Enzyme Kinetics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What do enzymes do to the transition state
Lower its energy
What are co-factors
non-protein molecules needed for full catalytic activity. They can be permanent prosthetic groups or transient co-substrates.
Types of enzyme names
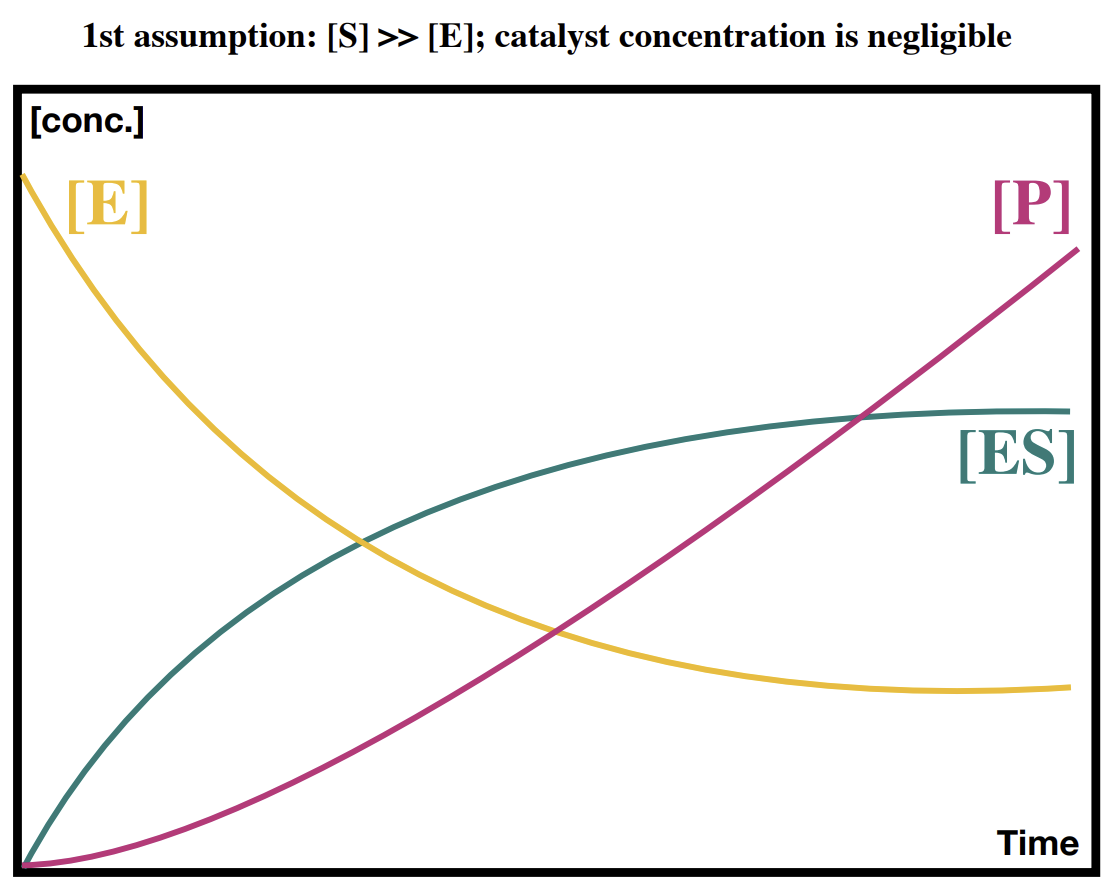
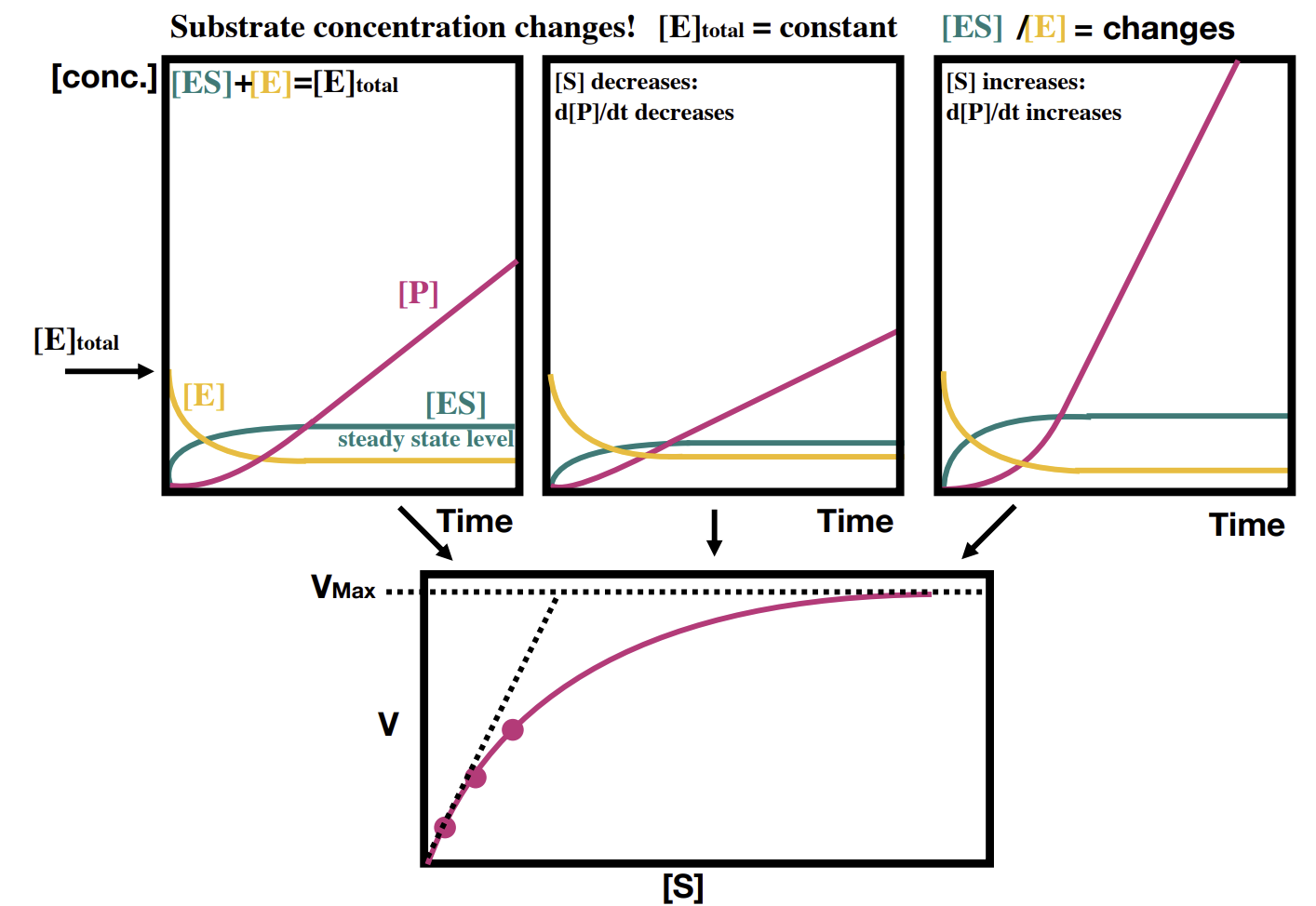
How does the concentration of enzyme and product change over time in a reaction
The product line gradient maxes out as the ES line plateaus.
