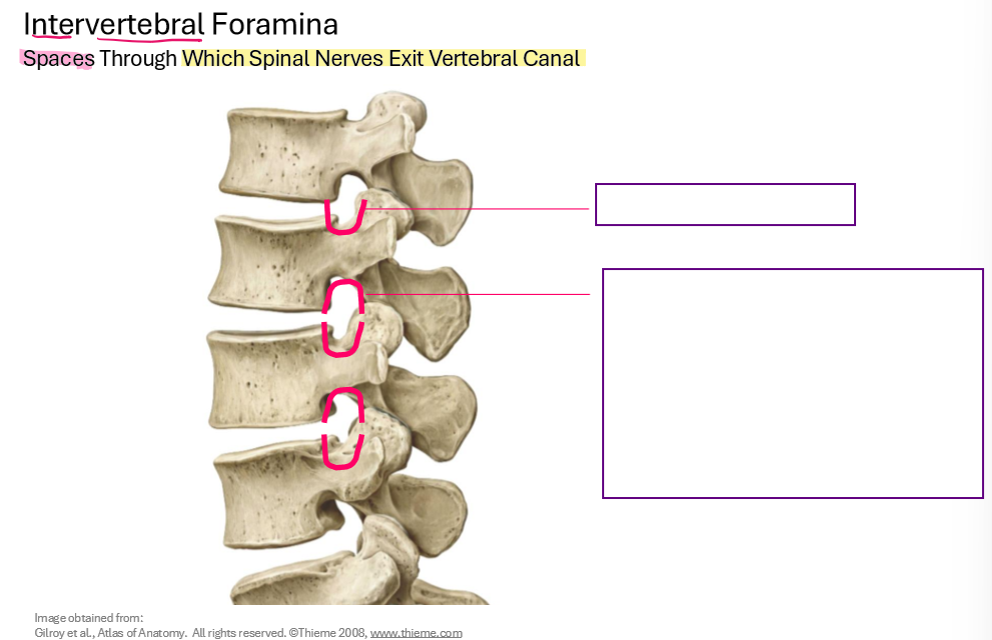
Describe the Intervertebral Foramen
*They’re on one vertebrae, so while it may look like superior is inferior, consider the perspective of one vertebrae instead of the whole spine!
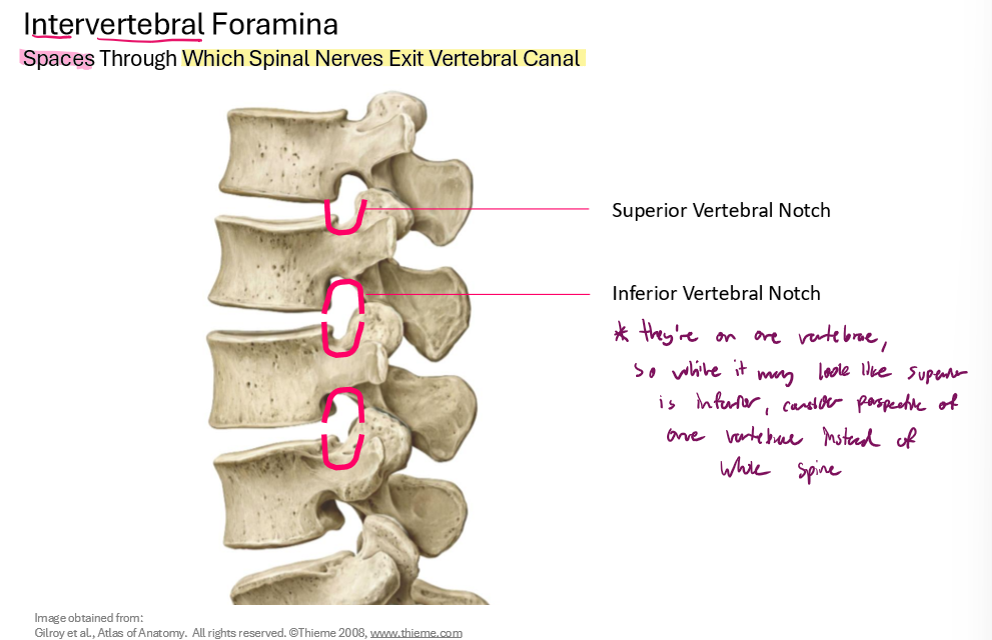
Describe the Intervertebral Foramen
