Bio 212L Practical Iowa State University
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Gallbladder
stores and concentrates bile
Nephron
functional unit of the kidney
Testes
produce sperm and reproductive hormones
Kidney
Filters waste from the blood like urea, water, salt and proteins.
Stomach
Breaks down and digests food
Small Intestine
Absorb nutrients and minerals from food
Liver
Metabolize nutrients; detoxifies
Ovary
Produces eggs and reproductive hormones
Why are intestines so long?
It needs to absorb all minerals and nutrients absorbed with every bite of food we take
Villi and Microvilli
increase surface area for absorption
Esophagus
Conduit for food and liquids that have been swallowed to stomach
Trachea
provides air flow to and from lungs for respiration
Salivary glands
helps break down carbohydrates
Spleen
filter for blood as part of the immune system
Thyroid
metabolism, growth, and development of the human body
Thymus
generate mature T lymphocytes (white blood cells)
Egg pathway leaving the body
ovaries -> oviduct -> uterus -> cervix -> vagina
Sperm pathway leaving the body
testes -> seminiferous -> epididymus -> vas deferens -> urethra
Systolic pressure
when blood pressure is at its highest (1st number)
Diastolic pressure
when blood pressure is at its lowest (2nd number)
Normal BP
Systolic <120
Diastolic <80
Prehypertension BP
Systolic: 120-139
Diastolic: 80-89
High BP
Systolic > 140
Diastolic > 90
Vein color (dissection) and shape
blue; rounded with thicker wall
Artery color (dissection) and shape
red; smaller with odd shape
Umbilical artery
is attached to placenta. The artery takes deoxygenated blood back to mother.
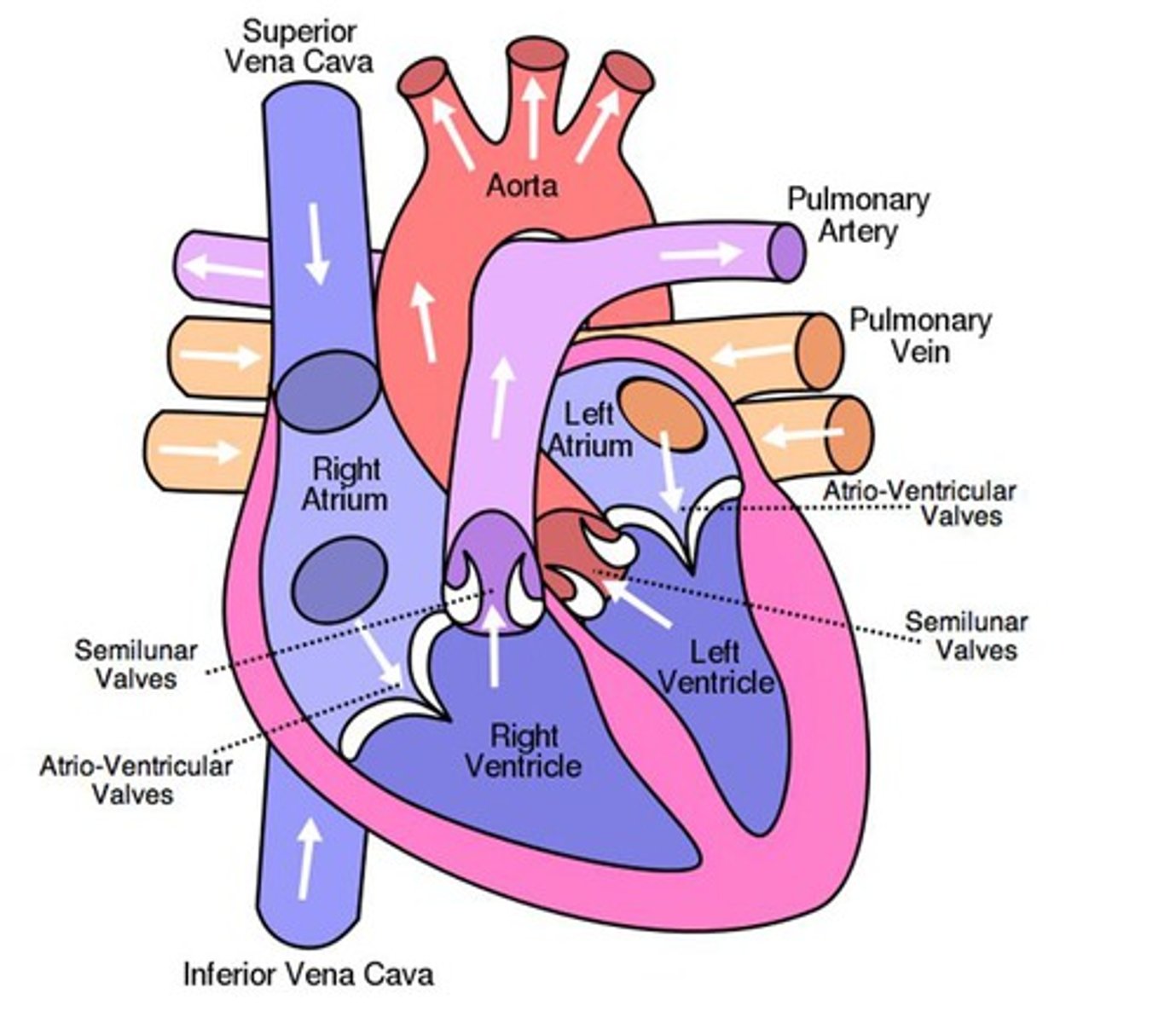
Path of blood from lung -> kidney
Exits lungs -> goes through left atrium to ventricle -> leaves out aorta into kidneys
Path of blood from R. atrium -> head
Leaves R. atrium and enters R. ventricle -> pumped out of heart by pulmonary artery -> lungs to L. atrium -> L. ventricle and out aorta -> enters head
Path of blood from liver -> L. ventricle
Leaves liver and enters atrium -> enters R. ventricle -> pulmonary artery -> through lungs into L. atrium -> into L. ventricle
Erythrocytes
carry oxygen from lungs to body and bring CO2 back to lungs to be expelled.