How does the overall reaction look over a longer time
Binding efficiency can be determined.
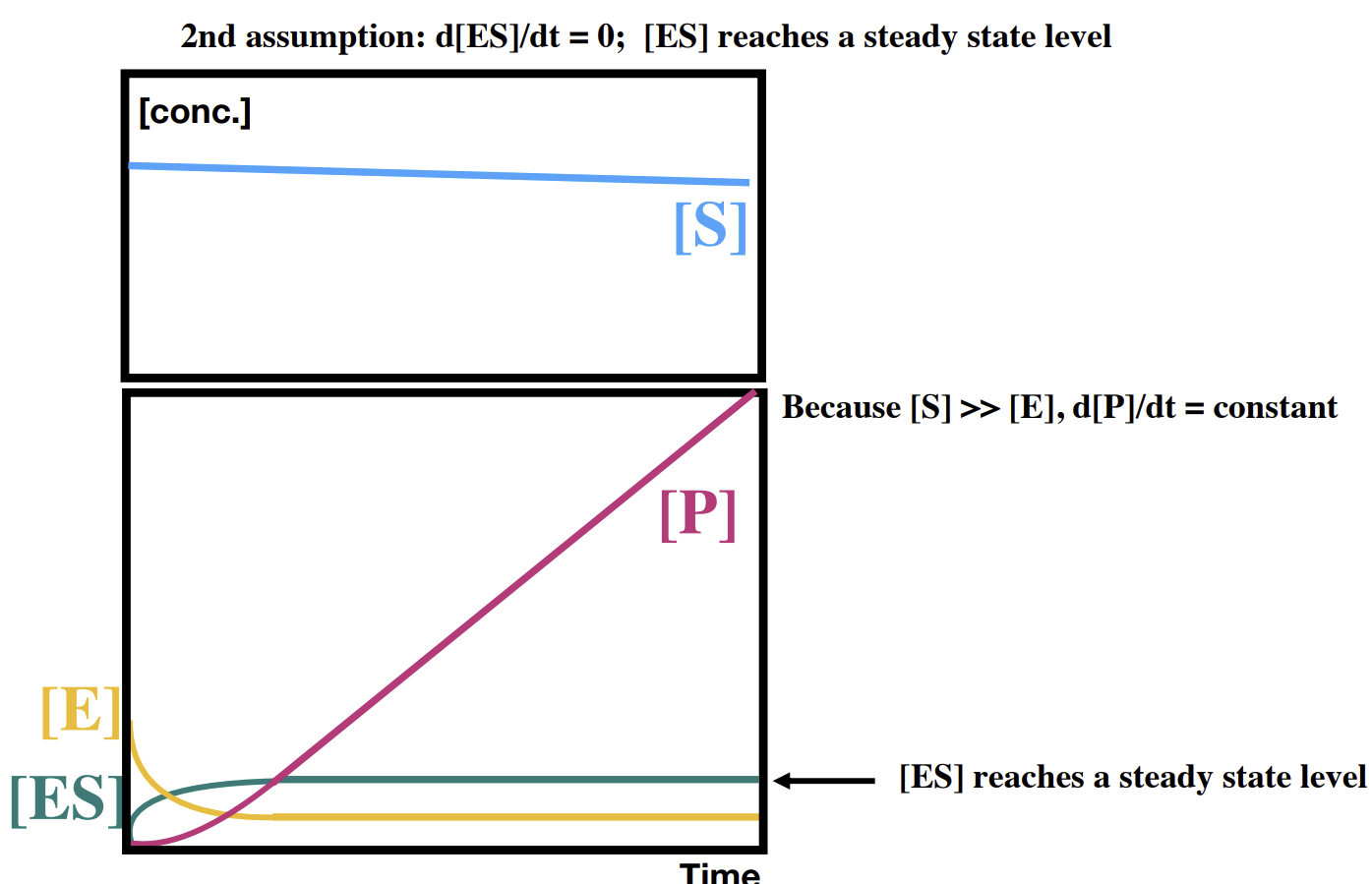
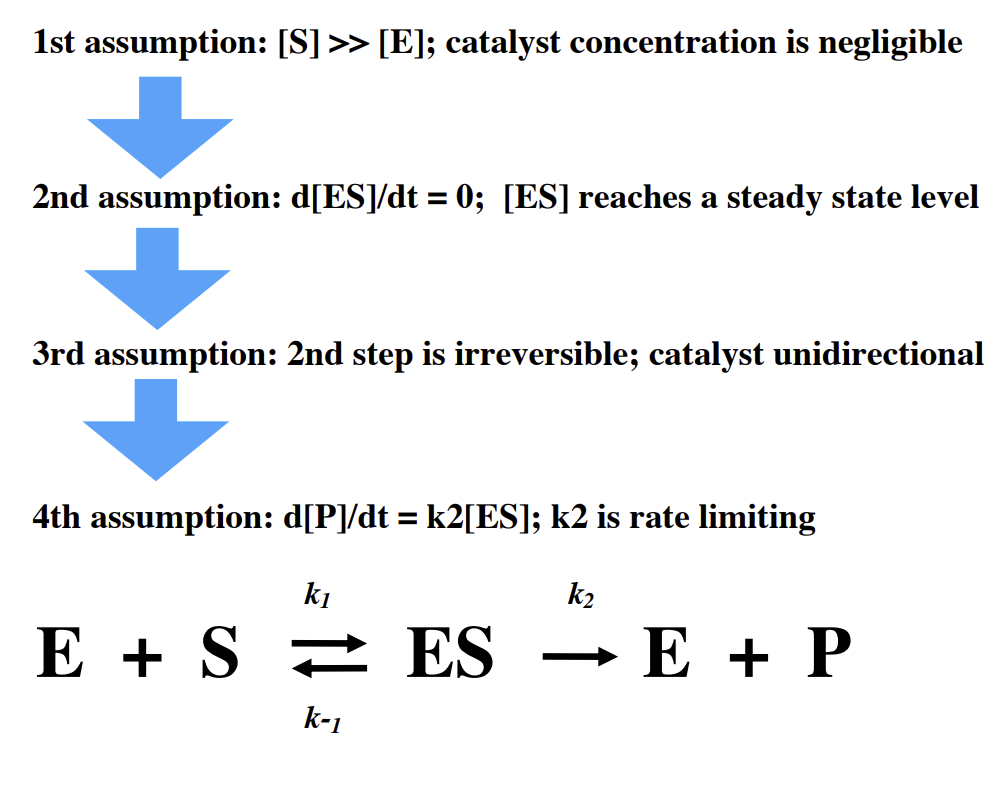
What 4 assumptions do we make about catalytic reactions for kinetics
What happens if you increase concentration of the substrate while enzyme conc does not change
Increased concentration of substrate allows more complexes to form. Once Vmax is reached, the enzyme is fully saturated and no further increases will occur.