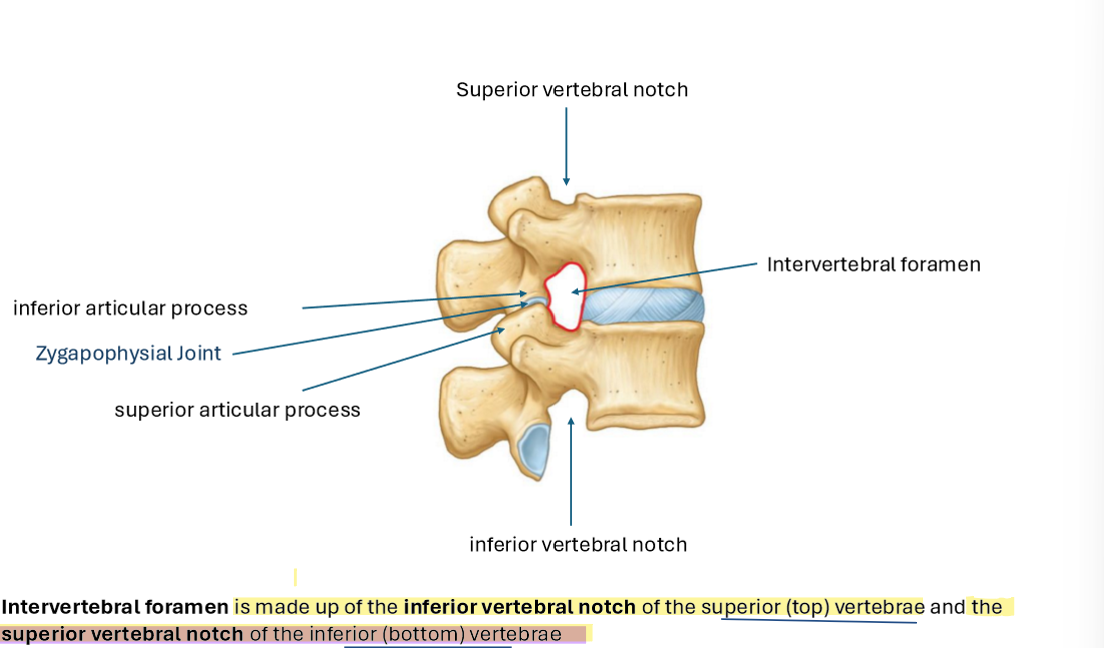
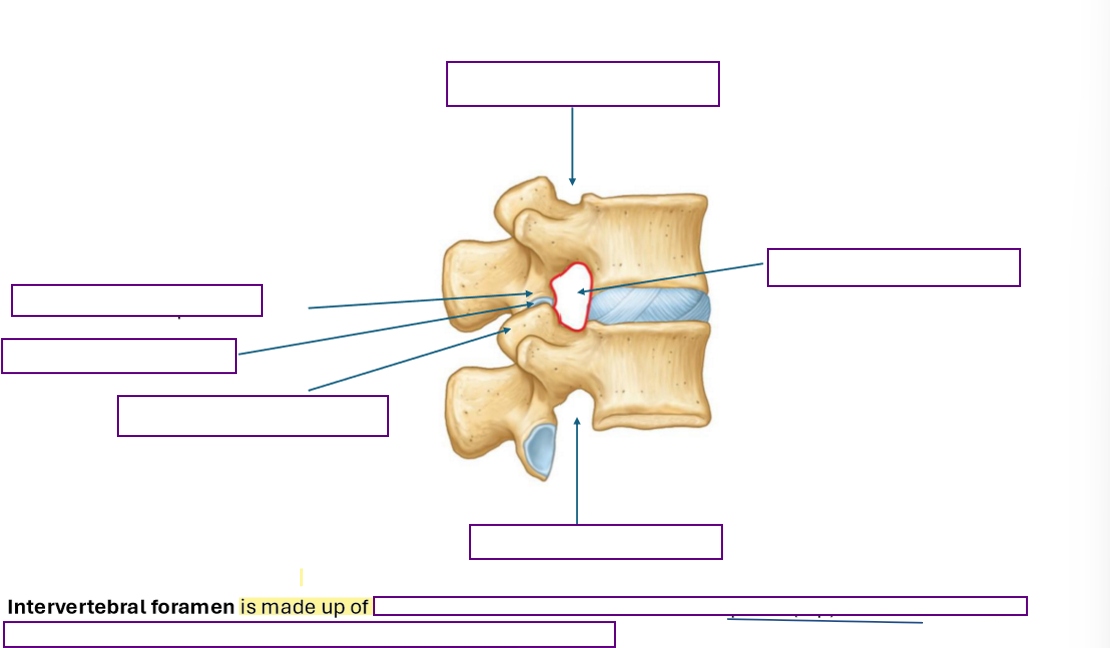
Describe furthermore the spaces through which spinal nerves exit the vertebral canal
Intervertebral Foramen & Vertebral Canal
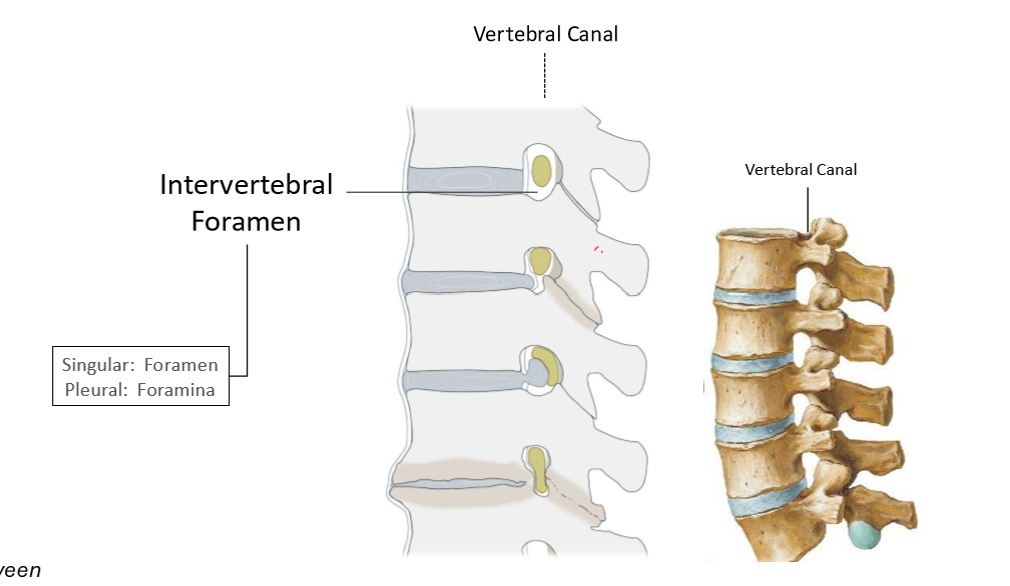