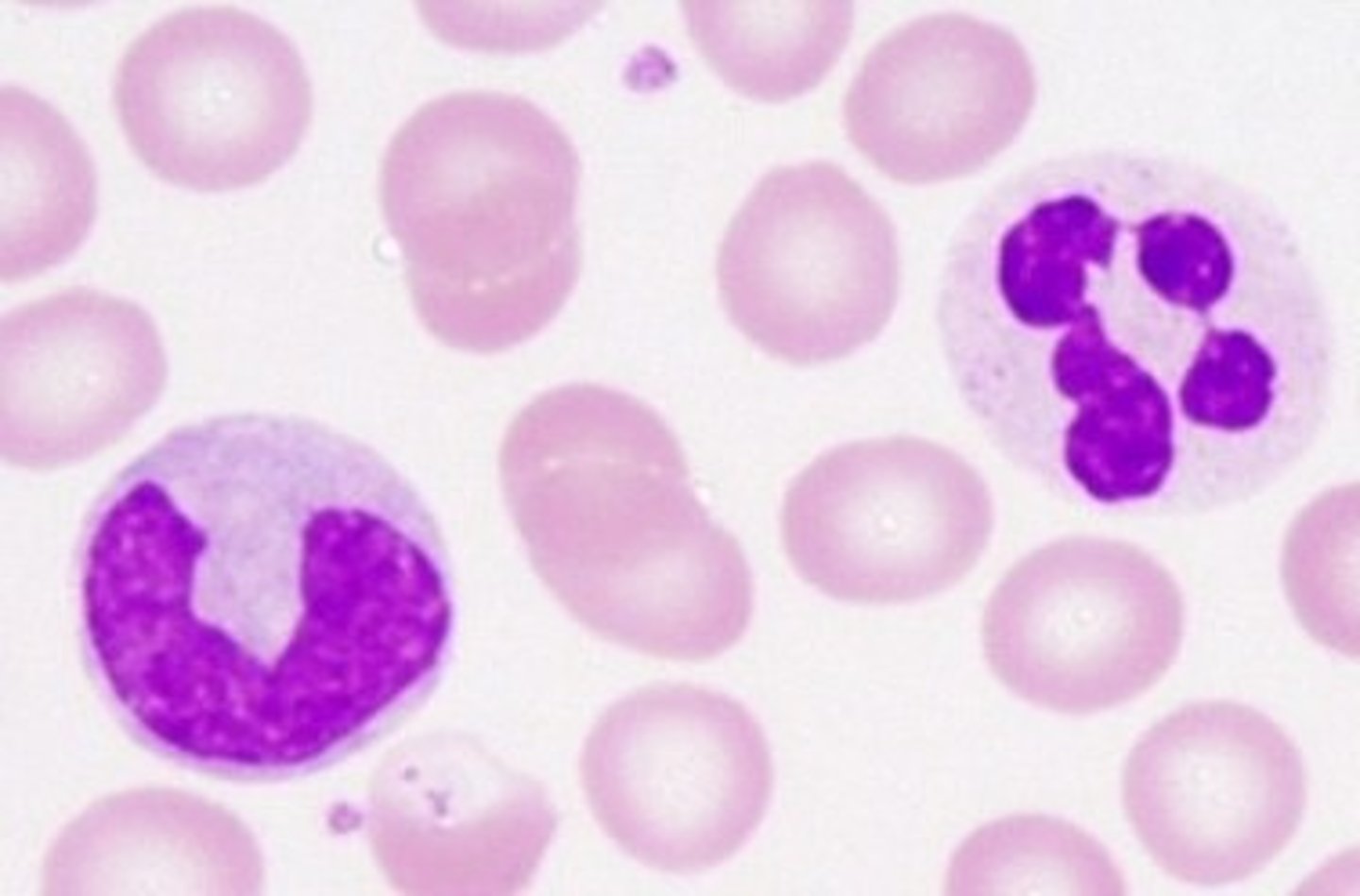
Leukocytes
protect body against both infectious diseases and foreign invaders
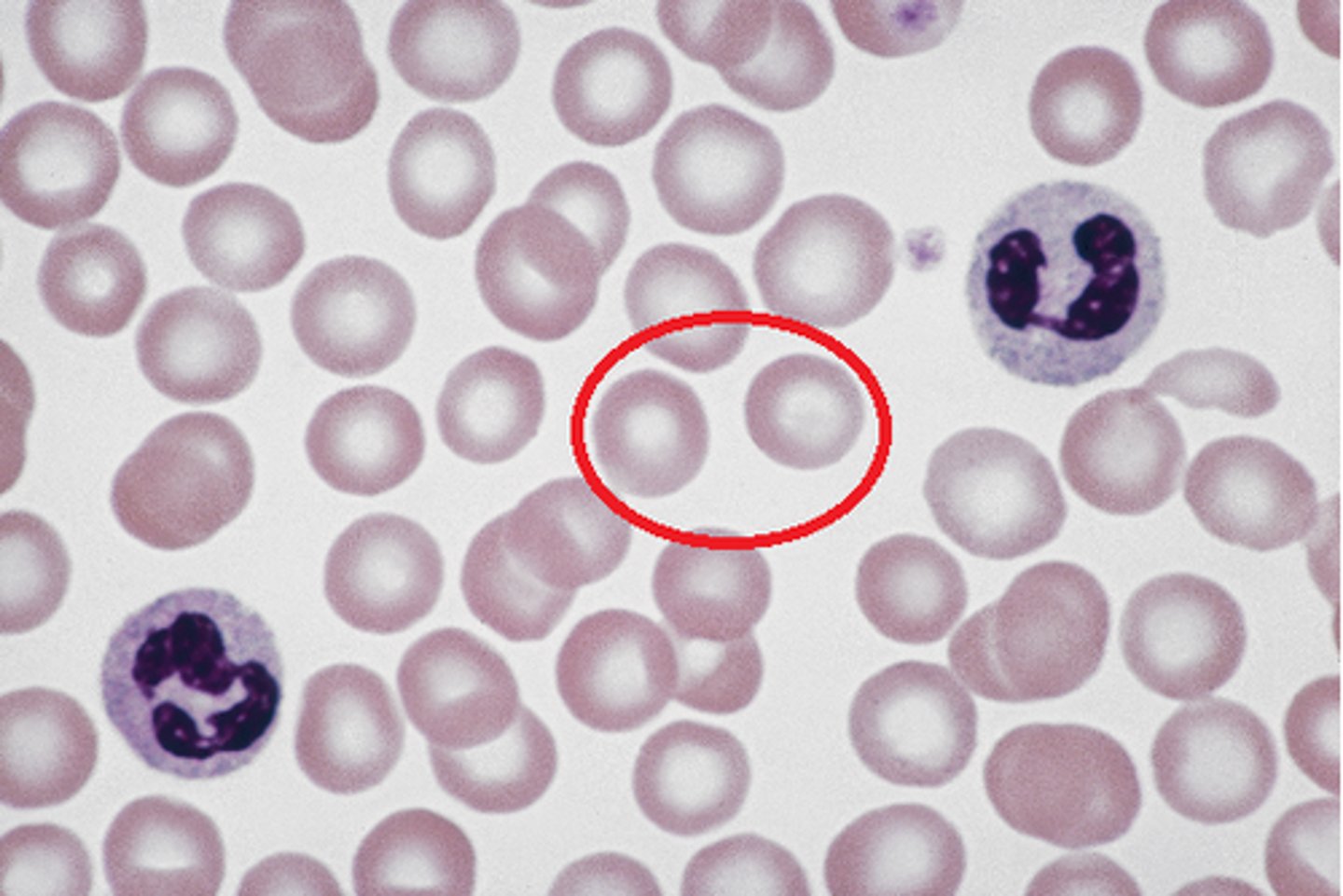
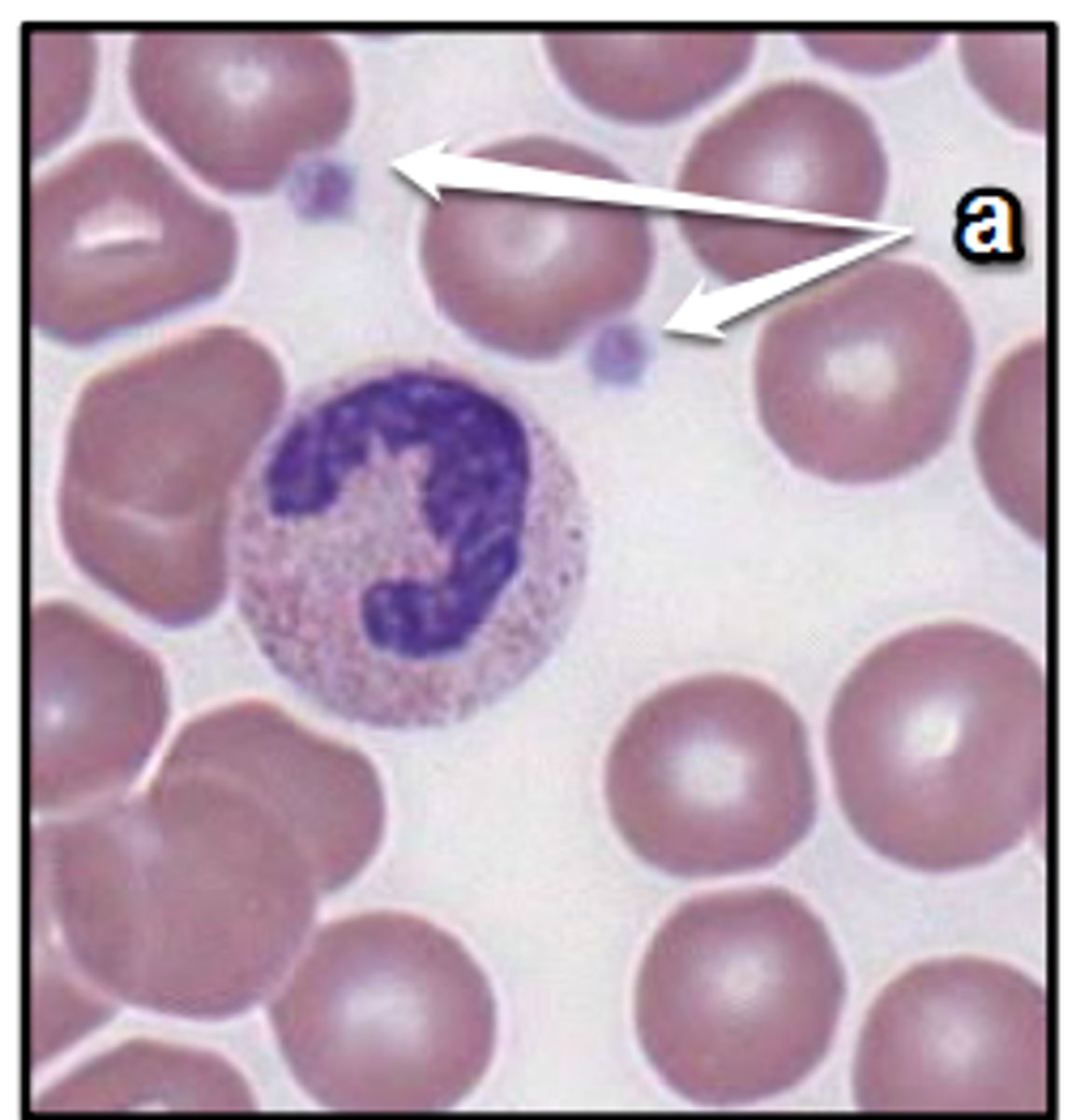
Platelets
react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping; creating a blood clot
heart diagram
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
Men: 3.1
Women: 1.9
Tidal Volume (TV)
Men: 0.5
Women: 0.5
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
Men: 1.2
Women: 0.7
Vital Capacity (VC)
Men: 5.8
Women: 4.2
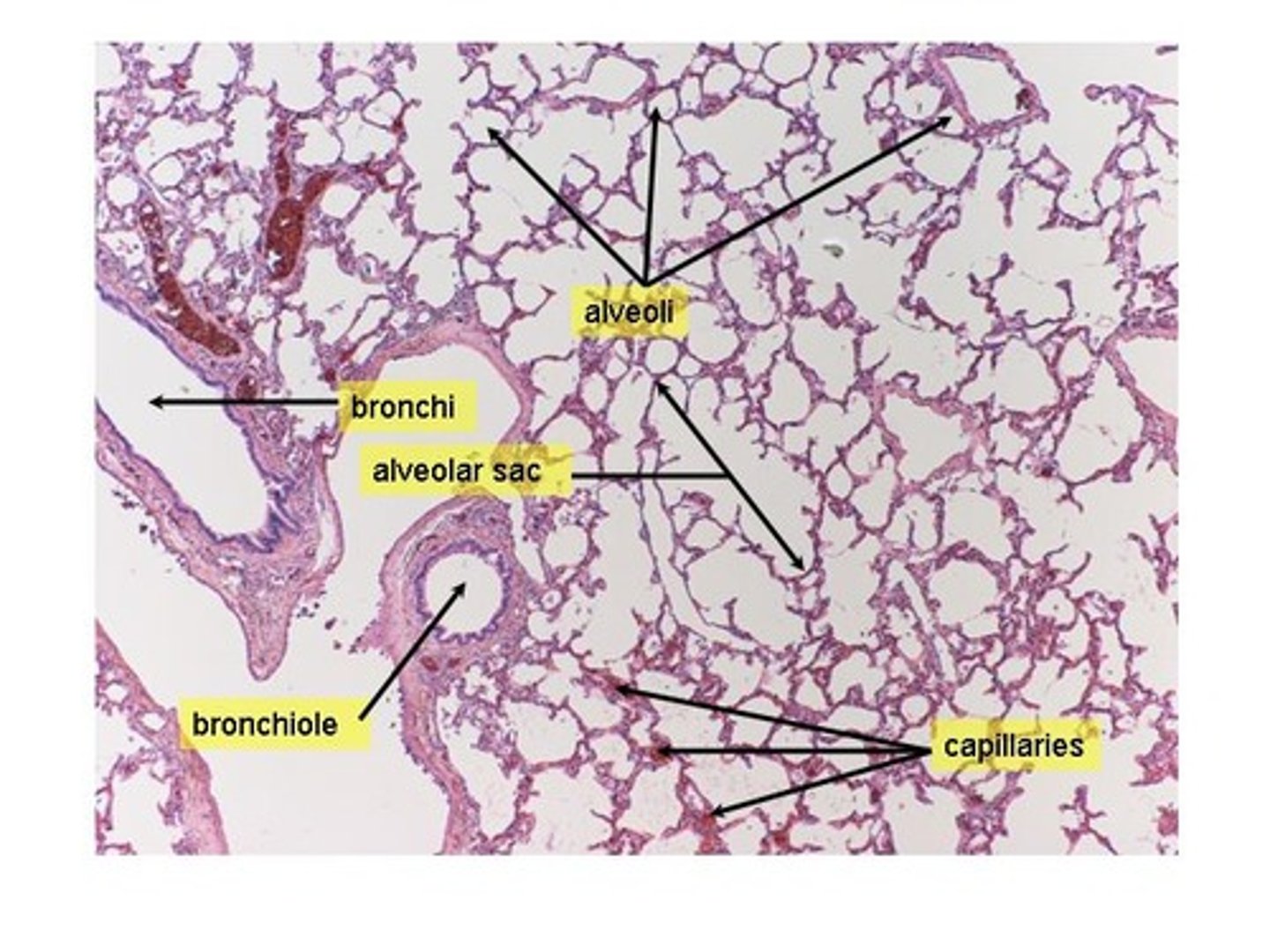
Mammal respiratory structure
Have 2 lungs; air is split between lungs by bronchi -> bronchioles -> alveoli (gas exchange occurs)
