15.2 Genetic Imprinting
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
genomic imprinting
an epigenetic phenomenon in which expression of a gene depends on which parent it was inherited from
leads to monoallelic expression
monoallelic expression
if maternally imprinted, all expression comes from the paternal chromosome (and vice versa)
maternally imprinted
a small number of genes are turned off in the chromosomes inherited from our mother, gene transcriptionally silent
rely on expression from father
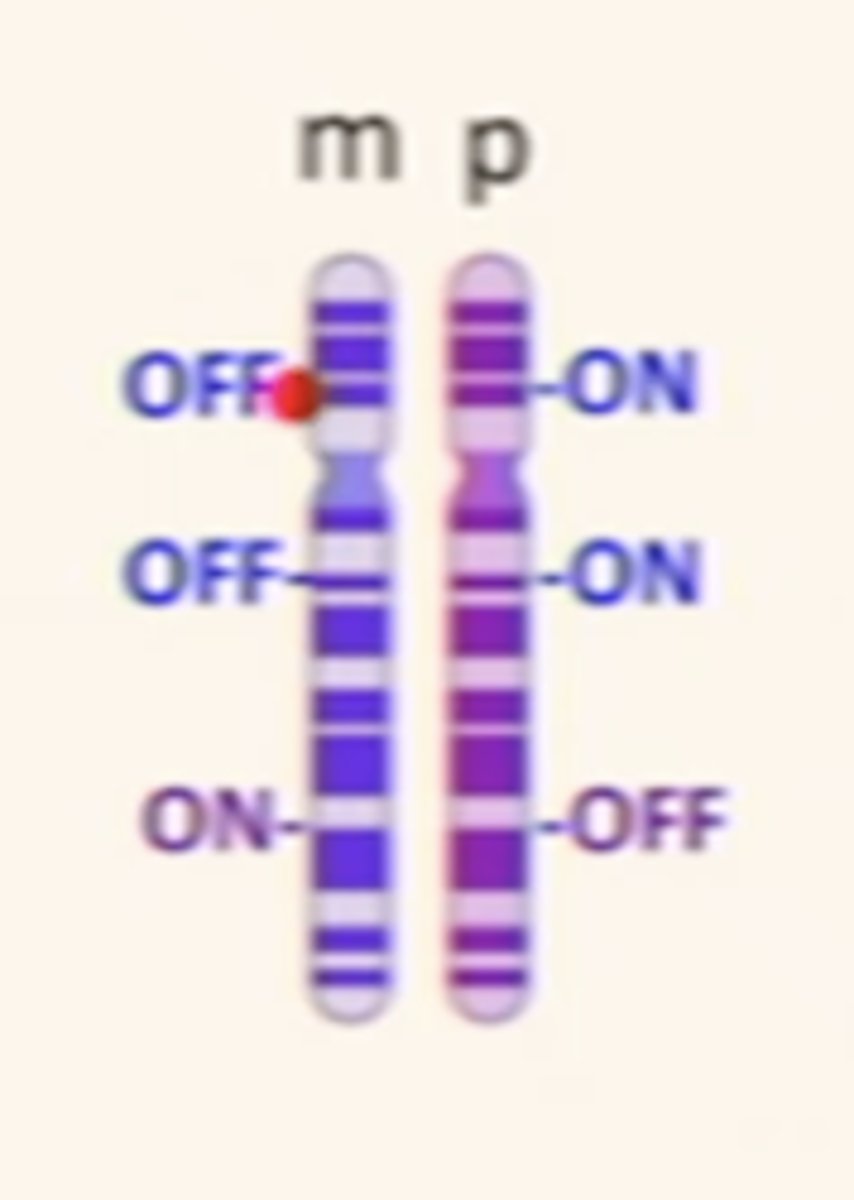
paternally imprinted
a small number of genes are turned off in the chromosomes inherited from our fathers, gene transcriptionally silent
rely on expression from mother
DNA methylation
can block transcription