Identify the osteological structures contributing to intervertebral foramen
Superior and Inferior Vertebral notch
intervertebral discs
Adjacent vertebral bodies
Adjacent pedicles
Zygapophysical (facet) jints and articular process
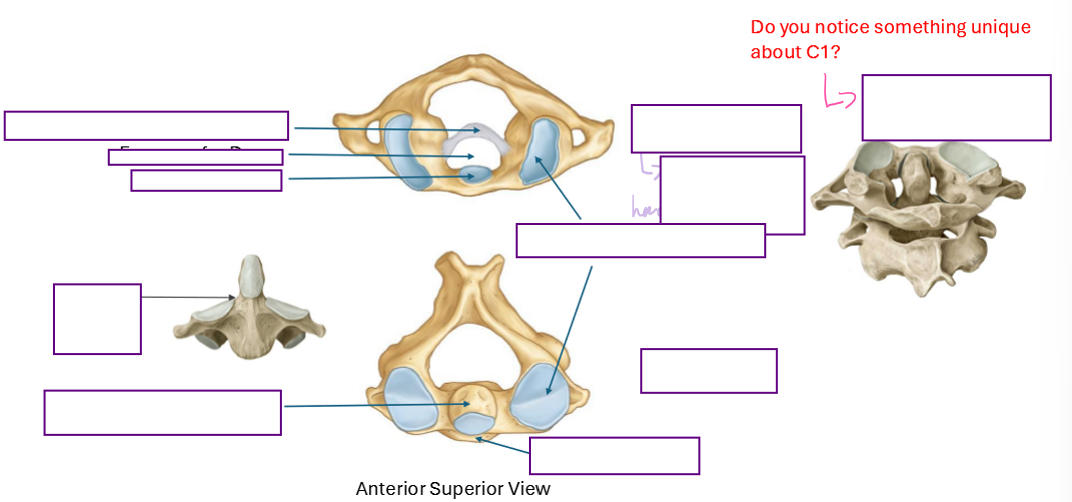
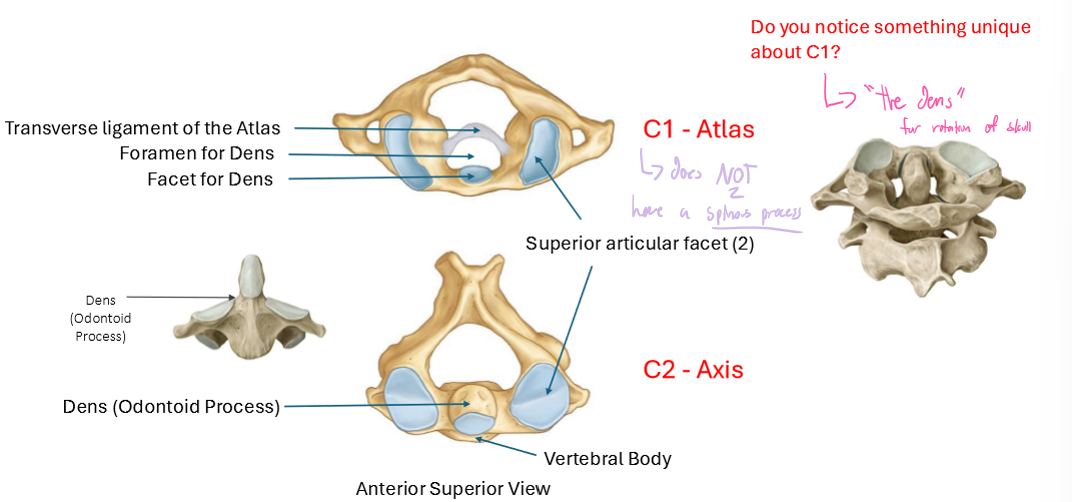