Mammal respiratory ventilation
Occurs via respiratory centers in medulla and brainstem
Mammal respiratory delivery to cells
protein inside red blood cells carry O2 to cells and CO2 to lungs
Fish respiratory structure
Gills mediate gas exchange. Located on sides of head
Fish respiratory ventilation
Gills absorb O2 from water
Fish respiratory delivery to cells
O2 itself enters blood and is picked up by hemoglobin -> fishes body
Insect respiratory structure
Air enters through spiracles
Insect respiratory ventilation
Trachea opens to outside through spiracles
Insect respiratory delivery to cells
O2 travels through spiracles then trachea throughout body
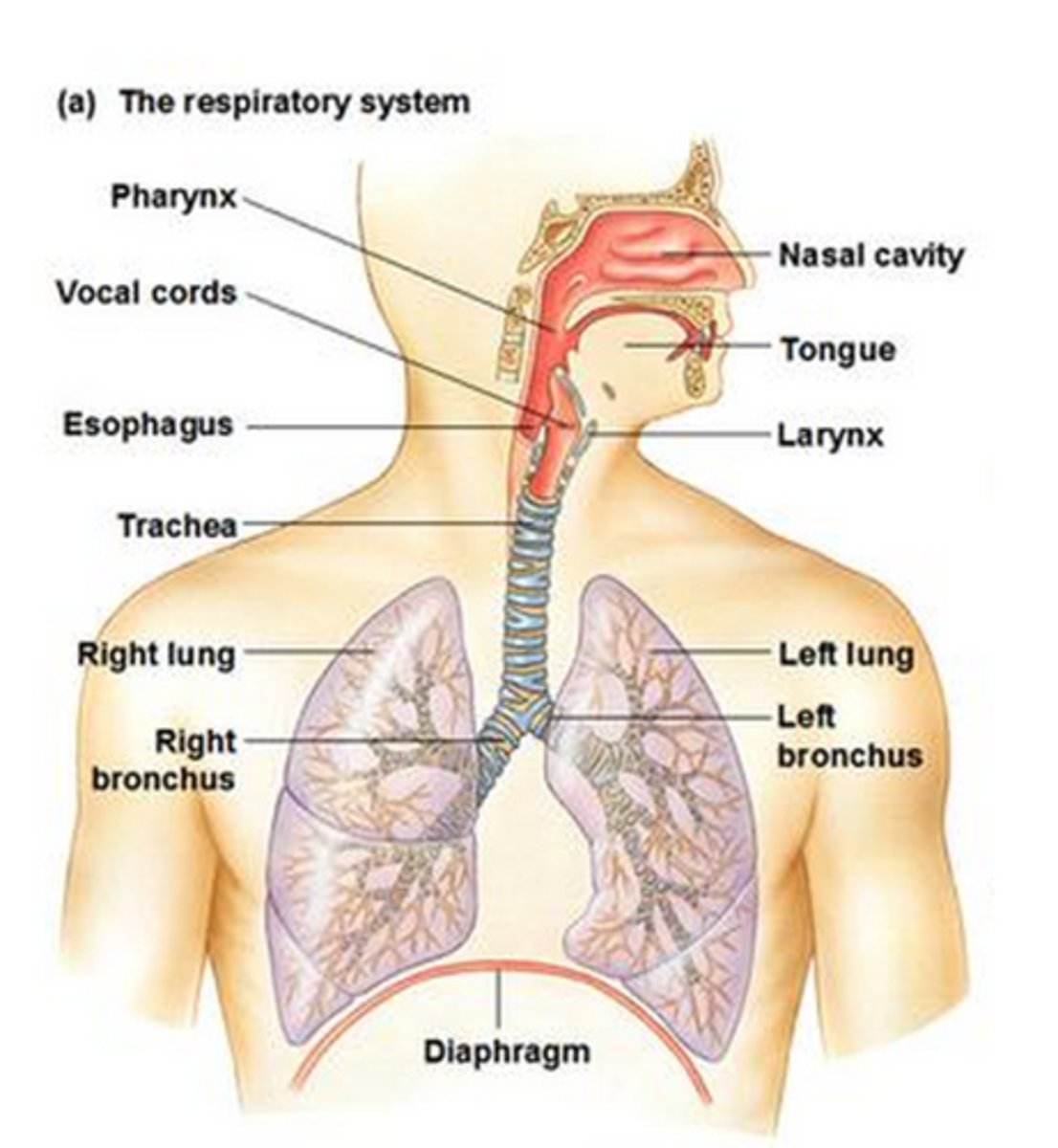
Food through pharynx -> esophagus
food enters oropharynx -> laryngopharynx -> esophagus
Air through pharynx -> trachea
larynx
Epiglottis
helps make sure air and food goes down correct pipe
What goes down esophagus?
food
What goes down trachea?
air
Human lung under microscope
Insects have
-spiracles that help O2 reach internal respiratory organs.
-do not have lungs they have trachea
Gills function
-take O2 out of the water. Water leaves gills taking CO2 with it
-have lamellae on filaments
What happens when a fish is on land?
projections on gills that normally float collapses, blocking most surface area
Operculum
a bony flap that covers gills and allows fish to breathe and protects gills.
What happens in operculum is damaged?
the fish could die and not get enough O2
Respiratory system
Glial cells
surround neurons and provide support for and insulation between them
Neuron
a specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses; a nerve cell.
Why is white matter white?
It contains a high concentration of myelin.
What is gray matter gray?
cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons
How many neuromuscular junctions are there in each muscle cell?
1
With how many muscle cells does a single neuron synapse?