often occurs at cytosine (C) residues next to guanine (G)
DNA methyltransferases
DNMTs transfer a methyl group from S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) to cytosine
igf2
insulin-like growth factor
maternally imprinted
igf2R
insulin-like growth factor receptor
paternally imprinted
inactivates growth factor
normal sized mouse
igf2 = igf2R
large sized mouse
igf2 > igf2R
small sized mouse
igf2 < igf2R
picture of maternal and paternal chromosomes for igf2 and igf2R
maternal:
igf2 is OFF (methylated)
igfR2 is ON
paternal:
igf2 is ON
igfR2 is OFF (methylated)
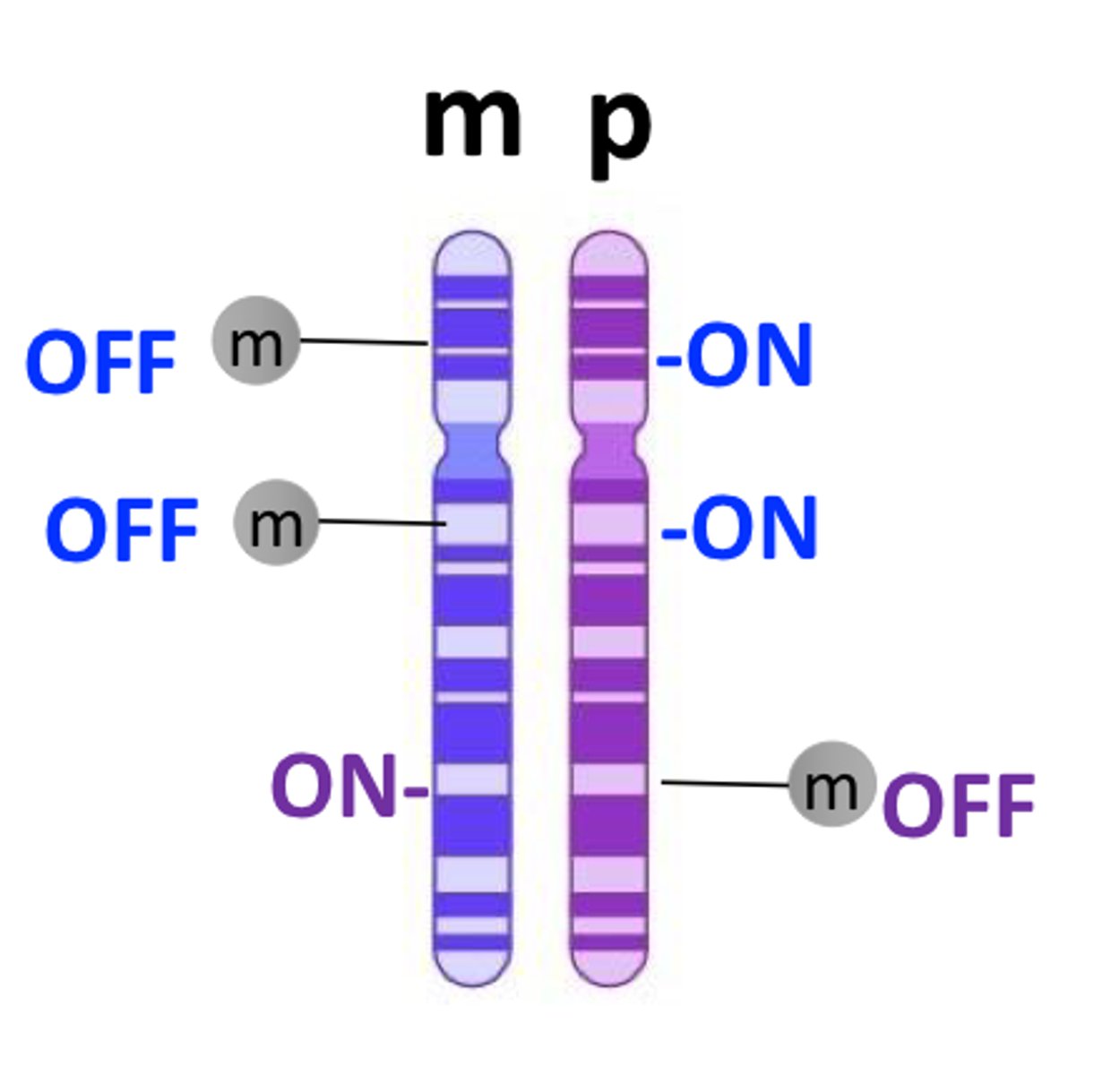
the child on left has a frameshift mutation in igf2 that leads to a non-functional protein (let's call this the igf2-2 allele). what parent did this child inherit the igf2-2 allele from?
