PLTW Medical Interventions Unit 1
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Medical Intervention
Any measure whose purpose is to improve health or alter the course of disease
Medical interventions help maintain health and homeostasis in the body.
Pathogen
A specific causative agent of disease
Outbreak
A sudden rise in the incidence of a disease
Patient Symptoms/Risk Factors Organizer
Chart detailing information about patients' symptoms and any part of their lifestyle or background that may increase their risk for certain diseases.
Primer
Complimentary DNA segment that allows the enzyme to bind to the DNA for DNA replication.
Bioinformatics
The collection, classification, storage, and analysis of biochemical and biological information using computers especially as applied in molecular genetics and genomics.
Genome
An organisms genetic material
PCR Amplification
Melt: Highest temp, separates strands
Anneal: Lowest temp, primers attach
Extend: Medium temp, DNA replicates (Polymerase)
Final Extension: Ten minutes at medium temp, ensure DNA has finished replicating
DNA Sequencing
The DNA is placed in order by size (smallest to largest) using gel electrophoresis or a similar method. It is then tagged by color (using fluorescent markers on the stoppers of the DNA) as to what nucleotide it represents. The nucleotides in size order are the DNA sequence. The bacteria can be identified using BLAST
Solute
Substance dissolved in another substance
Solvent
A substance, usually a liquid, in which another substance is dissolved.
Solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. They may be in any state of matter.
Concentration
The amount of a specified substance in a unit amount of another substance
Antibody
An antigen-binding immunoglobulin, produced by B cells, that functions as the effector in an immune response
Antigen
A foreign macromolecule that does not belong to the host organism and elicits an immune response
ELISA
(Enzyme-linked Immunosorbant Assay) A quantitative in vitro test for an antibody or antigen in which the test material is absorbed on a surface and exposed either to a complex of an enzyme linked to an antibody specific for the antigen or an enzyme linked to an anti-immunoglobulin specific for the antibody followed by reaction of the enzyme with a substrate to yield a colored product corresponding to the concentration of the test material.
ELISA Steps
1. The sample is added to a plastic well, where the proteins are bound to the cell wall. A detergent washes away unbound proteins while preventing more proteins from binding to the cell wall.
2. The Primary Antibody binds to a specific antigen in the cell. Excess is washed away.
3. The Secondary Antibody, which is bound to the enzyme, is added. Excess is washed away.
4. The enzyme substrate is added, causing the liquid to turn blue (oxidation)
Enzyme
A protein serving as a catalyst; a chemical agent that changes the rate of reaction without being consumed by the reaction
Serial Dilution
A stepwise dilution of a substance in a solution
Nucleoid
Contains the genophore
Plasmid
Small, circular piece of DNA. Located in the cytoplasm and contain information for antibiotic resistance.
Ribosomes
Produce proteins
Cell Wall
Differ between Gram-Positive (no outer membrane, stains blue) and Gram-Negative (stains red, contains a second membrane)
Plasma Membrane
Found in the envelope, protects the cell and controls what goes in and out.
Capsule
Most outer layer of the cell, protects it from phagocytosis (white blood cells)
Flagella
Responsible for movement
Pili
(Fimbriae) Hollow hair-like structures that extend from the cell and allow it to attach to other cells
Endotoxins
Bacterial toxins, found in the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. They are released when the cell disintegrates.
Penicillins
Interferes with the making of peptidoglycan, weakening the cell wall so that the bacteria eventually bursts.
Resistance: Some bacteria create enzymes that destroy it
Tetracyclines
Prevents bacteria from making necessary proteins. (Binds to ribosome)
Resistance: Efflux pump
Fluoroquinolones
Attack DNA Gyrase to prevent bacteria from replicating.
Resistance: Change in target, (DNA Gyrase)
Sulfa antibiotics (Sulfonamids)
Inhibit the making of folate, which is an essential nutrient. Does not hurt humans because we consume folate, but bacteria must manufacture it.
Resistance: Enzyme changes
Meningitis (Positive or negative)
Gram-Negative
What are we doing to help bacteria become resistant to antibiotics?
Not taking medicines to completion-- chance to mutate
Feeding antibiotics to farm animals to increase growth-- chance to mutate
Mutation
DNA mutates, creating a change in the gene product (Form of resistance to antibiotics)
Destruction/Inactivation
Exchange enzymes that chemically degrade the antibiotic (Form of resistance to antibiotics)
Efflux
Efflux pump actively transports antibiotic out of cell before it can cause harm (Form of resistance to antibiotics)
Conjugation
Plasmid carrying resistance is transferred from one cell to another using a pilus bridge (Form of sharing resistance)
Transformation
DNA is transferred as "naked" DNA-- The cell dies, cell wall deteriorates, and living bacteria take DNA (Form of sharing resistance)
Transduction
Bacteria is transferred through viruses that effect bacteria (bacteria-phages)
Frequency
How often the waves occur. Effects pitch (more waves, higher pitch)
Amplitude
How large waves are (how much air they displace, larger waves=louder sound)
Sound
Mechanical energy that is transmitted by longitudinal pressure waves in a medium (such as water or air)
Pinna
Helps to collect sound waves and rather poorly directs them to the external auditory canal.
