Unit 3: Chp 3 - Animalia
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/28
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
What are *animals?*
* most complex organisms
* multi-cellular eukaryotes
* multi-cellular eukaryotes
2
New cards
Why are *animals important?*
* help us understand humans better
* provide resources and comfort (pets)
* provide resources and comfort (pets)
3
New cards
What is believed to be the *common ancestor* *for all animals?*
* lived approximately 800 million years ago
* small, flagellated, unicellular organism
* small, flagellated, unicellular organism
4
New cards
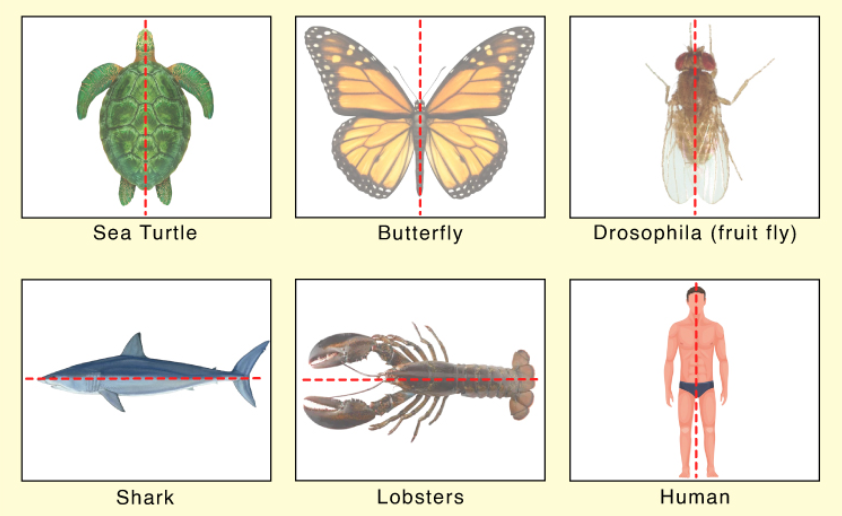
What is *bilateral symmetry?*
It’s the symmetry of animals that splits body parts along the midline with mirror images on either side (usually left and right)
5
New cards
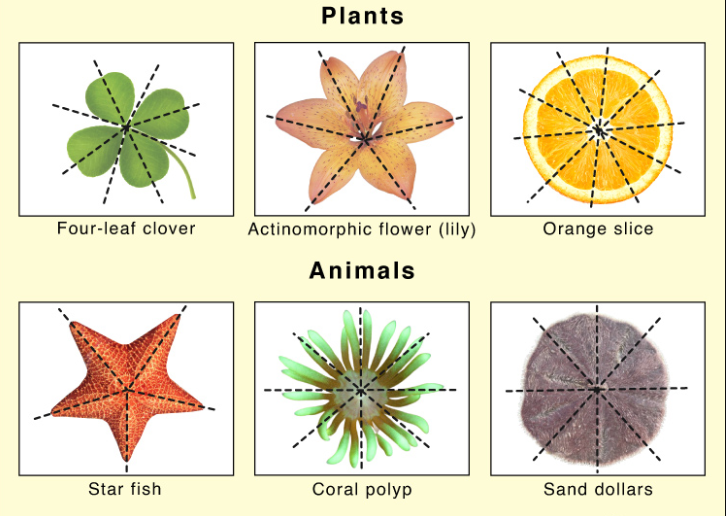
What is *radial symmetry?*
It’s the symmetry of animals that splits body parts **around a central point** with **multiple planes** of symmetry
6
New cards
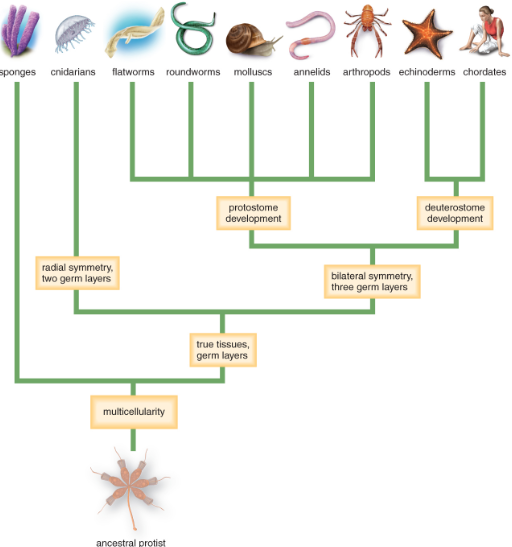
How can animals be *classified*?
