IB Biology Year 1 - Cell Division and Signaling
What is a function of histones?
Condensation of DNA
When does DNA replication occur?
S phase of interphase
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is a function of histones?
Condensation of DNA
When does DNA replication occur?
S phase of interphase
The diagram shows the movement of ions that can occur across the membrane of a neuron. From the diagram, what can be deduced about the movement of sodium ions?
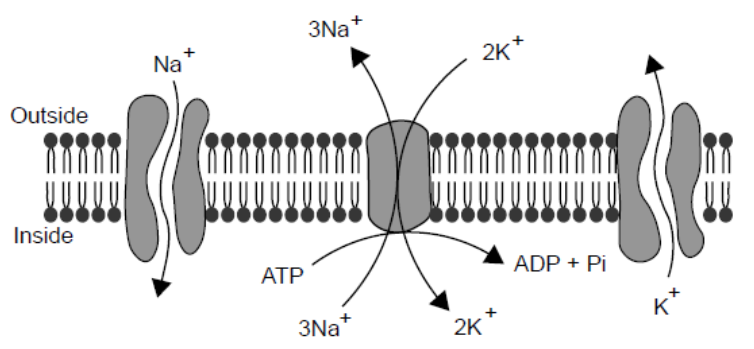
They are actively pumped out and some re-enter by facilitated diffusion.
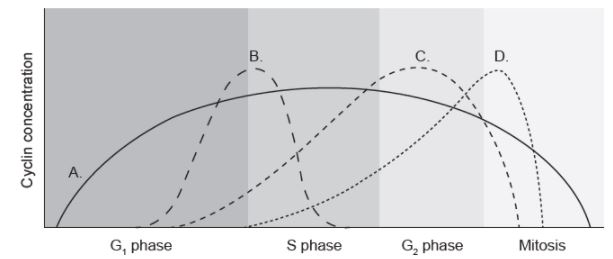
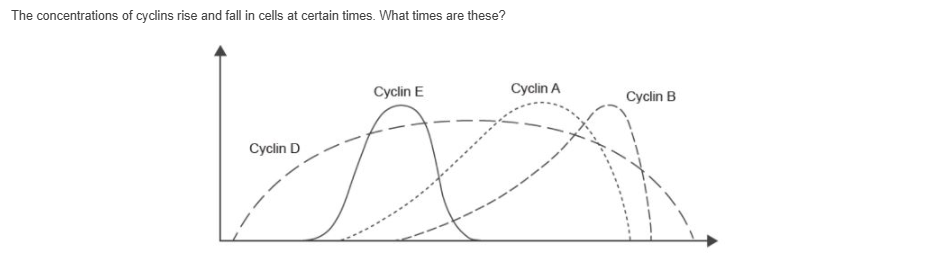
The diagram shows the concentration of four cyclins during the cell cycle. Which curve represents the cyclin that promotes the assembly of the mitotic spindle?
D
The graph shows the change in the membrane potential of an axon during an action potential.
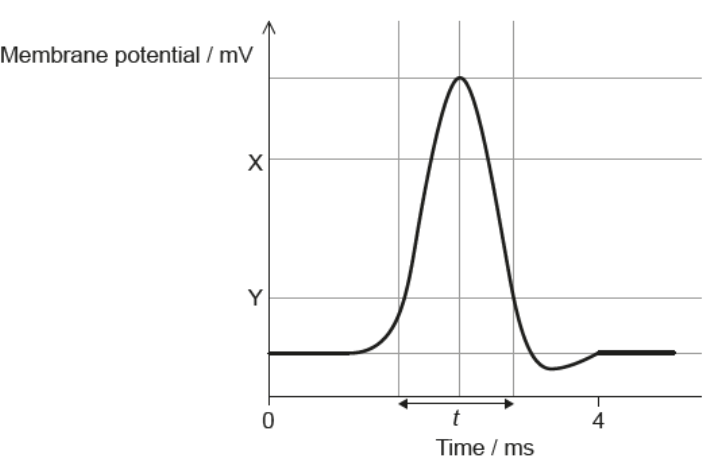
(a) State the approximate value of the membrane potential at X. [1]
(b) Y is the threshold potential. State what happens when the threshold potential is reached. [1]
(c) Describe the movements in ions that occur during time t. [2]
(a) The approximate value of the membrane potential at X is -10mV to 10mV
(b) When the threshold potential is reached, that indicates that the stimulus was powerful enough to make the voltage reach -55mV, initiating the action potential cycle.