Many
Are muscle cells controlled individually or in groups?
In groups
Patellar reflex
lets doctor's know if signals are being sent to brain
CNS (central nervous system)
controls reflexes. Reflexes are involuntary.
Sympathetic nerves
stimulate body's fight-or-flight response
Spinal nerves
carries motor, sensory, and automatic signals between spinal cord and body
Meninges
three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord; also protects CNS
Ventral roots
carries neural signals away from CNS
Dorsal roots
transmits sensory info
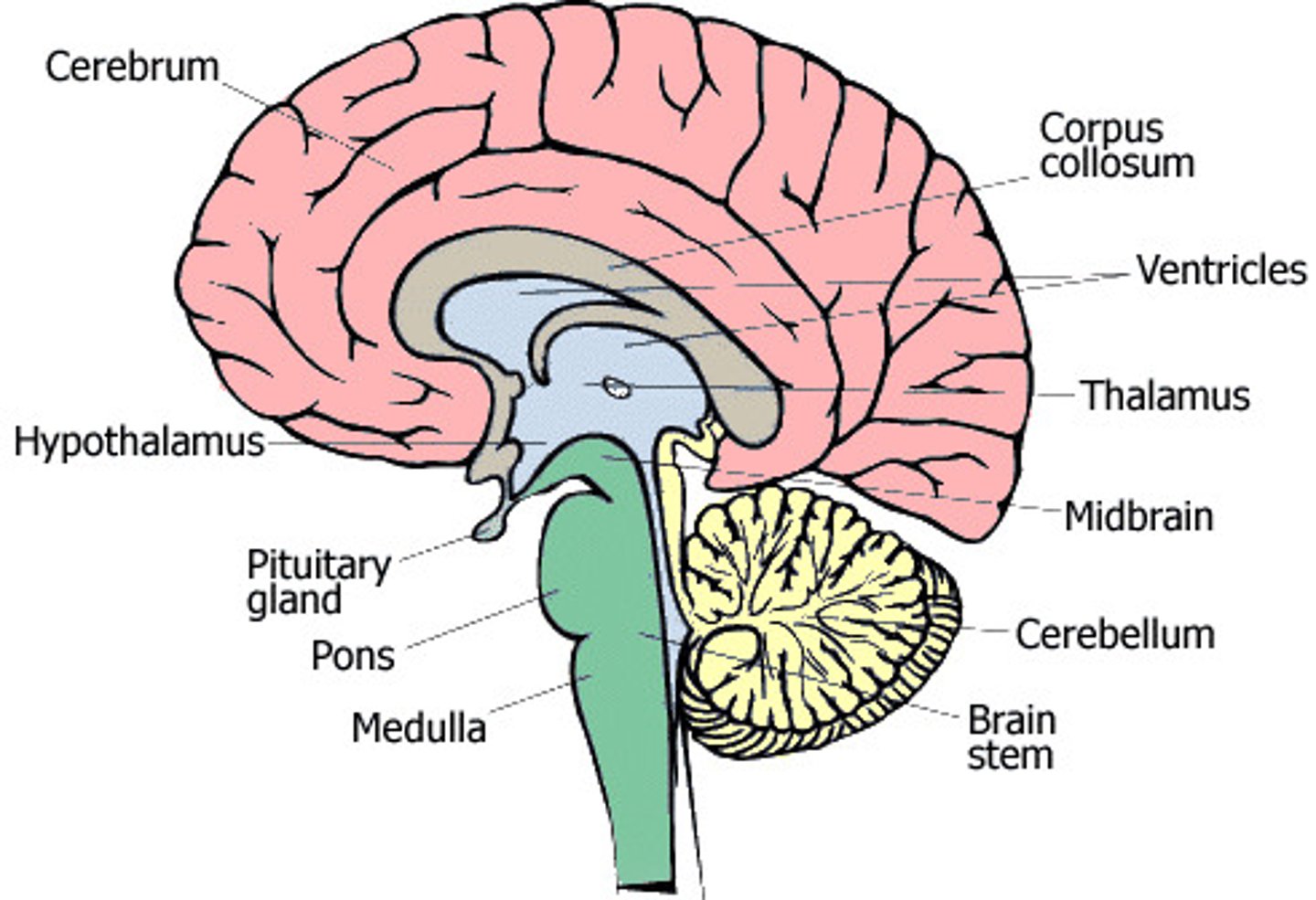
Cerebrum function
thought and action
Cerebellum function
receives info from sensory systems and spinal cord. Motor movements.
