The Nervous System
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from lecture notes on the structure, function, and organization of the nervous system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Neuron
Fundamental unit of the nervous system that transmits information via electrical and chemical signals; also called a nerve cell.
Electrical impulse
A wave of electrical activity that travels along a neuron to convey information and trigger responses.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The brain and spinal cord; responsible for processing, integration, and coordination of sensory input and motor output.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
All nerves outside the brain and spinal cord; carries signals between the CNS and the rest of the body.
Dendrite
Branched extension of a neuron that receives incoming signals and directs them toward the cell body.
Excitatory signal
Input that makes a neuron more likely to generate an action potential (fire).
Inhibitory signal
Input that makes a neuron less likely to generate an action potential.
Cell body (Soma)
Central part of a neuron containing the nucleus; metabolic and nutrient center of the cell.
Axon
Long, thin projection that conducts action potentials away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
Myelin sheath
Fatty insulating layer around many axons; speeds and increases efficiency of impulse transmission and prevents signal loss.
Schwann cell
Glial cell that forms myelin around axons in the peripheral nervous system.
Oligodendrocyte
Glial cell that forms myelin around axons in the central nervous system.
Node of Ranvier
Periodic gap in the myelin sheath rich in voltage-gated sodium channels; enables rapid impulse “jumping.”
Saltatory conduction
Process by which action potentials leap from one Node of Ranvier to the next, greatly increasing conduction speed.
Axon terminal
Specialized ending of an axon that releases neurotransmitters to communicate with another cell.
Synapse
Junction where a neuron communicates with another cell across a small gap called the synaptic cleft.
Synaptic cleft
Microscopic gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes across which neurotransmitters diffuse.
Nerve
Bundle of neuron fibers (primarily axons) wrapped in connective tissue within the PNS.
Nerve fibre
Another term for an individual axon, especially when myelinated.
Somatic nervous system
Division of the PNS that controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles.
Autonomic nervous system
Division of the PNS that regulates involuntary functions such as heart rate and digestion.
Sympathetic division