How can Km be determined
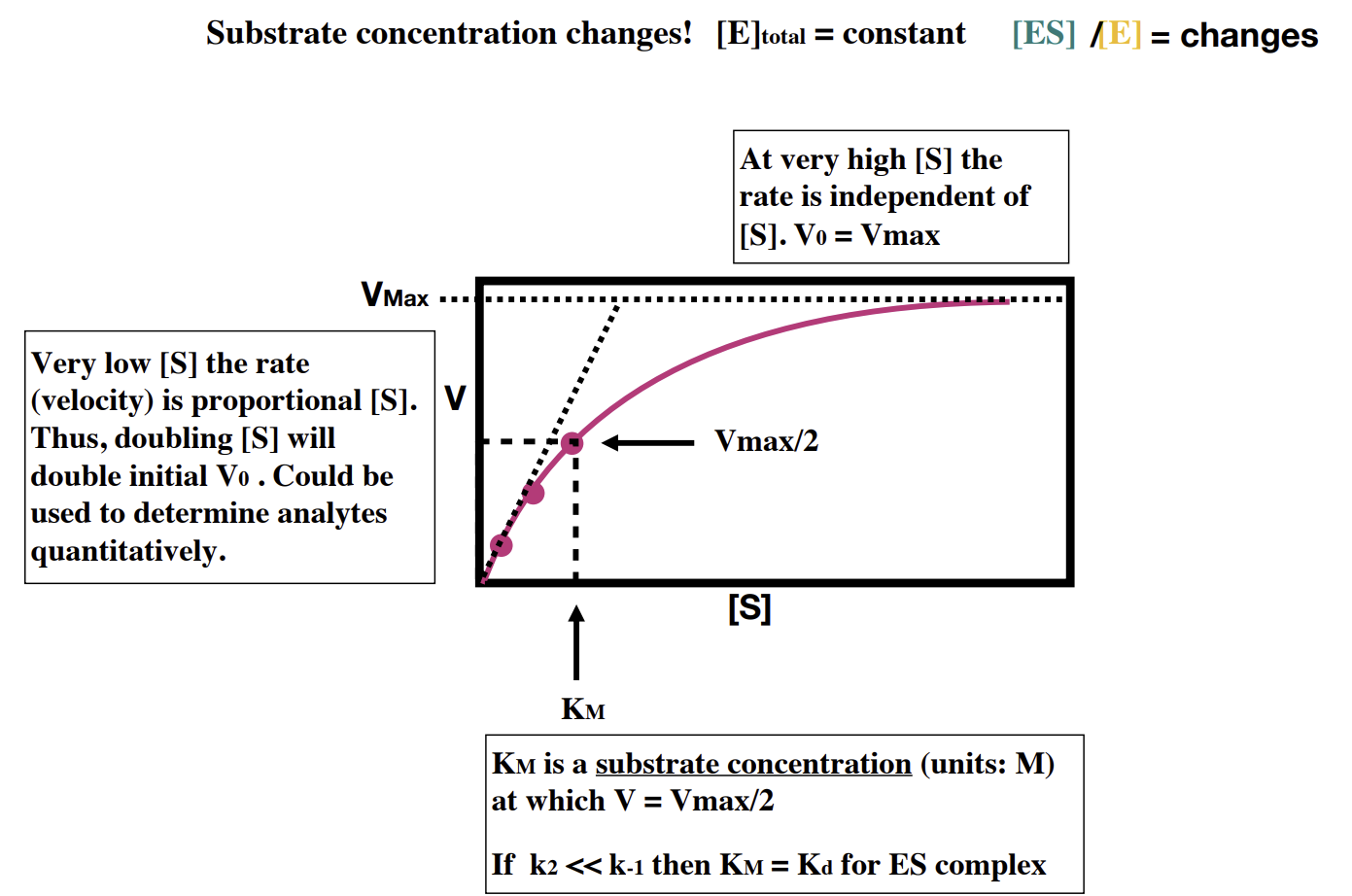
defining KM and Kcat (last few slides of lecture 16)
KM is the concentration of substrate which permits the enzyme to achieve half Vmax. Essentially it measures the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate i.e. how likely they are to bind to each other.
The catalytic constant (kcat) is another name for k2 and measures how fast the ES progresses to E + P i.e. how fast the enzyme reaction process occurs.