Medulla Oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
Optic chiasma
aid binocular vision and eye-hand coordination
Olfactory bulb
receives neural input about odors detected by cells in the nasal cavity
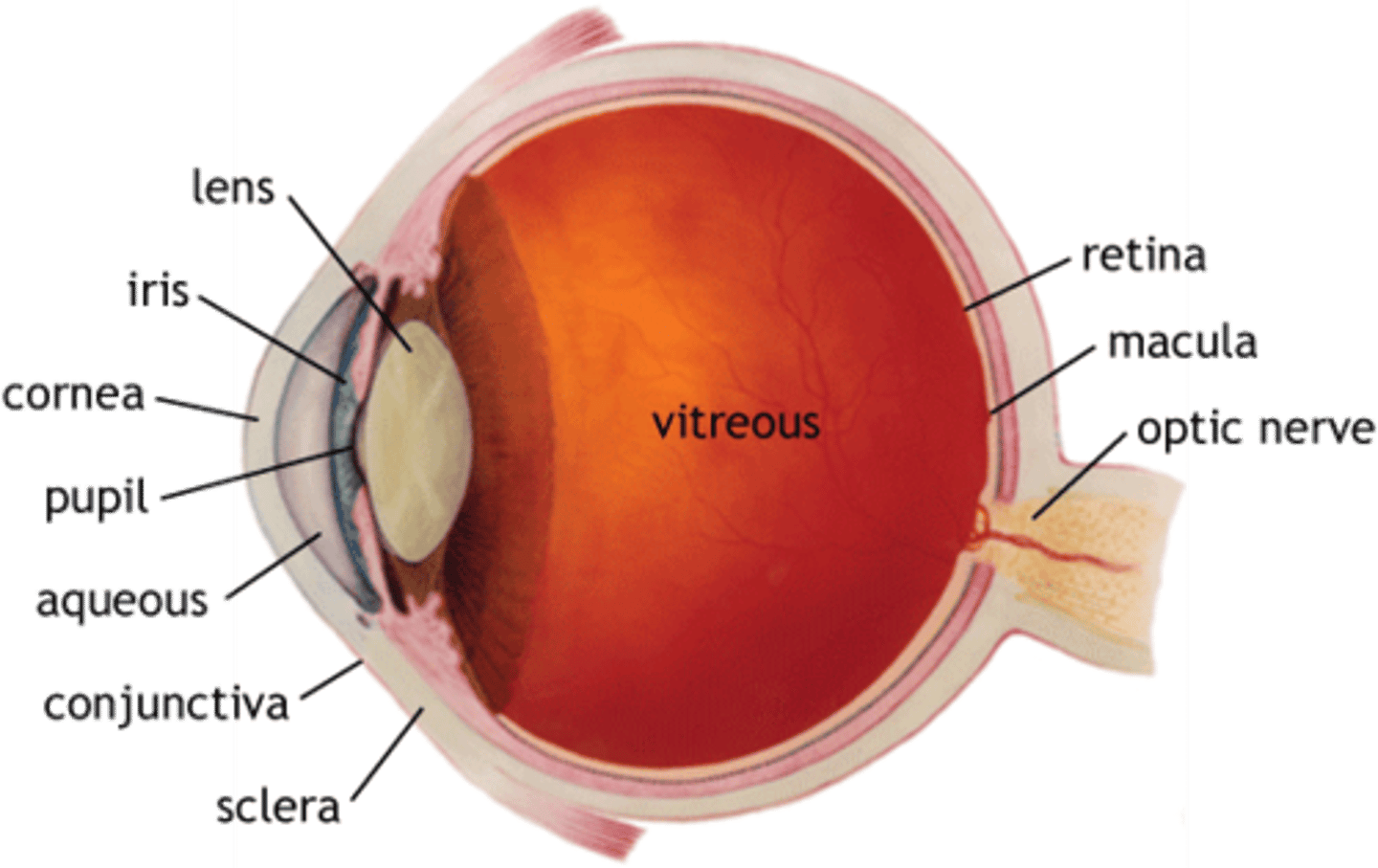
Pupil
absorbs light rays
Cornea
acts as eye's outermost lens. Controls and focuses entry of light into eye
Lens
change focal distances of eye to see things at different distances
Optic nerve
transfer visual information from the retina to the vision centers of the brain via electrical impulses
Optic disc
axons of retinal ganglion cells come together. Entry point for major blood vessels
Retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
Rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray; necessary for peripheral and twilight vision, when cones don't respond. Can detect dim light. 1 type
Cones
retinal receptor cells that are concentrated near the center of the retina and that function in daylight or in well-lit conditions. The cones detect fine detail and give rise to color sensations. 3 types.
