Surgery E2 random questions pt 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
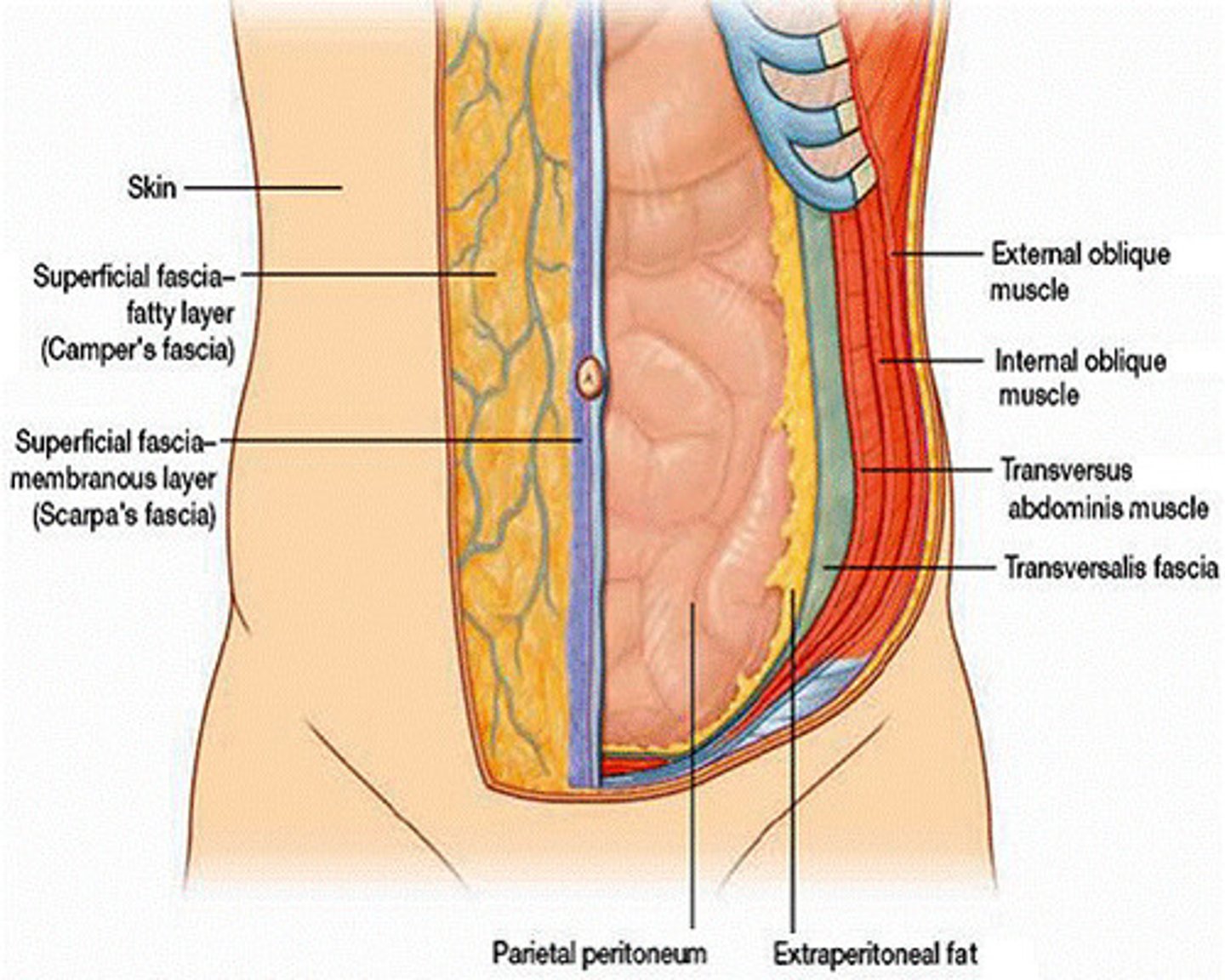
What are the 9 layers of the abdominal wall?**
1. skin
2. subcutaneous tissue
3. superficial fascia
4. external oblique
5. internal oblique
6. transversus abdominis
7. transversalis fascia
8. preperitoneal adipose
9. peritoneum
what are the 3 main branches of the aorta that supply the GI tract organs?**
1. celiac a. → supplies foregut
2. superior mesenteric a. → supplies midgut
