Principles and Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Therapy
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Antimicrobial Therapy
Use of drugs to treat infections effectively.
Selective Toxicity
Drug harms infective agent without harming host cells.
Ideal Antimicrobial Drug
Easily administered, effective, and safe for host.
Antibiotic
Microbial substance inhibiting another microbe's growth.
Pathogen Identification
Determining the specific infectious agent present.
Drug Susceptibility
Pathogen's sensitivity to various antimicrobial drugs.
Kirby-Bauer Technique
Method to test antibiotic effectiveness on bacteria.
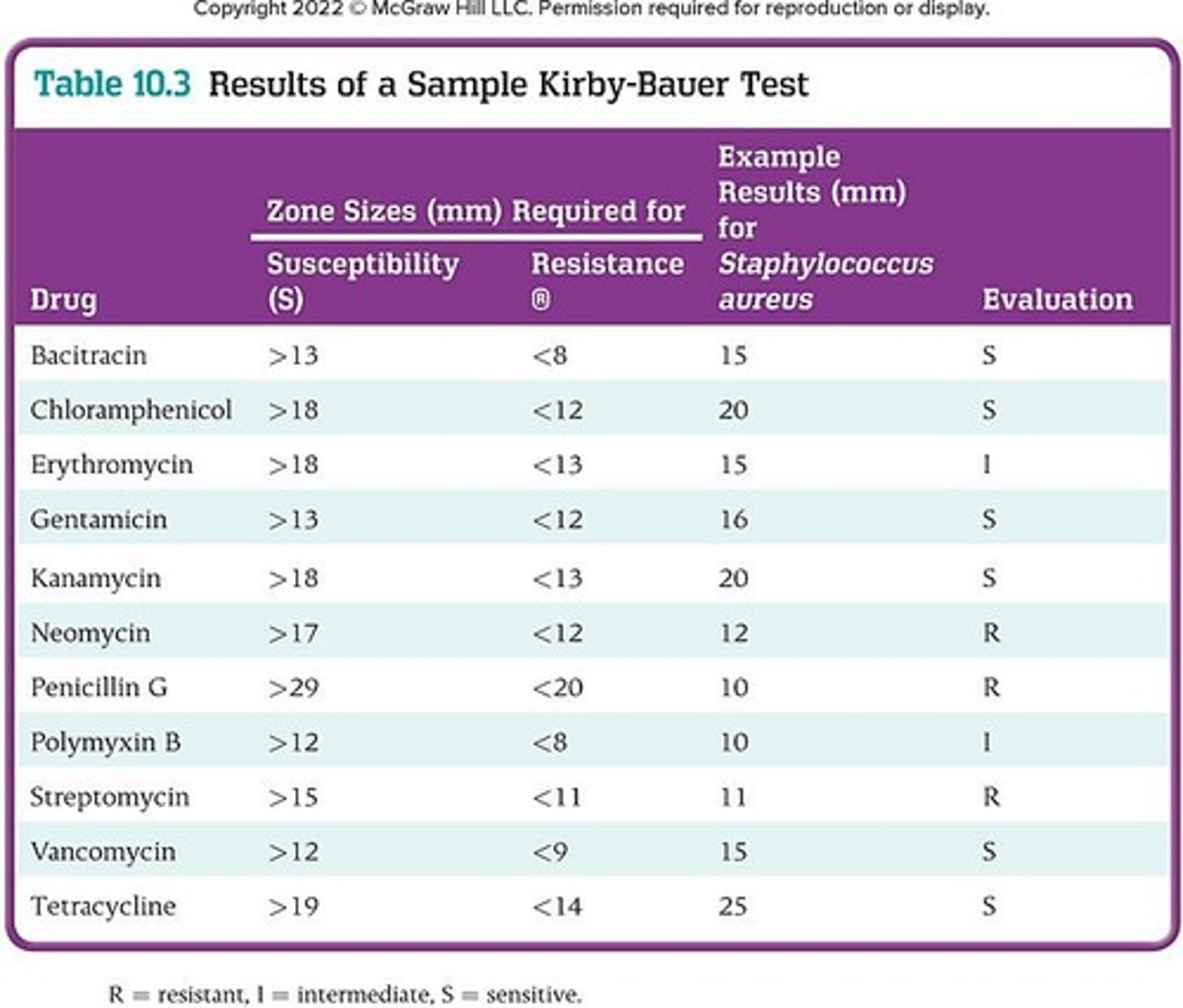
Zone of Inhibition
Area around antibiotic disc where bacteria cannot grow.