\
* **embryonic development:** protostome (mouth first then anus - vertebrate rankings) and deuterostomes (anus then mouth - aquatic creatures)
* **spinal column:** vertebrate (has one) and invertebrate (doesn’t have one)
* **symmetry**: bilateral (left and right) and radial (around central point/axis)
* **embryonic development:** protostome (mouth first then anus - vertebrate rankings) and deuterostomes (anus then mouth - aquatic creatures)
* **spinal column:** vertebrate (has one) and invertebrate (doesn’t have one)
* **symmetry**: bilateral (left and right) and radial (around central point/axis)
7
New cards
What is a *protosome*?
An organism that develops a **mouth first** then the **anus**; every other animal - tiger, dog, rat
8
New cards
What is a *deuterosome?*
An organism that develops an **anus first** then the **mouth**; aquatic creatures - starfish, urchin
9
New cards
What is a *vertebrate*?
It’s an animal *with* a vertebral column/spine
10
New cards
What is an *invertebrate?*
It’s an animal *without* a vertebral column/spine
11
New cards
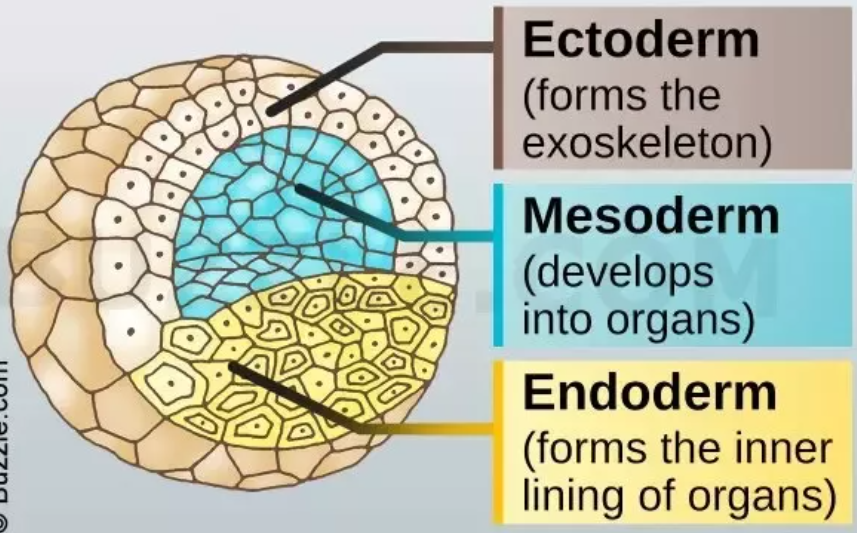
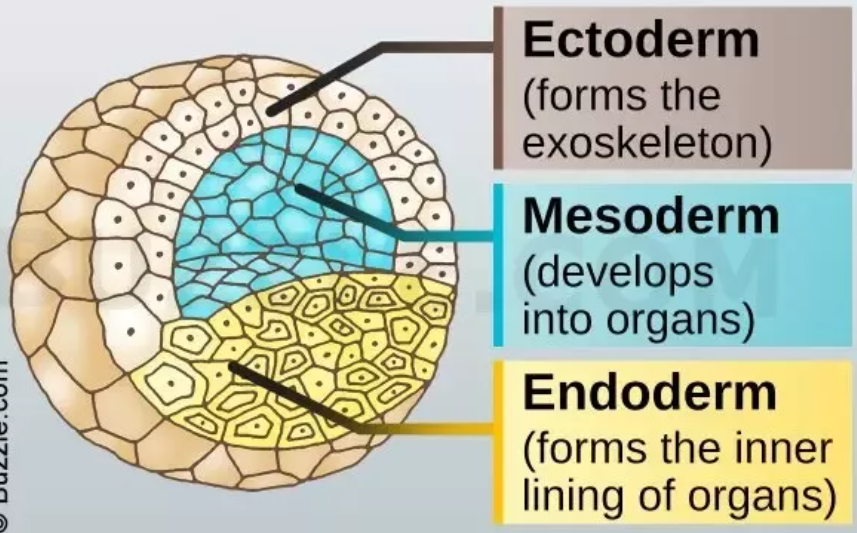
What are *germ layers?*
They’re layers of cells that become specialized tissues: *ectoderm (outer), mesoderm (middle), and endoderm (inner)*
12
New cards
What does the *ectoderm layer* do?