3. inferior mesenteric a. → supplies hindgut
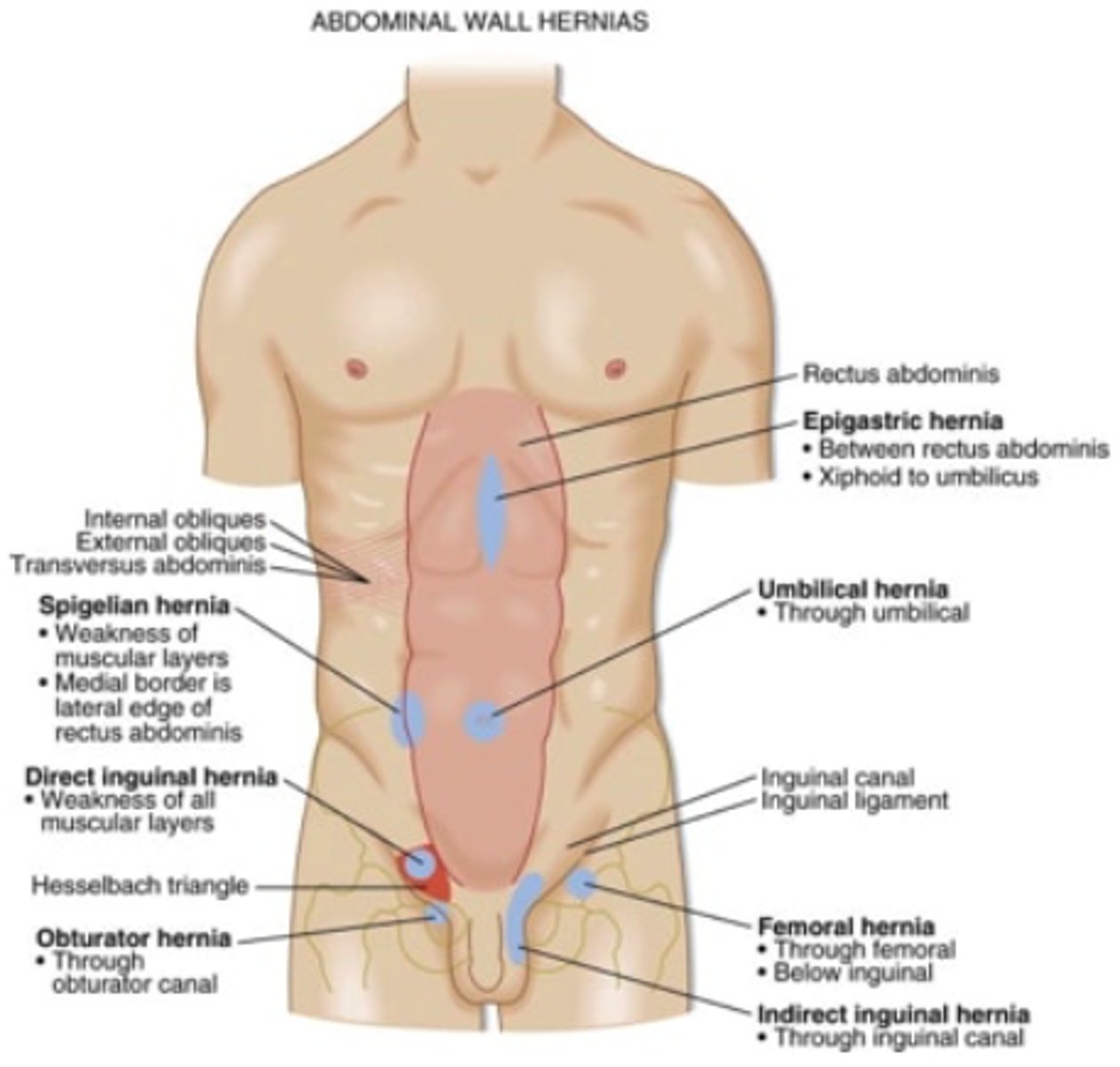
What is the MC type of hernia?
inguinal
which structures form Hesselbach's triangle?***
Medial → rectus abdominus
lateral → inferior epigastric
inferior → inguinal ligament
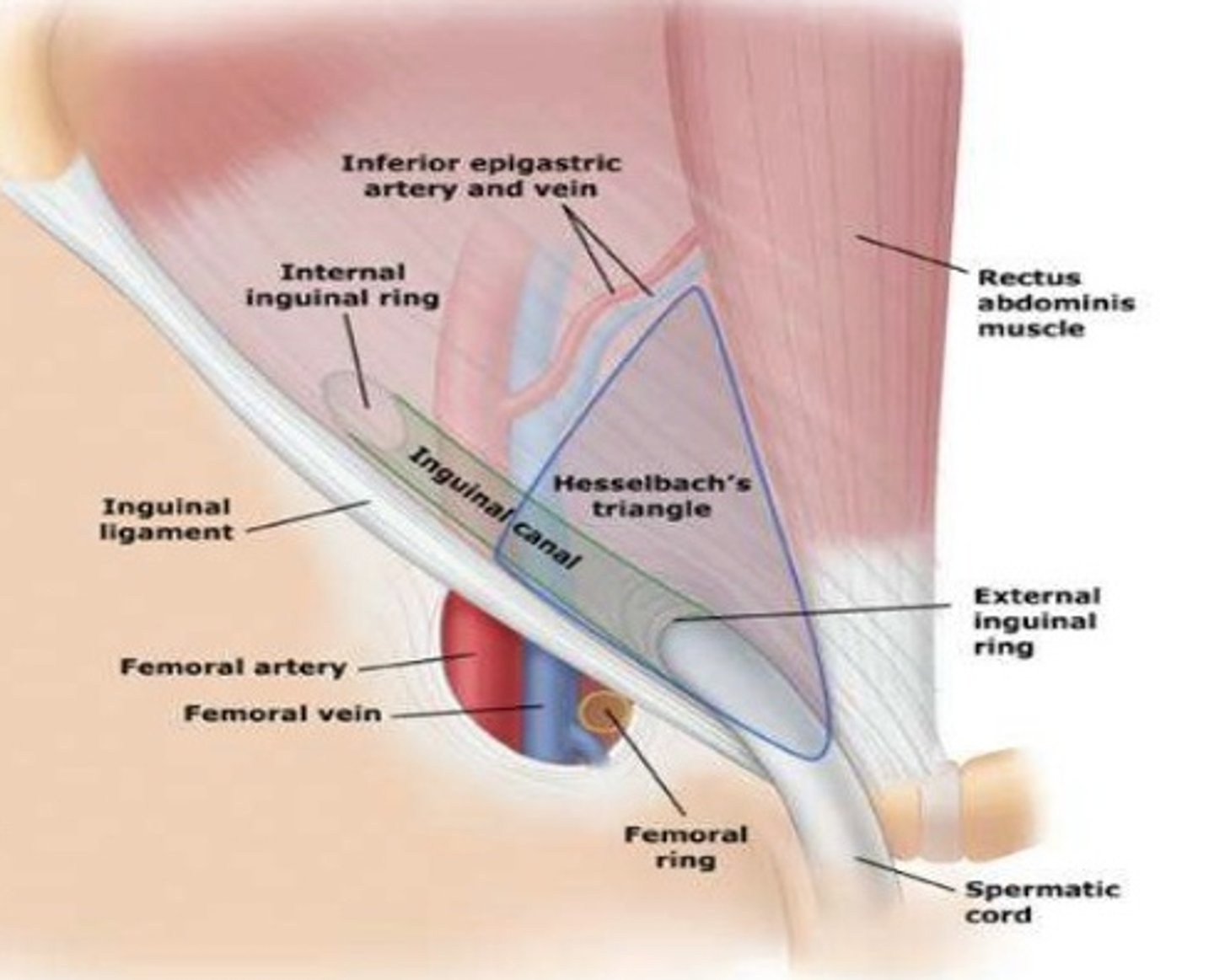
what structures lay in the inguinal canal?***
male → spermatic cord
female → round ligament of uterus
damage to which nerve could result in persistent testicular pain?