father (since mother is methylated and cannot express gene)

maternal imprinting (oogenesis)
genes that were methylated (silenced/imprinted) during oogenesis in egg cells
females put a maternally imprinted pattern on every gamete
methylation pattern same as mother
paternal imprinting (spermatogenesis)
genes that were methylated during spermatogenesis (in sperm cells)
males put a paternally imprinted pattern on every gamete
methylation pattern same as father
imprinting occurs during gametogenesis
imprinting patterns are erased in our germ line cells near the beginning of meiosis
reestablished during later steps of meiosis/gametogenesis (sex-specific manner)
imprinting and gametogenesis summary
every gamete from an individual receives the same imprinting pattern
the pattern depends on the sex of the person creating the gametes
all members of the same sex produce the same imprinting patterns
imprinting is independent of alleles
imprinting is common (but not universal)
not all genes are imprinted (~1% of genes in mammals and flowering plants are imprinted)
2014: 150 known imprinted genes
2019: 238 known imprinted genes
if there was an imprinting error during meiosis in a female (such that the mother no longer imprinted her genes), what is the expected size of the pups?
larger than normal
if mother's igf2 gene is not methylated, it will be transcribed along with igf2 gene on father
twice that amount of growth factor
if there was an imprinting error during meiosis in a male (such that the father no longer imprinted his genes), what is the expected size of the pups?
smaller than normal
cannot imprint igf2R on father
twice the amount of growth factor receptor, inhibiting growth factor
tigers
do not imprint igf2 or igf2R
lions are like mice
lgf2- maternally imprinted
igf2R- paternally imprinted
female tiger x male lion, what alleles will be methylated?
female tiger- igf2 on, igf2R on (transcriptionally active)
male lion- igf2 on (contributes growth factor maternally imprinted), igf2R off (paternally imprinted)