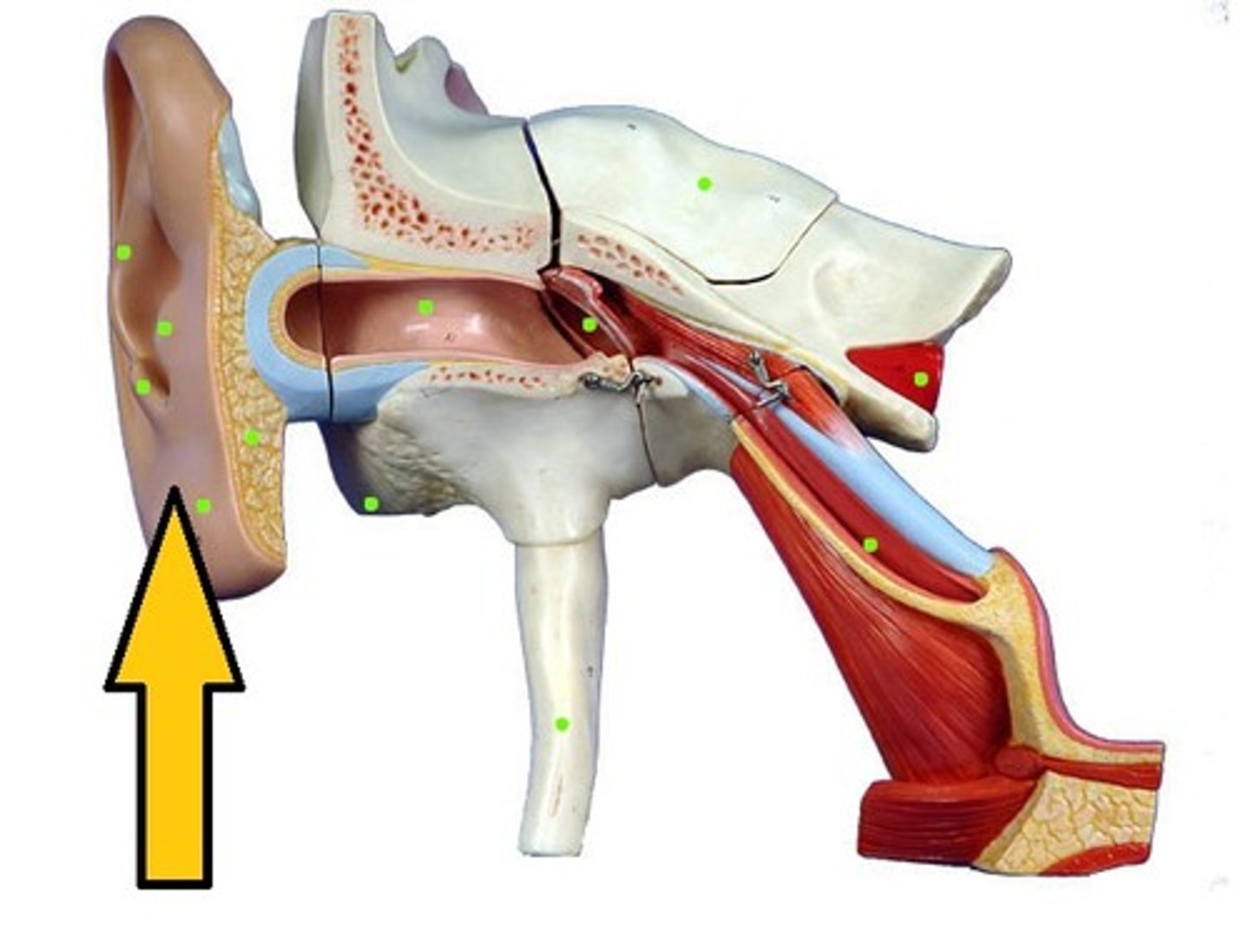
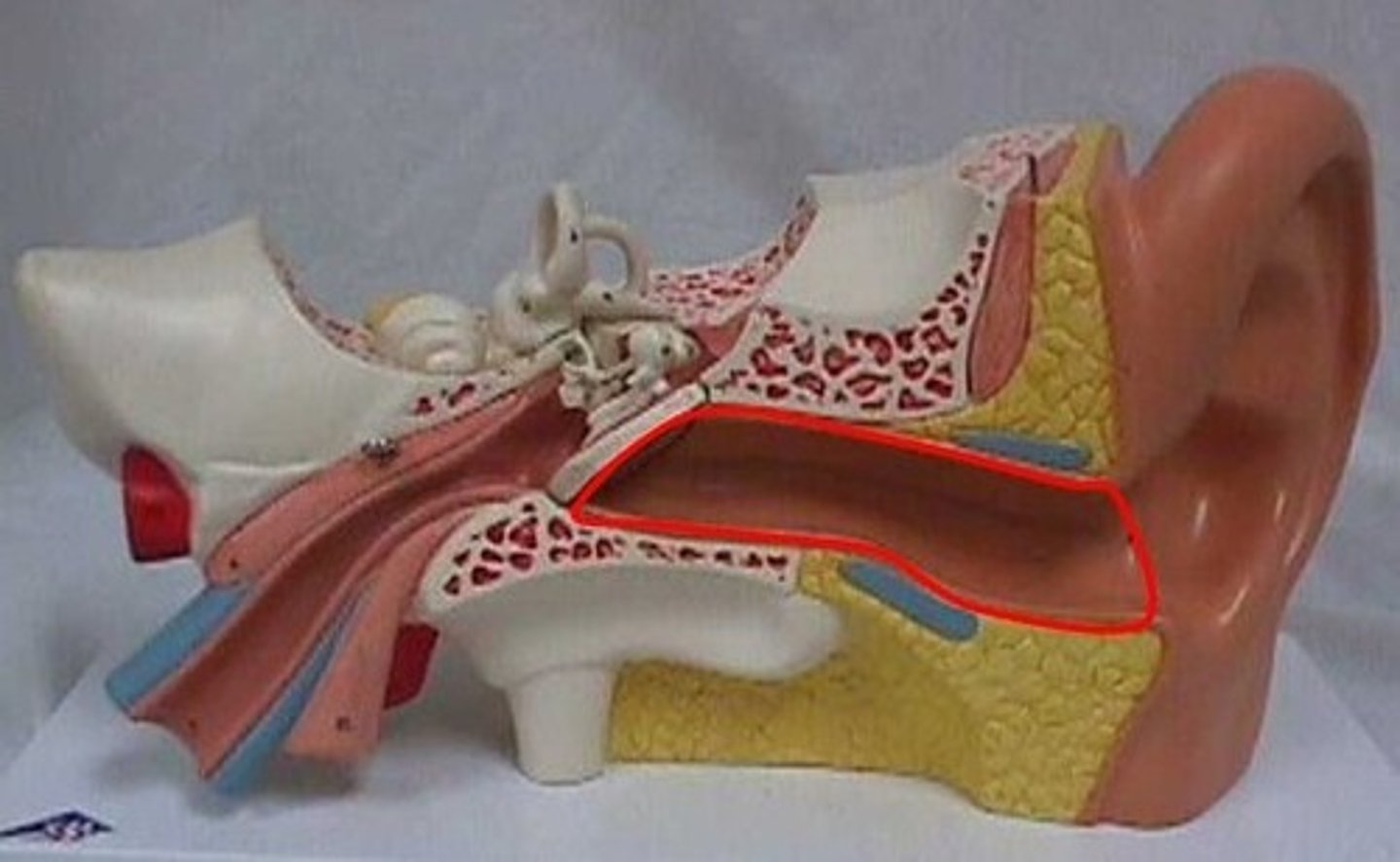
Auditory Canal
Sound waves are funneled through the tube and are amplified in the process. It has a natural acidity that protects against infection. Ear wax is produced to keep the ear from drying out and to ward off insects.
