Macro Exam 2 I'm so cooked
1/267
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pain and suffering and pain and suffering
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
The value of total saving must equal
The value of total spending
the demand for loanable funds is
downward sloping
the demand for loanable funds is downward sloping because
the lower the interest rate, the more investment projects firms can profitably undertake, and the greater the quantity of loanable funds they will demand.
The supply of loanable funds is determined by
the willingness of households to save and by the extent of government saving or dissaving.
The supply curve for loanable funds is
upward sloping
The supply curve for loanable funds is upward sloping because
the higher the interest rate, the greater the quantity of saving supplied.
equilibrium in the market for loanable funds determines the
real interest rate
Equilibrium in the market for loanable funds determines
the quantity of loanable funds that will flow from lenders to borrowers each period.
Reduced taxes
Increased demand for loanable funds
Increase in demand for loanable funds
shifts the demand curve to the right
Increasing investment
increases the capital stock and the quantity of capital per hour worked, helping to increase economic growth.
Increase in demand for loanable funds also increases
Interest rate
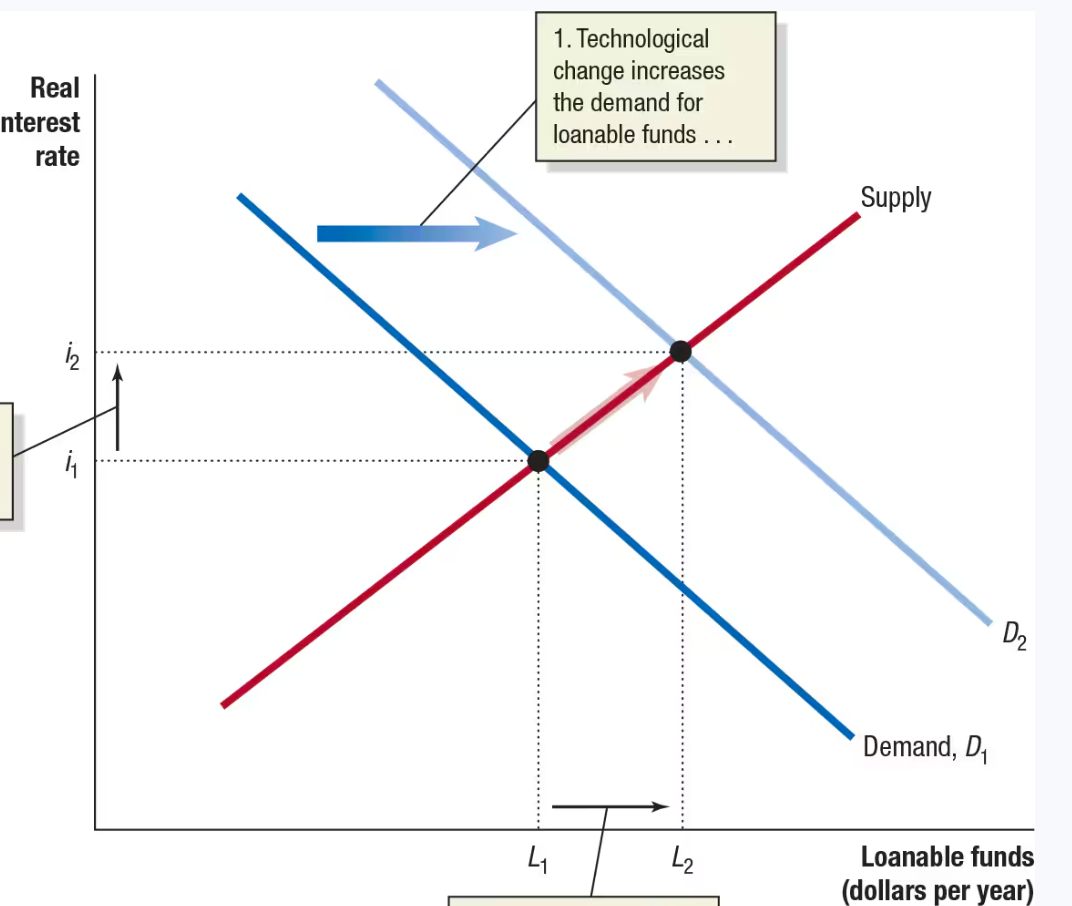
Increase in demand for loanable funds
if the government begins running a budget deficit
it reduces the total amount of saving in the economy.