Describe the “Special” Cervical Vertebrae
Atlas & Axis
The unique thing about C1 and C2 is that they have a dens for rotation of the skull
C1 has the facet for the Dens
C2 had the Dens itself (Odontoid process)
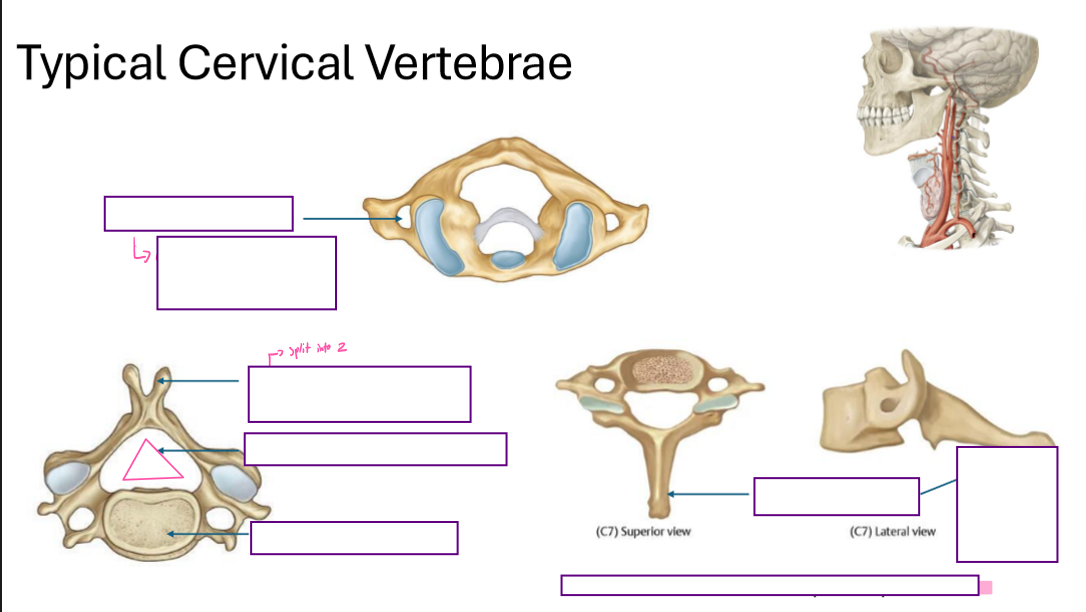