Eustuchian Tube
Equalizes pressure inside and outside of the tympanic membrane and allows for the drainage of normal and diseased middle ear secretions

Ossicles
Form the mechanical links between the tympanic membrane and the inner ear. They deliver sound vibrations to the inner ear and amplify sound.
Tympanic Membrane
Sound waves hit it and cause it to vibrate, transferring the sound wave into vibrations.
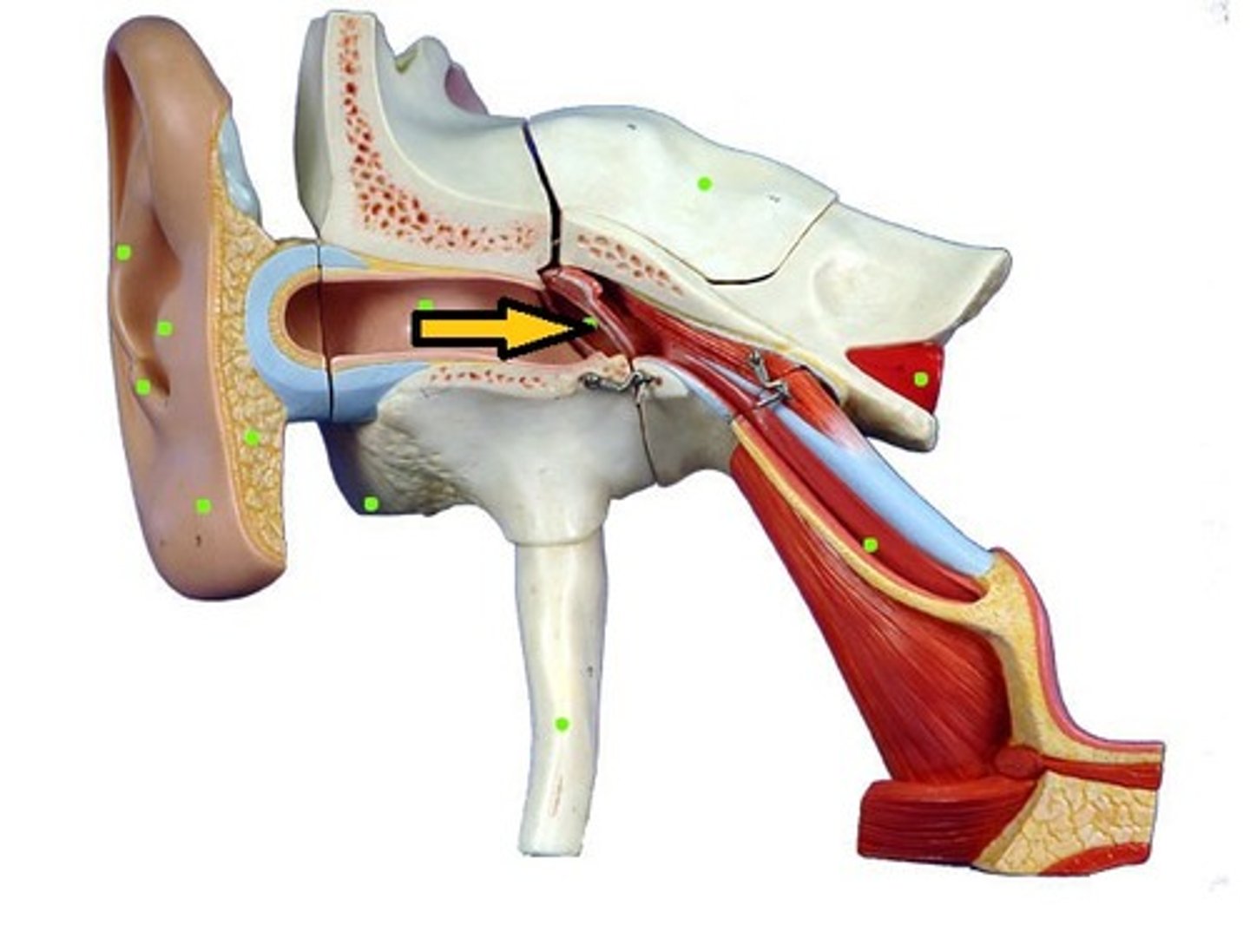
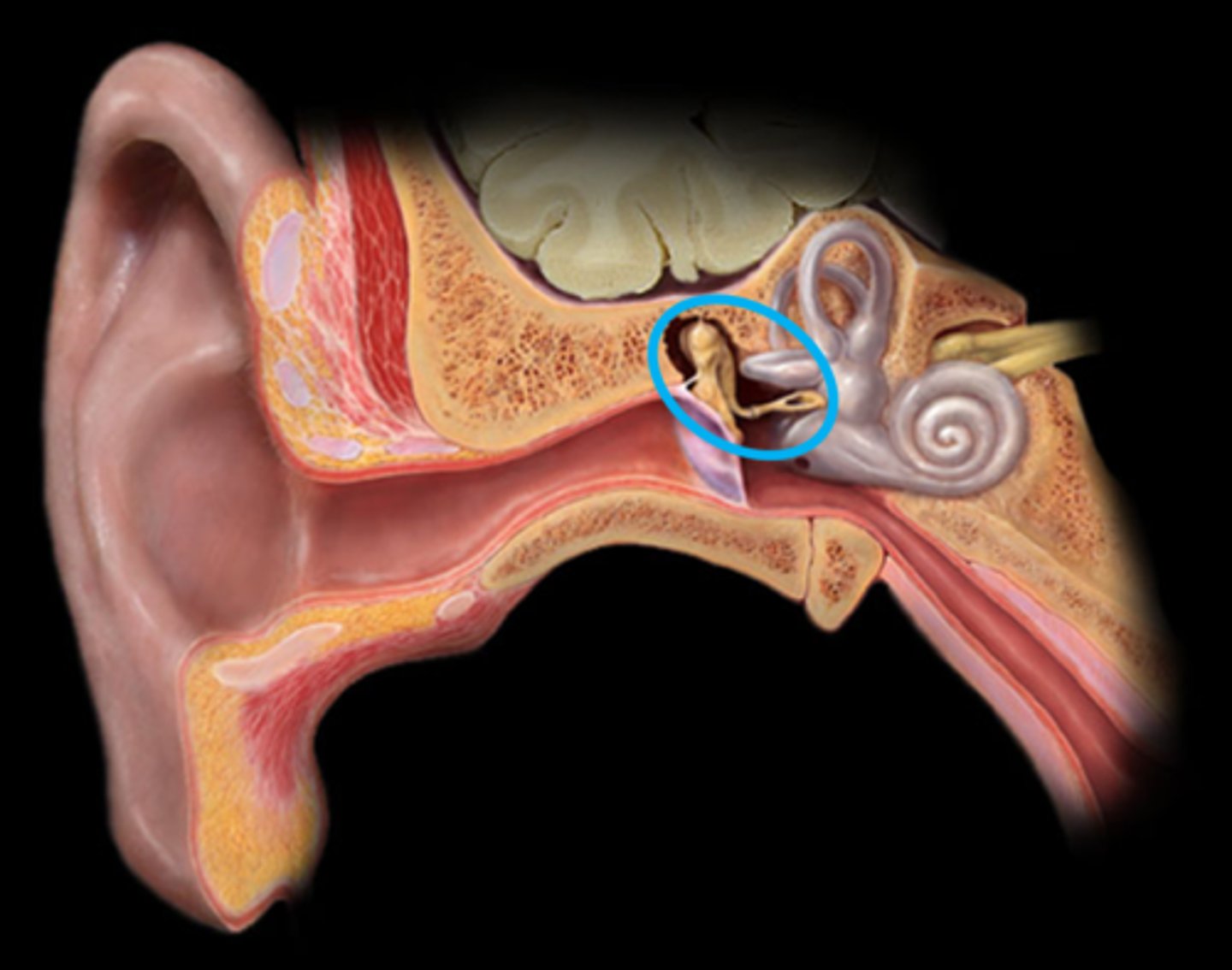
Cochlea
Transfers stimulus from the outside environment into nerve impulses for the brain
Sensory Hair Cells