(c) During time t, the process of action potential occurs. First, depolarization occurs, which shoots the voltages from -55mV to +30mV. This causes the calcium voltage-gated channels to open, allowing calcium ions to pass through the membrane with the help of facilitated diffusion. Later, the calcium channels close, and potassium channels to open, causing a rush of potassium ions to enter. Due to potassium channels taking a longer time to close, the influx of potassium ions inside the cells causes repolarization to occur, dramatically dropping the voltage levels from +30mV to -90mV (causing hyperpolarization to occur, too).
Calcium causes a chain reaction, causing it to enter synapse and n.t. to go out
Blocking reuptake forces n.t. stays in the synaptic gap and people to be high
Neonicotinoid bind to receptors similar to acetylcholine however, it doesn’t go away with reuptake, just stays there and organism fires it until it dies
Cisplatin is an anti-cancer drug that prevents tumour cells from dividing by mitosis as it inhibits cell processes at stage S of interphase. How does cisplatin prevent cancer cells from dividing?
It inhibits the replication of DNA.
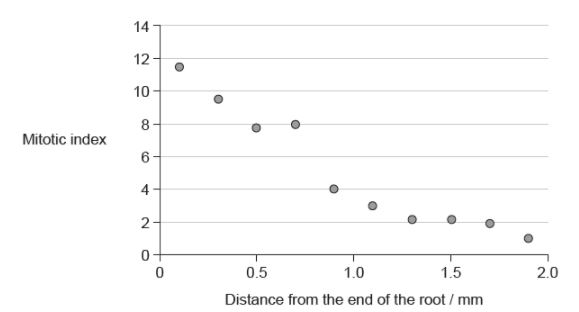
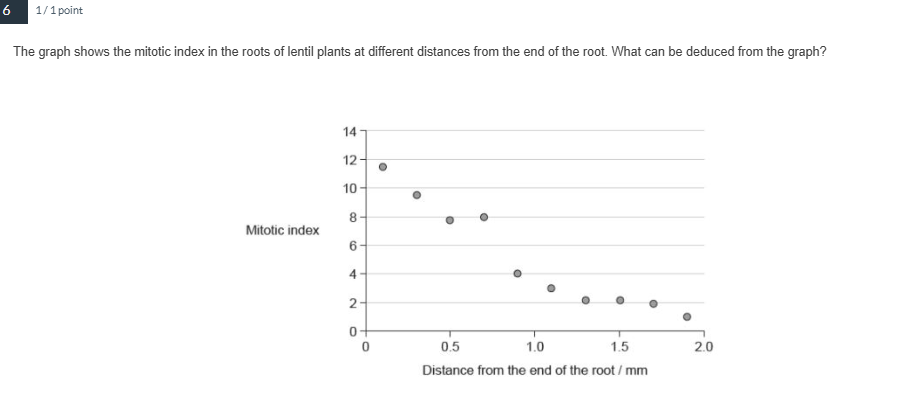
The graph shows the mitotic index in the roots of lentil plants at different distances from the end of the root. What can be deduced from the graph?
As the distance from the end of the root increases, the percentage of cells in interphase increases.
Which structural feature enables saltatory conduction?