Budget deficit
Shifting the supply curve for loanable funds tio the left (due to reduced saving)
Running a deficit
has reduced the level of total saving in the economy and, by increasing the real interest rate, has also reduced the level of investment spending by firms
Crowding out
refers to a decline in private expenditure (in this case, investment spending) as a result of an increase in government purchases.
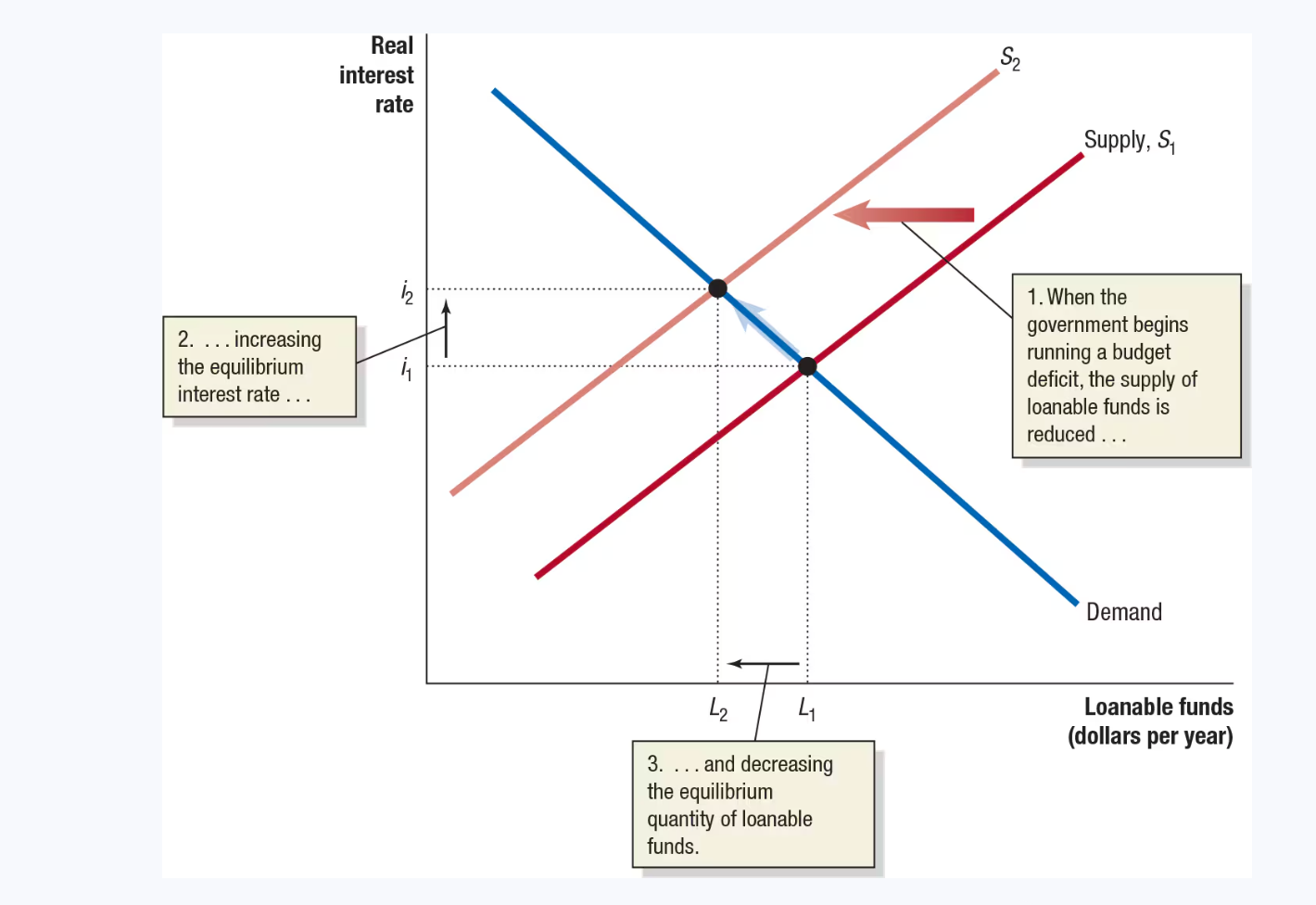
Budget deficit
A budget surplus increases the total amount of saving in the economy
shifting the supply curve for loanable funds to the right
We can conclude that a budget surplus increases
the level of saving and investment.
In 2023, many economists and policymakers were concerned that the large deficits projected for future years might
be an obstacle to growth.
Congress gives the _________ the responsibility of estimating how federal spending and taxing policies will affect the economy.