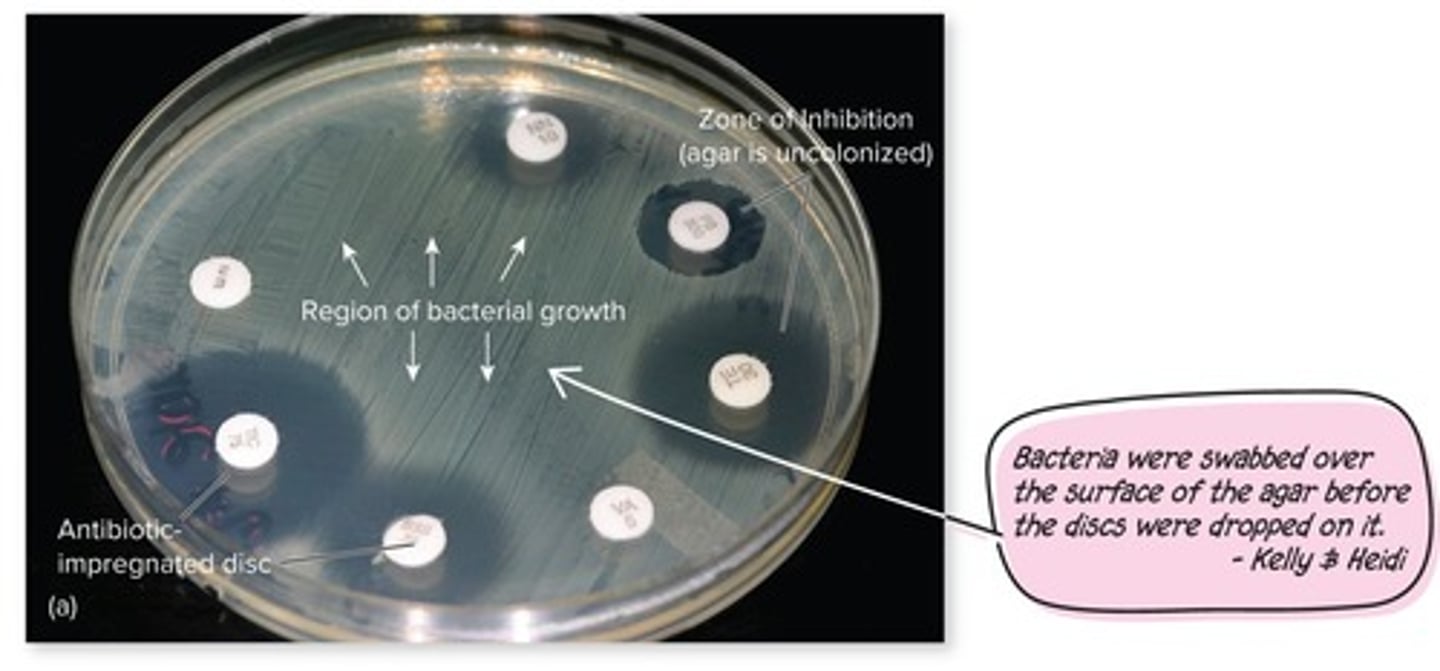
E Test
Determines minimal inhibitory concentration using plastic strip.
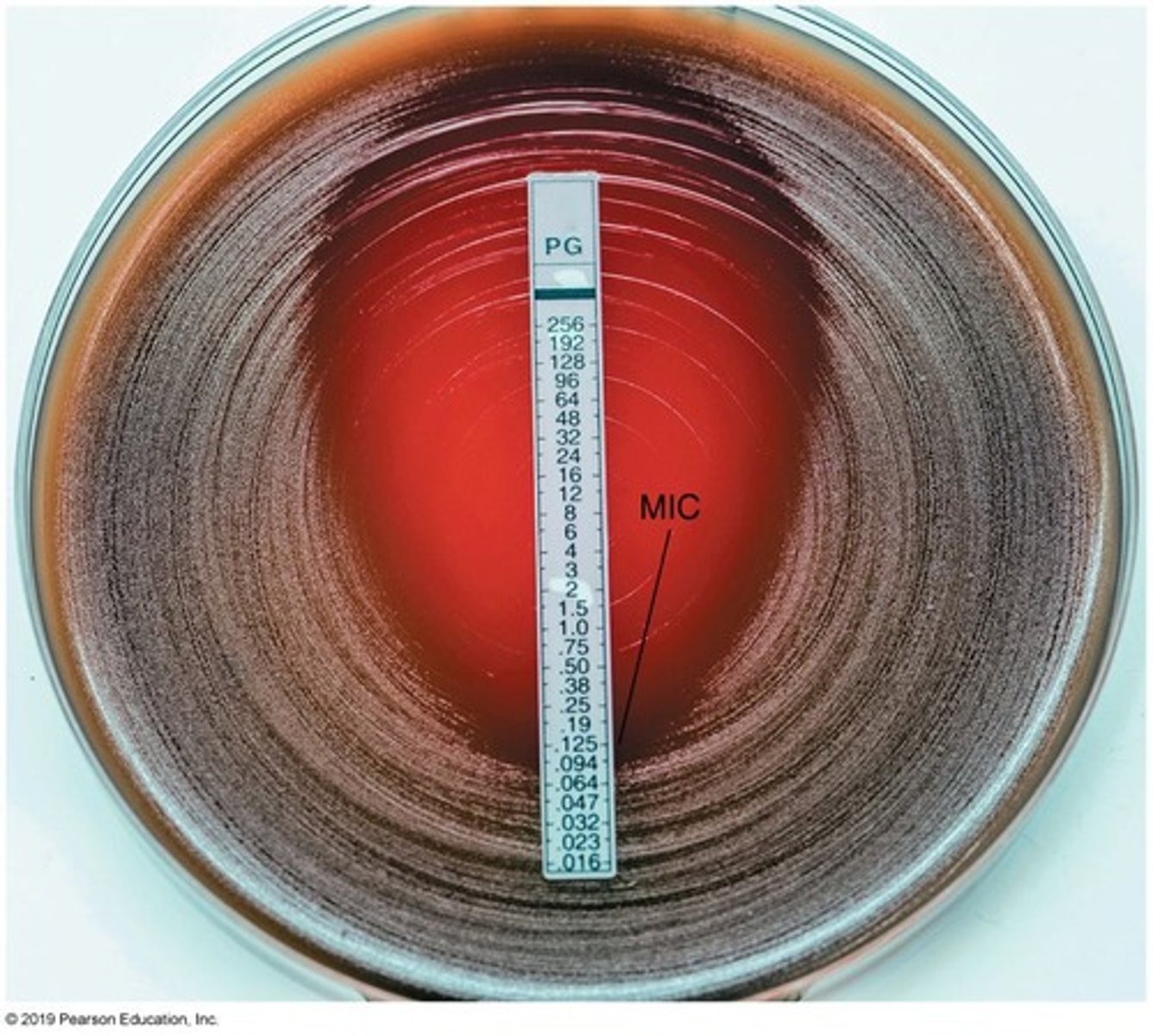
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
Smallest drug concentration inhibiting visible microbial growth.
