Practice Problems
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Which organ systems are primarily involved in controlling homeostasis?
A. muscular and excretory systems
B. integumentary and endocrine systems
C. muscular and circulatory systems
D. endocrine and nervous systems
E. only the nervous system
D
Which of the following is an example of the regulation of levels of substance X by negative feedback?
A. When level of X rises above a set point, that triggers more X to be secreted
B. When level of X rises above a set point, that triggers less X to be secreted
B
Endotherms DO regulate their own body temperature, while ectotherms do NOT regulate their body temperature
A. True
B. False
B
Your dark brown Labrador dog loves to lie down on a tile floor after a long walk in the sun. Which cooling process is your dog using?
A. radiation
B. evaporation
C. conduction
D. convection
C
Which of the following is true, and is a distinction between these two types of hormones?
A. Peptide hormones activate signal transduction pathways
B. Peptide hormones bind to an intra-cellular receptor
C. Steroid hormones do not require a receptor to activate target cells.
A
Adrenaline (epinephrine) is a hormone that elicits the flight-or-flight response. It has different receptors on different cell types, enabling a wide-range of effects. The receptors are located on the cell membrane of different cells. What does this tell you about the chemical structure of adrenaline?
A. It must be water soluble.
B. It must be lipid soluble.
A
The pH within the stomach is about 2, and most digestive enzymes in the small intestine have a pH optimum of 7-8. When the stomach’s acidic food mass starts to pass into the small intestine a hormone signal is released into the blood. To be effective, that hormone should trigger the release of which of these?
A. acid into the stomach
B. bicarbonate into the small intestine
C. hydrolytic enzymes into the small intestine
D. uptake of glucose into cells
E. aggregation of fats into globules
B
Which animal must eat a larger proportion of its weight in food each day: a house cat or an African lion caged in a zoo?
A. Cat, because smaller mammals have a higher metabolic rate per unit body mass
B. African lion, because larger mammals have a higher metabolic rate per unit body mass
A
Where in the digestive tract does the most chemical digestion occur?
A. Stomach
B. Small intestine
C. Large intestine
D. Mouth
A
Which of the following is an example of hydrolysis reactions that occur in the digestive system?
A. Mixing small drops of fats & oils in water
B. Chewing/mashing large pieces of meat to make small pieces of meat
C. Breaking down starch to sugar molecules
D. Muscle contractions churn the food in the stomach
C
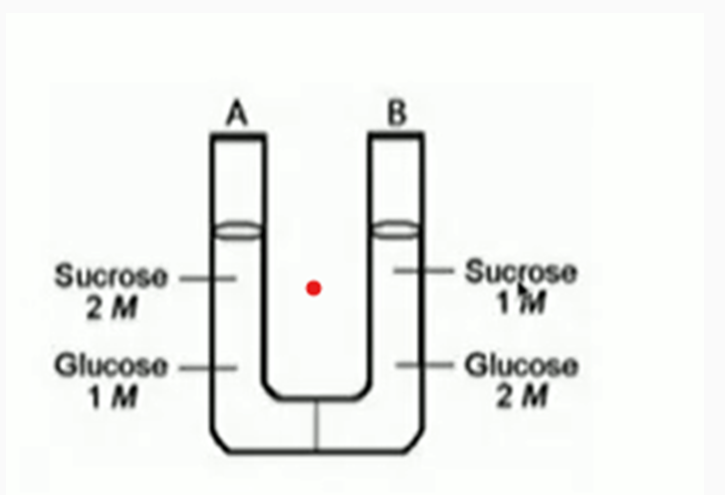
Which way will the liquid move?
A. The water will move toward tube A.
B. The water will move toward tube B.
C. The water will not move.
A
Salt-water fish and seabirds tend to take in too much salt. Which specific action in their transport epithelium membranes achieves osmotic homeostasis?
A. pump out Na+ ions
B. pump in Na+ ions
C. pump out water
D. Pump in Ca+ ions
A
Would you expect there to be more or less reabsorption of water (out of urine & back into blood) in kidney tubules of desert-adapted animals?
A. More
B. Less
A
Would the loop of Henle be longer or shorter in desert mammals relative to humans?
A. Longer
B. Shorter
A
Which happens when stomata are opened?
A. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration increases
B. CO2 intake increases; transpiration increases
C. CO2 intake decreases; transpiration decreases
D. CO2 intake increases; transpiration decreases
B
Fill in the blanks in the correct order.
An external stimulus is transmitted by a(n) (1) _______ to the (2) _______.