Congressional Budget Office (CBO)
The government’s budget deficit (firms will save less)
Supply of loanable funds curves to the left
The desire of households to consume today (ie the desire to not save)
Supply of loanable funds curves to the left
Tax benefits for saving (incentive to save)
Supply of loanable funds curves to the right
Expected future profits from new investments
Demand for loanable funds curves to the right
Corporate taxes
Demand for loanable funds curves to the left
When firms use funds to purchase robots, software, factories, and office buildings, they are engaging in
investment.
I = Y - C - G
This expression tells us that in a closed economy, investment spending is equal to total income minus consumption spending and minus government purchases
Sprivate = Y + TR - C - T
We can also derive an expression for total saving. Private saving is equal to what households retain of their income after purchasing goods and services (C) and paying taxes (T). Households receive income for supplying the factors of production to firms. This portion of household income is equal to Y. Households also receive income from governments in the form of transfer payments (TR), which include Social Security payments and unemployment insurance payments.
Financial markets and financial intermediaries together comprise the
financial system.
Financial intermediaries, such as banks, mutual funds, pension funds, and insurance companies,
act as go-betweens for borrowers and lenders.
Risk sharing
Risk is the chance that the value of a financial security will change relative to what you expect. For example, you may buy a share of stock in Apple at a price of $175, only to have the price fall to $125.
Liquidity
Liquidity is the ease with which a financial security can be exchanged for money.
Information.
The financial system collects and communicates information, or facts about borrowers and expectations about returns on financial securities.
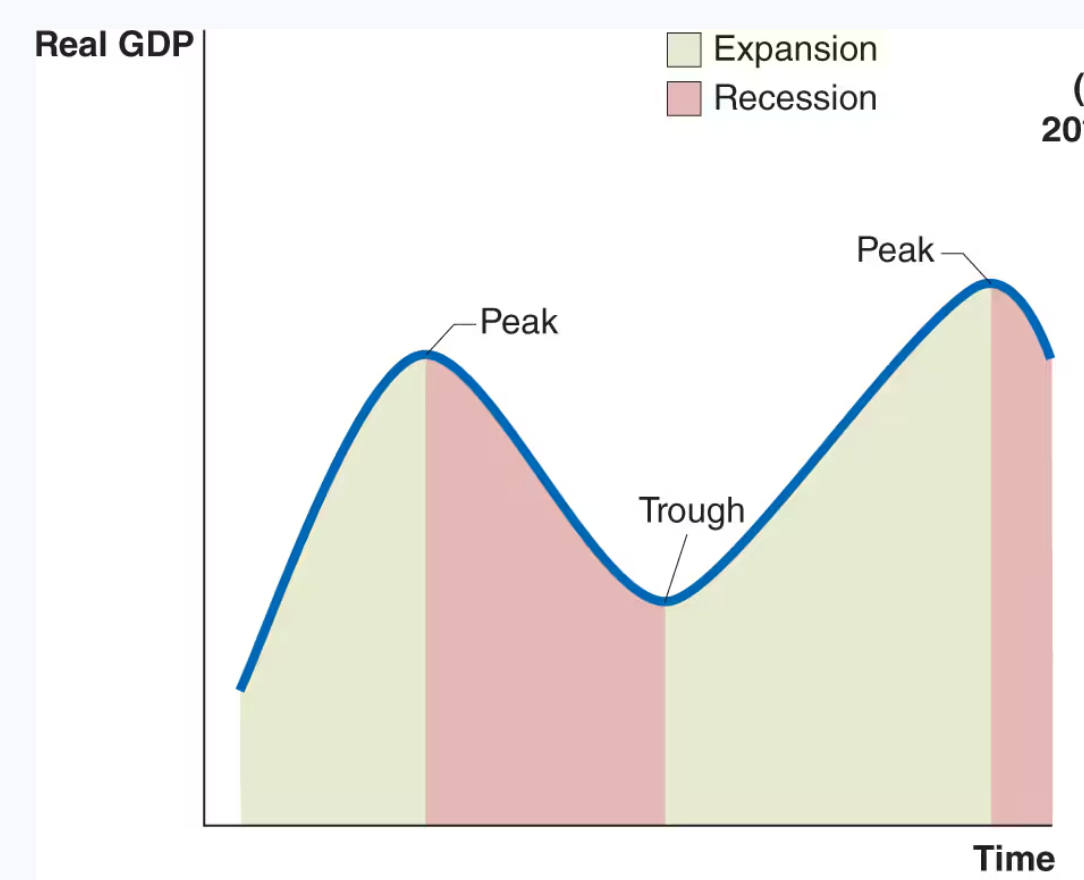
An idealized business cycle
What governing body declares a recession?