What is a way to represent enzyme catalytic ability
This value is substrate specific
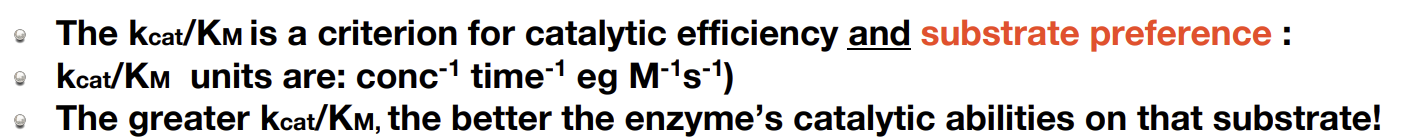
What are diffusion limits
Essentially a maximum affinity for enzymes relying on diffusion

What factors can inhibitors affect
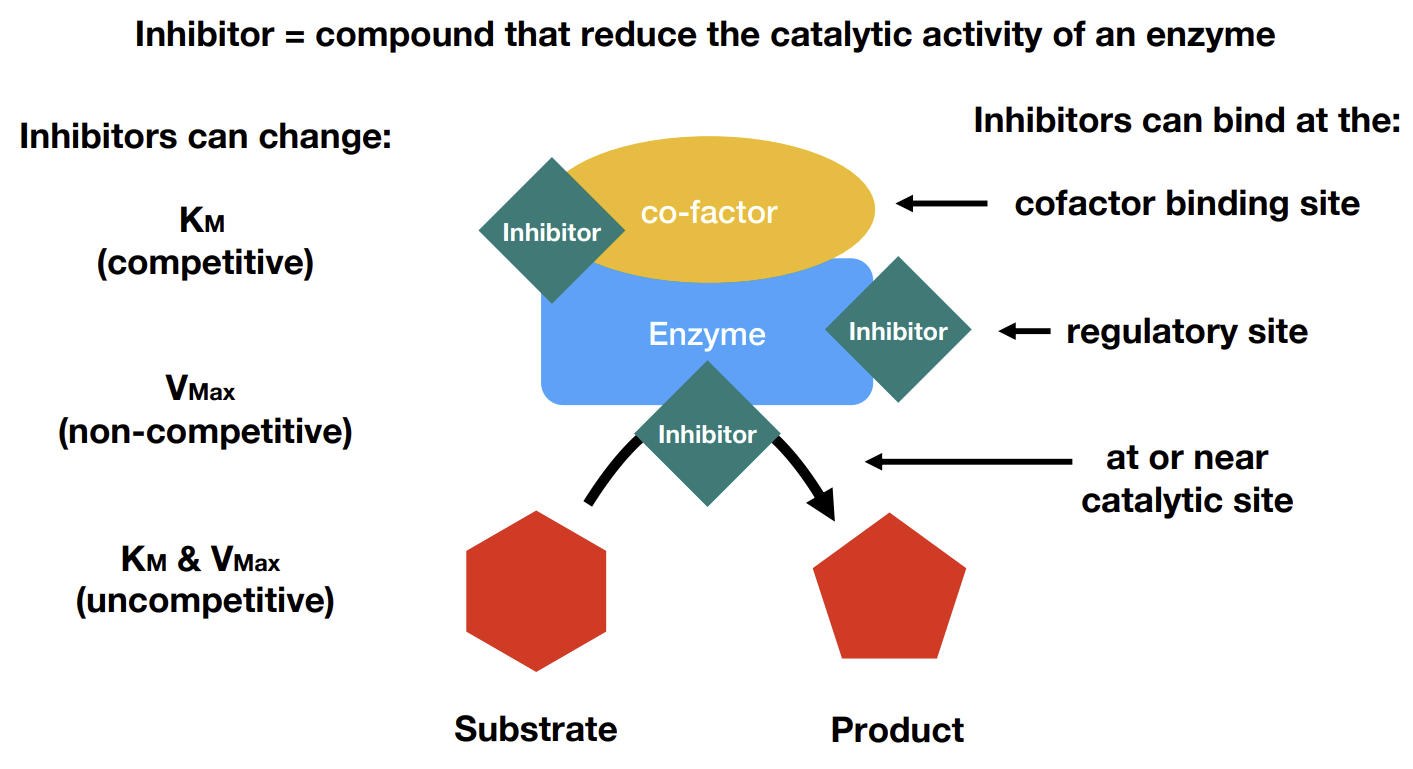
What are uncompetitive inhibitors
Only binds to the ES complex
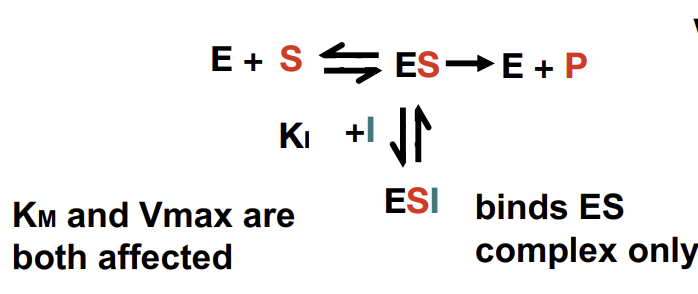
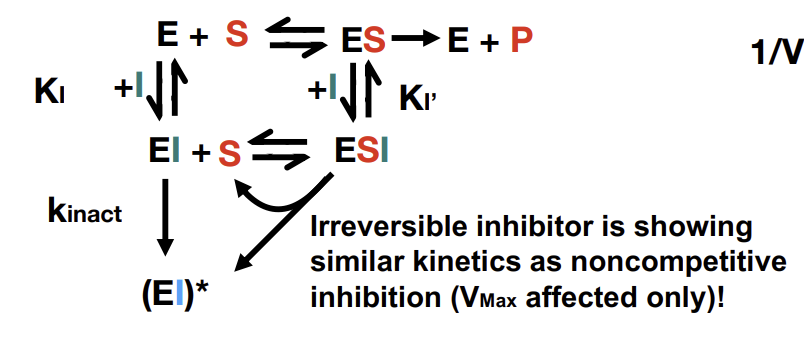
Irreversible inhibition
Functions similarly to non-competitive inhibition in that it only affects VMax. Eventually the inhibitor will be entirely used up.
