EH2 W1 - Changing Patterns of Health and Disease
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is demography?
The scientific study of human populations. Their size, composition, distribution across place, process through which populations change
What are the 2 ways to enter a population?
Birth and in-migration
What are the 2 ways to exit a population?
Death and out-migration
What is crude birth rate?
the number of live births per 1000 population
Crude birth rates limitations?
Denominator includes all Australians.
Cannot compare with other countries due to lack of age standardisation.
What is total fertility rate?
The average number of childrene a hypothetical women could expect to bear during her lifetime if she experiened current age-specific fertility rates at each age of her reproductive life.
Trend in Australias total fertility rate?
Declining and now below the replacement level of 2.1 babies per woman
What is infant mortality rate?
Number of infants dying before reaching one year of age per 1000 live births in a given year.
Difference in infant mortality rate in australian and ATSI populations?
ATSI much higher than in other populations
What is child mortality rate?
The number of child deaths aged 1-4 years per 1000 live births
Difference in child mortality rate in australian and ATSI populations?
Much higher in first nations people than in non-indigenous children
What proportion of under 5 child deaths occur in infancy?
85%
What are the infant and child mortality rates good indicators of?
a country's level of health or development
What do infant and child mortality rates reflect?
economic development, level of illness, social wellbeing and living conditions of that country
2 main influences on infant and child mortality?
Socioeconomic disadvantage and health care factors
3 leading cuasing of infant mortality?
Perinatal conditions, Congenital abnormalities, SIDs related
What ais the leading cause of death for children aged 1-4?
Injury and poisoning including accidents and drownings
What is Crude Death Rate?
Total number of deaths per 1000 population
What are age standardised mortality rates?
total number of death per 1000 population age adjusted/standardised to a standard population
What are the top 5 causes of death in Australia in 2022?
1. Ischaemic heart disease
2. Dementia inc. alzheimers
3. COVID-19
4. Cerebrovascular disease
5. Malignant neoplasm of trachea, bronchus and lung
What are the 3 main processes related to demography?
fertility, mortality and migration
What is a population pyramid?
A graph showing the age and sex distribution of a population
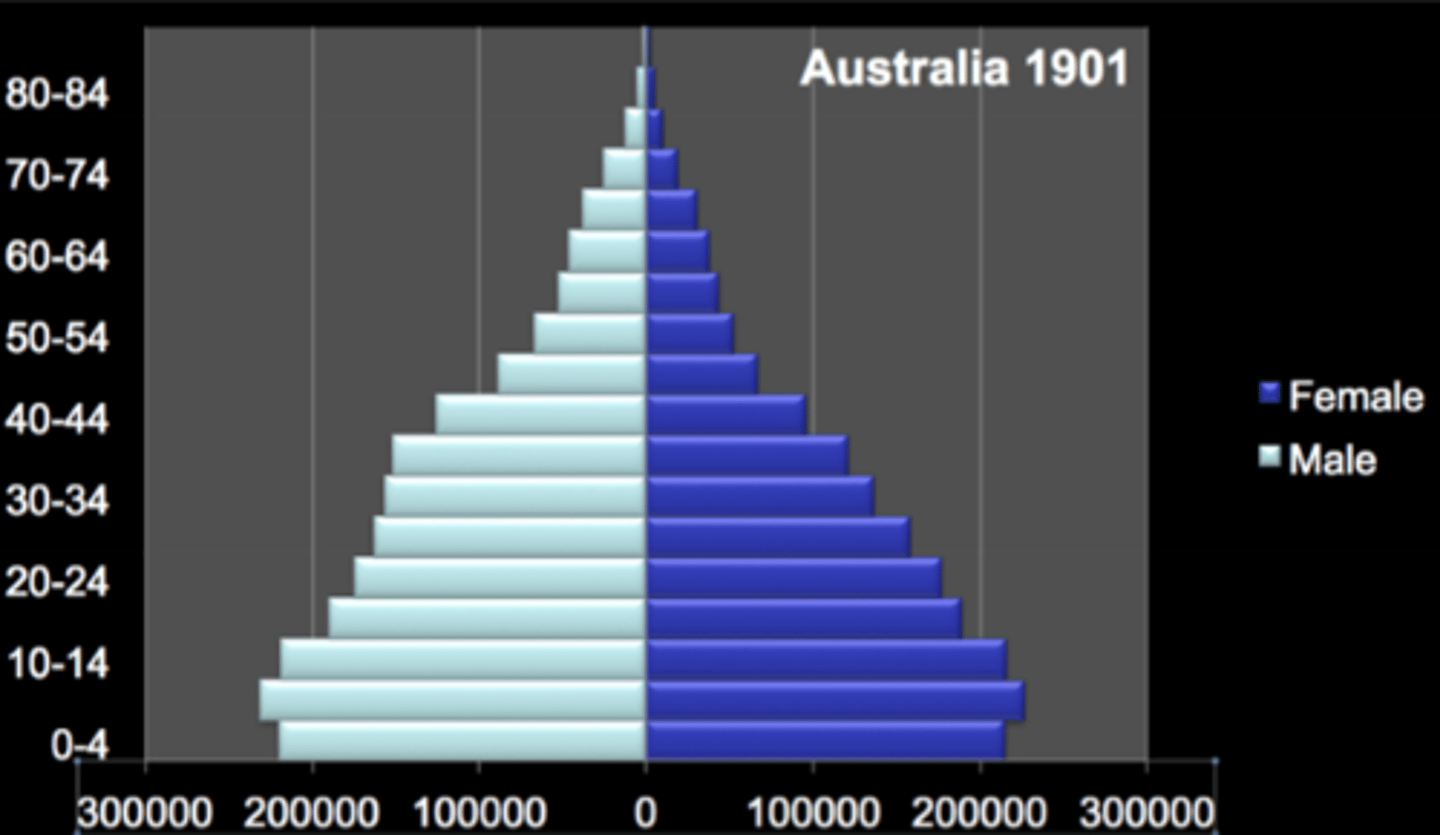
Expanding population pyramid?
Large number of young people, with population decreasing as age increases.
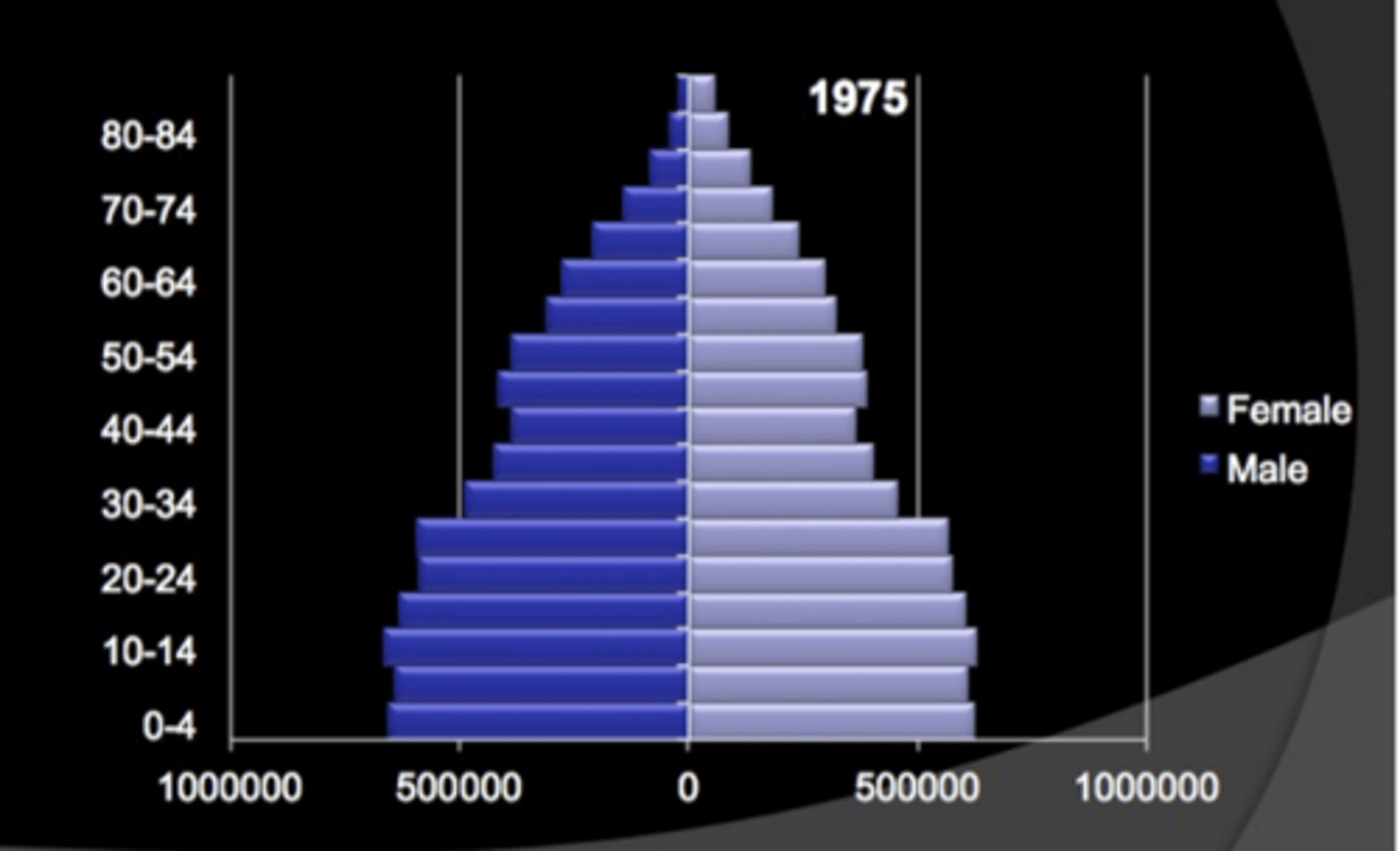
Stable population pyramid?
Pyramid stays relatively stable only narrowing at the top due to death at an old age
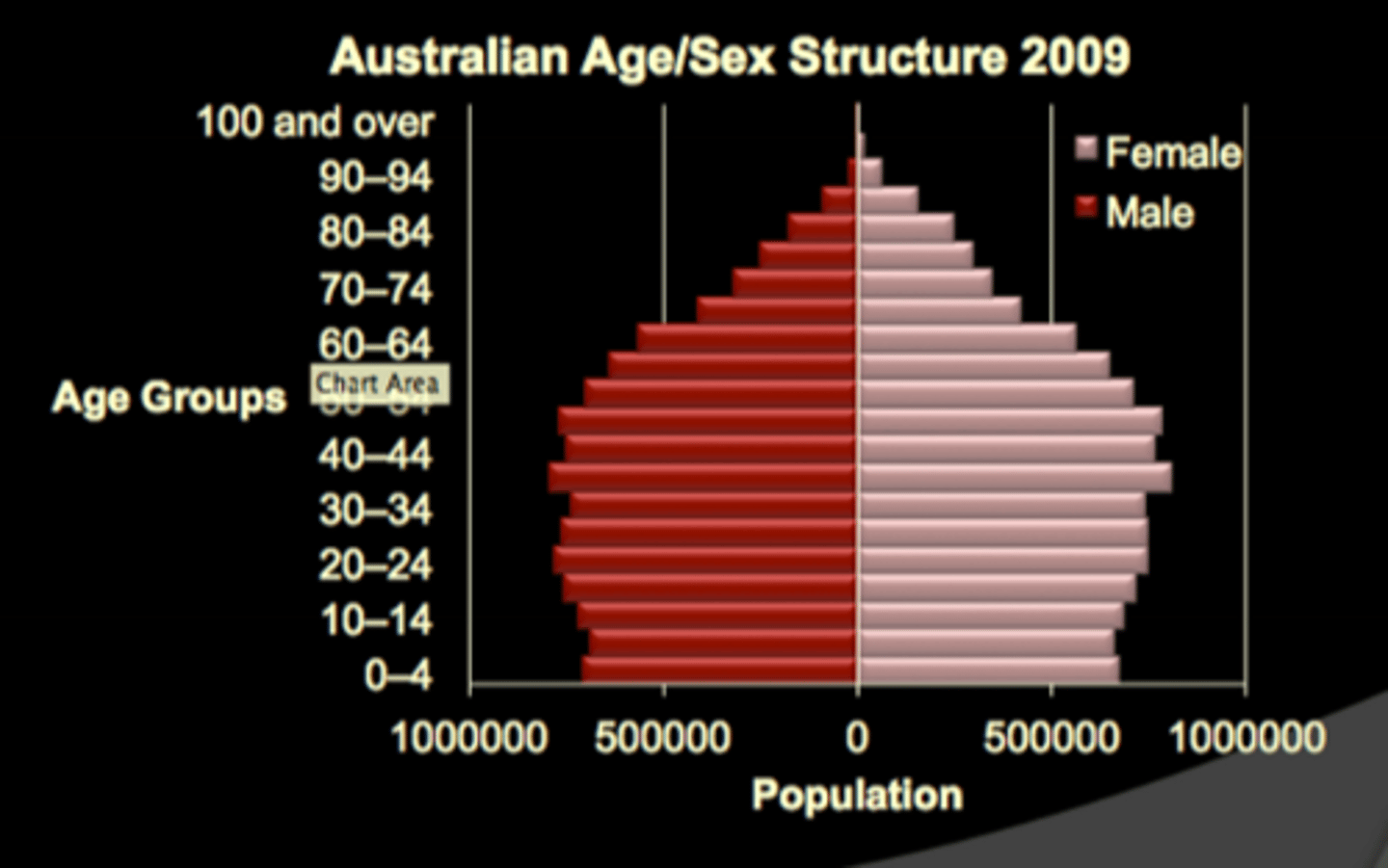
Contracting population pyramid?
Lower fertility rate, lots of 30-50 year olds and contracting towards the top due to death at old age