Tube Dilution Test
Serial dilution method to determine MIC in broth.
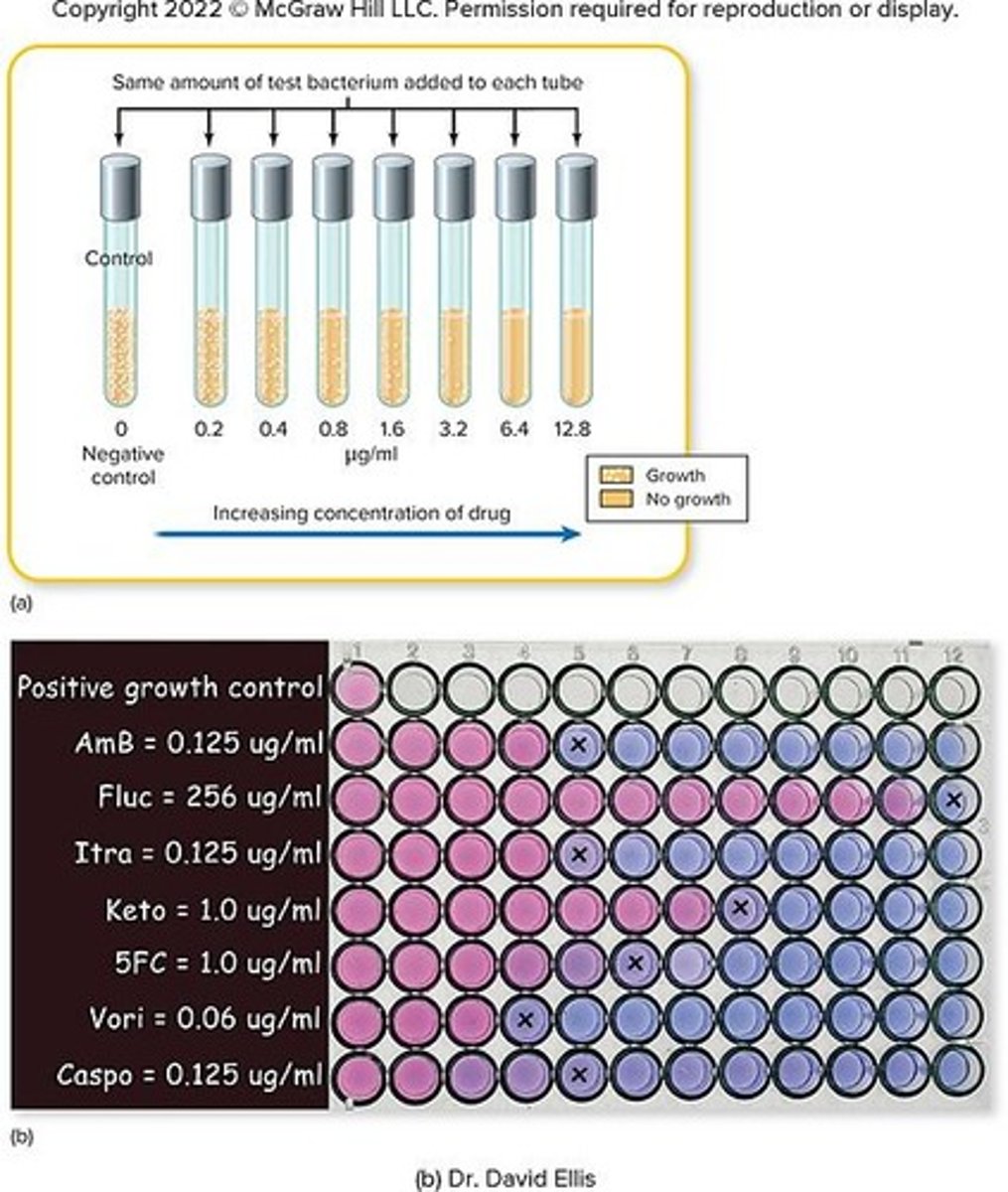
In Vitro Activity
Drug effectiveness tested outside a living organism.
In Vivo Effect
Drug effectiveness tested within a living organism.
Polymicrobial Infection
Infection caused by multiple pathogens simultaneously.
Therapeutic Index
Ratio of toxic dose to therapeutic dose of drug.
Preexisting Conditions
Patient's health issues affecting drug treatment.
Synergistic Effects
Combined drug effects enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibition
Targeting bacterial cell walls to kill bacteria.