ilioinguinal nerve**
what is the difference between direct and indirect inguinal hernias?***
indirect = through internal inguinal ring
direct = through transversalis fascia in hasselbach's triangle
which open hernia repair (herniorrhaphy) is tension-free?***
lichtenstein →no sutures or mesh
which hernias require emergent surgery?
incarcerated and strangulated
strangulated is more emergent
what are the types of ventral hernias?***
1. umbilical →common in kids
2. incisional →MC in obese/infection/smokers
3. spigelian →lateral edge of rectus muscle
4. obturator →passes through obturator foramen and muscles (elderly female)
which laparoscopic hernia repair approach is used for bilateral, large, and recurring hernias?**
transabdominal preperitoneal procedure (TAPP)
omphalocele or gastroschisis: covered by membrane?
omphalocele
gastroschisis is NOT covered
what is the procedure to treat acute peptic ulcer disease?
billroth procedure
which arteries are involved in acute peptic ulcer disease?***
gastric ulcer → erodes gastric and splenic vessels
duodenal ulcer → erodes gastroduodenal artery
what is the MCC of pneumoperitoneum?
perforated ulcer
pneumoperitoneum = free air in diaphragm
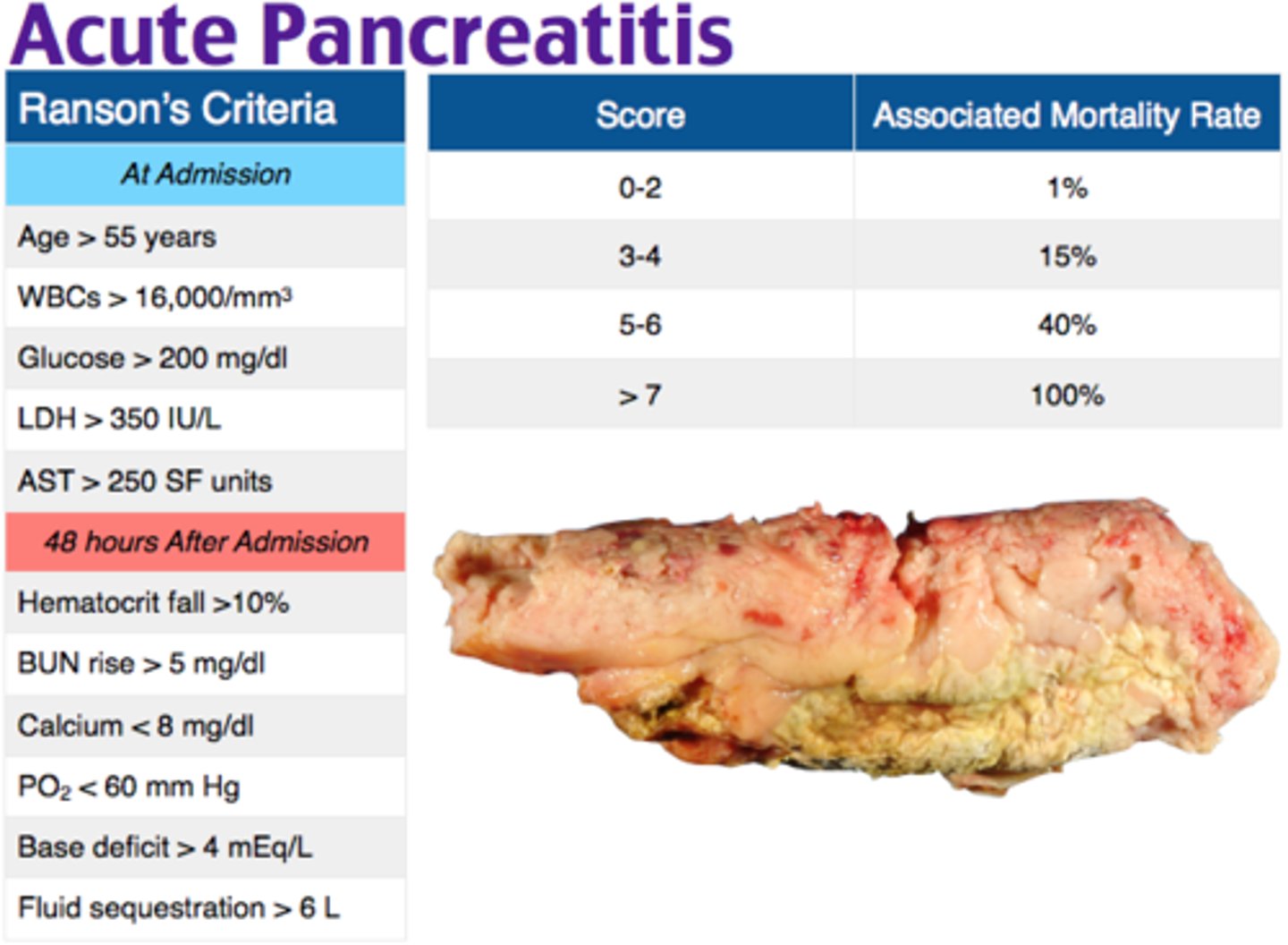
what criteria is used to evaluation pancreatitis?