A motor response is part of the (3) _______ and is transmitted by a(n) (4) ________
A. (1) afferent neuron; (2) central nervous system; (3) peripheral nervous system; (4) efferent neuron
B. (1) peripheral nervous system; (2) efferent neuron; (3) central nervous system; (4) afferent neuron
C. (1) central nervous system; (2) afferent neuron; (3) peripheral nervous system; (4) efferent neuron
D. (1) efferent neuron; (2) peripheral nervous system; (3) central nervous system; (4) afferent neuron
A
Fill in the blanks in the correct order.
A(n) (1) _______ is a highly branched structure on the neuron’s cell body that receives (2) _______.
The (3) _______ is a long projection from the cell body that allow the neuron to send signals to other cells. One kind of neuron called a(n) (4) _______ acts as a bridge between neurons as it receives information from one neuron and passes it to another neuron.
A. (1) neuron; (2) interneuron; (3) axon; (4) signals
B. (1) dendrite; (2) signals; (3) axon; (4) interneuron
C. (1) interneuron; (2) signals; (3) dendrite; (4) interneuron
D. (1) axon; (2) interneuron; (3) dendrite; (4) signals
B
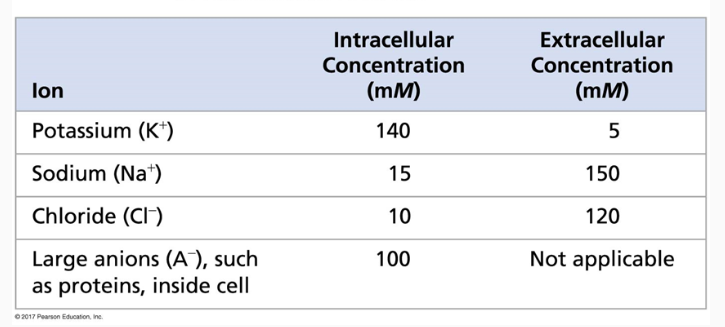
Which way would K flow if ion channels were open?
A. Into the cell
B. Out of the cell
B
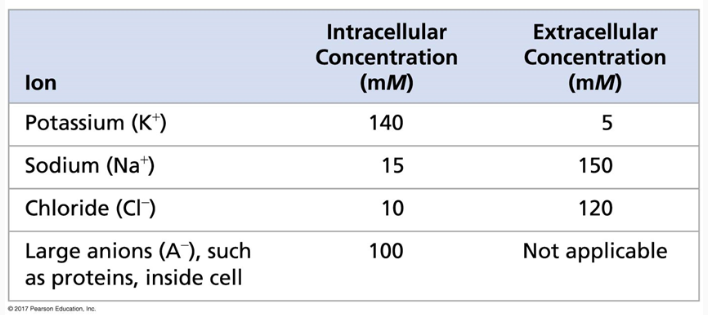
Which way would Na flow if ion channels are open?
A. Into the cell
B. Out of the cell
A
The stages of an action potential in voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels in a neuron’s plasma membrane are (1) resting state, (2) rising phase of the action potential, (3) depolarization, (4) falling phase of the action potential, and (5) undershoot. Which of the following lists the stages in the correct order?
A. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B. 1, 3, 4, 2, 5
C. 1, 3, 2, 4, 5
D. 5, 2, 3, 4, 1
C
What types of receptors would you expect to see in the skin?
A. Mechanoreceptors
B. Electromagnetic receptors
C. Thermoreceptors
D. Pain receptors
E. Chemoreceptors
F. Two of the above
G. Three of the above
G
What type of feed-back loops maintain homeostasis?
A. Positive Feedback
B. Negative Feedback
C. Both
D. Neither
B
True or false: Endotherms DO regulate their own body temperature, while ectotherms do NOT regulate their body temperature
A. True
B. False
B
You lie down on the cold tile floor after going on a run. Which cooling process are you using?
A. Radiation
B. Evaporation
C. Conduction
D. Convection
C
Which of the following is not an example of a signaling molecule?
A. Hormones
B. Neurotransmitters
C. Neurohormones
D. White Blood Cells
D
What is true of peptide hormones?
A. They can easily travel through the plasma membrane
B. They are made of lipids
C. Their receptors are located in the cytoplasm of cells
D. They bind to receptors on the outside of cells
D
Is blood hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
A. Hydrophilic
B. Hydrophobic
C. Both
D. Neither
A
Which of the following are ways to maximize diffusion?
A. Increase surface area
B. Shorten the distance
C. Have a steeper gradient
D. All of the above
D
True or False: Endotherms require more energy/kg than ectotherms of the same size
A. True
B. False
A
True or False: Condensation Reactions are where we use water to break apart polymers into monomers during digestion.
A. True
B. False
B
True or False: Only mechanical digestion occurs in the oral cavity (mouth).
A. True
B. False
B
Which of the following is correct? In a hypotonic solution…
A. an animal cell will become turgid
B. an animal cell will become plasmolyzed
C. an animal cell will lyse.
D. an animal cell will shrivel.
C
Humans excrete nitrogenous waste in the form of ___.