Saltatory conduction → A mode of rapid signal propagation along myelinated axon
Nodes of Ranvier between Schwann cells (Schwann cells form the myelinated sheath)
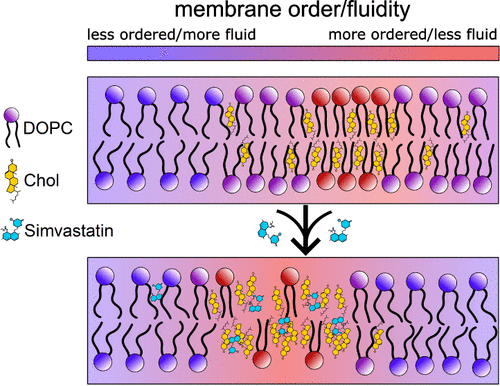
More than 90% of cellular cholesterol is located in the cell’s plasma membrane. What is the main role of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of mammalian cells?
To regulate membrane fluidity
In which stage of the cell cycle are chromosomes duplicated?
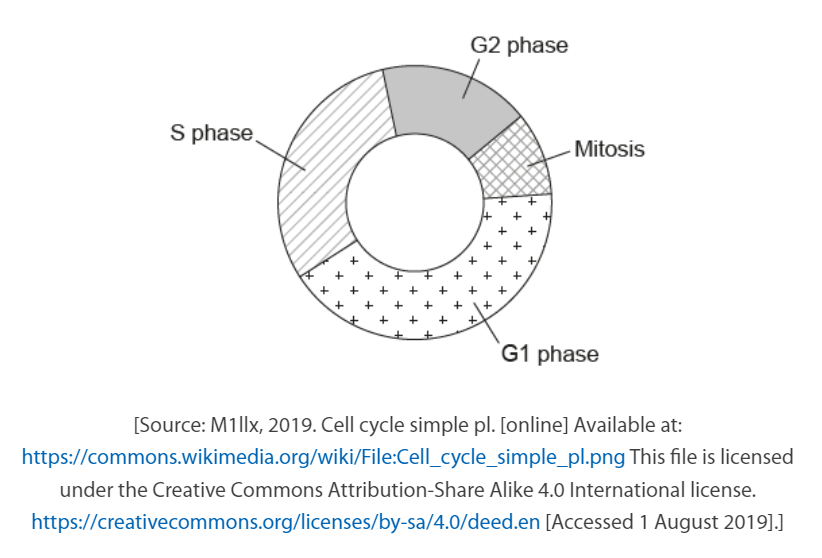
S phase
This phase of mitosis is characterized by the sister chromatids being separated at the kinetochores.
Anaphase
What plasma membrane is the least fluid at high temperatures?
B
What promotes membrane fluidity? What doesn’t?
Membrane fluidity, the ability of a membrane to move and change shape, is influenced by several factors. Higher temperatures, unsaturated fatty acids, and cholesterol levels can promote fluidity. Conversely, lower temperatures, saturated fatty acids, and the presence of saturated fatty acid chains in phospholipids can inhibit fluidity.
What conveys messages from the central nervous system to an endocrine gland?
Efferent neurons → Motor neurons
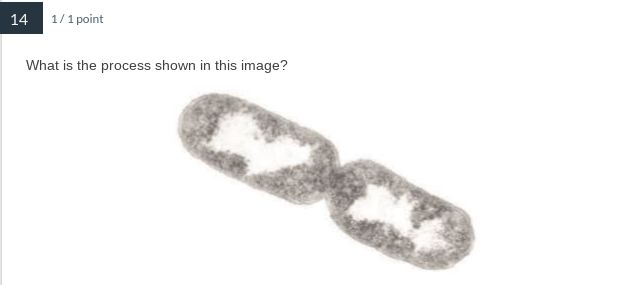
Binary fission of a prokaryotic cell
What activates a tyrosine kinase pathway in a cell following binding to a receptor?
Insulin
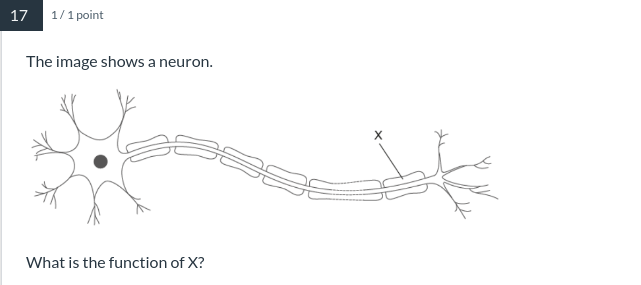
AND what is the name of X?