liger
hybrid of tiger and lion
has two copies igf2 growth factor, one copy of igf2R
imbalance of growth factor
do you expect the liger pups to be larger, smaller, or normal in size?
larger
excess growth factor, abnormally large size
liger hybrids health defects
enlarged hearts, organ failure, neurological disorders, prone to injury, sterile
female lion x male tiger (tigrons)
predicted to be smaller, but actually normal sized
parental conflict hypothesis
father- wants kids to be big and strong, use all maternal resources
mother- wants kids to be big enough and healthy, but save some resources for future kids
father (parental conflict)
igf2 on, igf2R off
growth factor always on, limit receptor
mother (parental conflict)
igf2 off, igf2R on
turn growth factor off, receptor on
imprinting disorders
prader willi syndrome (PWS)
angelman syndrome (AS)
prader willi syndrome symptoms
delayed development, flaccid muscles, short stature, intellectual disability, compulsive behavior
hormonal imbalances leading to constant hunger, delayed puberty
angelman's syndrome symptoms
delayed development, intellectual disability, ataxia, severe speech impairment, happy demeanor
PWS imprinting
PW genes are maternally imprinted
AS imprinting
AS genes are paternally imprinted
common cause of PWS and AS
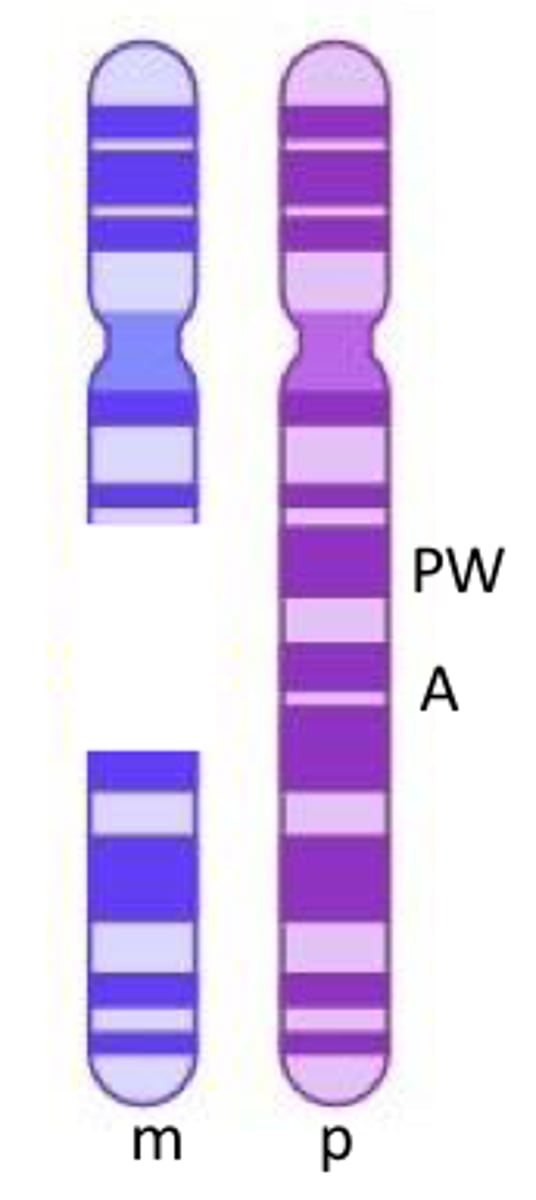
a de novo deletion of a region on chr.15 that removes both the PW and A genes
de novo mutation occurs during meiosis
what syndrome would the offspring have if the deletion occurred during oogenesis?
angelman
on paternal chromosome, PW is on and A is methylated/off
the disorder is caused when you DON'T make the genes associated with the disease (loss of function)
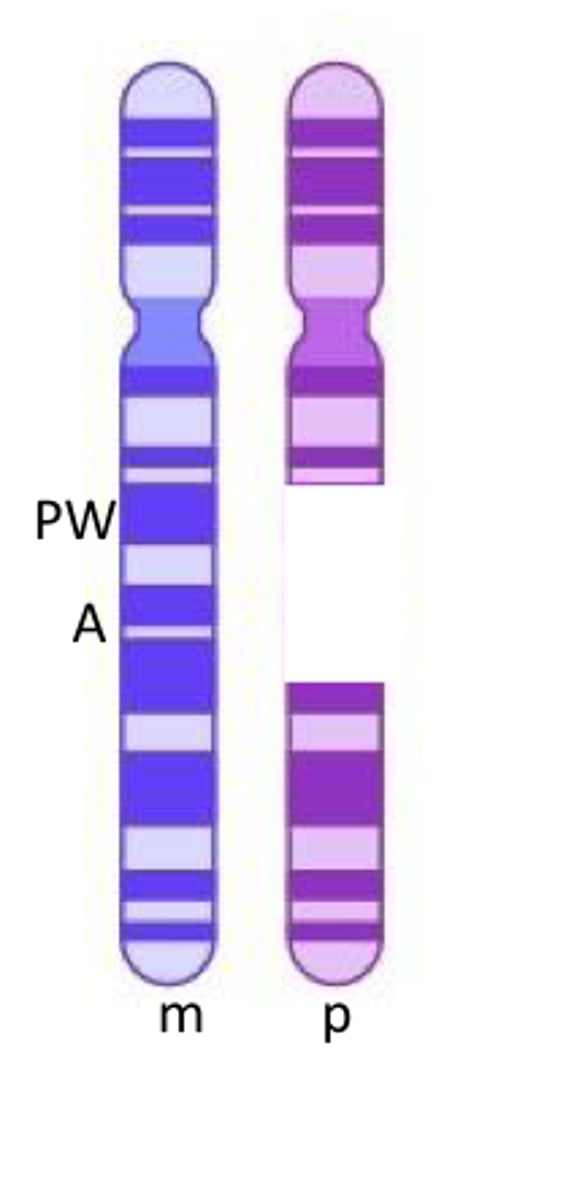
what syndrome would the offspring have if the deletion occurred during spermatogenesis?
prader-willi
on maternal chromosome, PW is methylated/off and A is on
MIG1 is maternally imprinted, which of the following is true?