ranson criteria
what is the MCC of SBO?***
adhesions from surgery
what are the complications of laparoscopic appendectomy?***
- post op infection
- intraabd abscess
- recurrence if remnants remain
if a child <3 has bilious emesis and abd distention, it is __________ until proven otherwise?
volvulus → r/o with stat upper GI series
which dx shows up as coffee/kidney bean on abd XR and birds beak on contrast enema***
volvulus
what is the surgical management of volvulus?***
sigmoid = proctosigmoidectomy w/o anastomosis and temporary colostomy (Hartmanns)
cecum - right hemicolectomy with ileocolic anastomosis
which organ is most frequently injured in blunt abd trauma?
spleen
what is the mainstay for eval of splenic rupture?
stat CT abd pelvis
what are the clinical features of splenic rupture?
seatbelt and kehr sign
hypovolemic shock and LUQ tenderness
lower rib fx
which vaccines should be given after splenectomy?***
pnuemovax
h. influenza
meningiditis
what is the TOC for hemodynamically stable pt with splenic rupture?
non-op management and monitoring***
what is the gold standard for choledocholithiasis?***
ERCP
how do you eval for pancreatic cancer?***
- inc. alk phosphatase
- inc. direct bilirubin
- CT abd
- ERCP→ determines obstruction, can do bx at same time
which dx shows string of pearls air fluid levels on abd XR?***
SBO → also see thickened dilated loops of bowel "stack of coins"
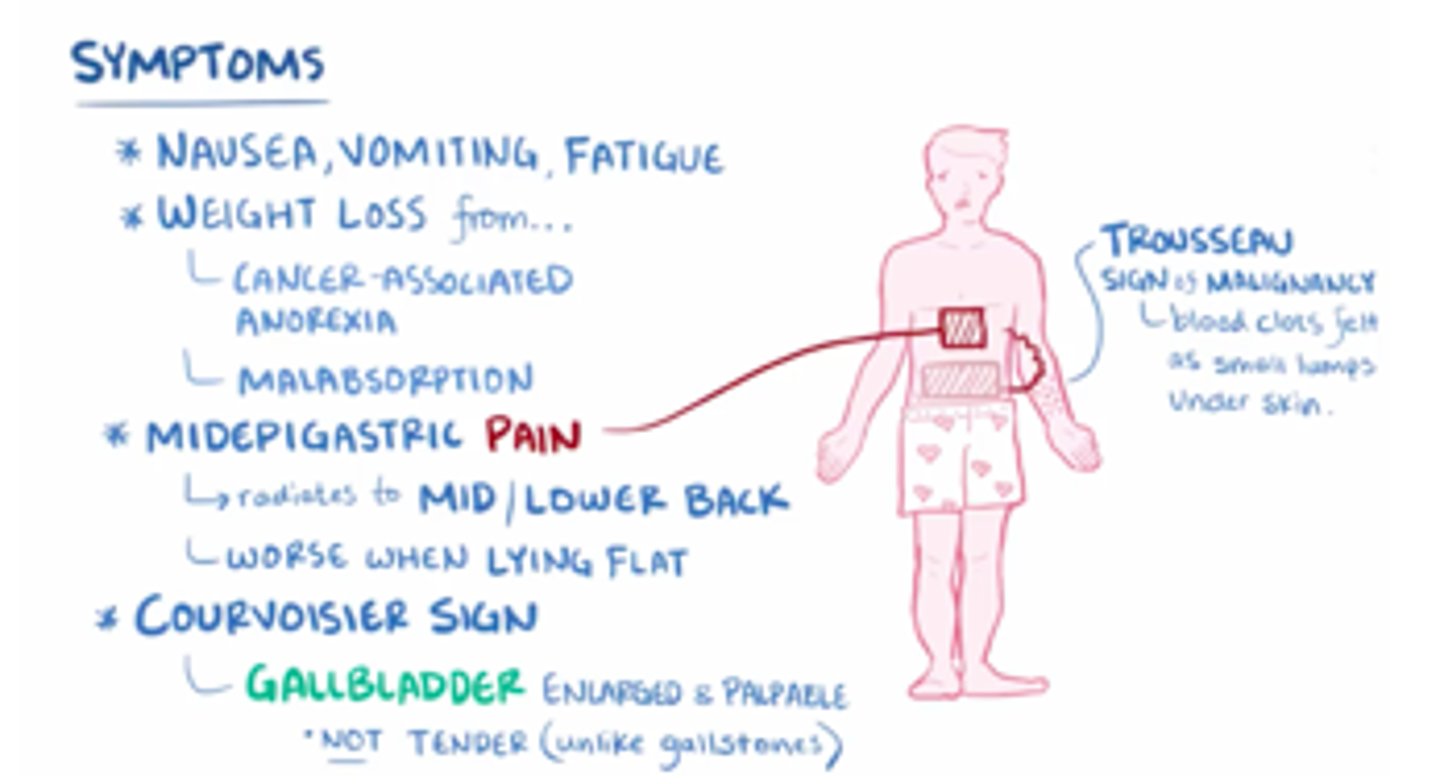
what are the clinical features of pancreatic cancer?***
- courvosier's sign→ jaundice and poalpable nontender GB
- cullen's sign
- obstructive jaundice
- weight loss and deep abd pain
- pruritis with jaundice
what is the treatment for pancreatic cancer?***
whipple → for pancreatic HEAD
distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy for tumors in tail/body → these tumors are usually fatal :(
can't do whipple if cancer involves hepatic artery
what is the MC congenital abnormality of the small intestine?**
meckel's diverticulum → MCC of GI bleeding in children
painless rectal bleeding
what is the most sensitive eval for meckel's diverticulum?
