Learning & Memory
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made by @agreyr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Learning
The process of aquiring information
Memory
The ability to store and retrieve the information learned
Patient H.M. (Henry Gustav Molaison)
Bicycle accident when young led to the development of severe epilepsy
At 27, surgeon performed bilateral medial temporal lobectomy in an attempt to stop his seizures
Bilateral medial temporal lobectomy
Removal of the medial portions of both temporal lobe, including most of the hippocampus, amygdala, and adjacent cortex
Amnesia
Severe impairment of memory
Retrograde amnesia
Loss of memories formed before a brain injury
Anterograde
Loss of memory for things occurring after a brain injury; inability to make new memories
Declarative memory
Explicit; things you know and can tell others; facts and information; semantic vs episodic memory
Semantic vs episodic memory
Semantic memory revolves around facts; episodic memory revolves around events
Non-declarative memory
Implicit; procedural memory; demonstrated by improved performance without conscious recall or recognition
Skill learning (sensorimotor), priming (words or pictures), and associative learning
Digit-span task
A test used to measure short-term memory where patients are asked to recall an increasingly longer series of numbers
Continued memory tests
Mirror drawing task, incomplete pictures task
Skill learning (sensorimotor)
Process of learning how to perform a challenging task by simply doing it over and over again; does not require the medial temporal lobe, but requires basal ganglia, cerebellum, and motor cortex
Priming (words or pictures)
A change in the way you perceive a stimulus, especially because you’ve seen it or something similar before; associated with reduced activation in the occipitotemporal cortex (word form) or left frontal cortex (word meaning)
Associative learning
Learning relationships between events (classical and instrumental conditioning)
Classical conditioning
In its simplest form, it requires cerebellum, not hippocampus
Instrumental conditioning
Learn that a certain action yields a certain consequence; no consistent brain region identified
Press the lever, food pellet; poke the nose hole, get foot shock
Global amnesia
Amnesia for information in all sensory modalities
Scientific contributions from H.M. and others
Memory functions are NOT diffusely and equivalently distributed throughout the brain
There are different modes of storage for short-term and long-term memories; demonstrated a role for medial temporal lobe in memory consolidation
Different mechanisms exist for procedural and non-procedural recall
Animal models of memory
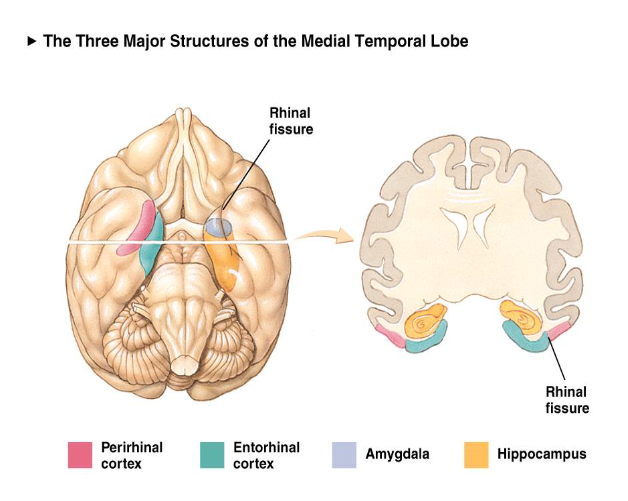
Hippocampus, amygdala, and rhinal cortex are all damaged by bilateral medial temporal lobectomy; necessitated the creation of animal models to study brain-damage-induced amnesia
Object recognition memory tests/studies
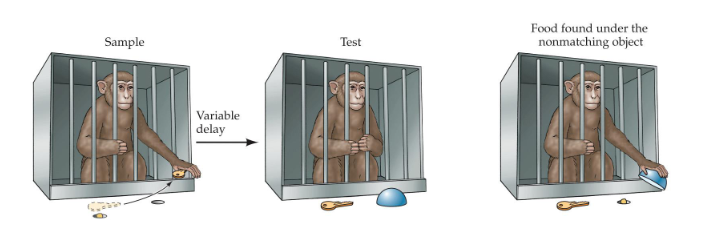
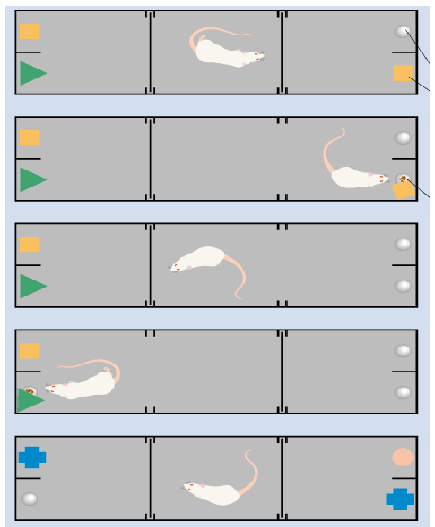
Delayed nonmatching-to-sample test, Mumby box
Delayed nonmatching-to-sample test (monkeys)
Loss of the hippocampus, amygdala, and associated cortex in monkeys leads to impairments in object recognition
Mumby box (rats)
Only loss of the rhinal cortex in rats showed deficits in object recognition
Spatial recognition memory
Bilateral lesions of the hippocampus disrupt performance in spacial recognition tasks; many hippocampal neurons are place cells
Birds that store food have large hippocampi!
Spatial recognition tasks
Radial arm maze, use of cognitive maps
Place cells
Neurons that respond when a subject is in a specific location in the test environment
Memory systems summary
Short-term memory (working memory) —> prefrontal cortex, different regions for different attributes
Long-term memory —> declarative (explicit) vs nondeclarative (implicit)

Components of memory
Sensory buffers/input: fleeting memories/glimpses of a scene that vanish quickly
Short-term memory: short period of time during which you are actively attending to the information; waking memory refers to the ability to actively manipulate information while in STM
Long-term memory: Long lasting memories that persist even when you no longer attend to the information
Memory processes
Encoding, consolidation, retrieval, reconsolidation
Encoding
Getting raw sensory information into STM
Consolidation
Moving info from volatile STM to more durable LTM
Retrieval
Calling stored information back into working memory (STM) for use
H.M. showed that the medial temporal lobe…
…is NOT required to encode sensory info or retrieve the info from STM
… is CRUCIAL for consolidating declarative information from STM to LTM