MIG1 will be expressed from a paternally inherited chromosome
Imprinted genes are
transcriptionally active
methylated during gametogenesis
unmethylated
trasncriptionally silenced
methylated during reproduction of somatic cells
transcriptionally silenced
methylated during gametogenesis
Imprinting leads to mono allelic expression (True/False)
True
Consider a trait caused by a particular variant of a maternally imprinted gene. An unaffected woman is heterozygous for the disease allele. Her partner is homozygous for the wild type, non-disease, allele. You expect that (indicate who will be carriers, who will develop the disease)
half of their offspring will be unaffected carriers of the disease allele
none of their offspring will develop the disease
If you examined the methylation patterns on DNA in eggs and sperm of the same species you would expect them to be (the same/different)
different
Which of the following is most accurate in describing the level of imprinting of mammalian gnees
very few ~1% are imprinted
about half are imprinted
more than half but not all, ~70% are imprinted
very few ~1% are imprinted
Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that
causes genes to be expressed or not depending on whetehr they are inherited from the mother or the father
explains how transcription is inactivated by histone modifications
is characterized by a rapid learning process that takes place early in the life of a social animal, and explains why baby geese will follow the first animal they meet (goose or human)
results in expression of a gene in females only
causes genes to be expressed or not depending on whether they are inherited from the mother or the father
A gene that undergoes maternal imprinting will be _______ in the paternally inherited chromosome (expressed/supressed)
expressed (turned on)
The major molecular mechanism that is used for imprinting involves
methylation of DNA near the promoter region of a gene, leading to increased gene expression
methylation of DNA near the promoter region of a gene, leading to lower levels of gene expression
methylation of DNA near the Shine-Dalgarno sequence, resulting in mRNAs to which ribosomes cannot bind, thereby lowering protein levels of the imprinting gene
deacetylation of histone tails, leading to the condensation of chromatin and reduced gene expression
methylation of DNA near the promoter region of a gene, leading to lower levels of gene expression
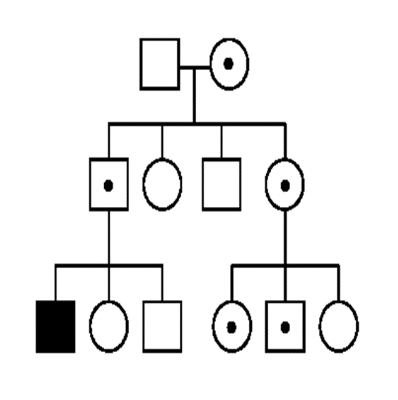
This pedigree is consistent with (maternal/paternal/neither)
maternal imprinting
During oogenesis (select all that apply)
all methylation patterns on chromosomes are erased