What is epidemiological transition?
The shift in the pattern of diseases in which degenerative and man-made diseases displace pandemics of infection as the primary causes of morbidity and mortality
How did epidemiological transition come about?
1. rise of living standards
2. improvements in hygiene
3. introduction of antibiotics
4. mass immunisation
5. progress of medical knowledge and skills
What are the 5 stages of epidemiological transition?
1. Age of Pestilence and Famine
2. Age of Receding Pandemics
3. Age of Degenerative and Man-made Diseases
4. Age of Delayed Degenerative Diseases
5. Age of Emergent and Re-emergent infections
What occurs during the age of pestilence and famine?
Reflected old world epidemics of infection and famine
What occurs during the age of receding pandemics?
Epidemics less frequent and reduction in causes of death due to infection
What occurs during the age of degenerative man-made diseases?
preponderance of lifestyle diseases and degernerative diseases
What occurs during the age of delayed degenerative diseases?
People live longer from modern health care. This increases the duration of degenerative diseases. Deaths from degenerative disease is shifted progressively towards older ages.
What occurs during the age of emergent and re-emergent infections?
resurgence of both old and new infectious diseases.
Limitations of the epidemiological transition model?
1. Had to add stage 4/5 to account for emergent and re-emergent infections.
2. Doesnt reflect regional differences in countries with co-existence of high rates of infectious and chronic disease.
3. Relationship between infections and chronic disease
4. Degenerative diseases have always been present but were less apparent in the past
What is demographic transition?
How birth rate and death rate influence population growth over time. Societies experiencing modernisation progress from a pre-modern regime of high fertility and high mortality to post-modern where both are low?
What are the 4 stages of the demographic transition model?
1. Pre-industrial stage/pre-modern
2. Urbanising/ industrialising
3. Mature industrial
4. Post industrial stage
What occurs during the pre-industrial stage of demographic transition?
high death rate, high birth rate, slow population growth
What occurs during the urbanising stage of demographic transition?
birth rates remain high, death rates fall sharply, population rises rapidly
What occurs during the mature industrial stage of demographic transition?
birth rate falls sharply, death rate stabalises, population still increasing
What occurs during the post industrial stage of demographic transition?
both birth and death rates level off at low levels, population stabalises
General demographic patterns in less economically developed countries
high fertility, high infant mortality, high death rates, high out-migration to more developed countries
General demographic patterns in more economically developed countries
low fertility, low infant mortality, low death rates, high in-migration from less developed countries