Mylein sheath - Increases the speed of transmission along the axon
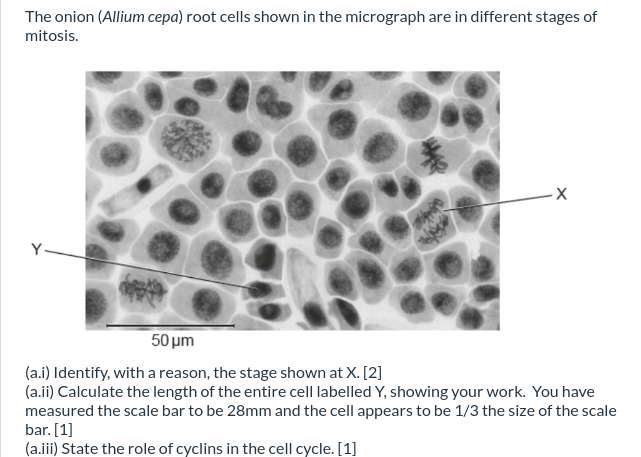
(a.i) The stage shown at X is anaphase, the final stage of mitosis, where the chromosomes separate into sister chromatids as spindle fibers retract.
(a.ii) The length of the cell "Y" is 50/3 micrometers because since the scale bar represents 50 micrometers, and the cell is merely a third of that, then you have to divide 50 micrometers by 3, and you get 50/3 micrometers.
(a.iii) The role of cyclins in the cell cycle is to aid in the progression from one stage of the cell cycle to the next. CDKs (cyclin-dependent kinases) rely on them to do so.
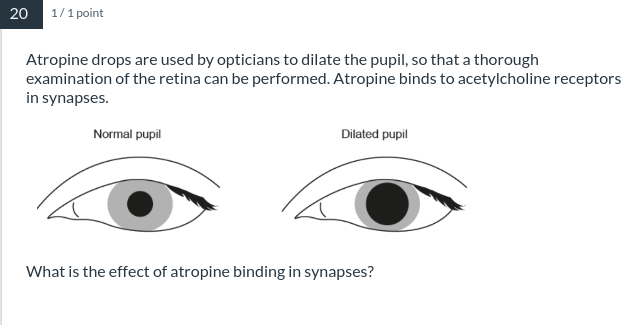
Prevents binding of acetylcholine at the postsynaptic membrane
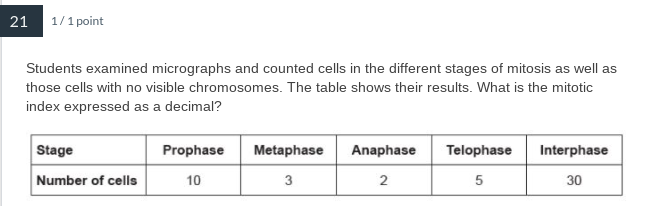
0.4
Many biological processes are cyclical. Examples of cycles can be found at the level of the cell, the organism and the ecosystem.
Explain how changes to the cell cycle can result in tumour formation.
Changes in the cell cycle---such as many mutation in tumor-surpressor genes and proto-oncogenes (which will turn them into oncogenes)---can result in tumor formation because if the components need to regulate the cycle cycle are riddled with errors, then it causes the parent cell to pass down incorrect DNA to its daughter cells and/or it does not have the ability to conducted apoptosis. Thus, the continuous replication of these "corrupted" cells will ensue at a relatively quick pace, causing a tumor.