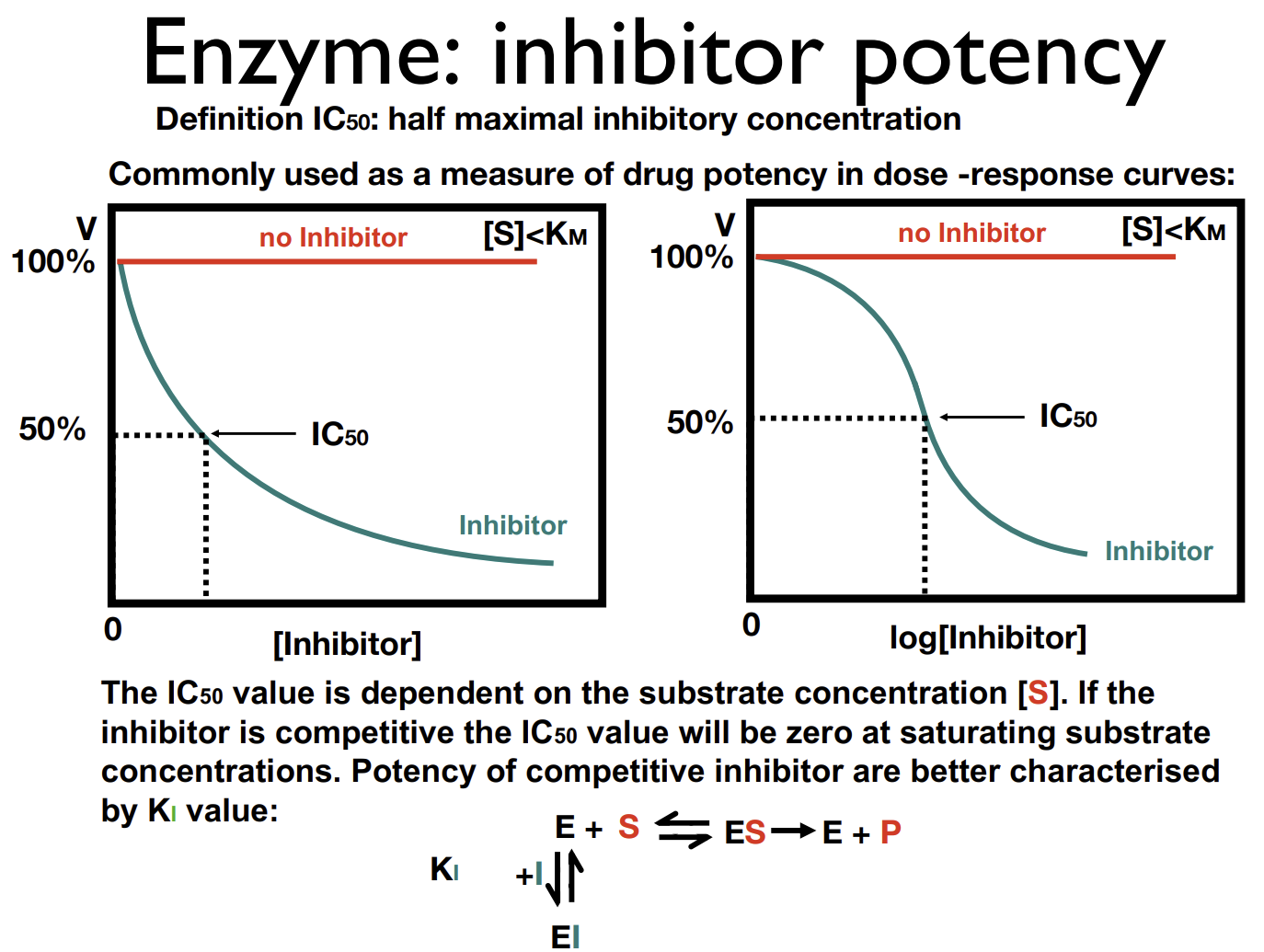
Measures of potency of an inhibitor
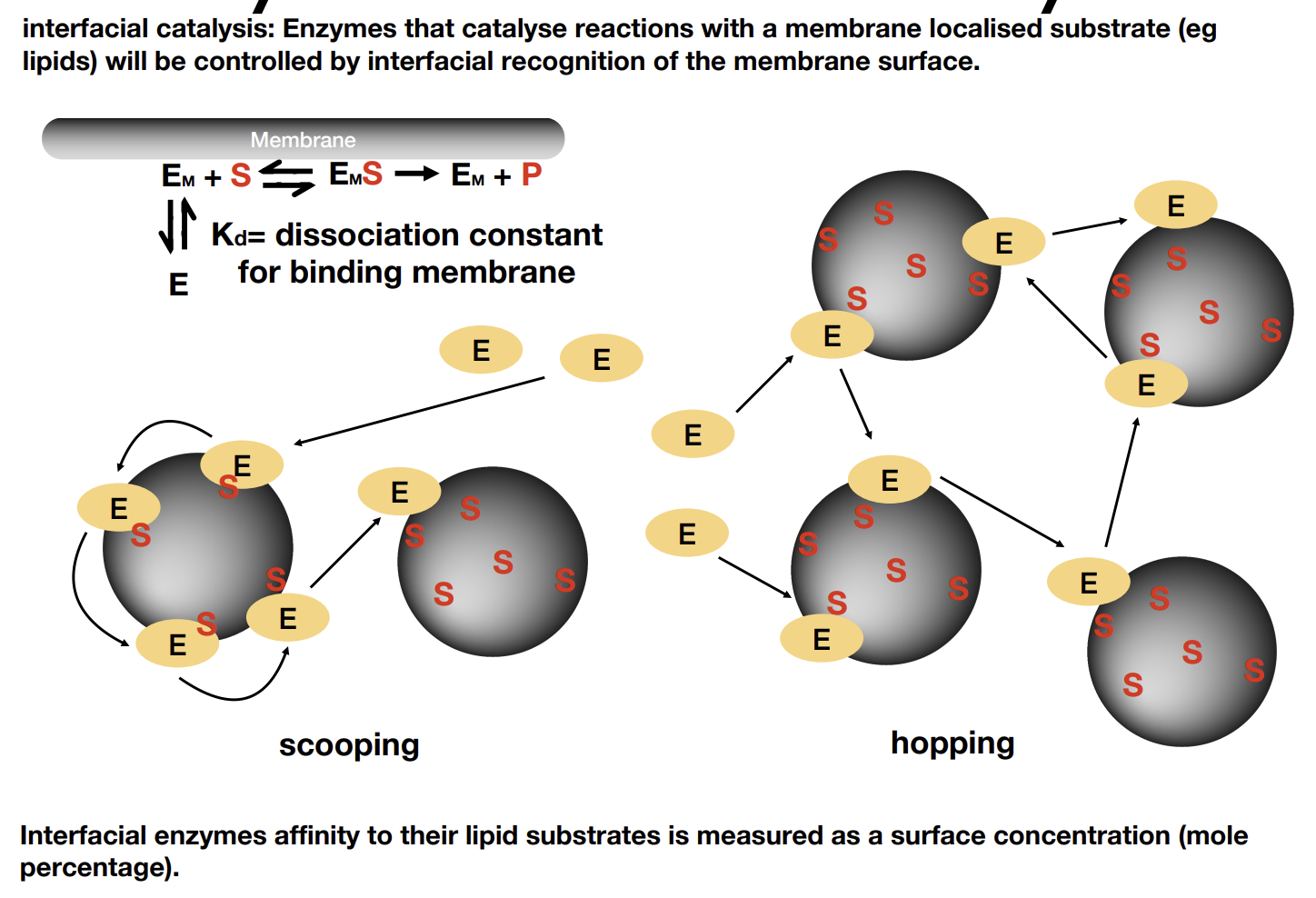
What is interfacial catalysis
Enzyme needs to be on the membrane to function. Scooping happens over hopping when the membrane affinity is low compared to that of the substrate
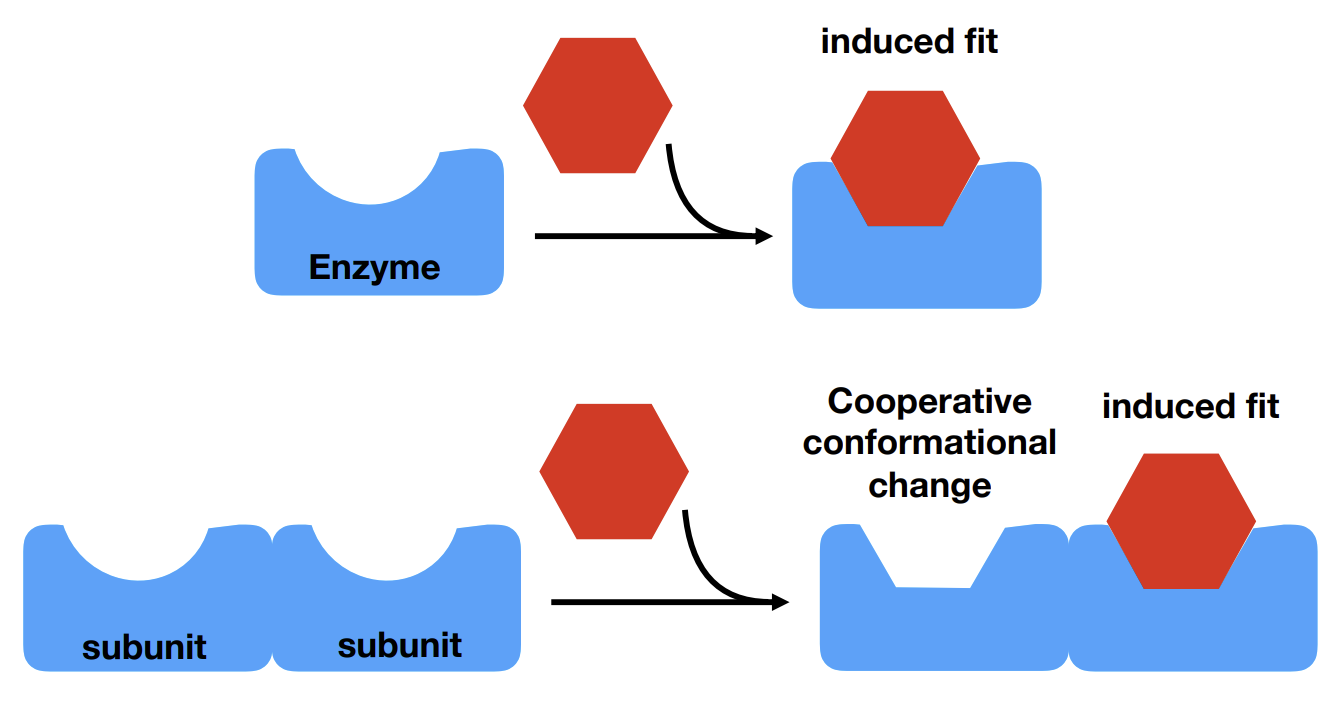
What is cooperativity