Vibrate inside of the cochlea generating the nerve signals
Cochlear Nerve
Part of the auditory nerve. Controls hearing
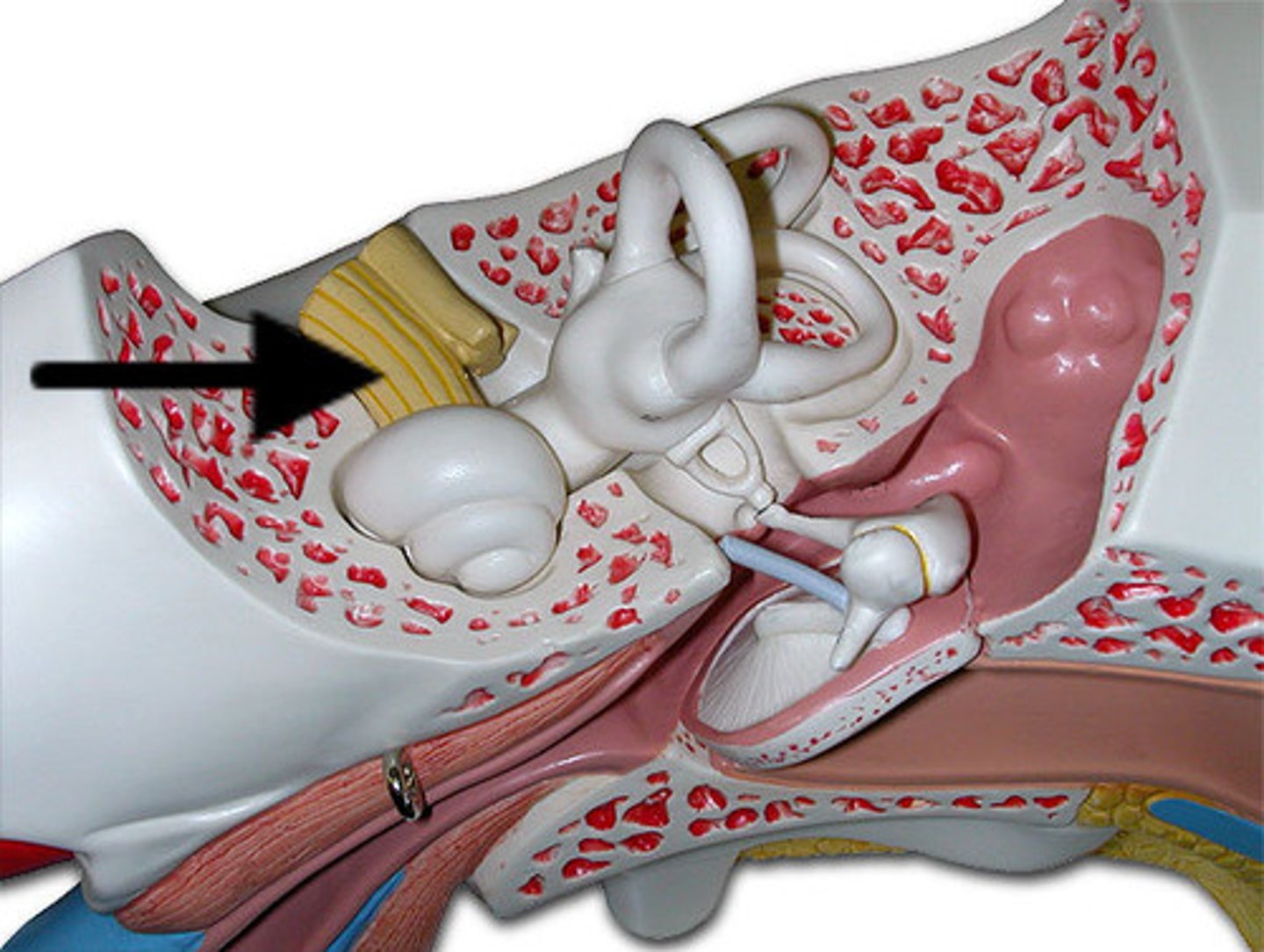
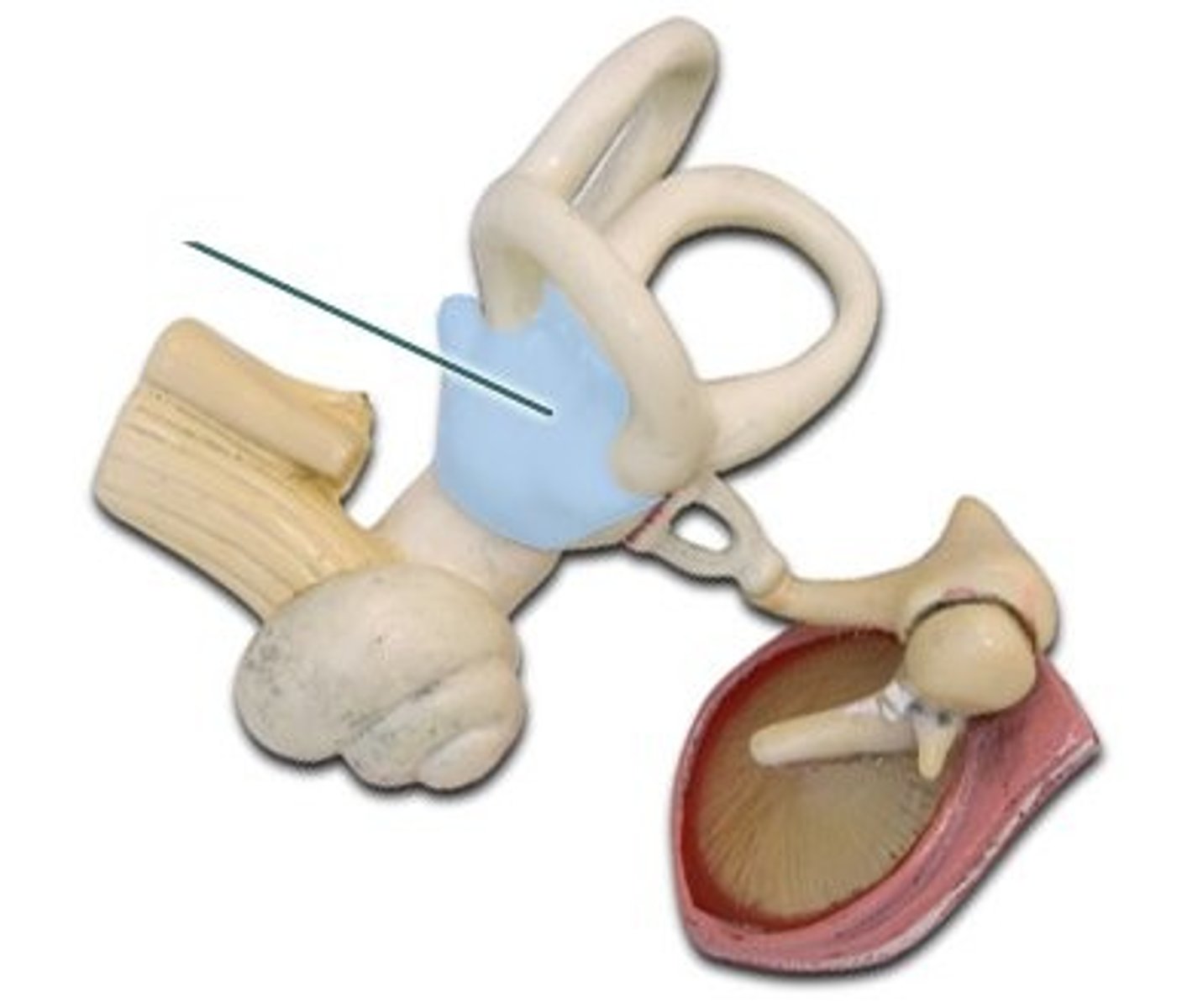
Oval Window
Connects middle ear with the upper half of the cochlea. Transfers vibrations.
Vestibule