Business Cycle Dating Community of the NBER
NBER’s broader definition of a recession
“A recession is a significant decline in activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months, visible in industrial production, employment, real income, and wholesale–retail trade.”
Typically, when will the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) announce that the economy is in a recession?
a year or more after the recession has begun
What are the typical characteristics of business cycles, including how expansions and recessions develop?
End of Expansion: Interest rates rise, wages increase faster than prices, and firm profits decline. Households and firms take on more debt.
Transition to Recession: High debt levels lead to reduced spending. Firms cut capital goods investment, and households reduce spending on houses and durable goods.
During Recession: Lower spending causes declining sales, production cuts, layoffs, rising unemployment, and falling profits, leading to further spending declines.
Exception: The 2020 recession was unique because it resulted from Covid-19 business shutdowns rather than declining spending.
End of Expansion:
Interest rates rise, wages increase faster than prices, and firm profits decline. Households and firms take on more debt.
Transition to Recession:
High debt levels lead to reduced spending. Firms cut capital goods investment, and households reduce spending on houses and durable goods.
During Recession:
Lower spending causes declining sales, production cuts, layoffs, rising unemployment, and falling profits, leading to further spending declines.
Exception:
The 2020 recession was unique because it resulted from Covid-19 business shutdowns rather than declining spending.
Inflation rate increases
late in an expansion, and early into the following recession - then decreases into the recession
Reason for average decline in inflation rate
During a business cycle expansion, spending by businesses and households is strong, and producers of goods and services find it easier to raise prices. As spending declines during a recession, firms have a more difficult time selling their goods and services and are likely to increase prices less than they otherwise might have.
Recession and unemployment
Unemployment rises
explanations for why the U.S. economy experienced a period of relative stability from 1950 to 2007
The increasing importance of services and the declining importance of goods.
The establishment of unemployment insurance and other government transfer programs that provide funds to the unemployed.
Active federal government policies to stabilize the economy.
The increased stability of the financial system.
Labor productivity
The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work.
Labor productivity is affected by two factors
1. Capital per hour worked: Refers to the manufactured goods that are used to produce other goods and services, such as computers, factory buildings, machine tools, and warehouses.
2. Technological change: Technology refers to the processes a firm uses to turn inputs into outputs of goods and services. Technological change is the increase in the quantity of output that firms can produce given a quantity of inputs.
Which of the following does NOT lead to
long-run economic growth?
Increase in average wages
Potential GDP is the level of real GDP attained when all firms are producing at
capacity
One way to judge how quickly an economy is growing is to calculate the number of years it would take
real GDP per capita to double. For example, if it doubles every 20 years, then the average person in the country will experience significant increases in their standard of living over the course of their lives. However, if real GDP per capita doubles only every 100 years, then increases in the standard of living will occur too slowly to notice.
number of years to double
70 / growth rate
Which one of the following statements regarding real and potential GDP is true?
Potential GDP increases every year
Firms that act as financial intermediaries match households that have excess funds with firms that want to borrow funds. What other key services does the financial system provide to savers and lenders?
Collects and communicates information about borrowers to savers
Provides an easy method of exchanging a financial security for money
Allows savers to spread their money among many financial investments
Financial markets
such as for stocks and bonds
financial intermediaries
such as banks, mutual funds, pension funds and insurance companieslong dash—together comprise the financial system.
Firms raise funds in financial markets by selling
financial securities
_____ are financial securities that represent partial ownership of a firm.
Stocks
_____ are financial securities that represent promises to repay a fixed amount of funds.
Bonds
Financial intermediaries do what?
pool the funds of many small savers and lend them to many individual borrowers, pay interest to savers for the use of their funds, earn profit by charging a higher rate of interest on loans to borrowers, and make investments in stocks and bonds on behalf of savers, including through mutual funds.
The financial system provides risk sharing by allowing savers to ______________ financial investments
spread their money among many
What is the general relationship between the business cycle and unemployment and inflation?
During an expansion, unemployment falls and inflation increases
Shorter recessions, longer expansions, and less severe fluctuations in real GDP have resulted in a significant improvement in the economic well-being of Americans. Explanations for this period of relative stability include
the increasing importance of services as a fraction of real GDP, which are less affected by recessions than goods production; the establishment of unemployment insurance and other government transfer programs that provide funds to the unemployed and help maintain higher spending levels; active federal government policies to stabilize the economy, and the increased stability of the financial system
Shorter recessions, longer expansions, and less severe fluctuations in real GDP have improved the well-being of Americans. Economists offer three explanations for this
1. Increasing importance of services and the declining importance of goods: During a recession, households reduce purchases of durable goods more than they reduce purchases of services, such as medical care.