* outer-layer
* gives rise to the skin and nervous system
* some can produce shells, scales, feathers, or hair
* gives rise to the skin and nervous system
* some can produce shells, scales, feathers, or hair
13
New cards
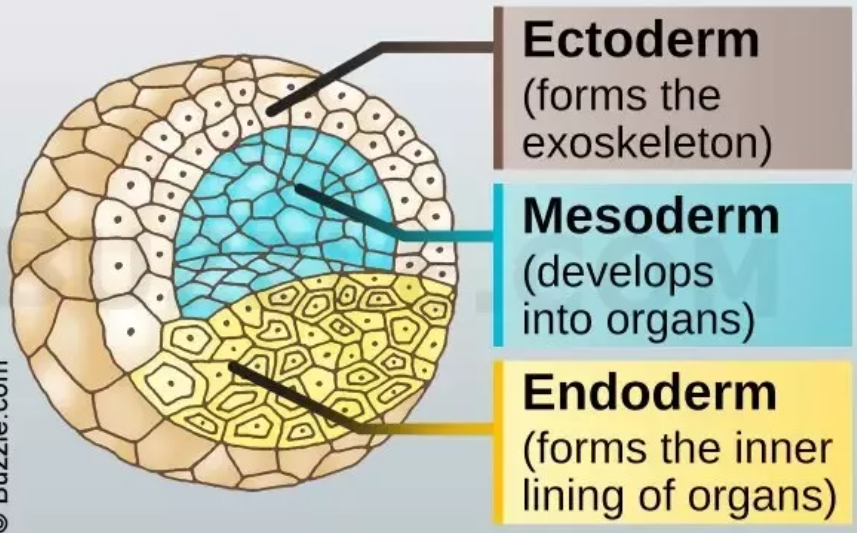
What does the *endoderm layer* do?
* inner-layer
* forms lining of the gut
* for some organisms, their respiratory system
* forms lining of the gut
* for some organisms, their respiratory system
14
New cards
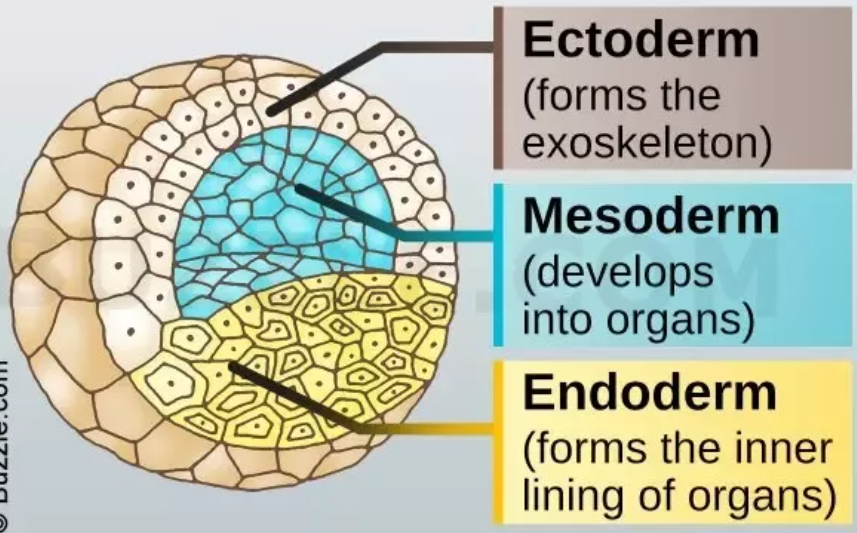
What does the *mesoderm layer* do?