Meckel radionuclide scan (Tch-99)
what is the tx for Meckel's diverticulum?***
Meckel's diverticulectomy
which IBD is transmural and has cobblestone appearance and skip lesions?
crohns
which IBD is friable and restricted to the mucosa and submucosa?
UC →microabscess in crypts of lieberkuhn → procedure of choice is proctocolectomy with ileal pouch anal anastomosis (IPAA)
what is the procedure of choice for UC?
proctolectomy with ileal pouch anal anastomosis
what is the tx for thrombosed hemorrhoids?
hemorrhoidectomy
what is the tx for internal incarcerated hemorrhoids?
immediate hemorrhoidectomy**
which type of hemorrhoid is above the dentate line?**
internal → painLESS
which hemorrhoids tend to thrombose?
external → painFUL
below dentate line***
what are the different classes of hemorrhoids?***
1 = no protrusion
2 = reduces spontaneously
3 = manual reduction necessary
4 = incarcerated→ need hemorrhoidectomy
what is the diff between perirectal and perianal abscesses?
perirectal → inflam of subQ tissue from obstructed crypt gland
perianal → inflam of superficial tissue
tx both with I&D :)
what is the indication for bariatric surgery?***
- BMI >40 or >35 with comorbidity
- unsuccessful weight loss
- mental health clearance
which type of hiatal hernia involves upward displacement of the GEJ causing the GE junction, LES, and part of the stomach to slide into the mediastinum?**
type 1 sliding →MC type
which type of hiatal hernia involves migration of part of the stomach into the mediastinum parallel to the esophagus?**
type 2 paraesophageal → part of the fundus herniates adjacent to the esophagus
which type of hiatal hernia involves both GEJ and part of the stomach migrating into the mediastinum?**
type 3 (both sliding and paraesophageal)
in which type of hiatal hernia do the stomach and other organs herniate into the chest?
type 4
what is the MC complaint of pts with hiatal hernia?
heartburn
what are the surgical options for tx of hiatal hernias?
1. Nissen fundoplication (360)
2. partial fundoplication
3. hill repair
4. belsey
what are the surgical options for GERD?
Nissen fundoplication →360 degree wrap
partial fundoplication (dor and toupet)
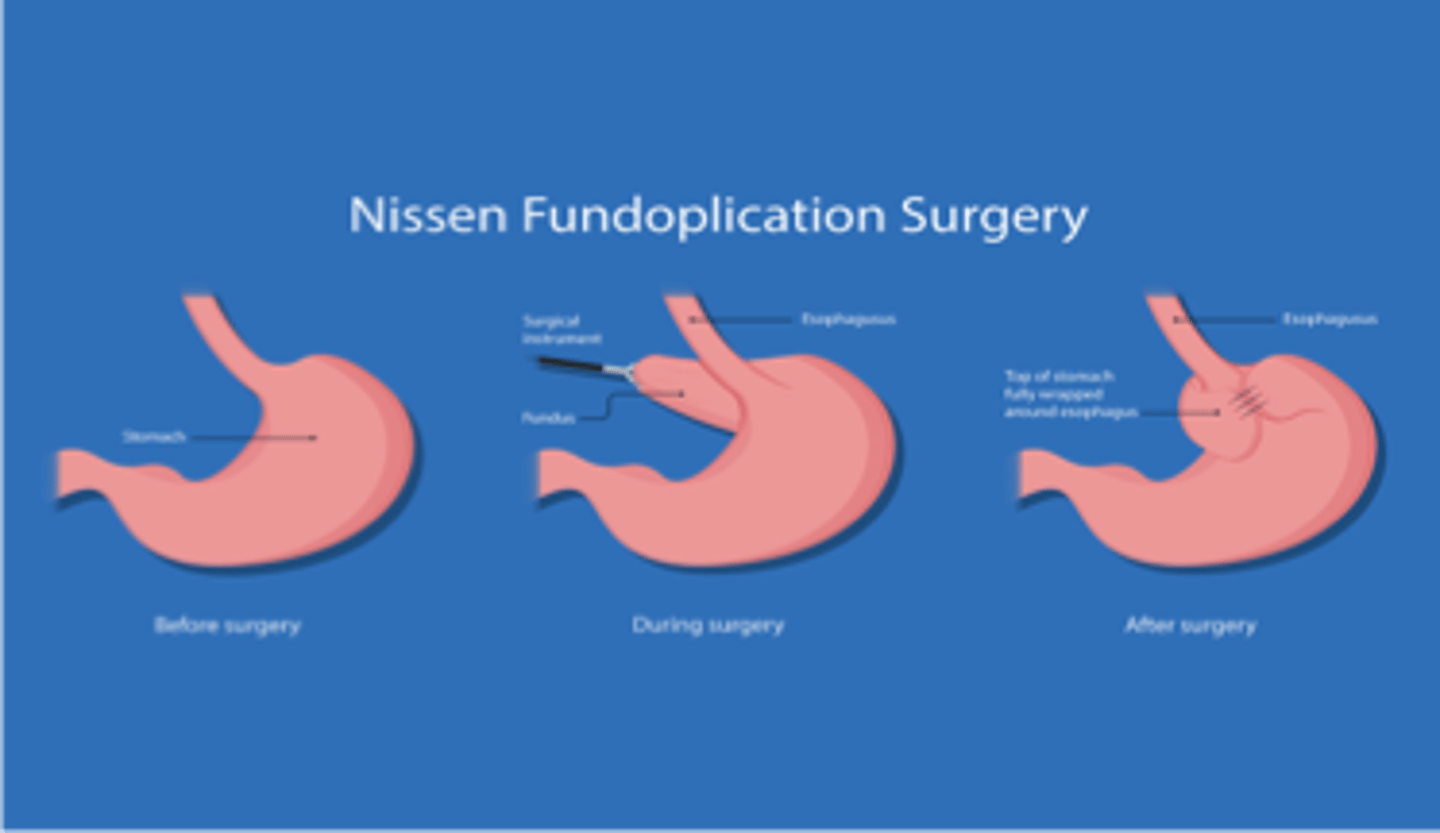
what is the gold standard procedure for GERD?