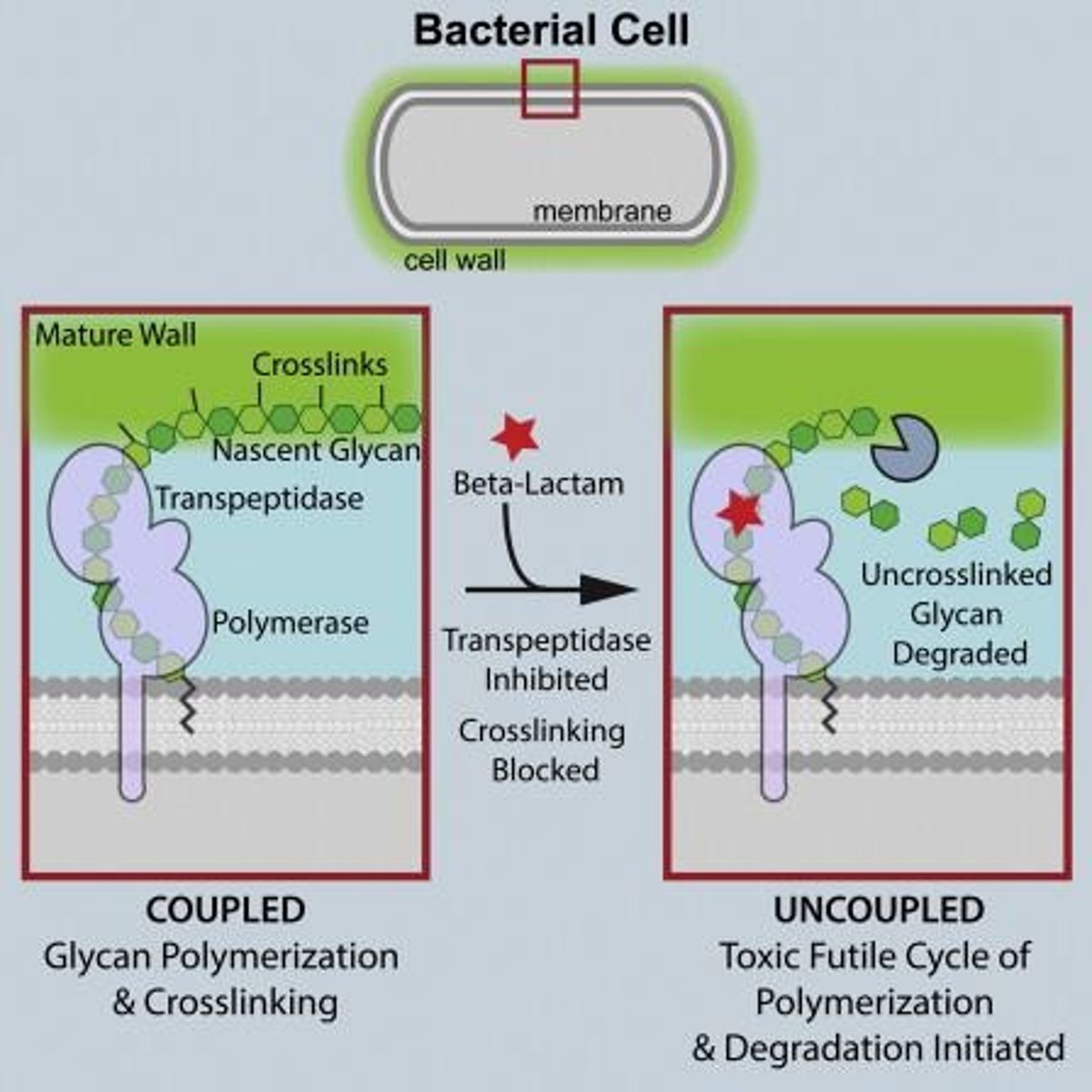
Peptidoglycan
Unique bacterial cell wall component absent in humans.
Antibacterial Drugs
Target differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics
Effective against a wide range of bacteria.
Narrow Spectrum Antibiotics
Target a limited range of microbial types.
Superinfection
Overgrowth of resistant pathogens after antibiotic use.
Normal Microbiota
Beneficial microbes normally present in the host.
Antimicrobial Sensitivity Testing
Assessing pathogen response to various antimicrobial agents.
Direct Examination
Rapid detection of pathogens in body fluids.
Incubation
Allowing microbial growth under controlled conditions.
Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Use of drugs to eliminate infectious agents.
Bactericidal
Kill microbes directly, leading to their death.
Bacteriostatic
Prevent microbial growth; relies on immune system.
Chemotherapy Goals
Disrupt organism's structure or function for survival.
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibition
Targeting bacterial cell wall construction mechanisms.
Ribosome Inhibition
Interfering with protein synthesis in bacteria.
Nucleic Acid Inhibition
Affecting RNA and DNA structure and function.
Cytoplasmic Membrane Interference
Disrupting membrane structure or function in microbes.
Folic Acid Synthesis Inhibition
Blocking essential metabolic pathways in bacteria.
Selective Toxicity
Targeting bacterial cells without harming host cells.
Penicillins
Group of antibiotics with a β-lactam ring.
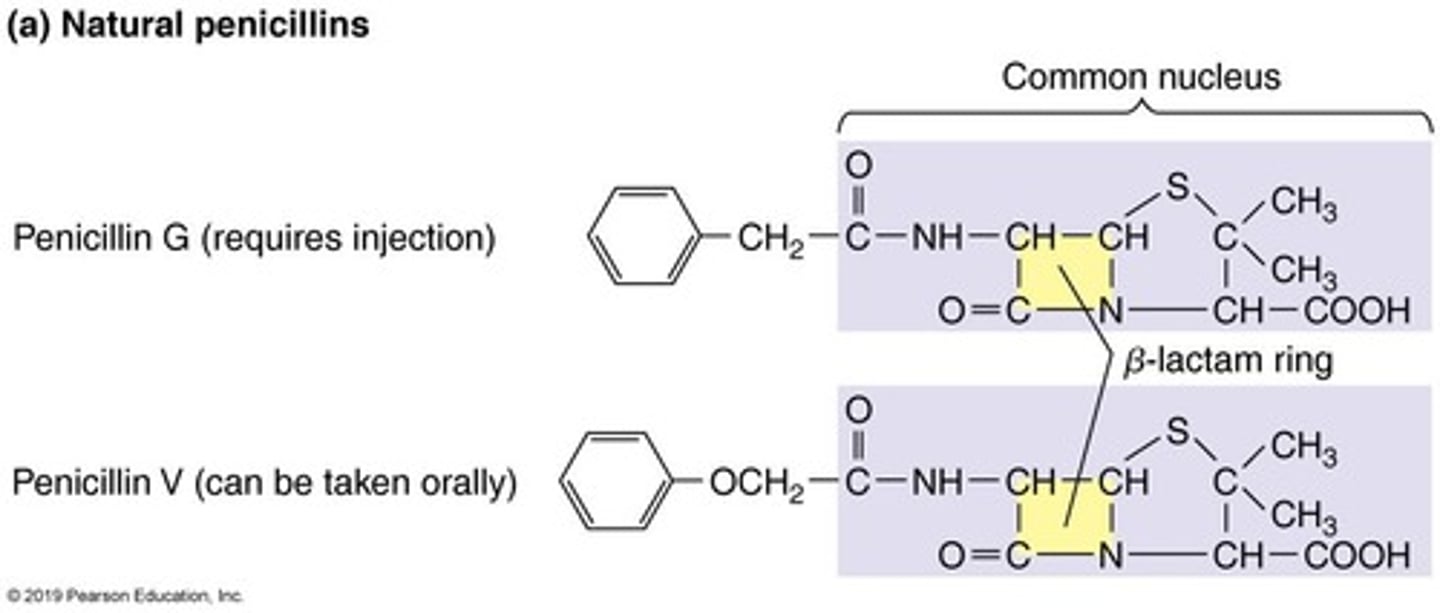
β-lactam Ring
Core structure found in penicillins and carbapenems.