* middle-layer
* gives rise to the circulatory, reproductive, excretory, and muscular systems
* gives rise to the circulatory, reproductive, excretory, and muscular systems
15
New cards
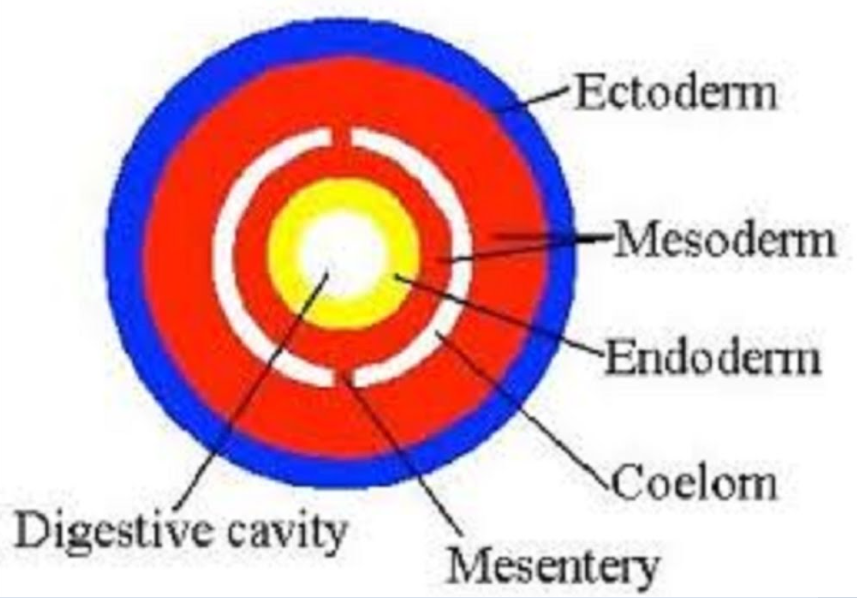
What is a *coelom?*
It’s a fluid filled body cavity that:
* separates the gut from the body wall
* provides space for internal organ growth
* grown from the *mesoderm layer*
* separates the gut from the body wall
* provides space for internal organ growth
* grown from the *mesoderm layer*
16
New cards
What are the *simplest invertebrates?*
Porifera and cnidaria
17
New cards
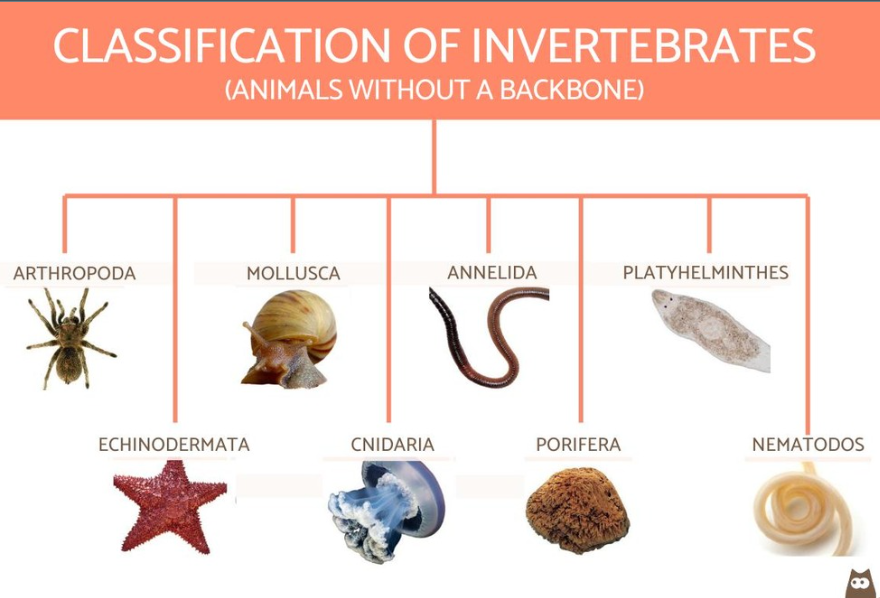
What are the key characteristics of *porifera?*
* look like coral
* immobile and range in size
* hermaphrodites (organisms with both male and female parts) pass through pores in the body wall
* immobile and range in size
* hermaphrodites (organisms with both male and female parts) pass through pores in the body wall
18
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *cnidaria?*
* look like jellyfish
* no mesoderm
* specialized nerve, muscle, digestive, and reproductive tissue
* skeletons made of calcium chloride
* no mesoderm
* specialized nerve, muscle, digestive, and reproductive tissue
* skeletons made of calcium chloride
19
New cards
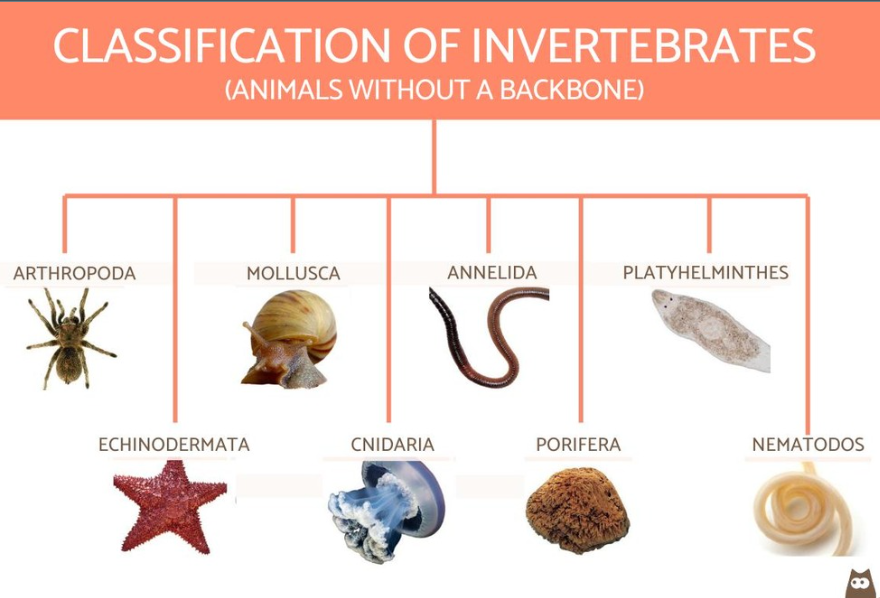
What are the *6 phyla of invertebrates*?
Arthropoda, nematoda, annelida, mollusca, rotifera, platyhelminthes
20
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *arthropoda?*
* creatures with grabby arms - crab, scorpion, spider
* segmented bodies with joint appendages
* complex sensory system
* vital in both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems
* segmented bodies with joint appendages
* complex sensory system
* vital in both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems
21
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *nematoda?*
* parasitic worms
* unsegmented, completely digestive, bodies
* parasites
* unsegmented, completely digestive, bodies
* parasites
22
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *annelida?*
* regular worms - earthworm
* mostly segmented bodies and organs
* gas exchange through skin/gill
* bristles on the outer bodies for movement
* mostly aquatic
* mostly segmented bodies and organs
* gas exchange through skin/gill