One molecule favours the binding of an additional molecule. In the context of enzymes induced fit can be induced by another substrate binding at a second binding site. This increases the enzyme’s affinity
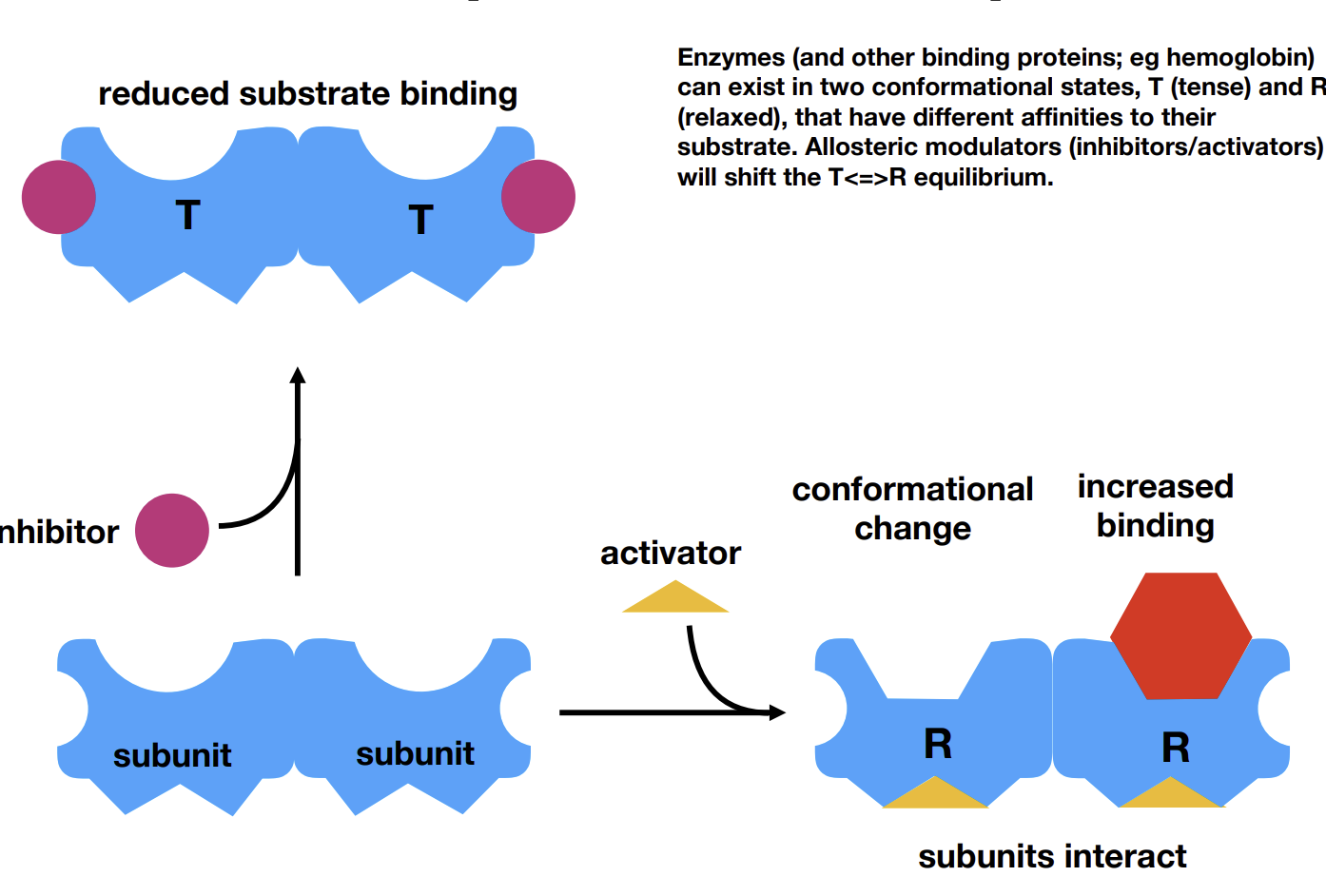
What is allostery
An activator can bind to an allosteric site (subunit), increasing affinity of the enzyme by inducing a change in the active site shape.