Natural Penicillins
Extracted from Penicillium fungi; susceptible to penicillinases.
Semisynthetic Penicillins
Modified penicillins resistant to penicillinases.
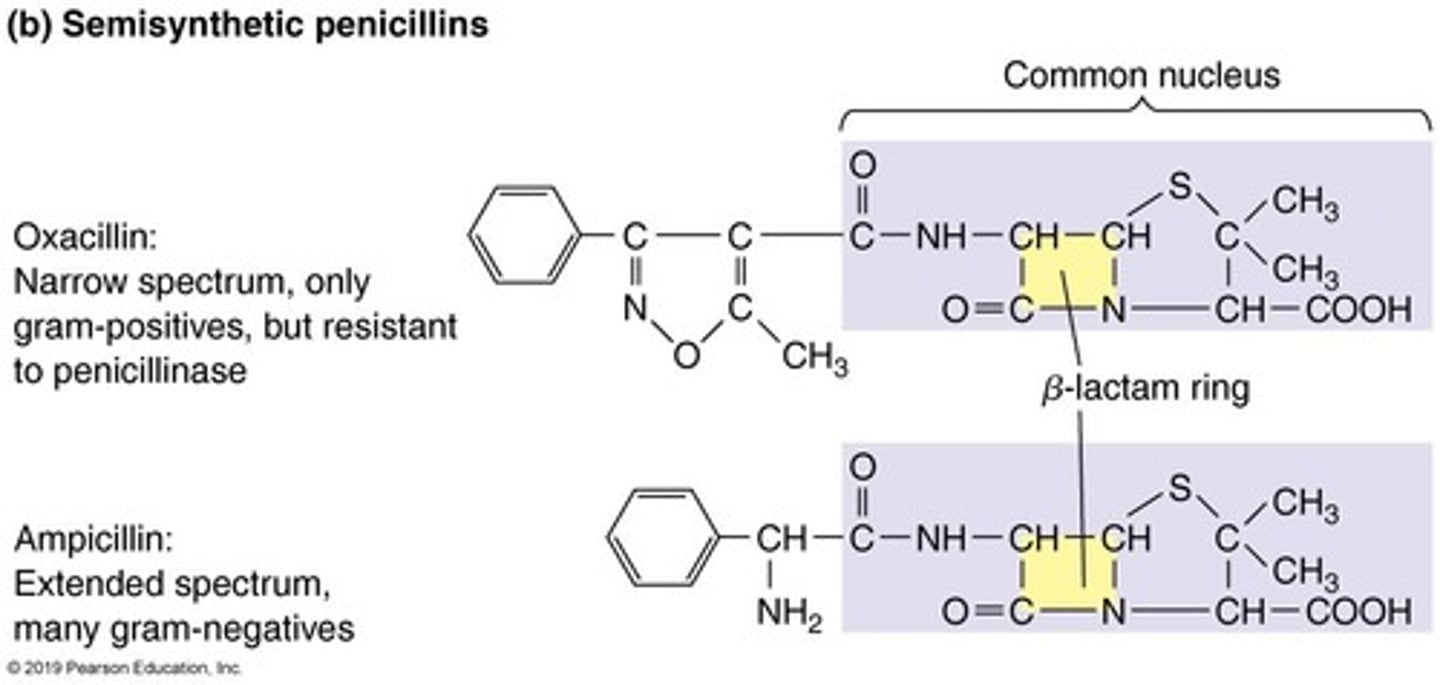
Ampicillin
A semisynthetic penicillin with broad-spectrum activity.
Amoxicillin
A semisynthetic penicillin, similar to ampicillin.
Carbapenems
Broad-spectrum antibiotics with β-lactam ring structure.
Cephalosporins
Antibiotics similar to penicillins; widely used.
Polypeptide Antibiotics
Small proteins with antimicrobial properties from bacteria.
Bacitracin
Topical antibiotic effective against gram-positive bacteria.