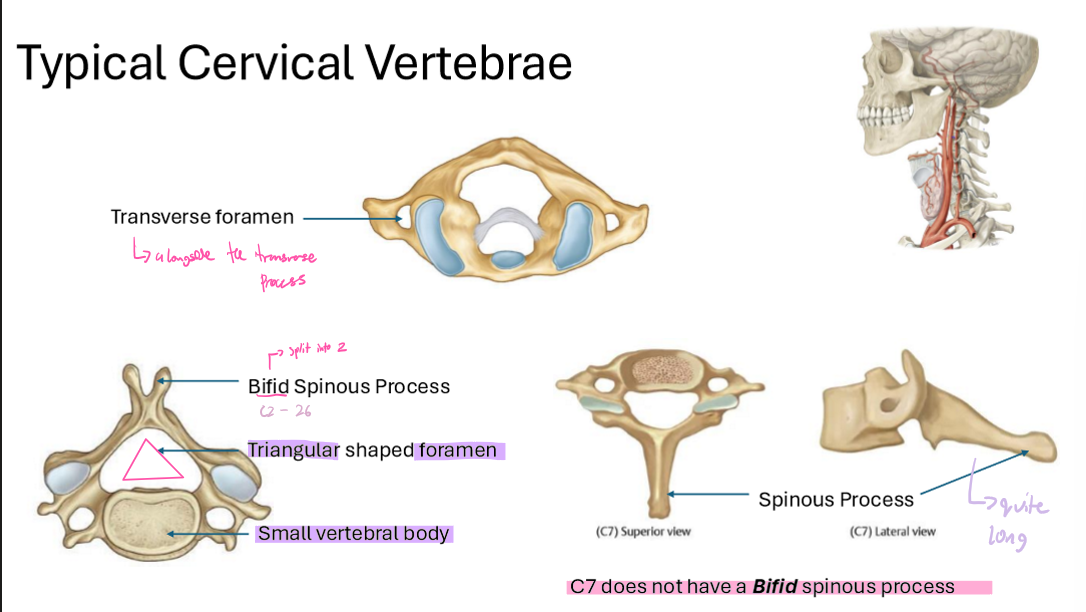
Describe the Typical Cervical Vertebrae
have a Transverse foramen
alongside the transverse process
has a bifid spinous process
triangular-shaped foramen
small vertebral body
C7’s spinous proceesses are quite long
C7 does not have a Bifid spinous process