Branch of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for ‘fight or flight’ responses.
Parasympathetic division
Branch of the autonomic nervous system that promotes ‘rest and digest’ activities.
Sensory neuron (Afferent)
Neuron that carries information from sensory receptors toward the CNS.
Interneuron
Neuron within the CNS that connects sensory neurons to motor neurons and processes information.
Motor neuron (Efferent)
Neuron that transmits commands from the CNS to muscles or glands (effectors).
Stimulus
Any internal or external change that can be detected by receptors and elicit a response.
Receptor
Specialized cell or structure that detects a stimulus and initiates neural signaling.
Control centre (Integration centre)
Part of the CNS that interprets sensory input and determines the appropriate response.
Effector
Muscle or gland that carries out the response commanded by the nervous system.
Reflex arc
Simple neural pathway of a reflex involving a sensory neuron, an interneuron (often), and a motor neuron.
Reflex action
Rapid, involuntary response to a stimulus that occurs before conscious brain processing.
Action potential
All-or-none electrical signal that travels along an axon to convey information.
Voltage-gated sodium channel
Ion channel that opens in response to membrane depolarization, essential for initiating and propagating action potentials.
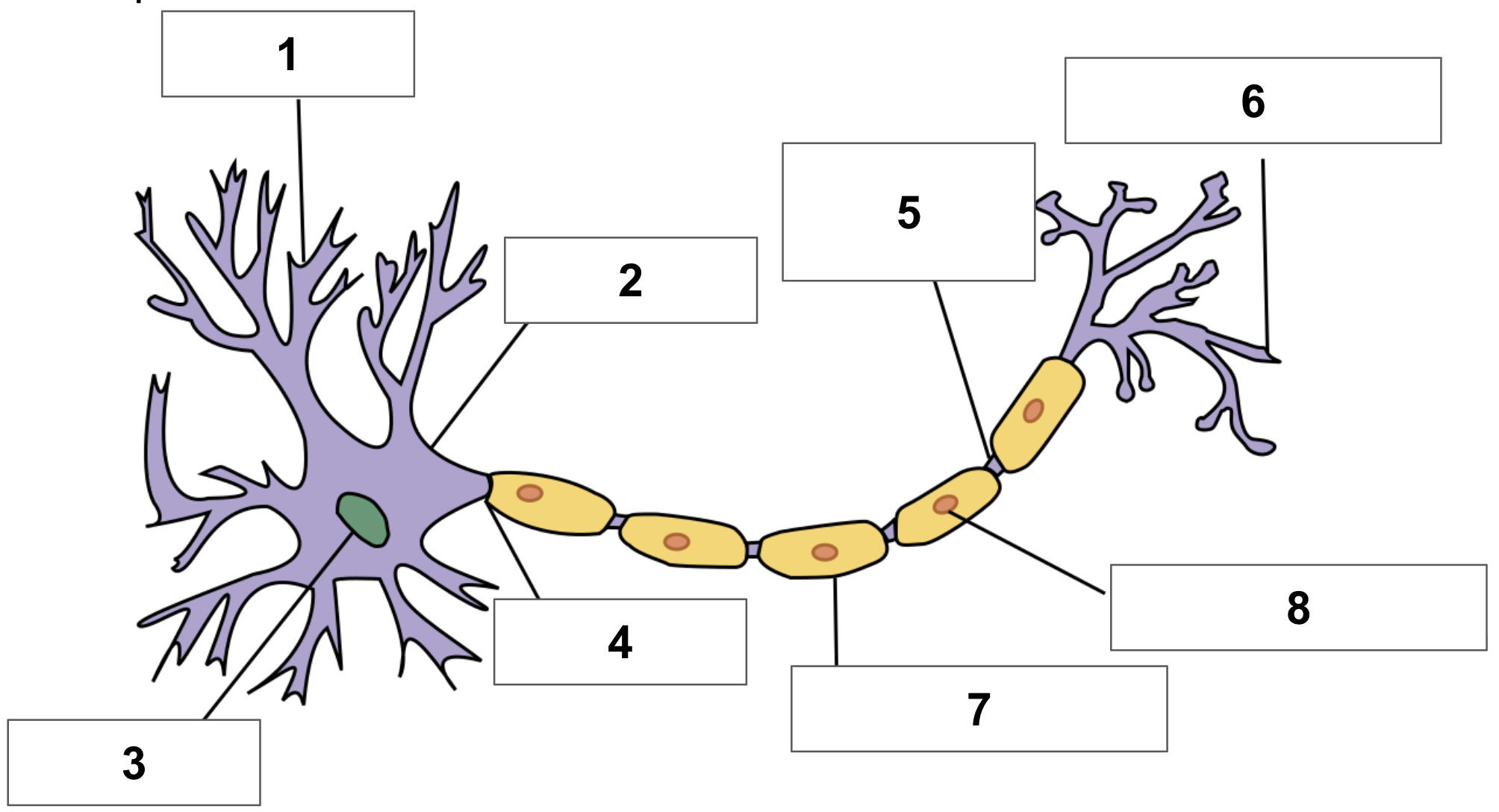
label 1
dendrite
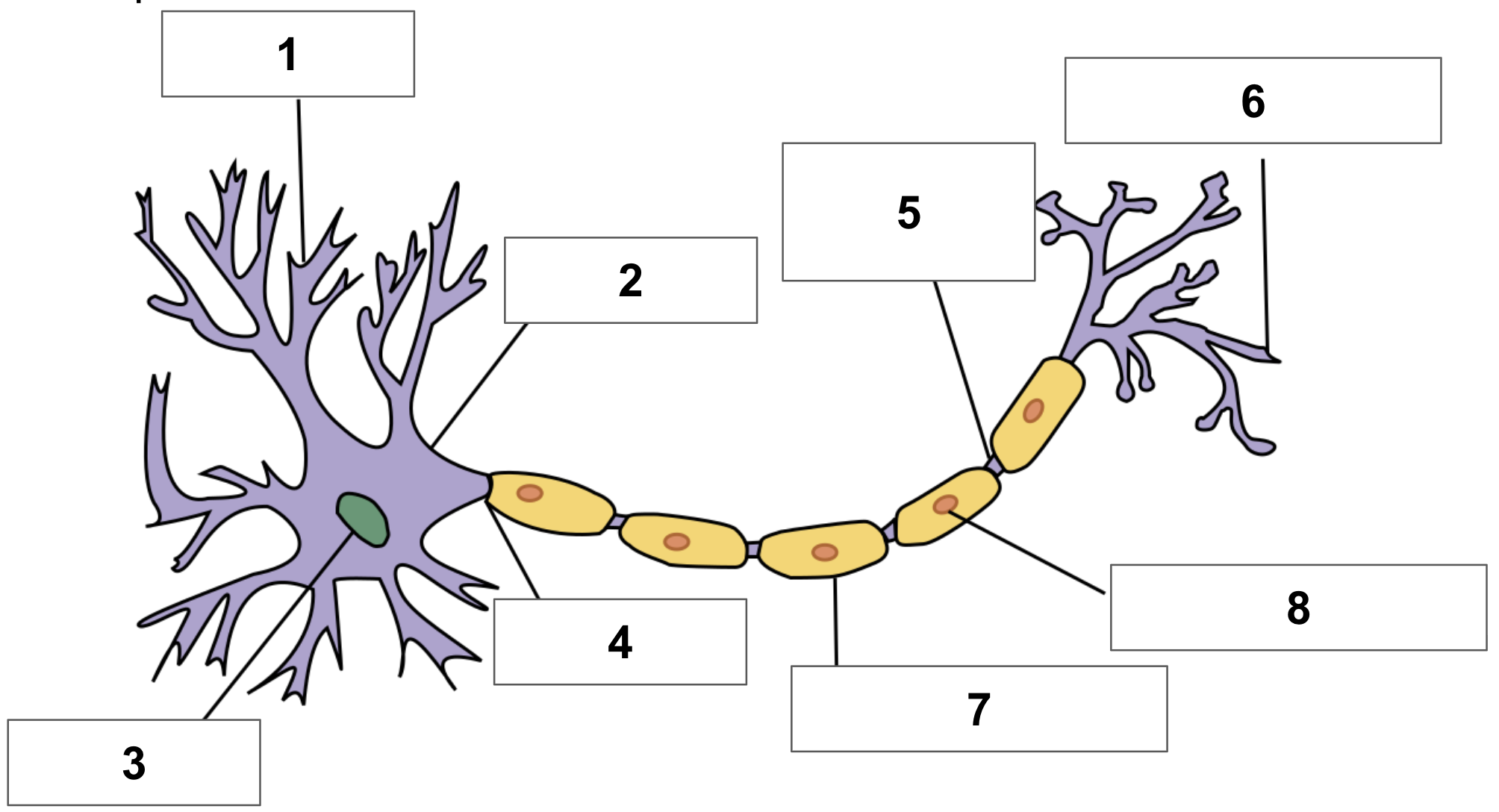
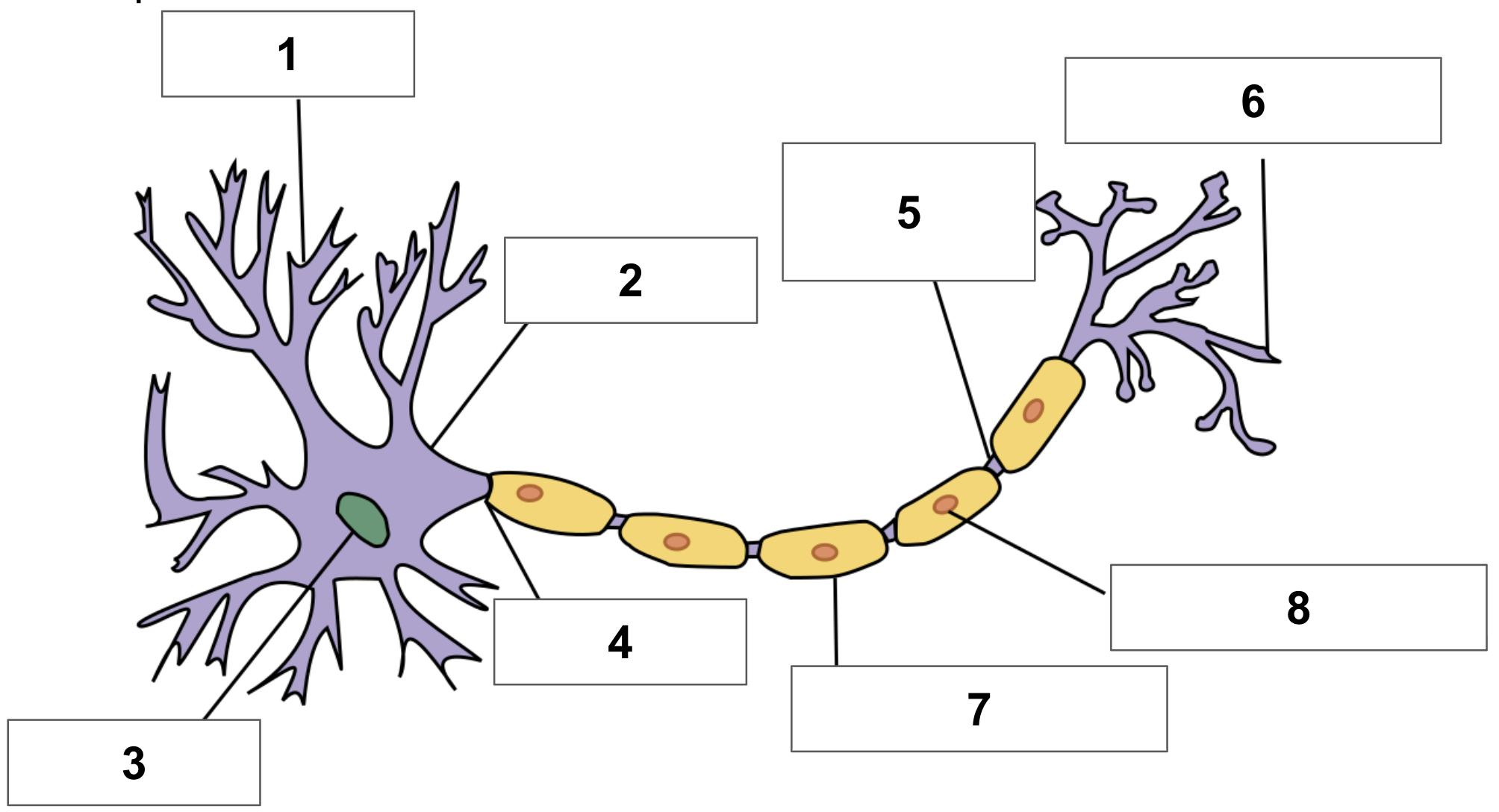
label 2
cell body
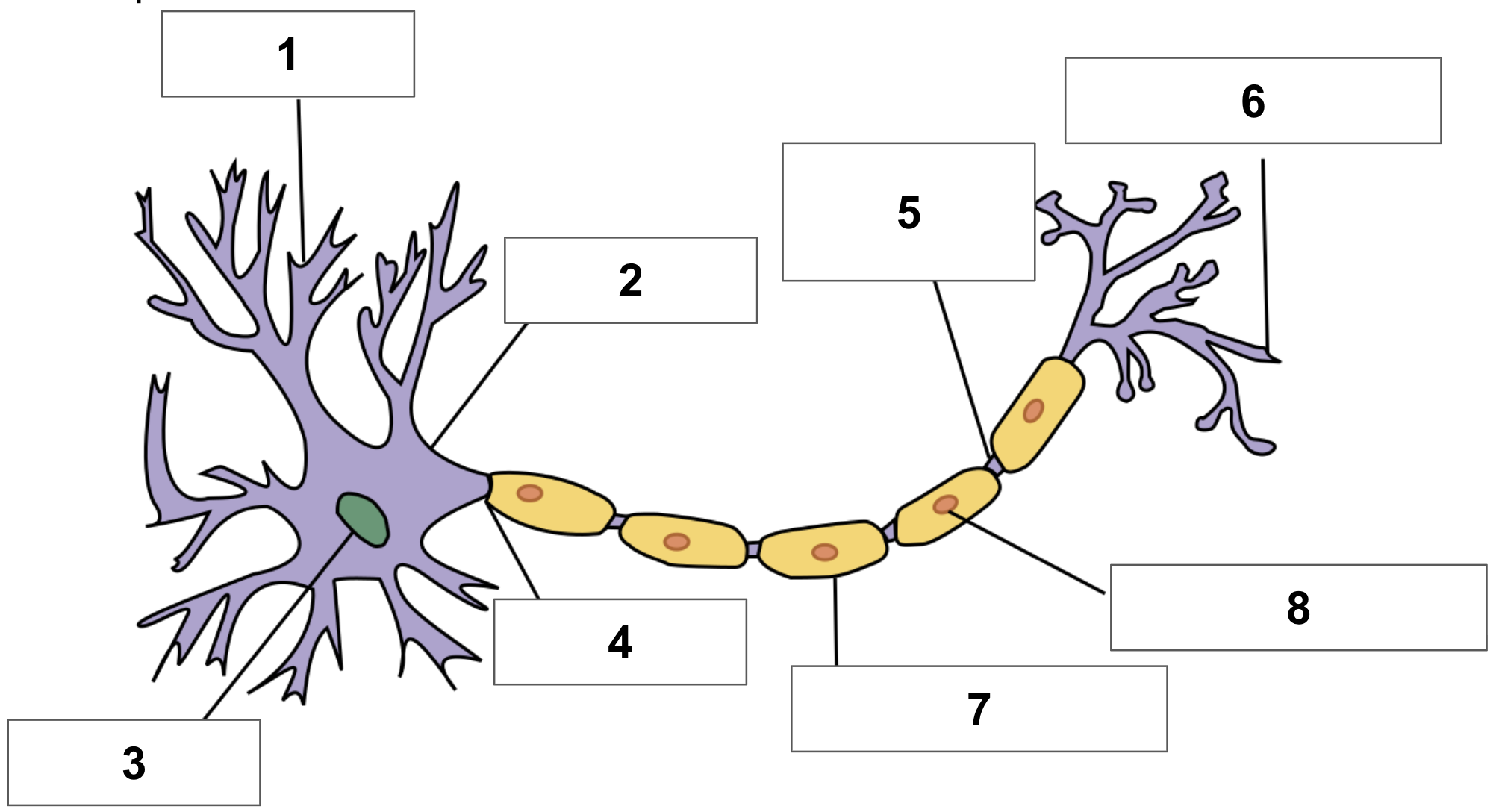
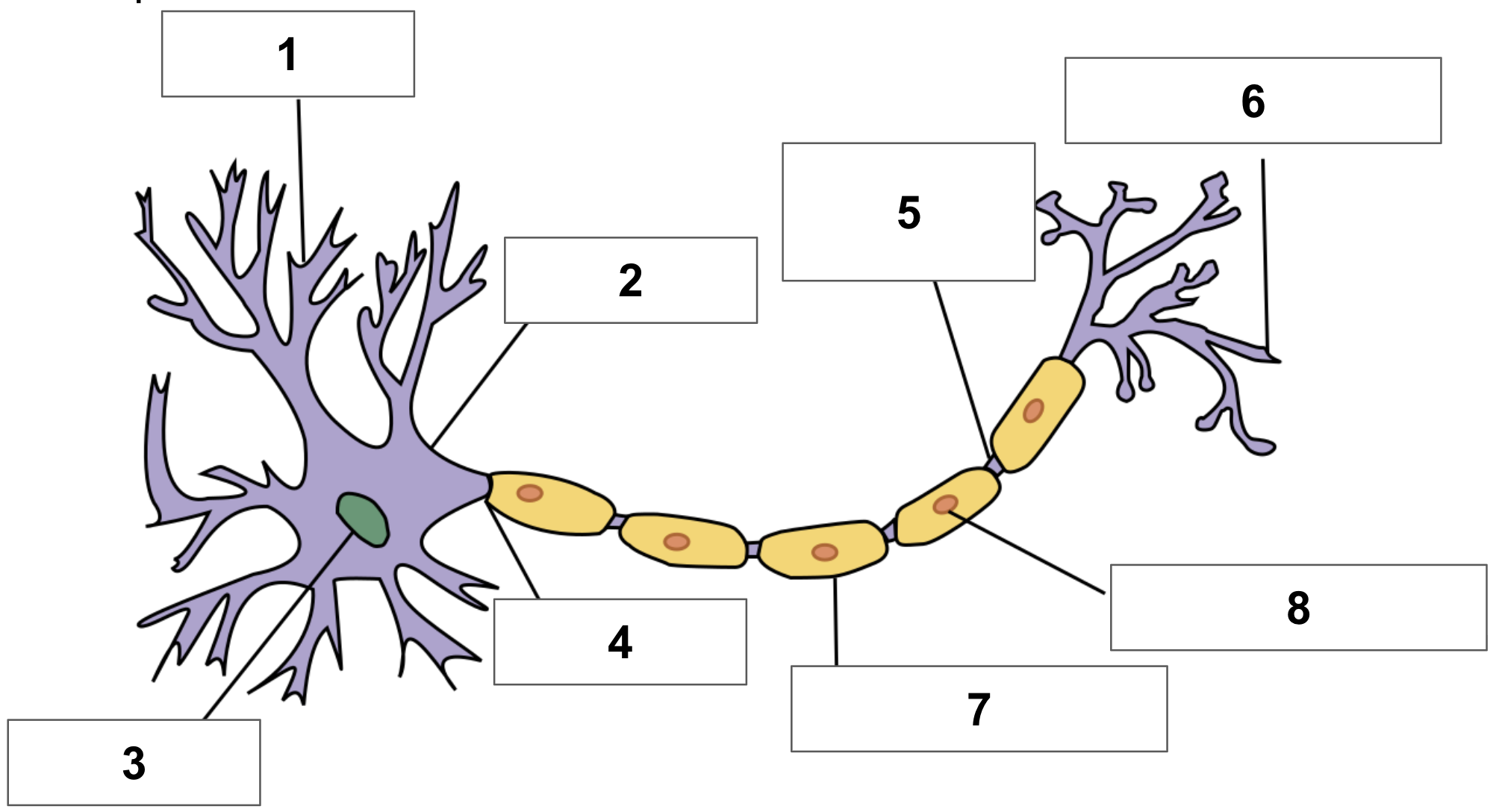
label 3
nucleus
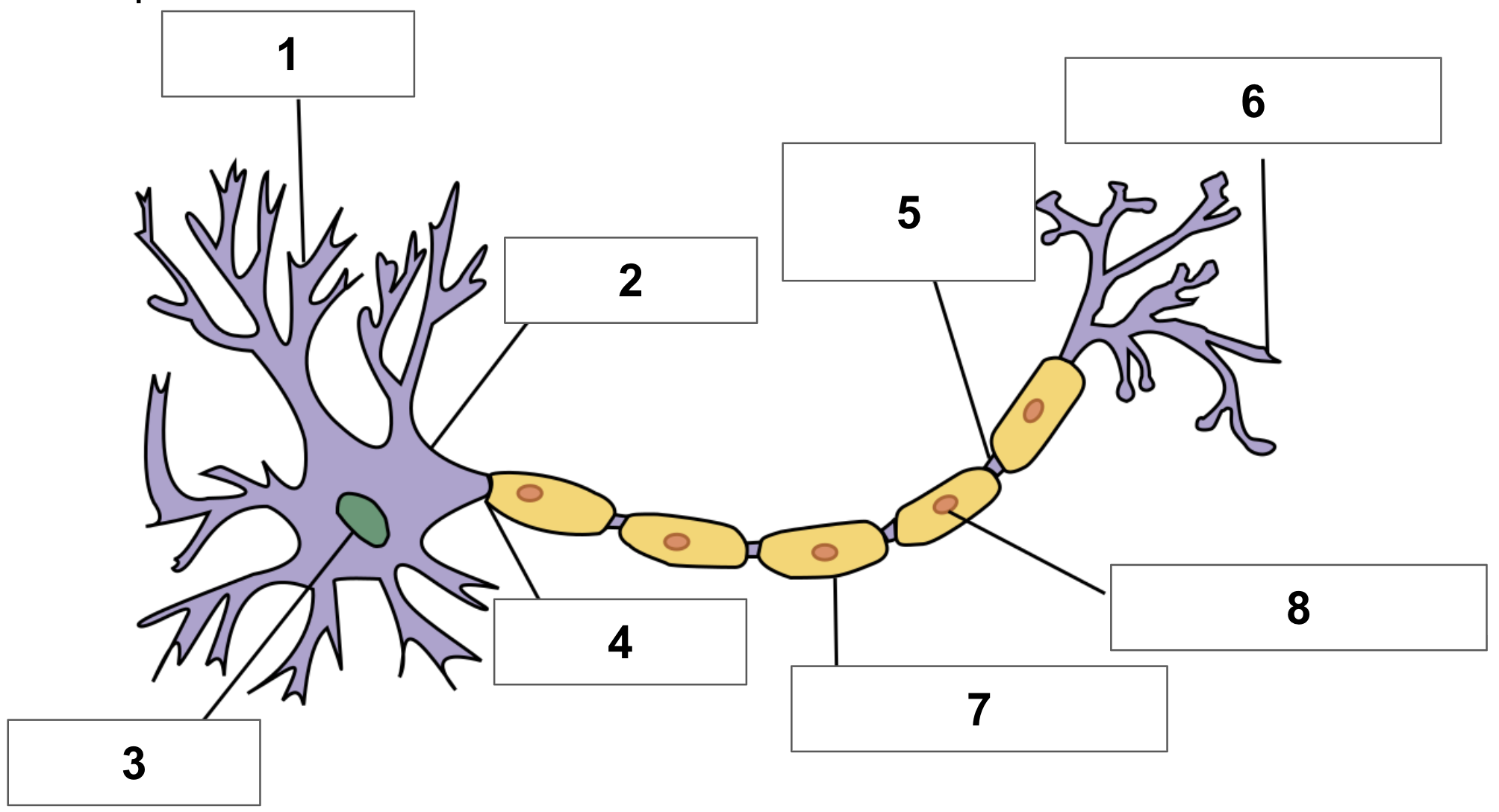
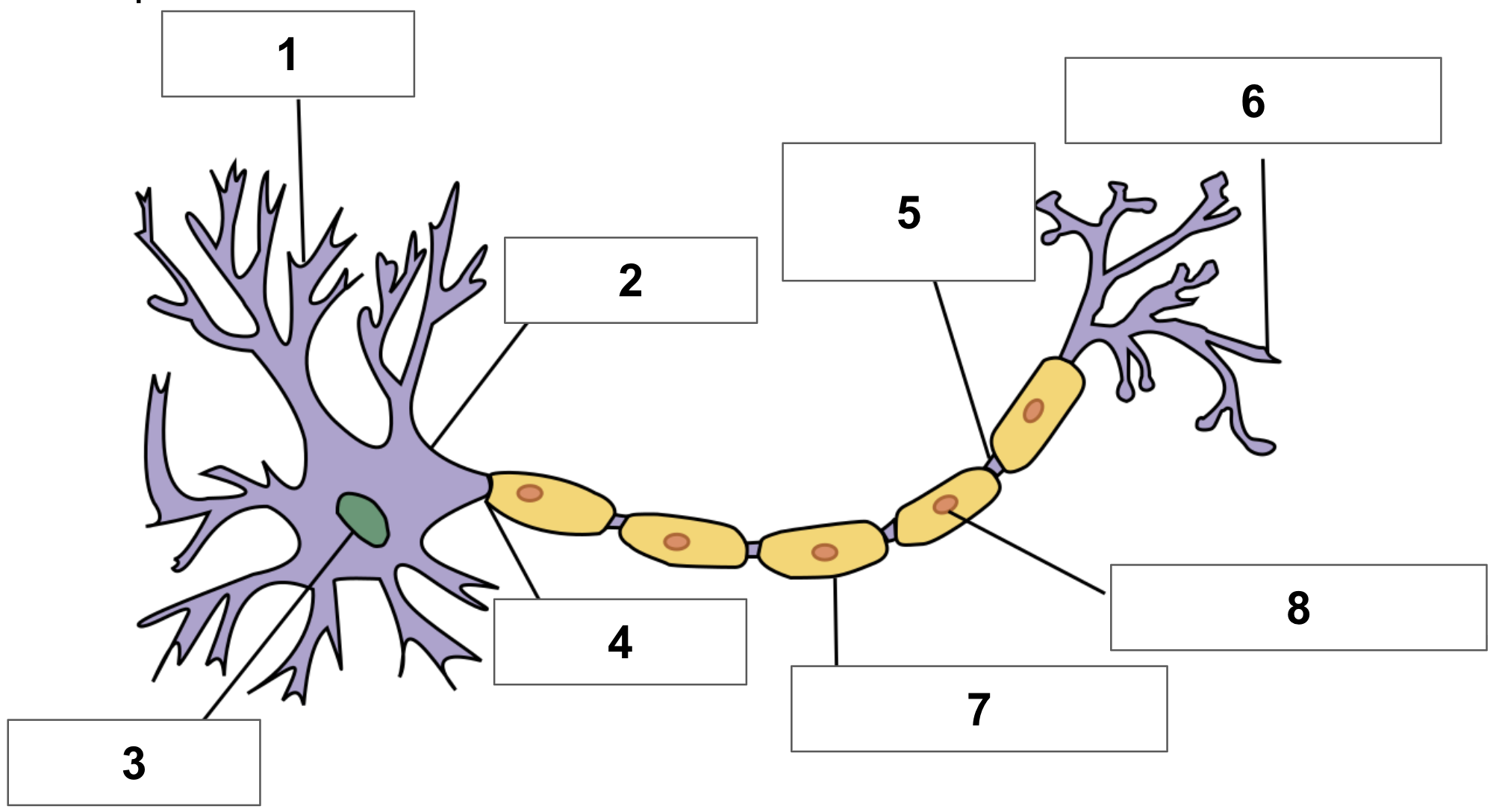
label 4
axon
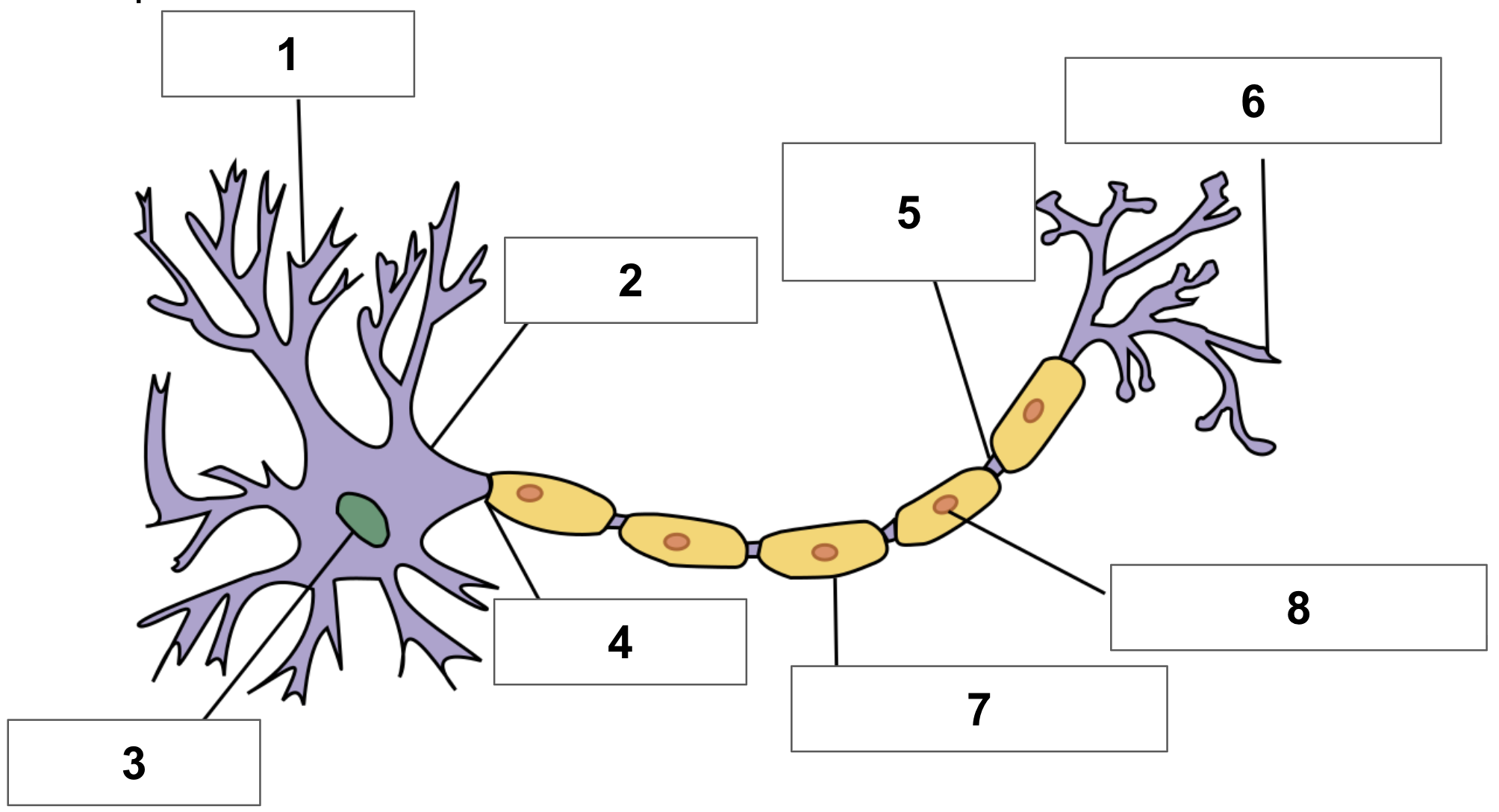
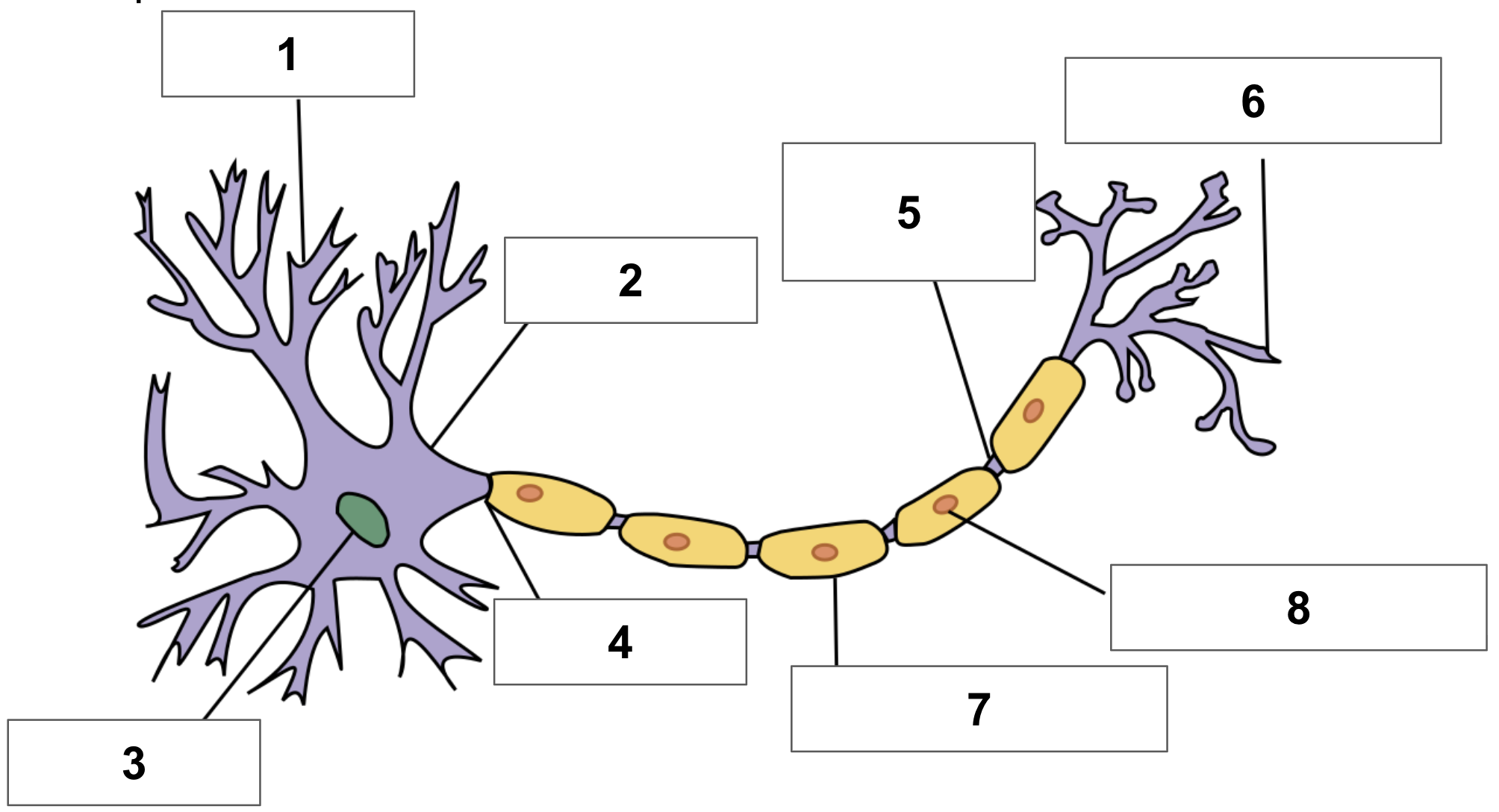
label 5
node of ranvier
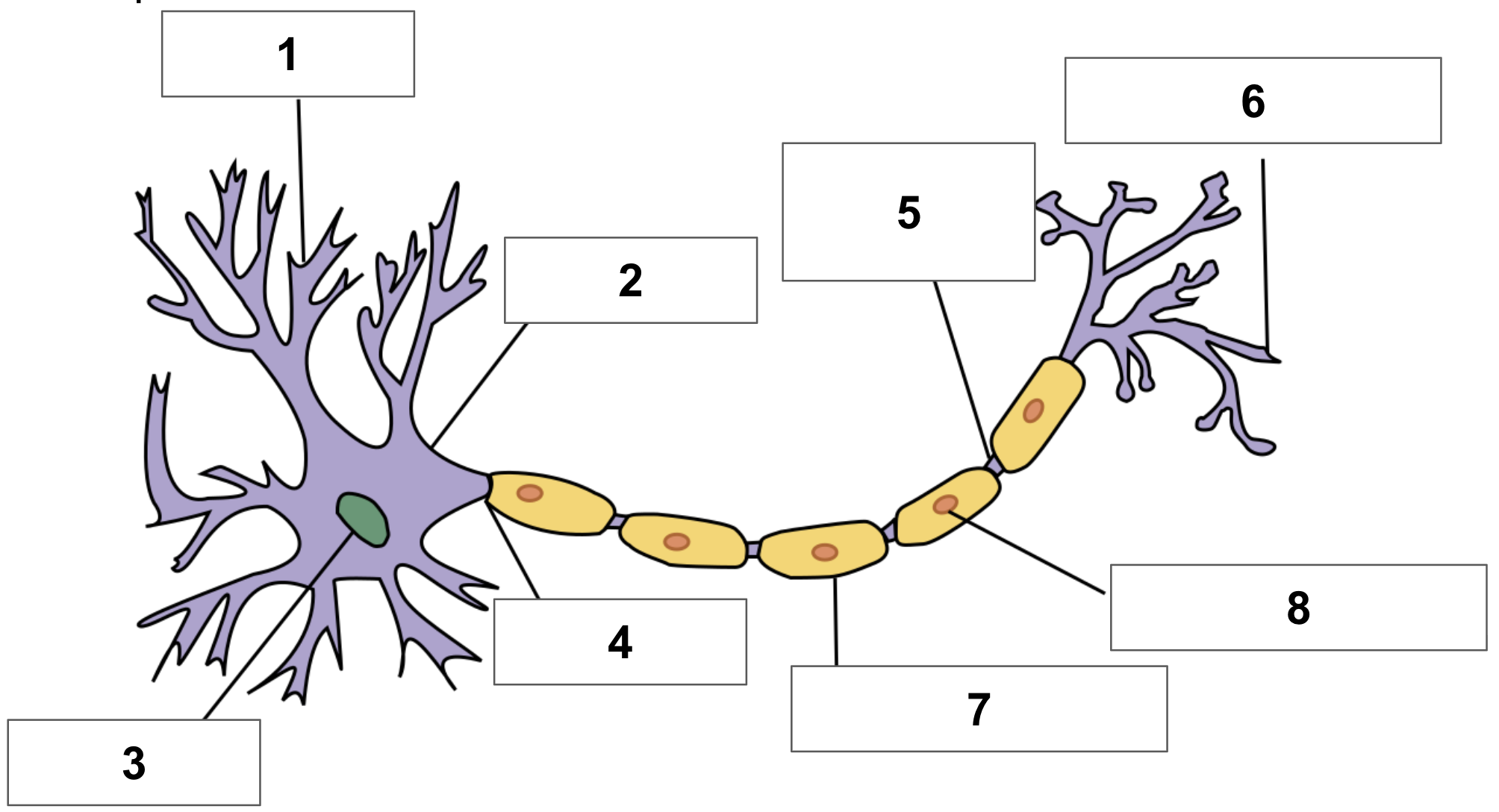
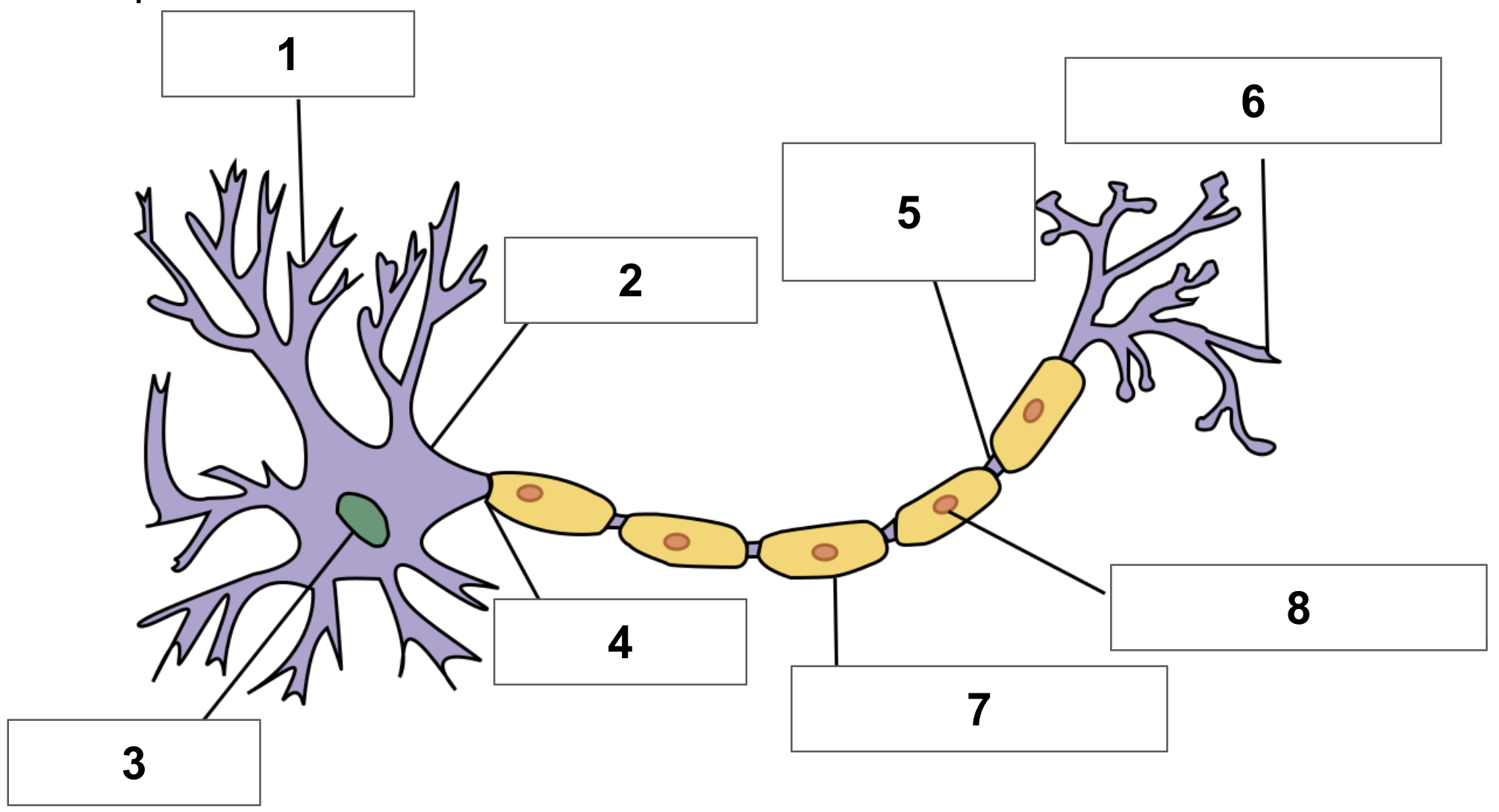
label 6
axon terminal
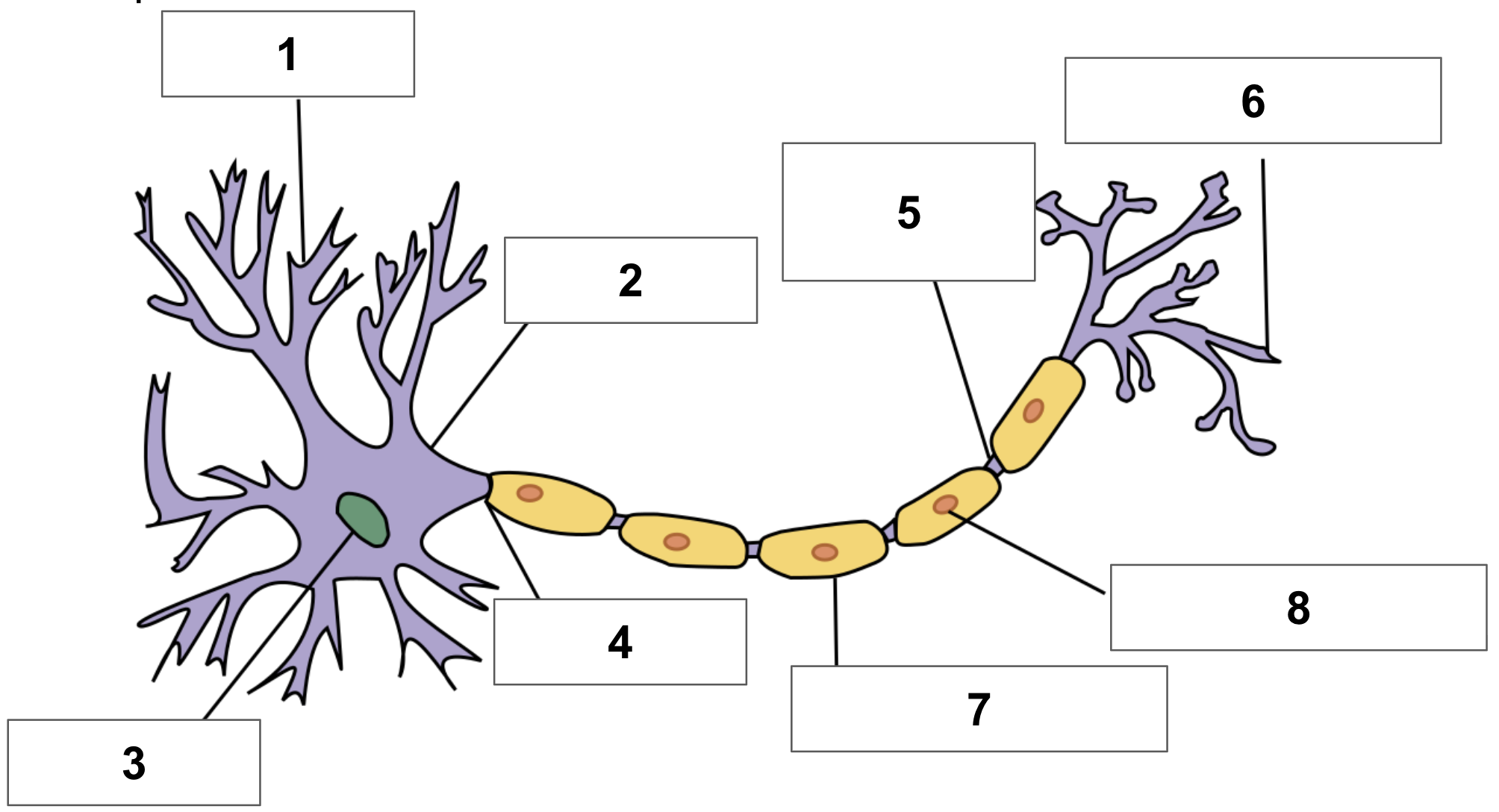
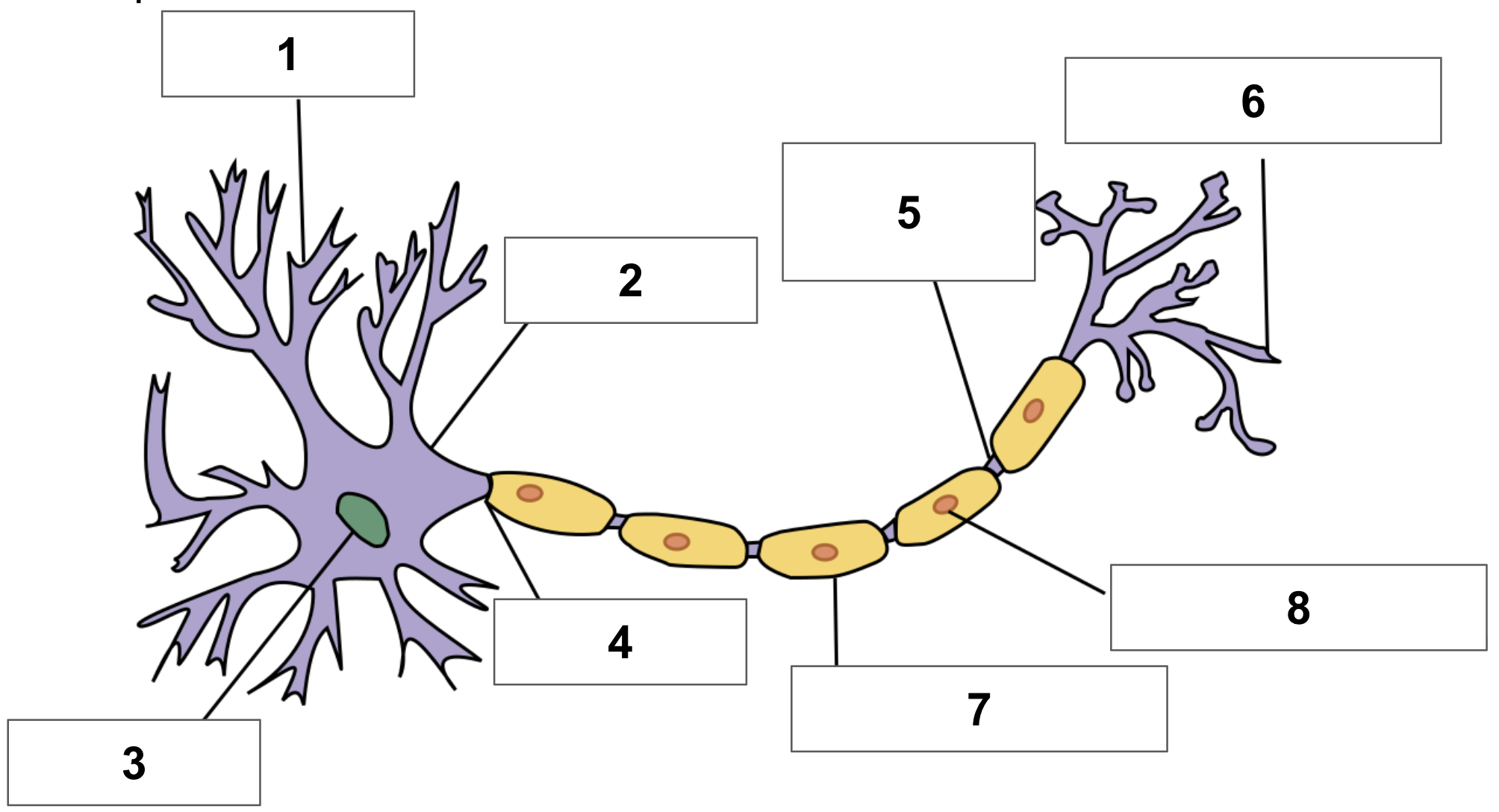
label 7
myelin sheath
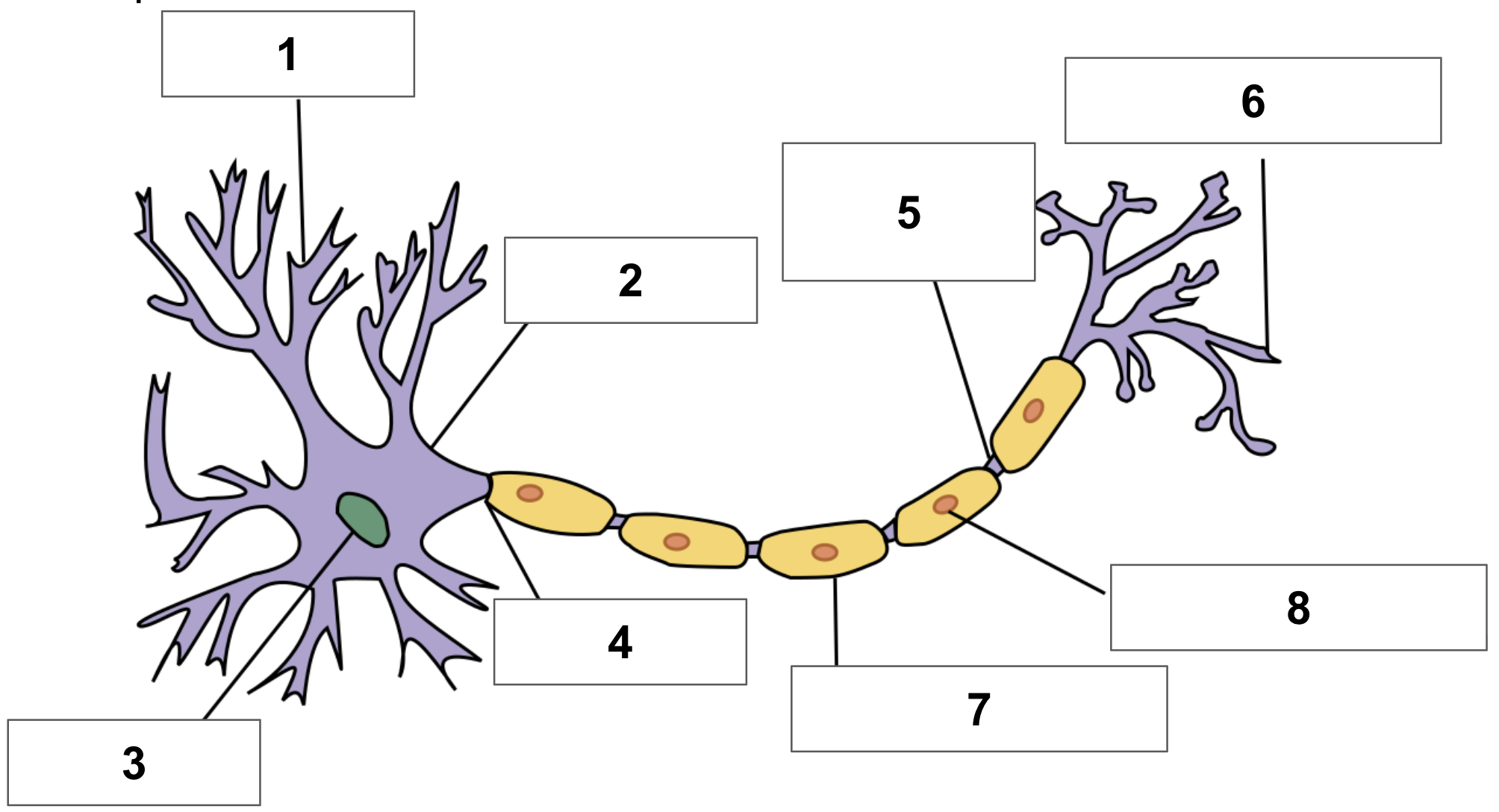
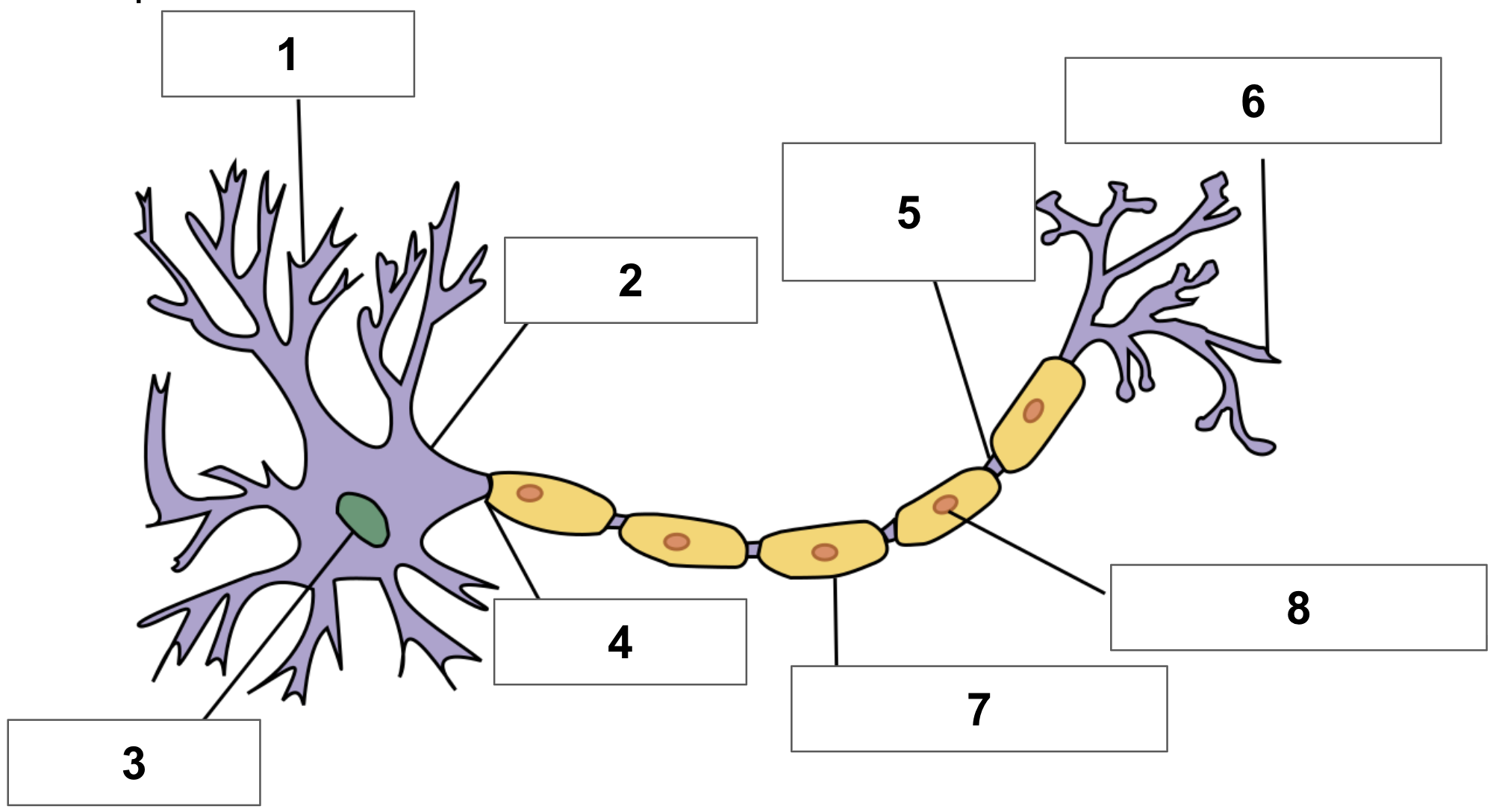
label 8
schwann cell
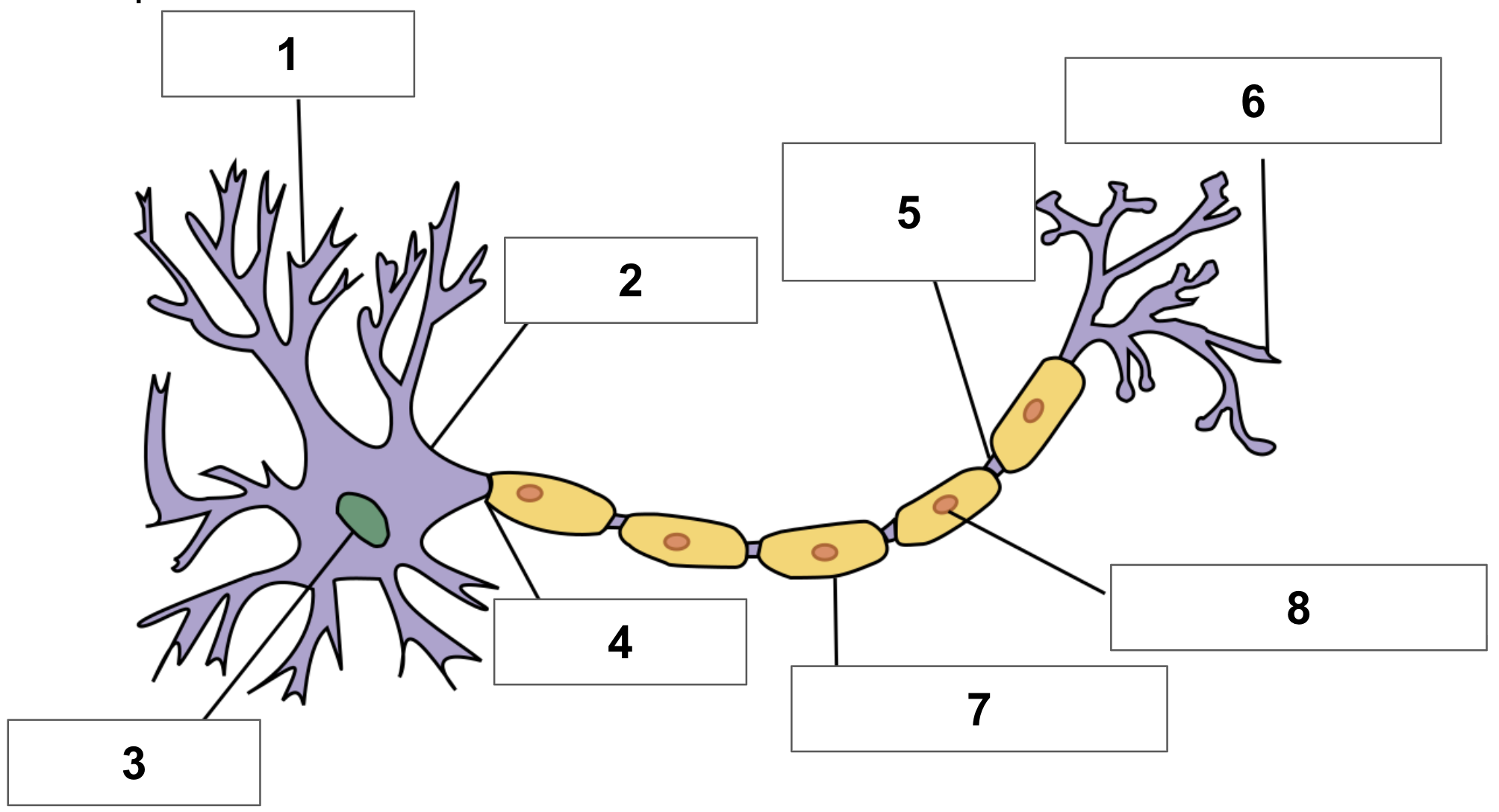
cerebrum function
responsible for higher-level functions (i.e. thinking, memory + voluntary movement
cerebellum function
coordinates movement, balance + maintains posture
brainstem function
controls essential + automatic functions (i.e. breathing, heart rate) connects cerebrum + cerebellum to spinal cord
brain death
when a person no longer has any brain functions
frontal lobe
largest lobe of the brain - controls voluntary movement, thinking, emotions + memory
