Economics, Microeconomics 2.1-2.3 Demand, Supply, & Market Equilibrium
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Demand
quantity of a good or service that customers are willing to buy at different prices in a given time period (effective demand = willing and able)
“law of demand”
as the price of a product falls, the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase, (ceteris paribus)
because of the law of demand
the demand curve is always downward sloping, showing the inverse relationship between price and quantity
the income effect
if the price of a product falls peoples income has more purchasing power
the substitution effect
as prices for a good increase, the quantity demanded decreases as consumers seek cheaper substitutes
the law of diminshing marginal utility
the more units of something is consumed, the less satisfaction it gives the consumer
therefore, as more units are consumed the price must decrease to offset the decreasing utility
a change in price therefore results in a
change in quantity demanded or a movement along the demand curve
Shifters of demand are
Change in number of buyers
Change in consumer income
Change in taste and preferences
Change in expectations for future
Related Goods
the two types of related goods are
Compliments
goods that may be bought with the product
these often share an inverse relationship between the price of one and the demand for the other
Substitutes
goods than can act as a repacement for the product
these often have a direct relationship between the price of one and the demand for the other
Normal goods are when
the demand for the product increases when the consumer income increases
inferior goods are when
the demand for the product decreases when the consumer income increases (or demand increases when income decreases) -
the law of supply is
as the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will usually increase (ceteris paribus)
suppliers will often produce more to
take advantage of the higher prices
there is a direct relationship between price and quantity, therefore
the supply curve is upward sloping
a change in price will result in
a change in quantity supplied or a movement along the supply curve
the shifters of supply are
Subsidies and taxes
Technology
Other goods
Number of sellers
Expectations
Resource costs
Shocks
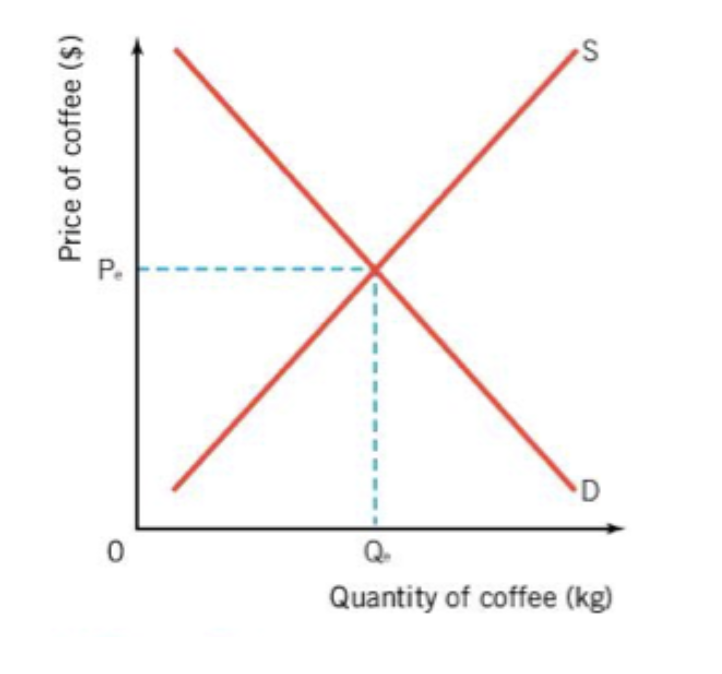
market equilibrium is where
the amount of goods people are willing to buy at the equilibrium price is equal to the amount of goods suppliers want to sell at the price
