Mobile units
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
what do mobile units look like
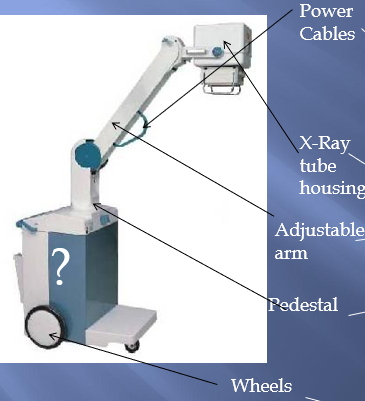
what are the features of mobile imaging equipment
X-ray tube:
•Standard X-Ray tube
•Tungsten-rhenium target & rotating anode
Tube Housing/telescopic arm,
•Tube housing: can be “tank head” design
•Mounted on a pivot joint for flexibility/manoeuvrability
•Telescopic arm to hold the tube housing/carry power cables/allow extendable “reach”
•Pedestal for attachment to telescopic arm: gives stability/allows varying height of tube
Console
•Controls to select appropriate exposure factors kVp and mAs / LED display/ programme selection
POWER INDICATOR ON CONSOLE
Wheels & control
•Wheels to allow movement/ motor assisted
•Handle with automatic locking device/wheel break when released
•Collision sensors
What are the functions of the base
Apart from stability the base has other functions:-
Houses a large Battery
Contains step-up and step down HT transformers
Provides a rectifier system
Contains an oil coolant
Made of grounded steel with fibreglass cover to provide durability
how do rectifiers work?
Electrical supply from mains is ALTERNATING current
If left like this = inefficient for photon production
Need DIRECT current to maintain constant flow of photons in beam [HALF WAVE RECTIFICATION]
Need double electrical current [SINGLE PHASE FULL WAVE RECTIFICATION]
Ideal current “smooth”= 3 PHASE FULL WAVE RECTIFICATION
what are the types of power supply?
1.Mains dependent (Single phase full wave rectified).
2.Capacitor powered.
3.Battery powered.
what is mains dependent current supply?
Mains dependent: single phase full wave rectified generators
Special hospital power supply required (30 A ring)
Causes issues!
Expensive & imposes limits on locations can be used
Also sudden fluctuations in voltage in mains supply following connection/disconnection other appliances drawing large current
Limited power output because of low available mA so full range of exposures cannot be obtained.

what is capacitor powered power supply
Does not operate on batteries and can produce x-ray-photons from electrical energy stored in a very large capacitor housed in the base;
The capacitor discharges a DC (direct current) producing a 450Hz supply to produce X-Ray photons;
Capacitor requires frequent recharge using normal hospital 13 A mains supply;
During exposure, x-ray tube voltage monitored, output controlled by a microprocessor to maintain constant output.
what is a battery powered power supply
Generally nickel-cadmium battery; stores equivalent 10,000 mAs at normal operating voltages;
DC voltage (130V) converted (by inverter) to AC before it can be used to supply the generator transformer;
Voltage produced is 10x frequency (500 Hz) of normal mains freq.
Higher frequency: transformer more efficient (“smoother” current) and therefore less ripple effect;
Battery depletes and voltage falls with each exposure, some form of compensation must be applied until recharged (any 13 A mains supply)
The battery stores electrical energy taken from the mains supply when the unit is plugged in- provides a constant potential
When fully charged the POWER INDICATOR on the console will show 100%/FULL
The unit can still be used with less than 100%
The battery discharges some of its energy during an exposure- INDEPENDANT OF MAINS

how do step up/down transformers work?
As in static X-Ray units voltage from battery needs adjustment before reaching the tube.
Step-up transformer increases voltage to cathode /anode creating a high potential across the tube to allow photon production
Step-down transformer decreases voltage to filament to allow thermionic emission without damage to the filament
Modern mobile units usually have a choice of two focal spot sizes
what are the three tenets of radiation protection
Time – Dose proportional to exposure time
Distance – Inverse square fall-off of dose with distance from the source
Shielding – Reduce exposure by putting an appropriate radiation absorber between yourself and the source
what are lead aprons
Made of powdered lead incorporated into rubber or vinyl.
Must be .25mm lead equivalent at 100 kVp if used as secondary barrier.
Must be .5mm lead equivalent if used as primary barrier.
What is a contingency plan
If the risk assessment identifies that a particular radiation accident is reasonably foreseeable the employer must prepare a contingency plan.
It is a plan designed to ensure the restriction of exposure and the health and safety of those affected by an accident as far as reasonably practicable.
Must be incorporated into the local rules
Rehearsals performed with relevant staff
If the plan has to be used:
Investigate whether any measures could be introduced to stop it happening again
Record any resulting staff exposure