Connects the cochlea and the semicircular canals
Vestibular Nerve
Part of the auditory nerve. Controls balance
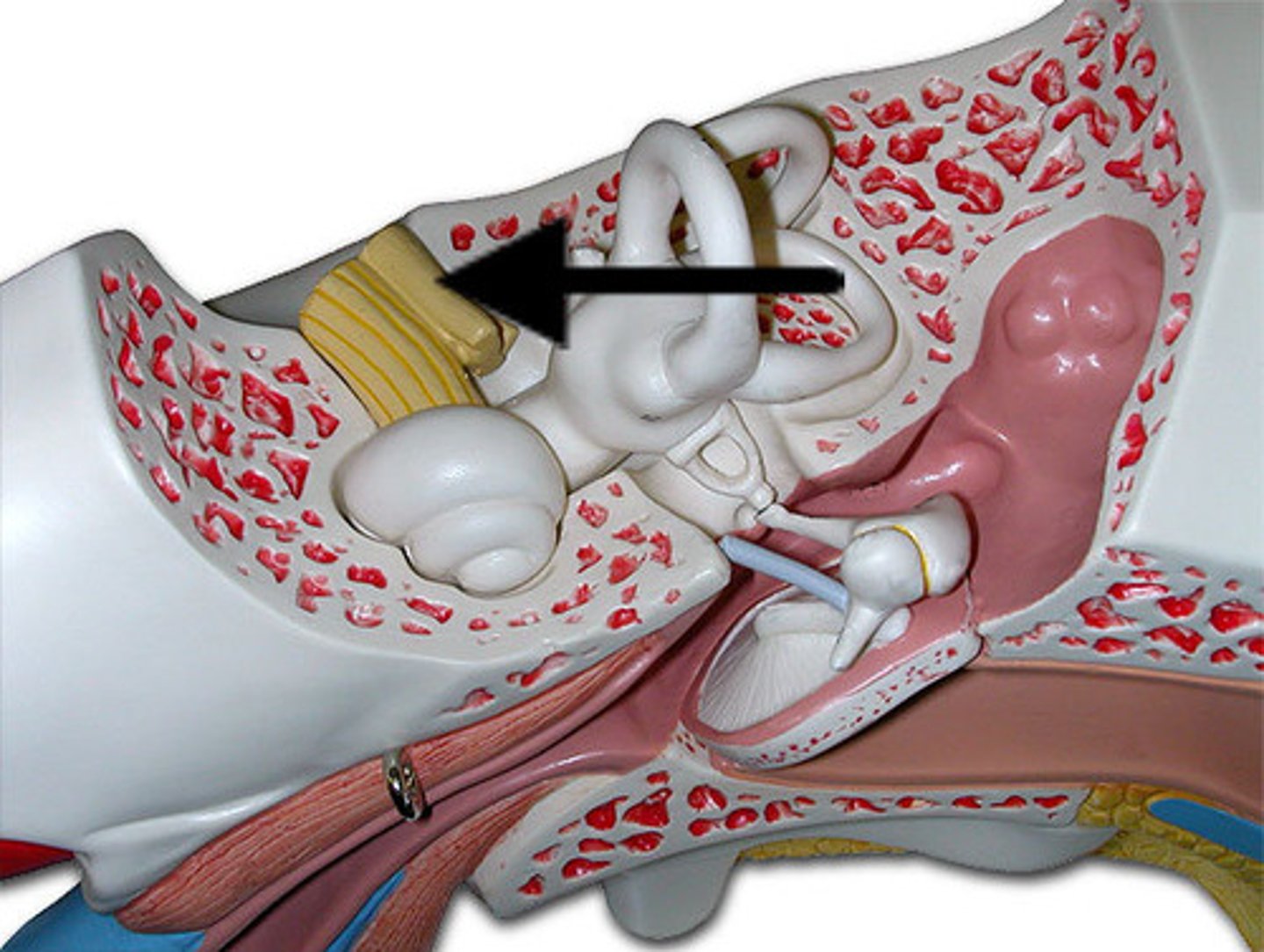
Inner Ear
The essential part of the vertebrate organ of hearing and equilibrium that includes the vestibule, the semicircular canals, and the cochlea.
