Antibody practical
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Why can antibodies be used to identify proteins
They are highly specific about which antigen they bind to so can be used to distinguish different proteins
What are the different methods of identifying proteins with antigens
Radial immunodiffusion
Double immunodiffusion
Immunoelectrophoresis
What is immunological testing used for
Serum immunoglobulin concentrations
Detecting specific antibodies
Distinguish between antigens
How many binding sites do antigens have
Several sites
How many binding sites do antibodies have
At least two
What does the size of immune complexes depend on
Relative amounts of antigen or antibody
Number of binding sites on the antigen
Class of antibody
What do immune complex formations look like
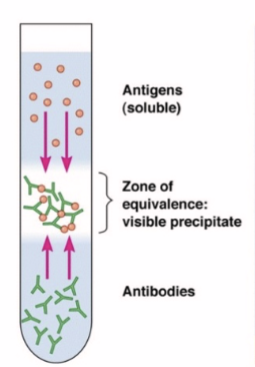
What is single radial immunodiffusion
Gel contains antibodies which will bind target molecules
The further the antigen diffuses from the well the more dilute it becomes
Higher concentrations of antigen will reach the zone of equivalence further from the well
Diameter of preciptin ring is proportional to Ag concentration
What happens in double immunodiffusion
Hot agar solution poured onto plate
Cools and sets
Holes punched
Ag and Ab added to well
Ags and Abs diffuse into gel setting up a concentration gradient
Ags and Abs combine forming large aggregates at approximately equimolar concentrations
Precipitation of large Ag:Ab aggregates form the preciptin line
What is immunoelectrophoresis
Technique used to identify any myelomas by demonstrating monoclonal immunoglobulins in sera
These are detected using antisera to specific IgG, IgA and IgM heaby chains and light chains
Deficiencies can also be identified as can acute bacterial infections
What is myeloma
A blood cancer arising from plasma cells
Tend to create huge amounts of a monoclonal antibody
Can identify this excess production in sera of patients as identical antibodies with only 1 kind of heavy chain and 1 light chain
What happens in immunoelectrophoresis
Patient or Normal serum goes into central well
Electrophoresis seperates proteins
Immunoglobulins detect by antisera in troughs