parietal lobe
processes sensory information, such as taste, touch + temperature
occipital lobe
related to visual stimuli - depth perception, colours + facial recognition
temporal lobe
forming visual + long-term memories, recognising speech, + automatic responses
right brain function
creativity, imagination, intuition, left-hand controls
left brain function
logic, language, reasoning, number skills, right-hand control
functions of the brain
sensory perception, motor control, cognitive functions, emotional regulation, homeostasis
anterior cerebral artery location
tissue behind the forehead and under the crown
middle cerebral artery location
further inside the brain
posterior cerebral artery location
back of head, lower part of brain + cerebellum
neuroplasticity
the nervous systems ability to change its activity in response to stimuli, reorganising structure, function, or connections after brain injury
MRI process
strong magnetic fields observe different types of body tissue, blood flow shows areas of brain working hardest
MRI function
can diagnose brain tumours + areas of damage
skull function
supporting brain + facial structures
cranium
passage through birth canal + growth of the brain
most common skull issue
fracture - break in bone
meninges layers
dura matter, arachnoid matter, pia matter
dura matter function
thick outer layer - connective tissue attaches to skull and arachnoid matter - allows blood to leave the brain and cerebrospinal fluid to enter
arachnoid matter function
middle layer - no blood vessels or nerves - web-like appearance of connective tissue projections
pia matter
innermost layer - tight against brain + spinal cord - supplies blood to brain tissue, contains cerebrospinal fluid
epidural space location + purpose
between skull + dura matter - pain medications + anaesthesia are injected here
subdural space location + purpose
between dura matter + arachnoid matter - can be opened to treat trauma to the brain
subarachnoid space location + purpose
between arachnoid matter + pia matter - filled with cerebrospinal fluid to protect brain + spinal cord
meningitis
infection of the meninges, caused by bacteria, fungus or virus - diagnosed by lumar puncture - fever, headache, rash
subdural hematoma
bleeding between dura matter and arachnoid matter due to tear in blood vessel
bleeding within meningeal layers
bleeding in blood vessels in meninges - caused by head trauma, creating swelling in the brain
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
clear colourless fluid surrounding brain + spinal cord - provides nutrients, cushioning for impact
ventricles