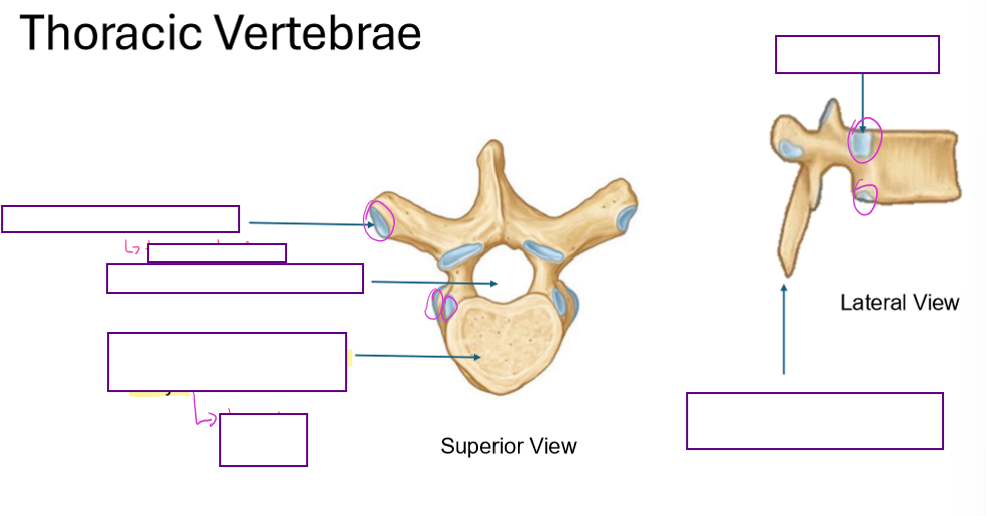
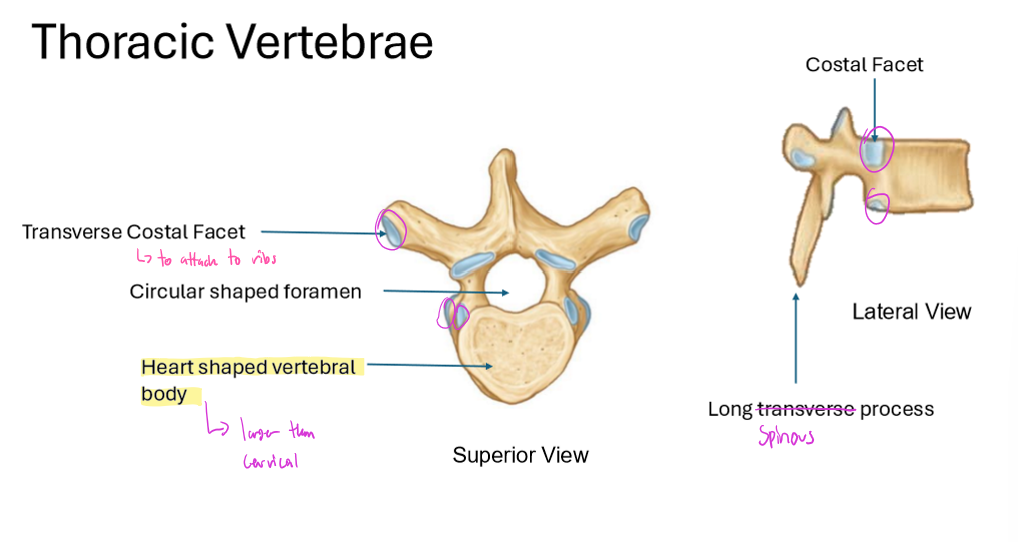
Describe the Thoracic Vertebrae
has a transverse costal facet
to attach to ribs
has a circular shaped foramen
and a heart shaped vertebral body
larger than cervical
Long Spinous process
has a costal facet