some methylation patterns are erased
erased methylation patterns are reintroduced according to the gender of the individual making the oocytes, eg female for eggs, male for sperm
erased methylation patterns are reintroduced according to the gender of the person who passed on the chromosome to the individual making the oocytes, female for the homologous chromosome inherited from mom, male for the homologous chromosome inherited from dad
Some methylation patterns are erased
Erased methylation patterns are reintroduced according to the gender of the person who passed on the chromosome to the individual making the oocytes, female for the homologous chromosome inherited from mom, male for the homologous chromosome inherited from dad
A woman is heterozygous for an imprinted gene (A1A2). During gametogenesis she will imprint gametes that inherit the A1 allele and gametes that inherit the A2 allele (True/False)
False
A woman is heterozygous for a paternally imprinted gene (A1A2). During gametogenesis, she will imprint gametes that inherit the A1 allele and gametes that inherit the A2 allele (True/False)
False
A man is heterozygous for a maternally imprinted gene (A1A2). During gametogenesis, he will imprint gametes that inherit the A1 allele and gametes that inherit the A2 allele. (True/False)
False
A man is heterozygous for a paternally imprinted gene (A1A2). During gametogenesis, he will imprint gametes that inherit the A1 allele and gametes that inherit the A2 allele. (True/False)
True
Imprinting does not alter Mendelian inheritance patterns of alleles. For example, if a person is heterozygous for an imprinted gene (A1A2), then 50% of their offspring will inherit the A1 allele and 50% of the offspring will inherit the A2 allele. (True/False)
True
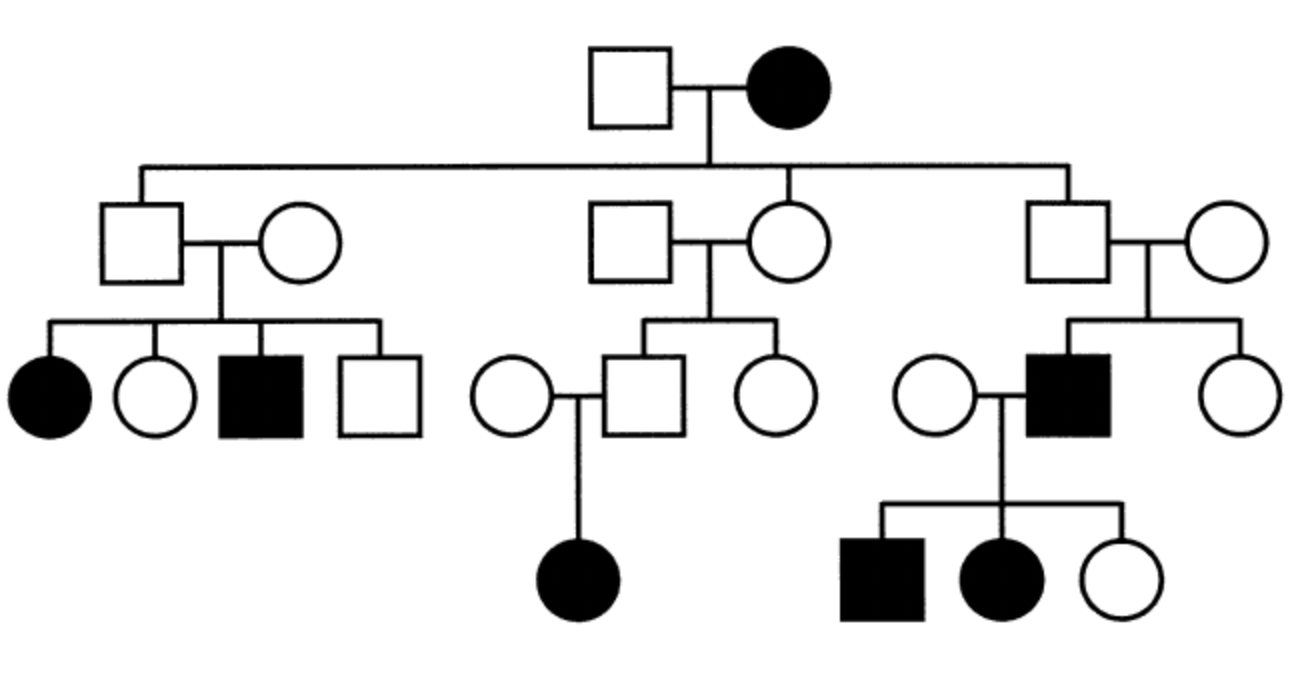
This pedigree is consistent with:
maternal imprinting
paternal imprinting
neither
maternal imprinting
A woman is an unaffected carrier for a gene that is maternally imprinted. Which of the following is true?
Half of her children will be affected, and the affected daughters will have affected children but the affected sons will have carrier children.
Sons that receive the disease allele will be affected while daughters that receive the disease allele will be unaffected.
The daughters that receive the disease allele will be affected while sons that receive the disease allele will be unaffected.
Her children will be unaffected, but the carrier sons will have affected children.
Her children will be unaffected, but the carrier daughters will have affected children.
Her children will be unaffected, but the carrier sons will have affected children.