laparoscopic nissen fundoplication
what is a common complication of thyroid surgery?
recurrent laryngeal nerve injury*
injury of which nerve results in paralysis of ipsilateral vocal cord leading to hoarseness and weak voice?
recurrent laryngeal nerve
bilateral injury = speech loss and loss of airway control :(
barret's esophagus is a complication of which dx?
GERD
what are the risk factors for squamous cell esophageal cancer?
smoking, alcohol, poor diet
what are the risk factors for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus?
barretts, GERD, obesity, smoking
what is the TOC for esophageal cancer?***
chemo followed by *En Bloc esophagectomy* → requires J-tube for life after surgery
chagas dz is an etiology for which dx?
achalasia ***→failure of LES to relax
dysphagia
regurg of UNDIGESTED food
chest pain
heartburn
what is the gold standard for dx of achalasia?
esophageal manometry**
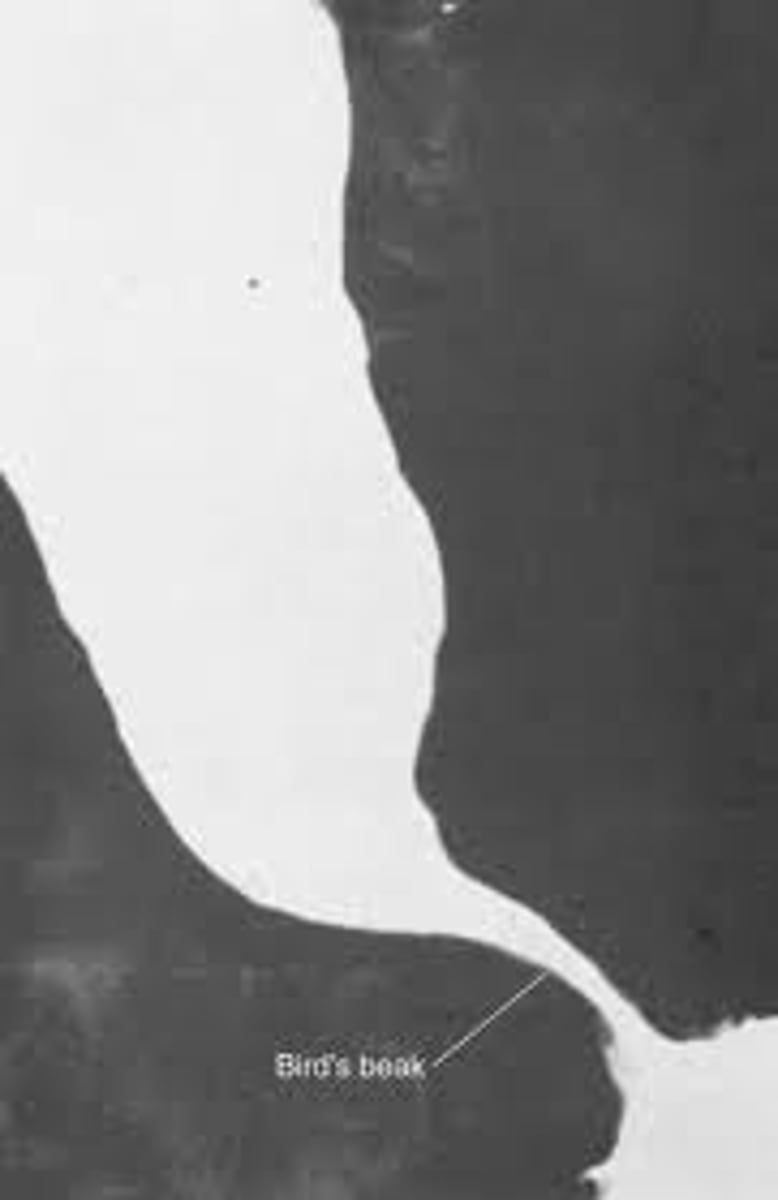
what does barium swallow in achalasia look like?***
birds beak

what is the first line tx for achalasia?