A. Uric Acid
B. Urea
C. Ammonia
D. Ammonium
B
Which of the following heart components match the correct definition?
A. Veins- carry blood away from heart
B. Arteries- carry blood away from heart
C. Ventricles- receive blood entering heart
D. Atria- pump blood out
B
True or False: All veins carry deoxygenated blood and all arteries carry oxygenated blood.
A. True
B. False
B
True or False: The loops of Henle in desert mammals are longer than human loops of Henle.
A. True
B. False
A
Which of the following happens when stomata are opened?
A. CO2 intake decreases, transpiration increases
B. CO2 intake increases, transpiration increases
C. CO2 intake decreases, transpiration decreases
D. CO2 intake increases, transpiration decreases
B
Which of the following is not a type of neuron
A. sensory
B. glial
C. inter
D. Motor
B
True or False: Motor Neurons are involved in afferent signaling from external stimuli to the Central Nervous System.
A. True
B. False
B
True or False: Afferent neurons can also be called sensory neurons.
A. True
B. False
A
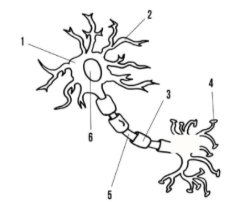
What are 2 and 4 on the diagram to the right?
A. 2=dendrite; 4=axon
B. 2=axon terminal; 4=dendrite
C. 2=axon; 4=dendrite
D. 2=dendrite; 4=axon terminal
D
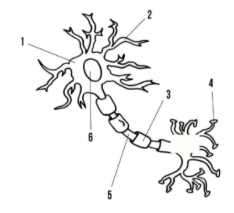
What are 3 and 5 on the diagram?
A. 3=axon; 5=schwann cell
B. 3=axon; 5=myelin sheath
C. 3=myelin sheath; 5=axon
D. 3=myelin sheath; 5=schwann cell
C
The resting membrane potential of a neuron is…
A. 70 mv
B. -70 mv
C. 50 mv
D. -50 mv
B
True or False: The sodium-potassium pump carries out a form of facilitated diffusion.
A. True
B. False
B
The sodium-potassium pump pumps…
A. 3 Na+ in the cell and 2 K+ out of the cell
B. 3 K+ in the cell and 2 Na+ out of the cell
C. 3 K+ out the cell and 2 Na+ out of the cell
D. 3 Na+ out the cell and 2 K+ into of the cell
D
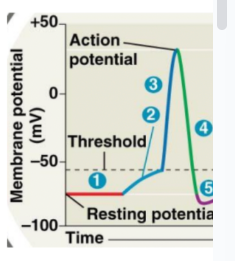
What is true at ‘1’ on the diagram to the right?
A. Na+ voltage-gated channels open
B. K+ voltage-gated channels open
C. Both Na+ and K+ voltage-gated channels open
D. Neither Na+ nor K+ voltage-gated channels are open
D
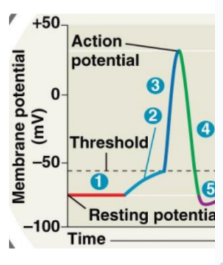
What is happening at 2 and 3 on the diagram?
A. Cell membrane is repolarizing
B. Cell membrane is hyperpolarizing
C. Cell membrane is depolarizing
D. Cell membrane is getting more negative
C
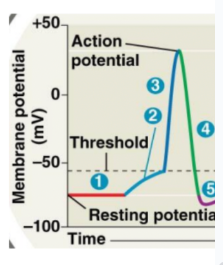
What happens at 4?
A. Cell membrane is repolarizing
B. Cell membrane is hyperpolarizing
C. Cell membrane is depolarizing
D. Cell membrane is getting more postive
A
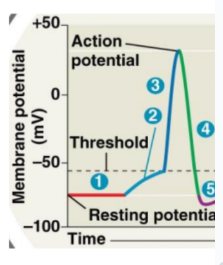
What is happening at 5 when the cell membrane is hyperpolarized?
A. K+ voltage-gated channels are closed and Na+ voltage-gated channels are open
B. K+ voltage-gated channels are open and Na+ voltage-gated channels are open
C. K+ voltage-gated channels are open and Na+ voltage-gated channels are closed
D. K+ voltage-gated channels are closed and Na+ voltage-gated channels are reactivated
C
Hair cells in the ear are
A. Mechanoreceptors
B. Electromagnetic receptors
C. Chemoreceptors
D. Nocireceptors
A
True or False: Rods and cones are found in the iris.
A. True
B. False
B
True or False: Cones allow us to experience color.
A. True
B. False
A
Which is not a type of cone?
A. Red-sensing
B. Green-sensing
C. blue-sensing
D. Yellow-sensing
D