This goes the other way with inhibitors
Activators/inhibitors are modulators.
What is homotropic allostery
Cooperativity as seen in Hb - the modulator is the substrate.
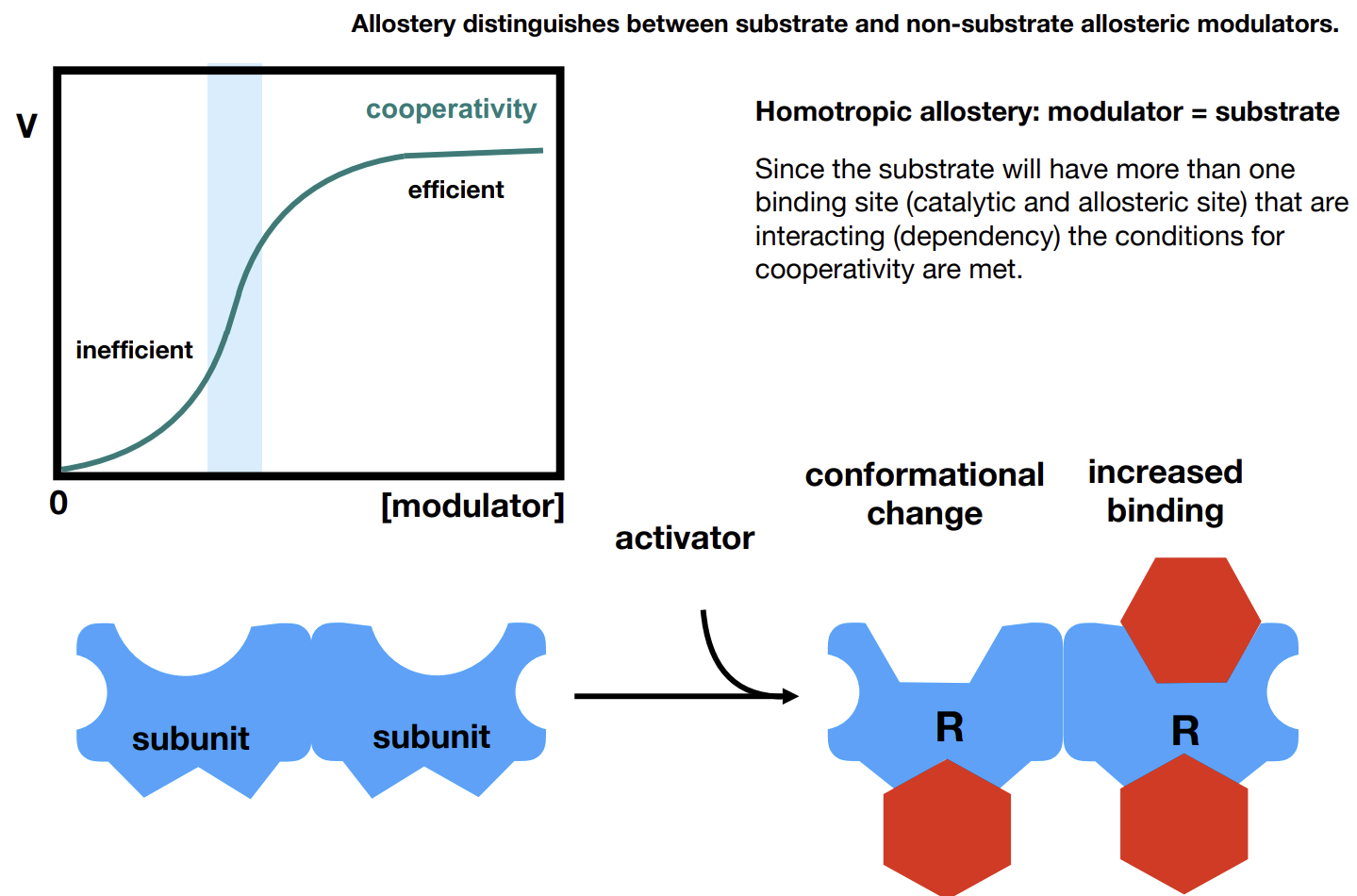
Heterotropic modulators
Modulators that are not substrates.
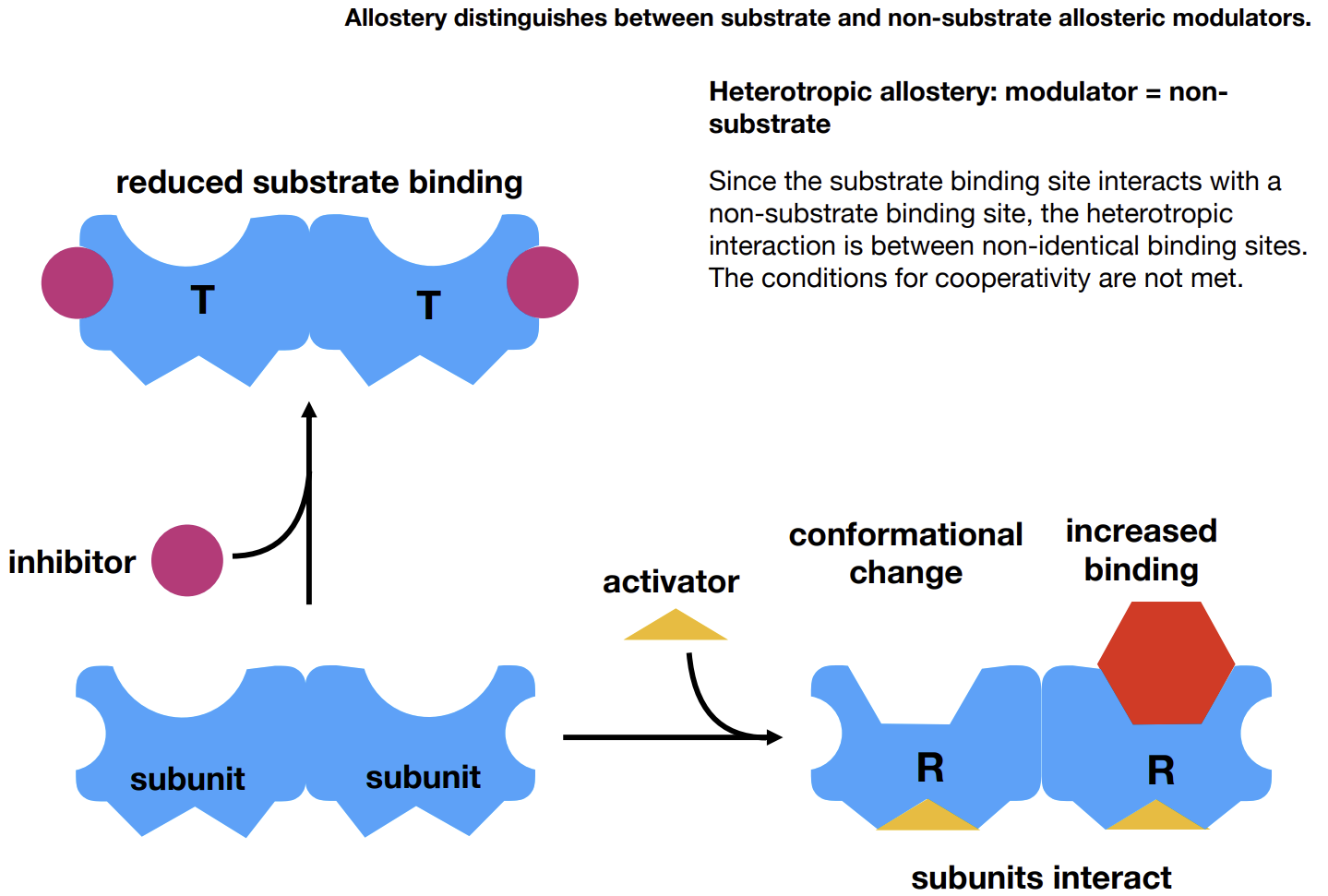