CCBs and PDEIs
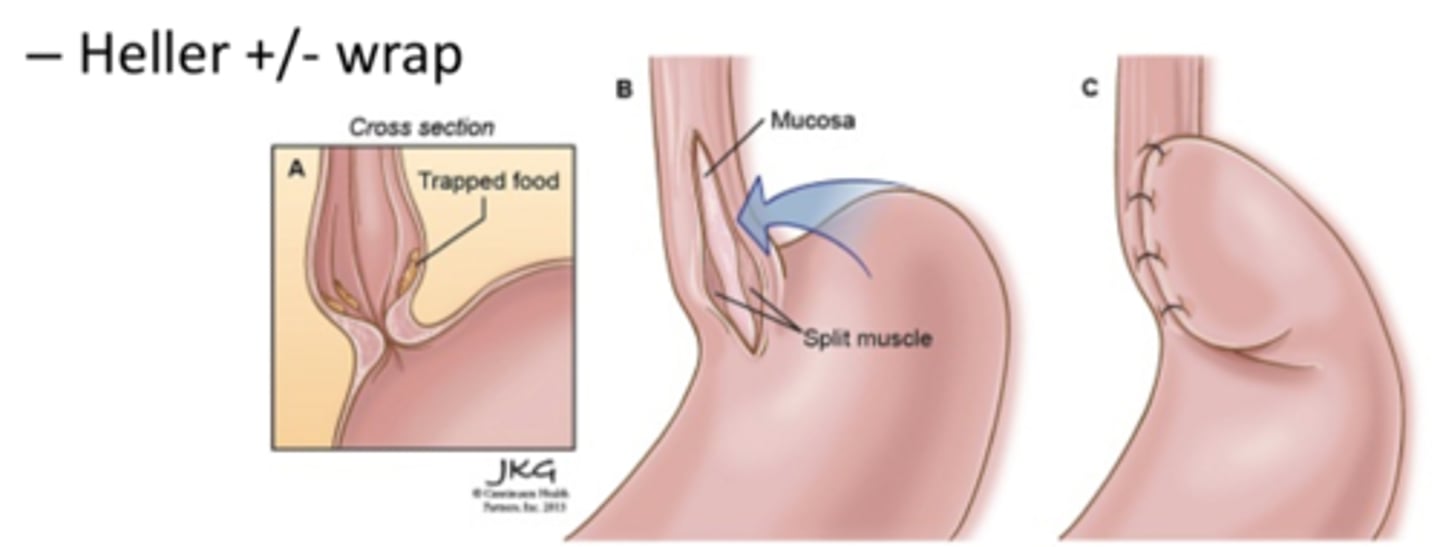
what is the surgical management for achalasia?***
laparoscopic heller myotomy with partial fundoplication (to prevent GERD)
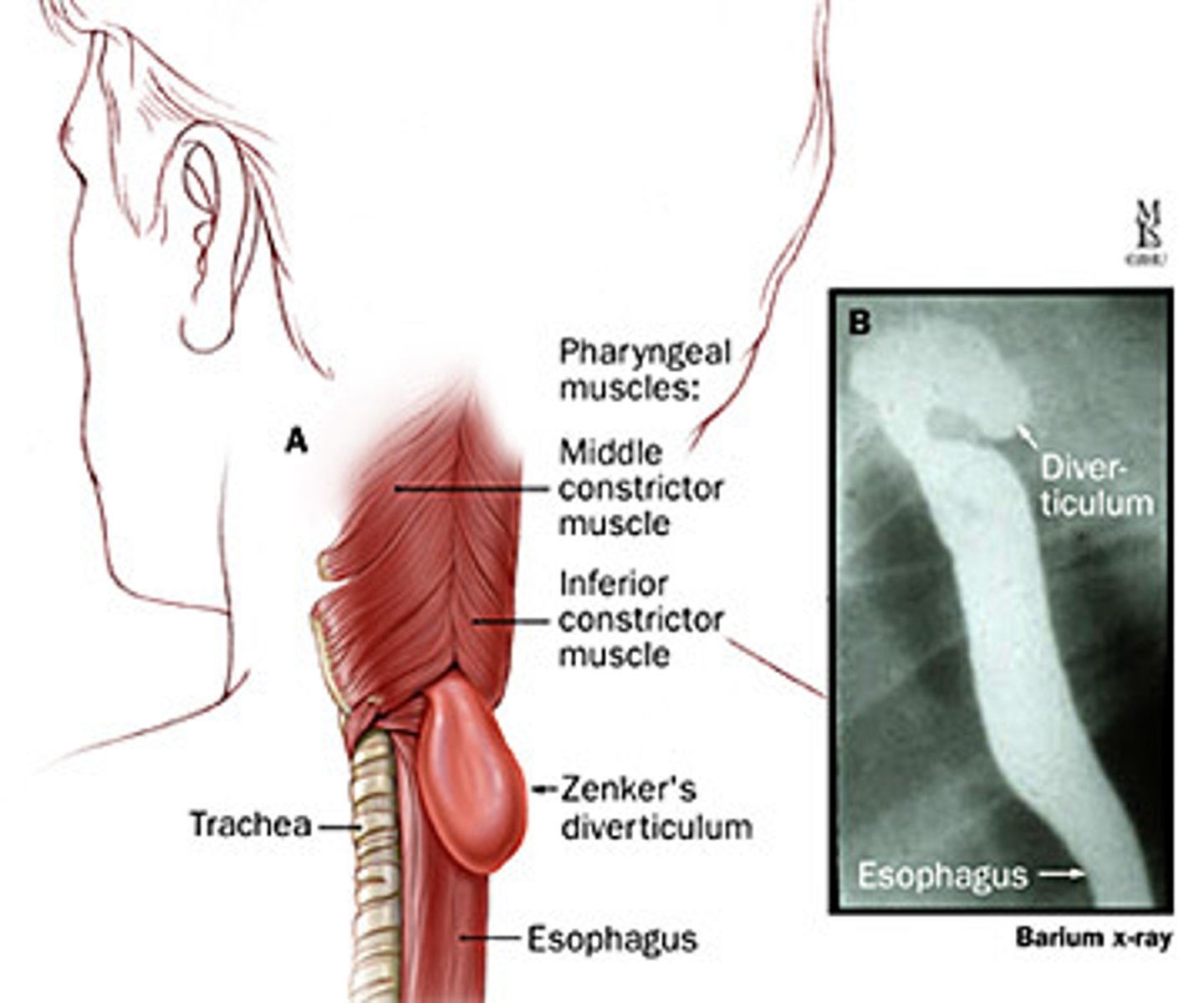
what is a Zenker's diverticulum?