ZFP57 is a maternally imprinted gene involved in insulin production. A woman with a form of diabetes is homozygous for a mutation in ZFP57. Her partner is homozygous for a wild type allele. They have 4 children.(assume Mendelian ratios and no additional environmental influences)
Which of the following is true?
only sons will have diabetes
all children will have diabetes
50% of children will have diabetes, irregardless of sex
no children will have diabetes
only daughters will have diabetes
no children will have diabetes
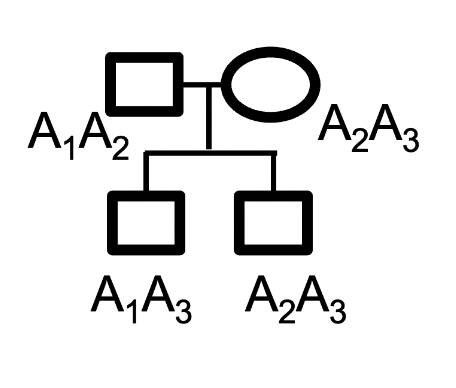
A is a maternally imprinted gene. There are 3 known alleles for this gene, A1, A2 and A3. Consider this family pedigree. Which alleles will be expressed in the offspring?
In II-1, A1 will be expressed and in II-2, A2 will be expressed.
In II-1, A3 will be expressed and in II-2, A2 will be expressed.
It is not possible to determine, based on the information provided.
In II-1, A1 will be expressed and in II-2, A3 will be expressed.
In II-1, A3 will be expressed and in II-2, A3 will be expressed.
In II-1, A1 will be expressed and in II-2, A2 will be expressed.
Imprinting refers to the phenomenon where only one copy of a gene in an individual is expressed (either the maternally or paternally inherited copy), while the other copy is suppressed. A gene that undergoes maternal imprinting will be _______ in the maternally inherited chromosome.
expressed (turned on)
suppressed (turned off)
suppressed (turned off)
A gene that undergoes maternal imprinting will be _____ in the paternally inherited chromosome.
suppressed (turned off)
expressed (turned on)
expressed (turned on)
Imprinting patterns are established during gametogenesis. (True/False)
True
Female offspring will receive different imprinting patterns than male offspring. (True/False)
False
An individual’s gametes all receive the same imprinting patterns (True/False)
True
Imprinted genes predominantly reside on sex chromosomes (True/False)
False
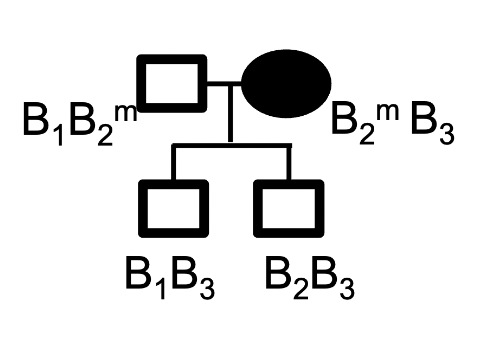
B is a maternally imprinted gene. There are 3 known alleles for this gene, B1, B2 and B3.
Consider this family pedigree that shows both the genotype and disease state of each individual. Carrier status is not indicated. The methylation state is shown (m) for Gen I only.
Which is most likely the disease causing allele?
B1
B2
B3
cannot be determined with the information provided.
B3
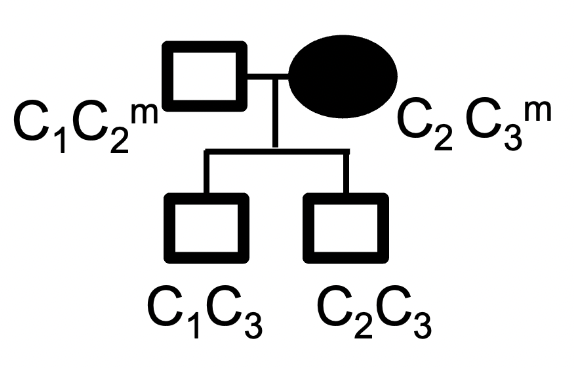
There are 3 known alleles for the gene C (C1, C2 and C3).
Consider this family pedigree that shows both the genotype and phenotype of each individual. Methylation state is shown for Gen I only. Note that carrier status is not indicated.
What type of imprinting is this pedigree consistent with?
autosomal recessive
it is not possible to determine with the information provided
autosomal dominant
maternal imprinting
paternal imprinting
paternal imprinting