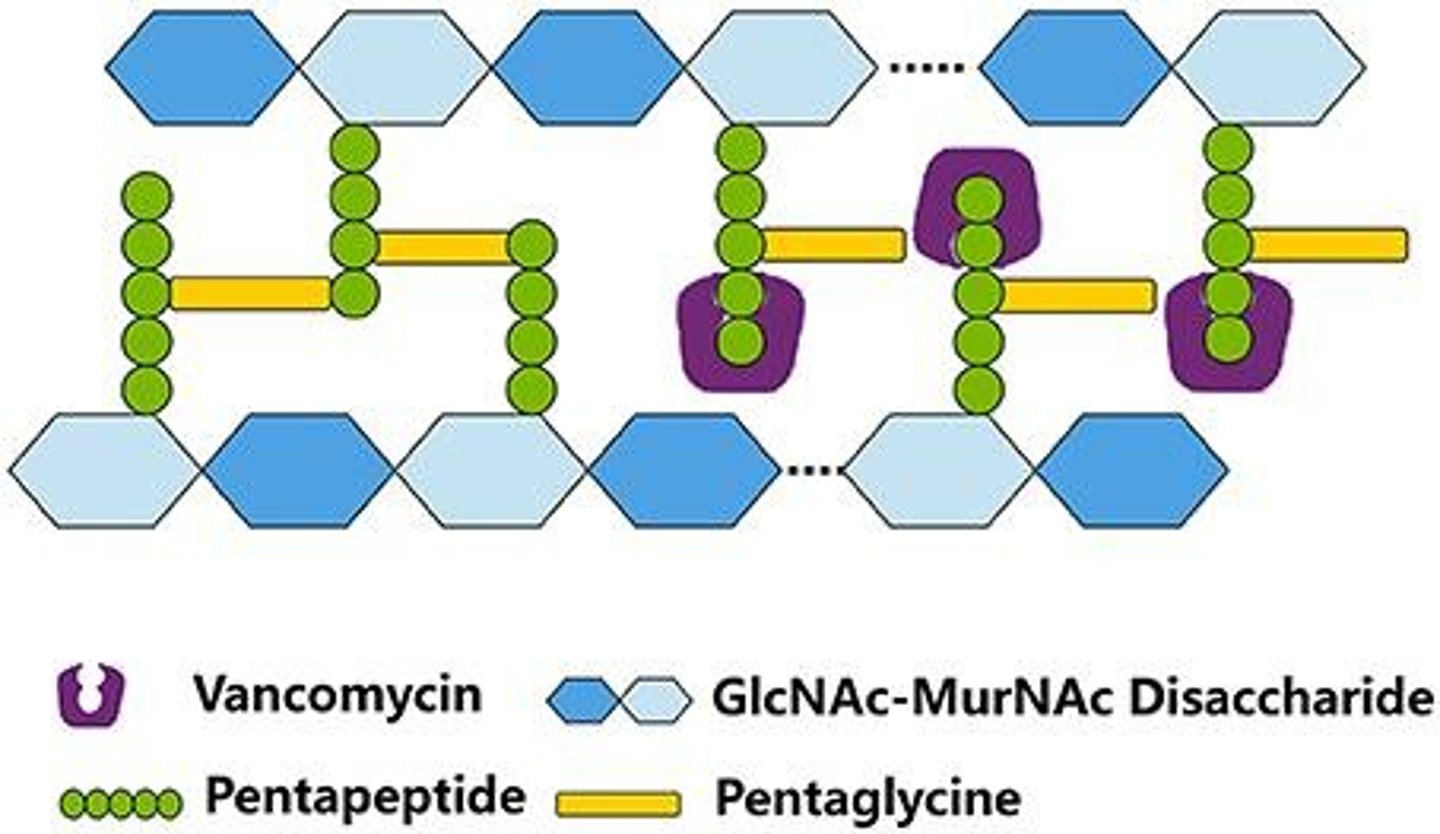
Vancomycin
Last-resort antibiotic against MRSA, prevents peptidoglycan incorporation.
MRSA
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Peptidoglycan
Structural component of bacterial cell walls.
Penicillinases
Enzymes that inactivate penicillins and β-lactam antibiotics.
Gram-positive Bacteria
Bacteria with thick peptidoglycan cell walls.
Antimicrobial Spectrum
Range of activity against different microbial types.
Antibacterial Antibiotics
Drugs that inhibit bacterial growth or replication.
Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis
Antibiotics that disrupt bacterial cell wall formation.
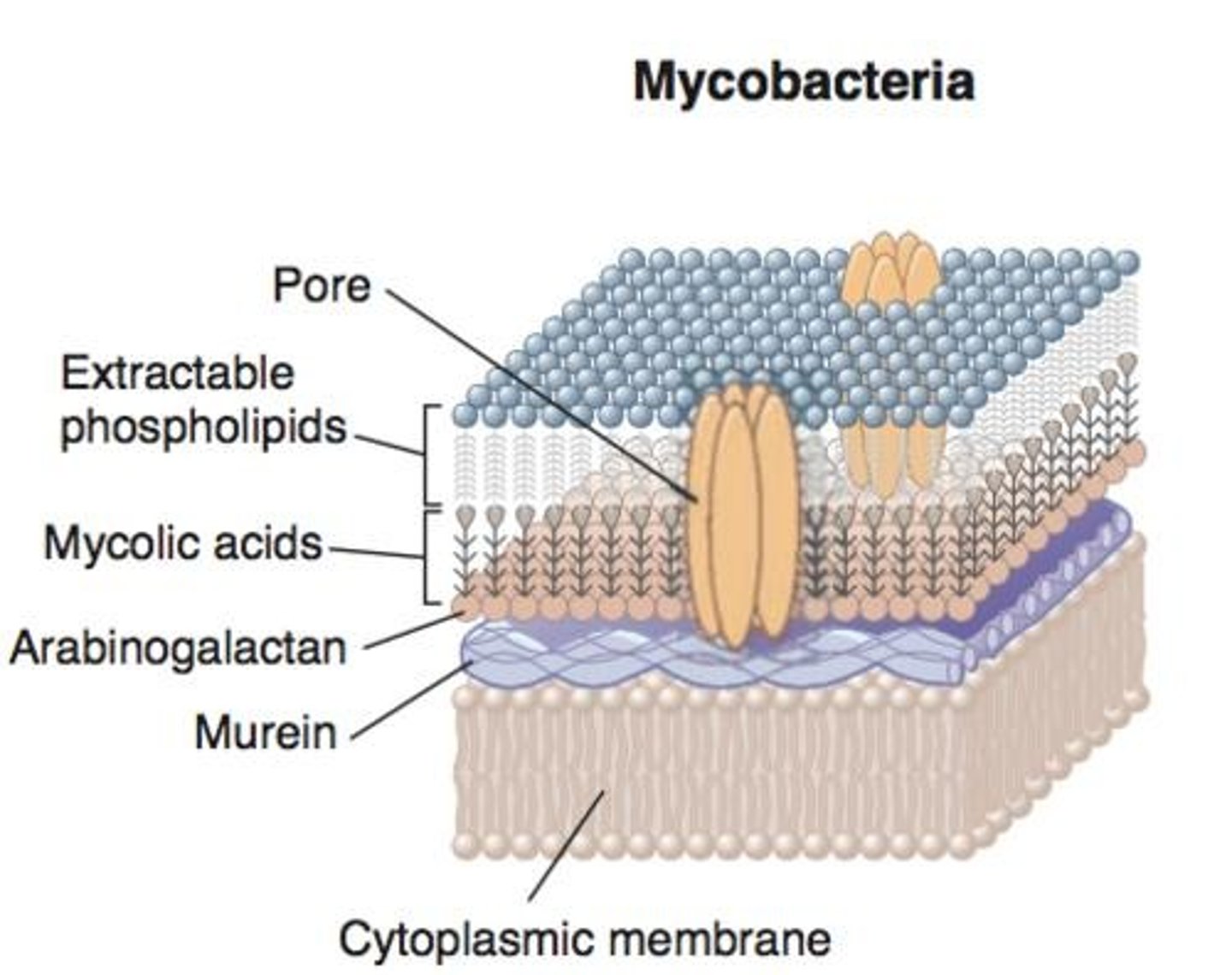
Antimycobacterial Antibiotics
Target mycolic acid in mycobacterial cell walls.
Isoniazid
Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis in bacteria.
Selective Toxicity
Targets bacterial structures without harming host cells.
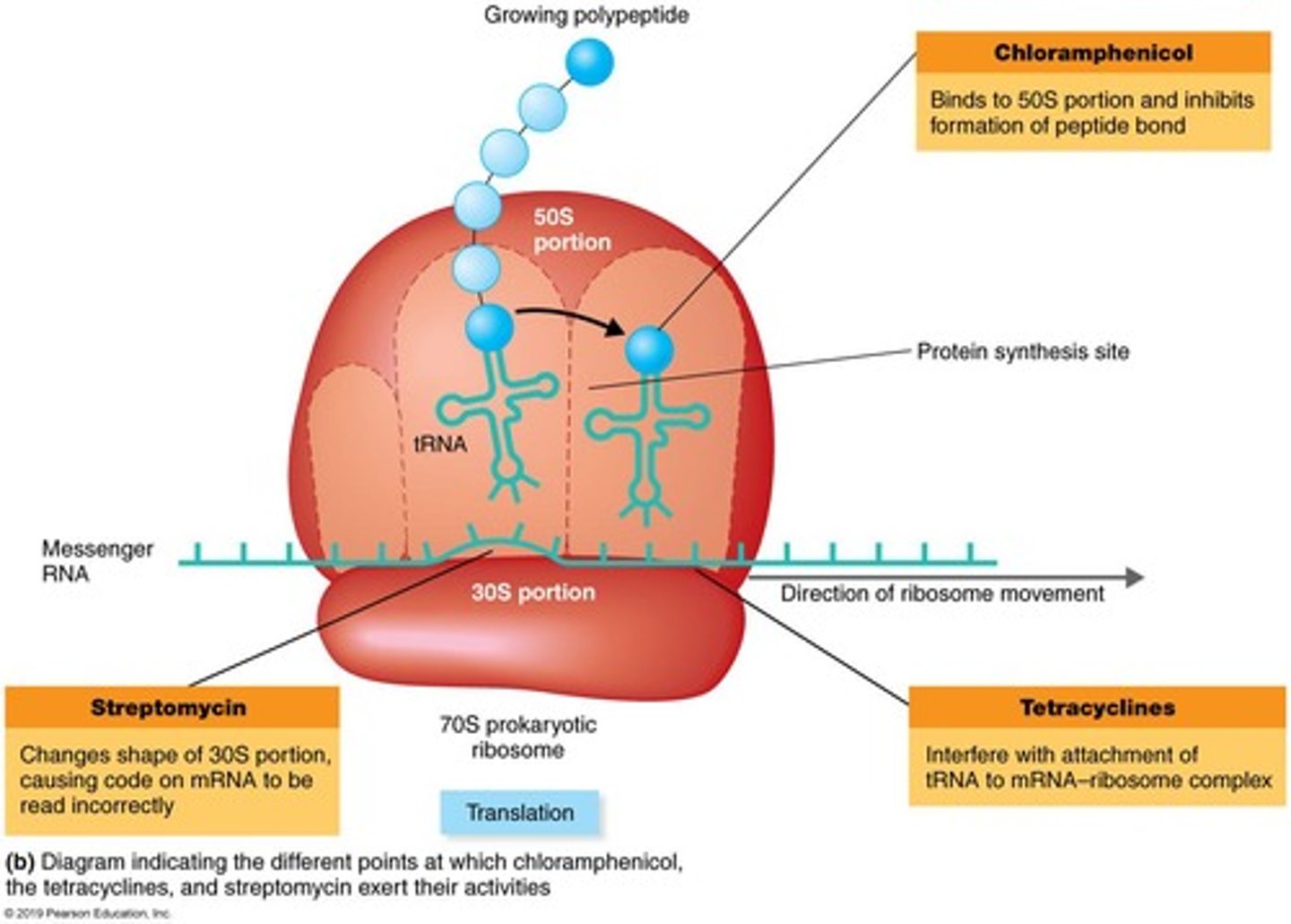
70S Ribosomes
Bacterial ribosomes targeted by certain antibiotics.