diverticulum in the hypopharynx d/t dysfunction of the cricopharyngeal muscle in Killian's triangle
how would you manage diverticulitis with a large abscess or perforation?***
large abscess → IR drainage
perf/free air→ hartmann procedure
what is the diff between boerhaave's and mallory weiss tear?
boerhaaves = complete perofation
mallory weiss tear = longitudial tear
tx both w stent palcement, debridement/drainage
what are the risk factors for thyroid nodules?**
- increasing age
- female
- iron deficiency
- hx of thyroid radiation
what is the MC type of thyroid cancer?*
Papillary carcinoma → good prognosis
assoc. with radiation exposure
which type of thyroid cancer has the worst prognosis?*
anaplastic
which type of thyroid cancer is seen as part of MEN 2A or 2B?
medullary thyroid → autosomal dominant inheritance
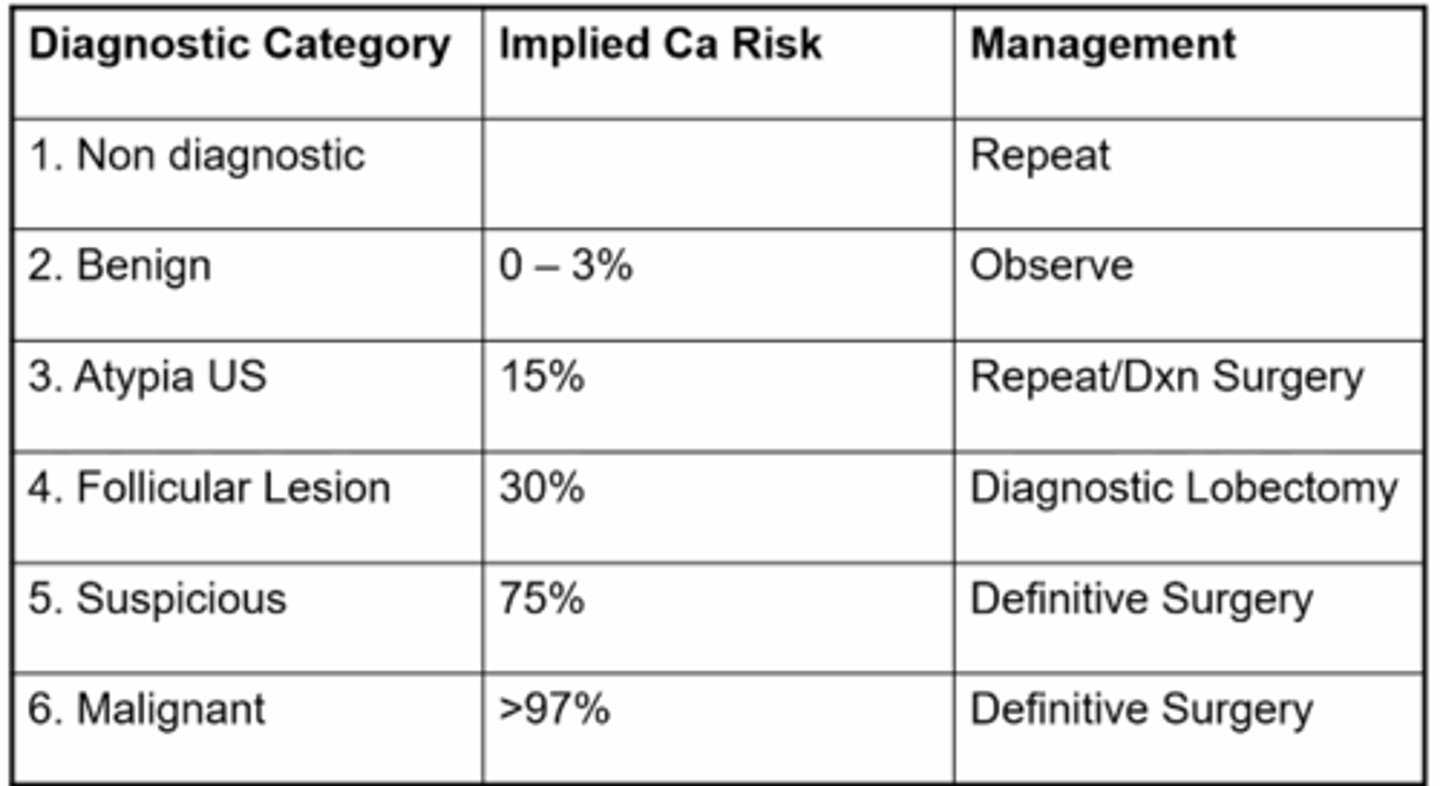
what is the classification system for thyroid nodules?
bethesda
3/4 = FNA q 6-12 months or scan
5/6 = surgery for sure
what are the labs for primary hyperparathyroidism?**
excess PTH → inc. Ca++ and dec. PO4
what are the labs for secondary hyperparathyroidism?**
seen w renal dz or vit D deficiency → inc. PO4, dec Ca+, PTH stimulation
what are the labs for hyperthyroidism?*
Low TSH, high T3 and T4
opposite for hypo
what sx is commonly seen with pituitary adenoma?***
bilateral hemianopsia
other sx depend on the hormone secreted
what is the medical management of prolactinoma?
cabergoline or bromocriptine
what is the surgery management for pituitary adenomas?***
transsphenoidal resection → indicated for MACROadenomas (>10mm)
what are the post op complications of parathyroidectomy?***
- perioral numbness/paresthesia
- carpopedal spasm
- seizures
- Chvosteck's sign →tap on facial nerve
what will pts s/p parathyroidectomy need to supplement?***
calcium
what med will pts s/p thyroidectomy need to be on for life?***
levothyroxine