2. Unemployment insurance and government transfer programs: These programs make it possible for workers who lose their jobs during recessions to have higher incomes. As a result, they spend more than they would otherwise.
3. Government policies: Arguably, policies, such as monetary policy (conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank) and fiscal policy (conducted by the federal government), have played a key role in stabilizing the economy.
The best measure of the standard of living is
real GDP per person, which is usually called real GDP per capita.
It is the ______ trend in real GDP per capita that we focus on when discussing long-run economic growth
upward
Labor productivity
is the quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work.
If the quantity of goods and services consumed by the average person is to increase
the quantity of goods and services produced per hour of work must also increase.
Economists believe two key factors determine labor productivity:
The quantity of capital per hour worked
The level of technology
Technological change is
an increase in the quantity of output firms can produce, using a given quantity of inputs, and can come from many sources.
Spviet Union living standards
For example, by the 1970s, living standards in the Soviet Union had stagnated, even though the country was continuing to increase the quantity of capital available per hour worked, because it experienced relatively little technological change.
Which of the following changes does not cause an increase in the quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker, or in one hour of work?
an increase in the number of workers
Which of the following changes will ensure that an economy experiences sustained economic growth?
technological change
The factory’s _______, however, is measured by its production when operating on normal hours, using a normal workforce
capacity
Which of the following are financial securities that represent promises to repay a fixed amount of funds?
bonds
Which of the following is not a service that the financial system provides for savers and borrowers?
guaranteeing savers high rates of return
When firms use funds to purchase robots, software, factories, and office buildings, they are engaging in _______.
investment
The business cycle involves the interaction of many economic variables. A simple model called the _________________ model can help us understand the relationships among some of these variables.
aggregate expenditure
The aggregate expenditure model focuses on the short-run relationship between _____ and _____.
total spending and real GDP
Price level is constant in the _____.
aggregate expenditure model
The key idea of the aggregate expenditure model is that in any particular year, the level of GDP is determined mainly by the level of _____.
aggregate expenditure.
Economists first began to study the relationship between changes in aggregate expenditure and changes in GDP during __________.
the Great Depression of the 1930s.
Keynes identified four components of aggregate expenditure that together equal GDP
Consumption (C). Spending by households on goods and services, such as automobiles and haircuts.
Planned investment (I). Planned spending by firms on capital goods, such as factories, office buildings, and machine tools, and on research and development, as well as spending by households and firms on new houses.
Government purchases (G). Spending by local, state, and federal governments on goods and services, such as aircraft carriers, bridges, and the salaries of FBI agents.
Net exports (NX). Spending by foreign firms and households on goods and services produced in the United States minus spending by U.S. firms and households on goods and services produced in other countries.
Aggregate expenditure =
consumption + planned investment + government purchases + net exports
Aggregate expenditure, or the total amount of spending in the economy, equals
consumption spending plus planned investment spending plus government purchases plus net exports
Goods that have been produced but haven’t yet been sold are referred to as _____.
inventories
For example, Doubleday Publishing may print 1.5 million copies of the latest John Grisham novel, expecting to sell them all. If Doubleday does sell all 1.5 million, its inventories will be unchanged, but if it sells only 1.2 million, it will have an unplanned _____ in inventories.
increase
Note that actual investment will equal planned investment only when there is __________.
no unplanned change in inventories
If the economy does not experience an unplanned change in inventories,
actual investment equals planned investment.
If the economy experiences an unplanned increase in inventories,
actual investment will be greater than planned investment
If the economy experiences an unplanned decrease in inventories
actual investment will be less than planned investment
macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when _______________.
total spending, or aggregate expenditure, equals total production, or GDP
When aggregate expenditure is greater than GDP, the total amount of spending in the economy is _____ than the total amount of production.
greater
if aggregate expenditure is greater than GDP, inventories will _____, causing GDP and total employment to increase.
decline
Only when __________ will firms sell what they expected to sell.
aggregate expenditure equals GDP
The 2020 recession resulted in by far the largest _____ in consumption in U.S. history, as many state and local governments closed or reduced the capacity of businesses to help slow the spread of Covid–19.
decline
These are the five most important variables that determine the level of consumption:
Current disposable income
Household wealth
Expected future income
The price level
The interest rate
The most important determinant of consumption is ________
the current disposable income of households