Middle Ear
The intermediate portion of the ear containing a chain of three ossicles that extends from the tympanic membrane to the oval window and transmits vibrations to the inner ear
Outer Ear
The outer visible portion of the ear that collects and directs sound waves toward the tympanic membrane by way of a canal which extends inward through the temporal bone
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Hearing loss or impairment resulting from problems with the auditory nerves
Conductive Hearing Loss
Hearing loss or impairment resulting from interference with the transmission of sound waves to the cochlea.
Signified with <>
Better when vibrated through bones
Audiogram
A graphic representation of the relation of vibration frequency and the minimum sound intensity for hearing
Normal at very top
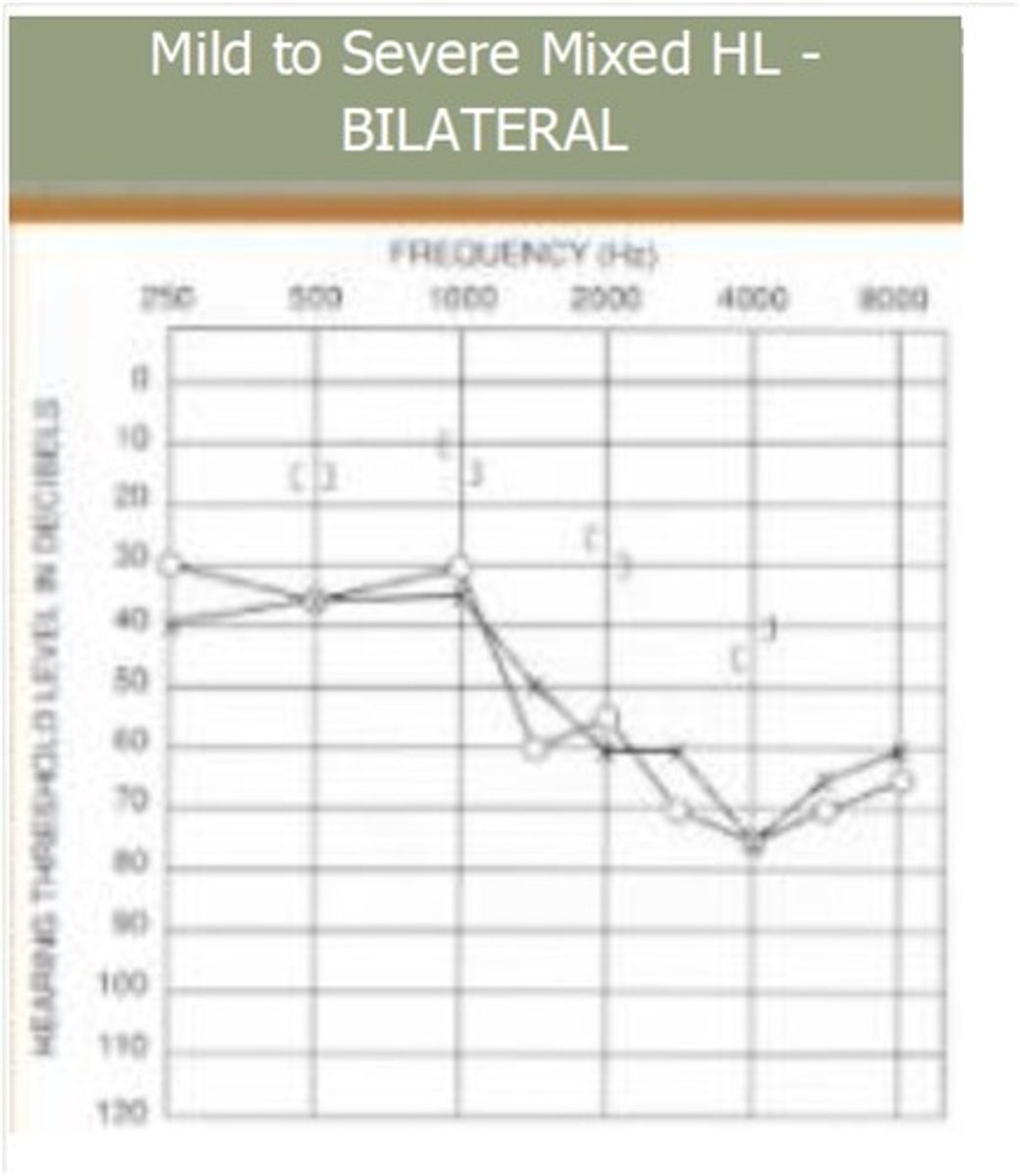
Pure Tone Test
Audiometer measures hearing. Sounds are played at distinct frequencies. The patient raises a finger/pushes a button/etc. each time they hear a sound.