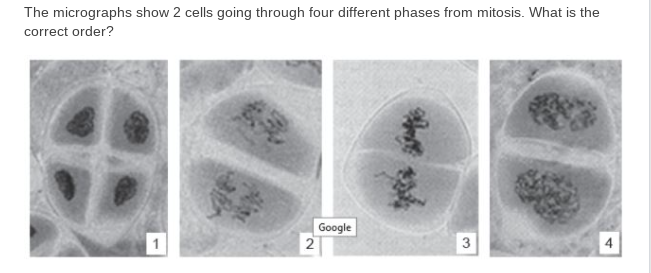
4-3-2-1
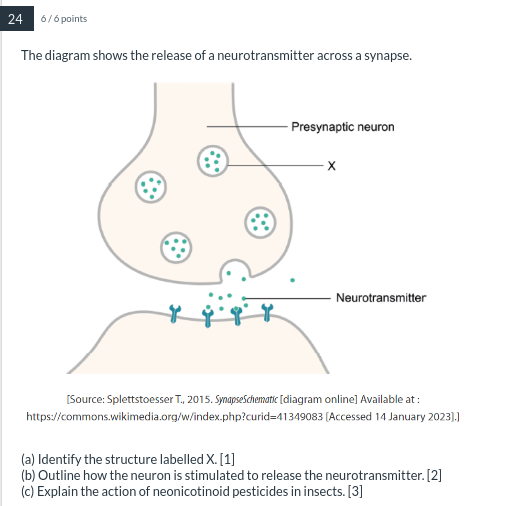
a) The structure labelled "X" is a vesicle containing neurotransmitters.
b) A neuron is stimulated to release the neurotransmitter if action potential (or the process of depolarizing and repolaring of membrane protential through the help of the myelin sheath, located in the gaps between them---known as the nodes of Raniver) occurs when a stimulus sent is strong enough to start this process (allowing the membrane potential to go from -70mV to -55mV), sending the message down axon. After reaching the axon terminal branches, the neurotransmitters will have vesicles incasing them, where the signal will open the voltage-gated sodium channels, causing a rush of sodium to enter. This rush will allow the neurotransmitters to bind with the membrane and be "released" from their vesicles, where they will then enter the synaptic gap, and bind to the ligand gated channels, allowing sodium to rush into the postsynaptic neuron.
c) Neonicotinoid pesticides act as inhibitory neurotransmitters, which will stop acetycholine from binding to it respective receptors. This, in turn, causes neurons within an insect to stop firing, resulting in paralyzation and an eventually death.
What does amphipathic mean?
Amphipathic means that a substance contains parts that are both hydrophillic (water-loving/polar) and hydrophobic (water-hating/nonpolar). An example of this would be phospholipids, which have a hydrophobic tail and hydrophillic head.
Predict the effect of cholesterol on the fluidity of the cell membrane as temperature increases.
Cholesterol would cause the cell membrane fluidity to _______.
decrease
Which statement applies to cholesterol?
It impacts membrane fluidity.
The amphipathic properties of phospholipids result in -
The formation of a bilayer of phospholipids, with the heads facing the water and the tails facing each other.
Which of the following is NOT a function of a membrane protein?
chromosome separation
Match the organisms with their fatty acid tail composition:

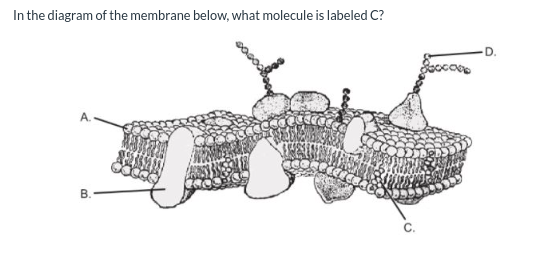
That molecule is a cholesterol.
Which processes involve mitosis?
Asexual reproduction
Tissue repair
Embryonic development
Growth
Categorize the events of mitosis into the correct phase.
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase


0.25
When does DNA replication occur?
S
How would the mitotic index differ between cancerous and non-cancerous cells?
The mitotic index would be drastically higher for cancerous cells when compared to non-cancerous cells because cancerous cells divide at a uncontrollable pace due to their many mutations, which prevents them from going through checkpoints placed in the cell cycle. Non-cancerous cells, however, do the opposite; they go through each checkpoint and have properly functioning proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, as they lack a high number of mutations that would prevent these components from doing their jobs.


Which processes occur during interphase?

Prokaryotic organisms reproduce utilizing...
asexual binary fission