the market equilibrium is also known as
the market clearing price and will remain until it is changed by an outside factor
market equilibria are self correcting
meaning they will always return to equilibrium unless supply or demand are shifted by an outside factor
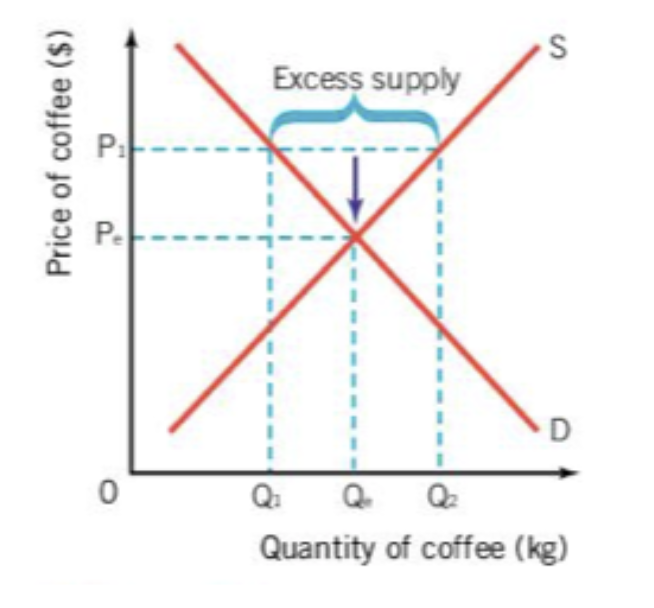
when there is excess supply this causes a
surplus
if producers were to raise the price of coffee to P1, the demand for coffee will fall to Q1 and the supply of coffee will increase to Q2
in reality this means the price of coffee is too high for consumers to willingly buy it, leading to an excess amount of coffee
to sell off the excess amount of coffee producers will have to lower the price resulting in an increase in demand and a return to equilibrium price and quantity
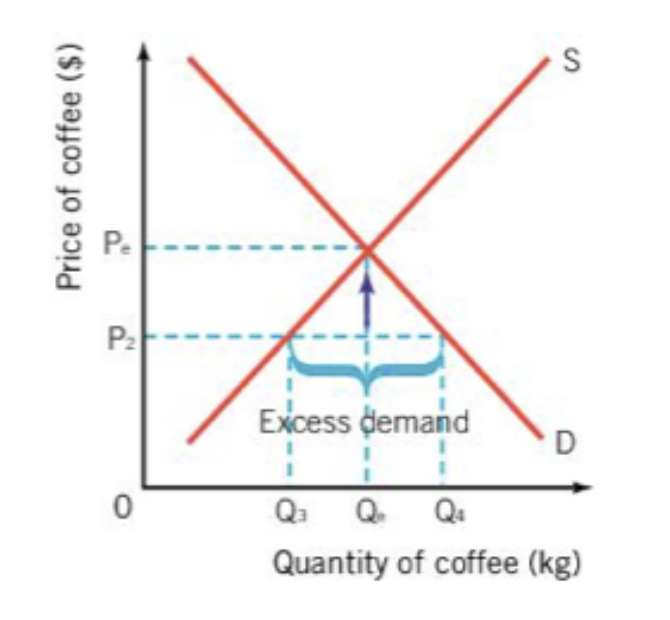
when there is a lack of supply this causes a
shortage
if producers lower the price of coffee to P2 the demand for coffee will increase to Q4 and the supply of coffee will decrease to Q3
in reality this means that consumers demand for coffee exceeds the supply at price P2, resulting in a shortage of coffee
to eliminate the shortage suppliers will have to raise the price to result in a decrease in demand, increase in supply and a return to equilibrium price and quantity
the price mechanism, or the forces of supply and demand
is what moves the market to equilibrium and allocates scarce resources
the price mechanism has three functions
signalling function
Prices of goods act as a signal, providing information for consumers and producers
incentive function
the price signal creates an incentive for producers and consumers to act in the market
rationing function
producers and consumers action ration and allocate resources within the market
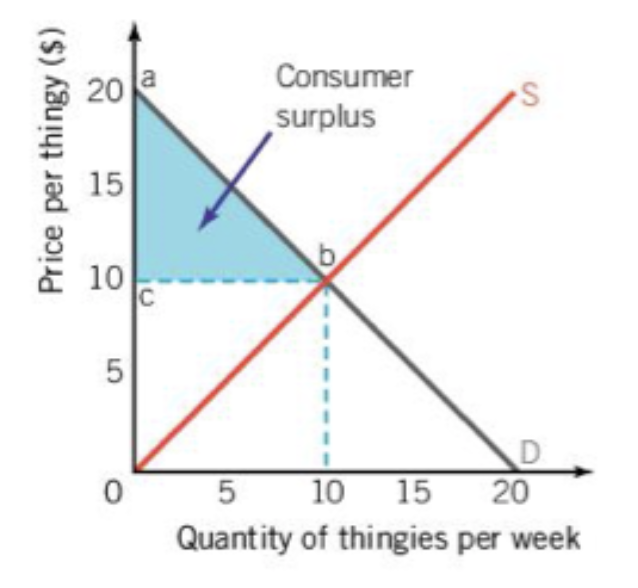
if you have wanted to buy something and then learnt you are paying less than what you were willing to pay, this is called
consumer surplus
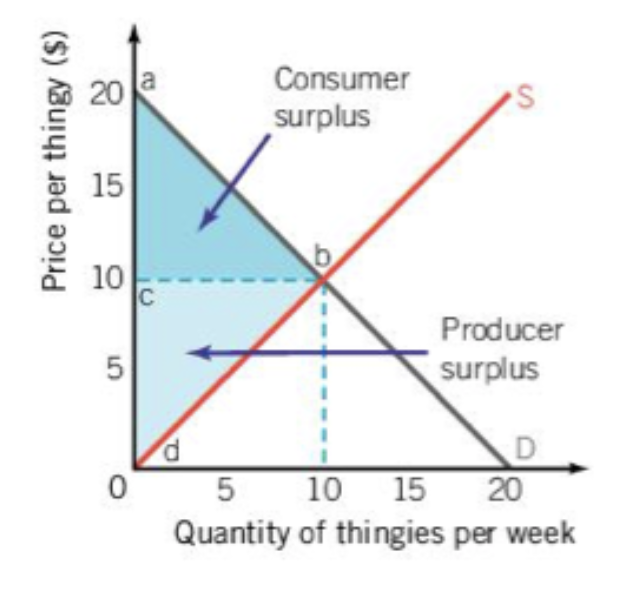
if a producer was willing to sell their product at a lower price but didn’t have this would be called
producer surpluss
when the space of consumer surplus and producer surplus are combined it creates
community surplus
when a market has achieved equilibrium it has reached
allocative efficiency
allocative efficiency means that
the market is producing the optimal level of goods to satisfy customers and producers in society