* bristles on the outer bodies for movement
* mostly aquatic
23
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *protosome* *mollusa?*
* snails
* three unsegmented sections: foot, mass (body), and mantle
* special radula (tongue) for scraping
* three unsegmented sections: foot, mass (body), and mantle
* special radula (tongue) for scraping
24
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *protosome* *rotifera?*
* tiny aquatic ‘animals’ (smaller thna 2mm)
* live in fresh water
* no respiratory or circulatory system
* live in fresh water
* no respiratory or circulatory system
25
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *platy-helminthes?*
* flat, tiny (1-5mm), unsegmented on worms
* digestive cavity with only one opening
* no coelom
* digestive cavity with only one opening
* no coelom
26
New cards
What are the two *subgroups* off the *Deuterostomes?*
Echinoderms and chordates
27
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *echinoderms?*
* subgroup of deuterosomes
* no head (eyeless animals - starfish, urchin)
* no respiratory, circulatory, or excretoy system
* no head (eyeless animals - starfish, urchin)
* no respiratory, circulatory, or excretoy system
28
New cards
What are the key characteristics of *chordates?*
* subgroup of deuterosomes
* includes almost every animal
* success from the **development of**: notochord (enhance mobility), limbs, waterproof amniotic egg, large internal skeleton and vertebrate skeleton
* includes almost every animal
* success from the **development of**: notochord (enhance mobility), limbs, waterproof amniotic egg, large internal skeleton and vertebrate skeleton
29
New cards
What are the *7 major phyla of vertebrates*?
* **Agnathans** (jawless fishes - eels, lamprey)
* **Chondrichthyes** (cartilaginous fishes - predators: sharks, rays)
* **Actinopterygii** (bony fish - salmon, bass, tuna)
* **Amphibia** (cold-blooded - frog, salamander)
* **Reptilia** (cold - lizard, snake, turtle)
* **Aves** (birds - warm-blooded), M
* **Mammalia** (warm, humans, whales, bats)
* **Chondrichthyes** (cartilaginous fishes - predators: sharks, rays)
* **Actinopterygii** (bony fish - salmon, bass, tuna)
* **Amphibia** (cold-blooded - frog, salamander)
* **Reptilia** (cold - lizard, snake, turtle)
* **Aves** (birds - warm-blooded), M
* **Mammalia** (warm, humans, whales, bats)