Blind spot
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a "blind" spot because no receptor cells are located there
Why don't you normally see blind spots?
Your brain fills blind spot by painting in surroundings
After image
an image that remains after a stimulus is removed, especially one in which the colors are reversed
Optical illusion
misinterpretation of a visual stimulus
Bleached cones
see opposite color
Stare at red color
see blue
Stare at blue color
see orange
Stare at green color
see purple
Eye diagram
Brain diagram
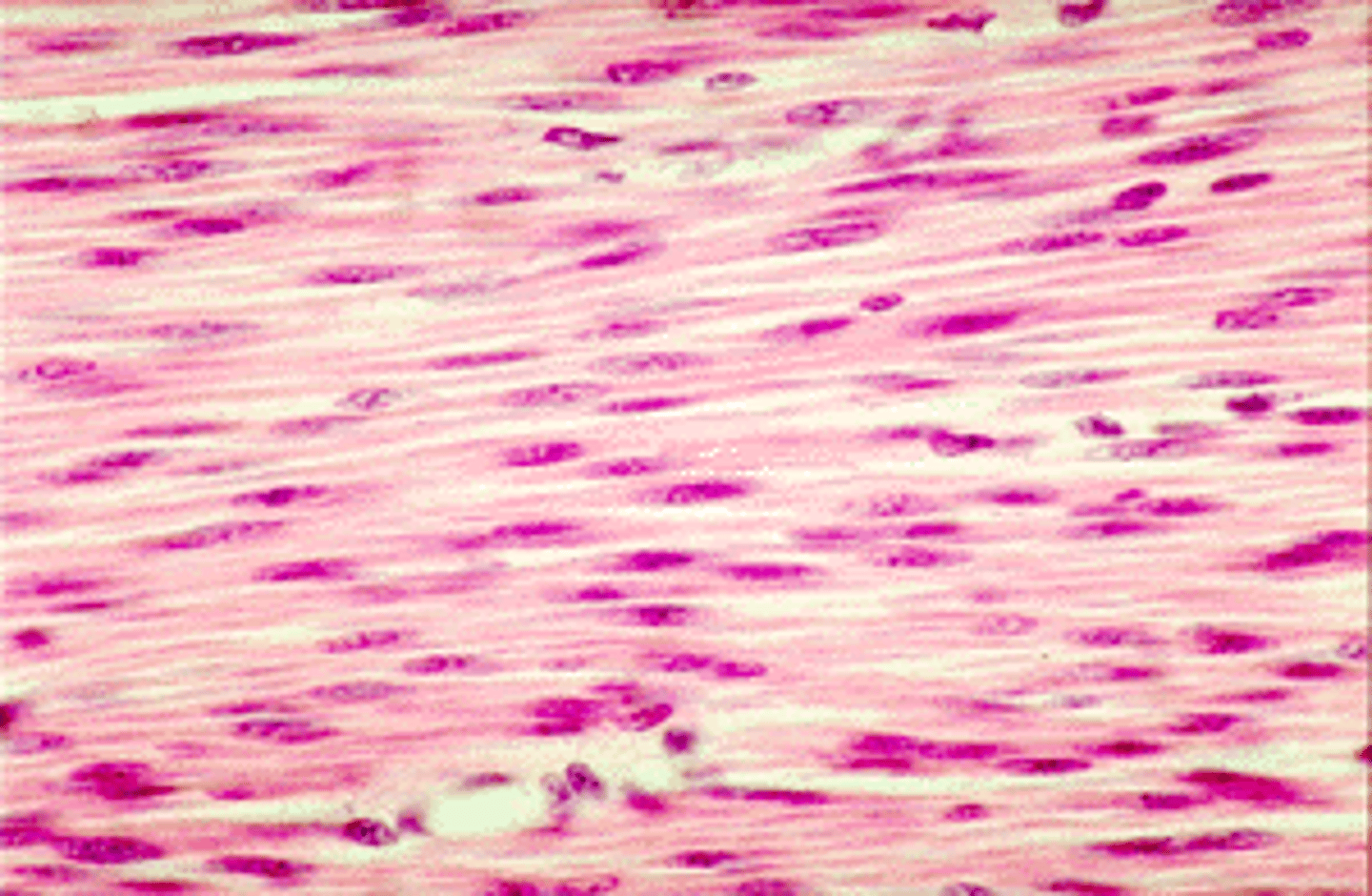
Smooth muscle cells
-Involuntary, non-striated muscle.
-single nucleus
-unbranched
-located in intestines, arteries, other
-move food, help regulate blood pressure, etc.
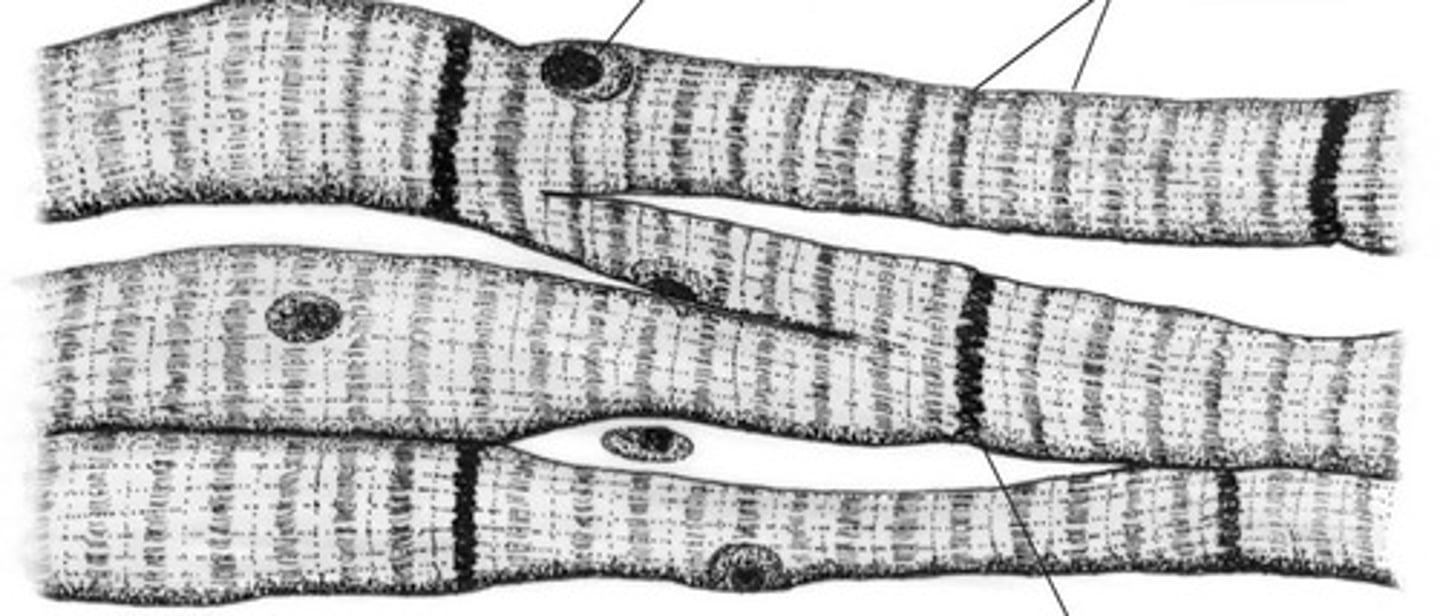
Cardiac muscle cells
-involuntary, striated muscle.
-1 or 2 nuclei
-branched
-located in heart
-pump blood