Threshold
Lowest level of each frequency patient is able to hear
Audiologist
$40,000-50,000, Doctorate program
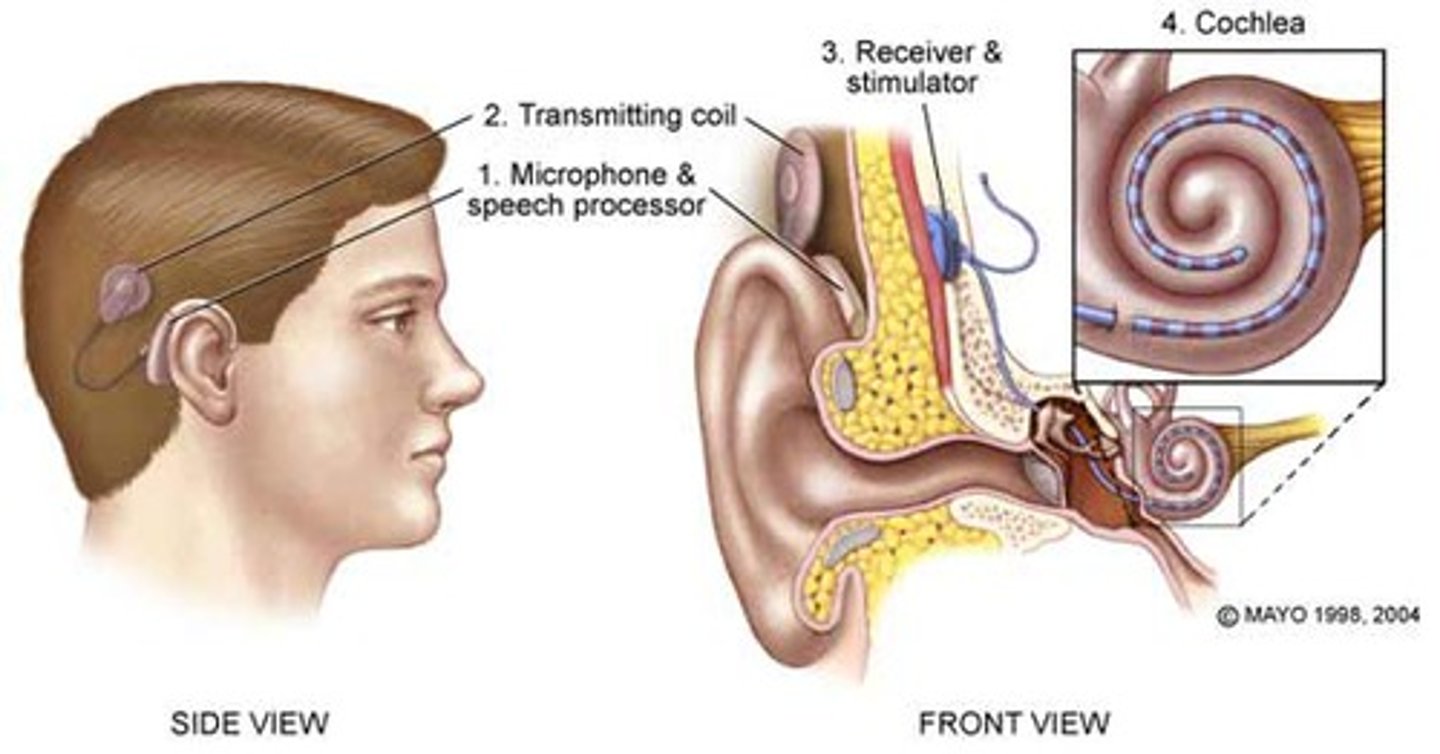
Cochlear Implant
An electrical prosthetic device that enables individuals with sensorineural hearing loss to recognize some sounds and that consists of an external microphone and speech processor that receive and convert sound waves into electrical signals which are transmitted to one or more electrodes implanted in the cochlea where they stimulate the auditory nerve.
Hearing Aid
An electronic device usually worn by a person for amplifying sound before it reaches the receptor organs.
Who developed vaccines
Edward Jenner (Small Pox with Cow Pox)
Live-attenuated Vaccines
Live pathogen, but weakened. May cause minor illness in rare cases.
Inactivated Vaccines
Pathogen has been completely killed. Frequently requires boosters.
Recombinant DNA
A DNA molecule made in vitro with segments from different sources
Restriction Enzyme
A degradative enzyme that recognizes specific nucleotide sequences and cuts up DNA
Vectors
Vehicles for DNA to move
Epidemiologist
Master's Degree and $65,000
Attack Rate
Sick/exposed