Adverse Effects
Unintended consequences of antibiotic treatment.
Aminoglycosides
Antibiotics that alter 30S ribosomal subunit shape.
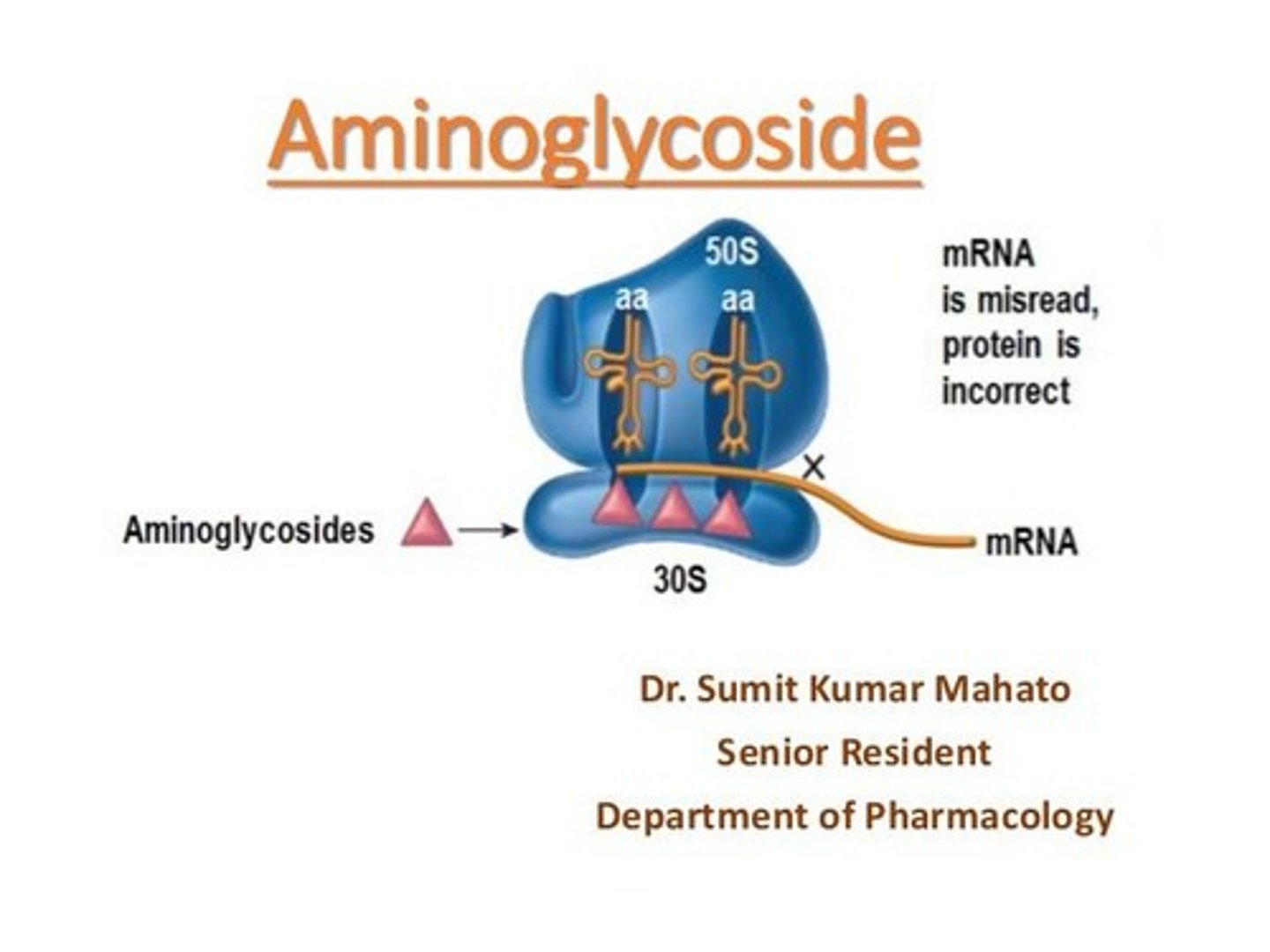
Streptomycin
An aminoglycoside antibiotic causing mRNA misreading.
Gentamicin
An aminoglycoside antibiotic used against gram-negative bacteria.
Tetracyclines
Broad-spectrum antibiotics interfering with tRNA attachment.
Polymyxin Antibiotics
Effective against gram-negative bacteria by damaging membranes.
Lipopeptides
Lipids linked to peptides with antibacterial properties.
Daptomycin
Targets gram-positive bacteria's cell membranes.
Polymyxin B
A polymyxin antibiotic effective against gram-negative bacteria.
Polyenes
Antifungal agents disrupting fungal membrane sterols.
Nystatin
A polyene antifungal used for skin infections.
Amphotericin B
Broad-spectrum antifungal targeting membrane sterols.
Quinolones
Inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase.
Rifampin
Inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase and mRNA synthesis.
Sulfonamides
Inhibit folic acid synthesis in bacteria.
Trimethoprim
Combined with sulfamethoxazole for enhanced antibacterial effect.
Antimetabolites
Compete with substrates for microbial enzymes.
Antiviral Drugs
Target various stages of viral replication.
Entry and Fusion Inhibitors
Block virus entry into host cells.
Nucleoside Analogs
Resemble nucleotides, terminating DNA/RNA synthesis.
Persister Cells
Survive antibiotic exposure due to genetic traits.
Superbugs
Bacteria resistant to multiple antibiotics.
B-lactamase
Enzyme that inactivates beta-lactam antibiotics.
Mechanisms of Resistance
Strategies bacteria use to evade antibiotic effects.
Antibiotic Misuse
Improper use leading to antibiotic resistance.