connected, fluid filled cavities that produce + circulate CSF
CSF fluid leaks
loss of CSF, dropping fluid pressure
hydrocephalus
build up of CSF → headaches, vision problems, cognitive changes
idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH)
increased pressure within skull → headaches + vision problems
blood-brain barrier
semi-permeable membrane - prevents harmful substances from entering the brain - maintaining a stable environment in the brain
what molecules CAN pass through the blood-brain barrier
small, lipid-soluble molecules, some gases + nutrient
what molecules CANNOT pass through the blood-brain barrier
larger molecules, proteins + drugs
blood-brain barrier conditions
inflammation/weakening (chronic or acute) - allows harmful substances in - brain cancer, infection, concussion, MS, parkinsons
nervous tissue
made up of neurons + neuroglial cells -
neuroglial cells (glial cells or glia)
do not produce electrical impulses, provide support + critical functions for neurons
neuroglial cell function
regulates neurotransmission, brain homeostasis, making myelin, forming blood-brain barrier
neuroglial cell types
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, schwann cells
astrocytes location
found in the CNS in both grey and white matter
astrocytes structure
star-shaped glial cells with many branches
astrocytes function
provide nutrients to neurons, maintaining extracellular environment + provide structural support
oligodendrocytes location
CNS in both grey and white matter - more abundant in white matter
oligodendrocytes structure
round + dense nucleus, surrounded by cytoplasm - processes extend and wrap around axons
oligodendrocytes function
axon myelination, providing a stable environment for neurons + tissue repair
microglia location
CNS - most abundant in brain stem, hippocampus + bansal ganglia
microglia structure
small cell body with branching cell processes - activated when they become larger - very mobile
microglia function
macrophage - white blood cells digest pathogens - triggering inflammatory responses to protect the brain
schwann cells location
main glial cells of the peripheral nervous system
schwann cells structure
shaped like a rolled up sheet of paper, layers of myelin between each roll
schwann cells function
myelination and non-myelinating - a number of schwann cells are needed to myelinate an axon
grey matter development
not fully developed until mid 20s - begins forming in utero
grey matter function
prefrontal cortex is responsible for planning, decision making, and impulse control - the last part of the brain to develop
grey matter decline
metabolic disorders, trauma, neurogenerative disease