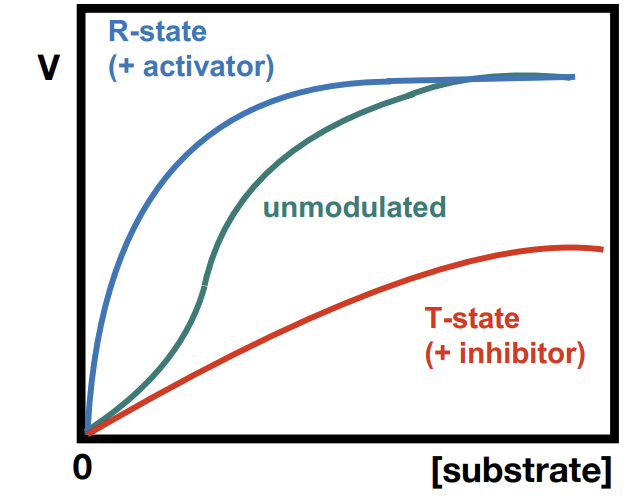
What is R-state and T-state
Relaxed state - heightened affinity, cooperativity
Tense state - reduced affinity, inhibition
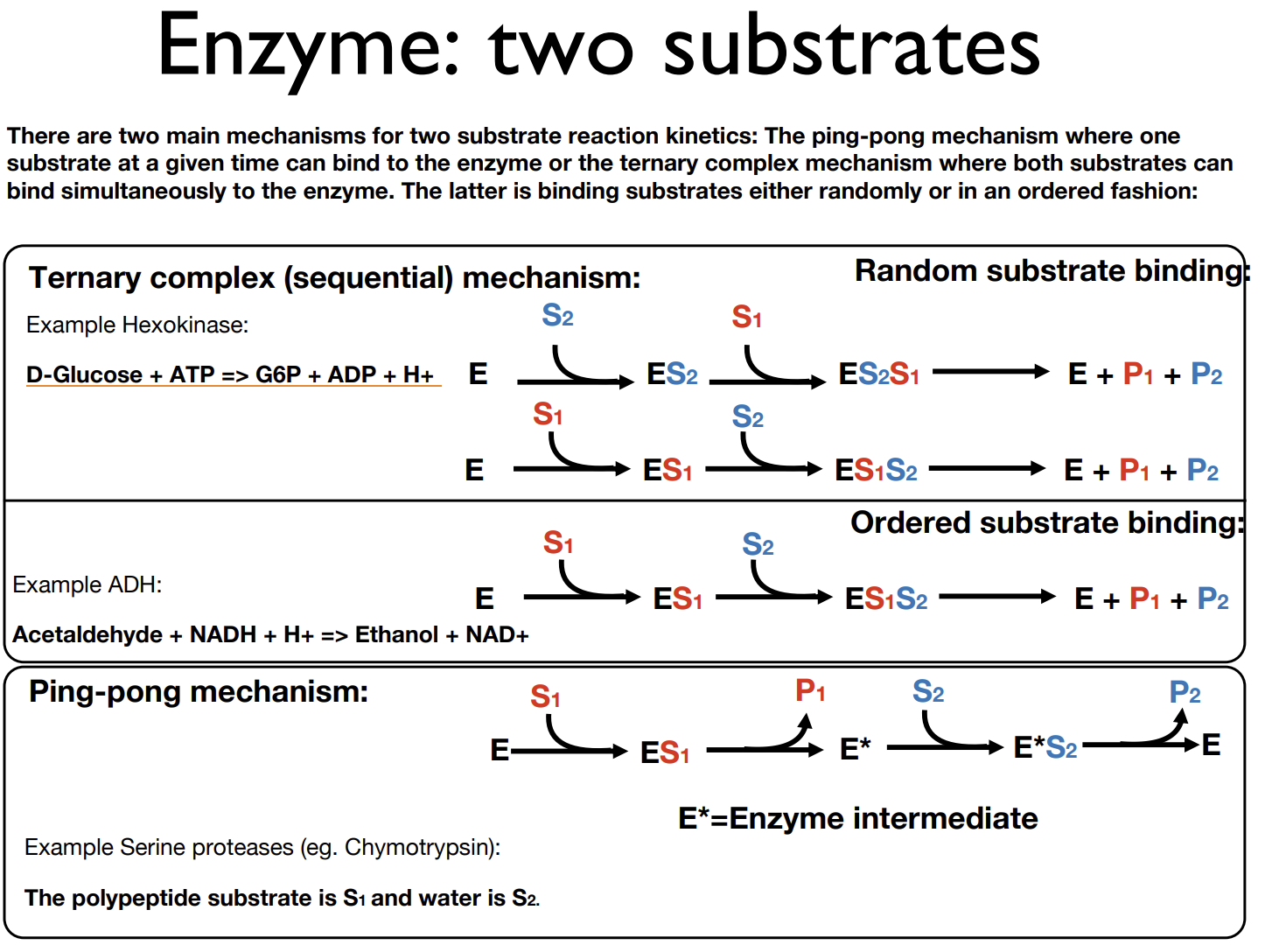
What ways can enzymatic reactions proceed if there are 2 substrates