Testes: Stroma & Parenchyma
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the 2 structures that form testes?
Stroma (supporting tissue) #00a5ff
Parenchyma (functional tissue) #ff8300
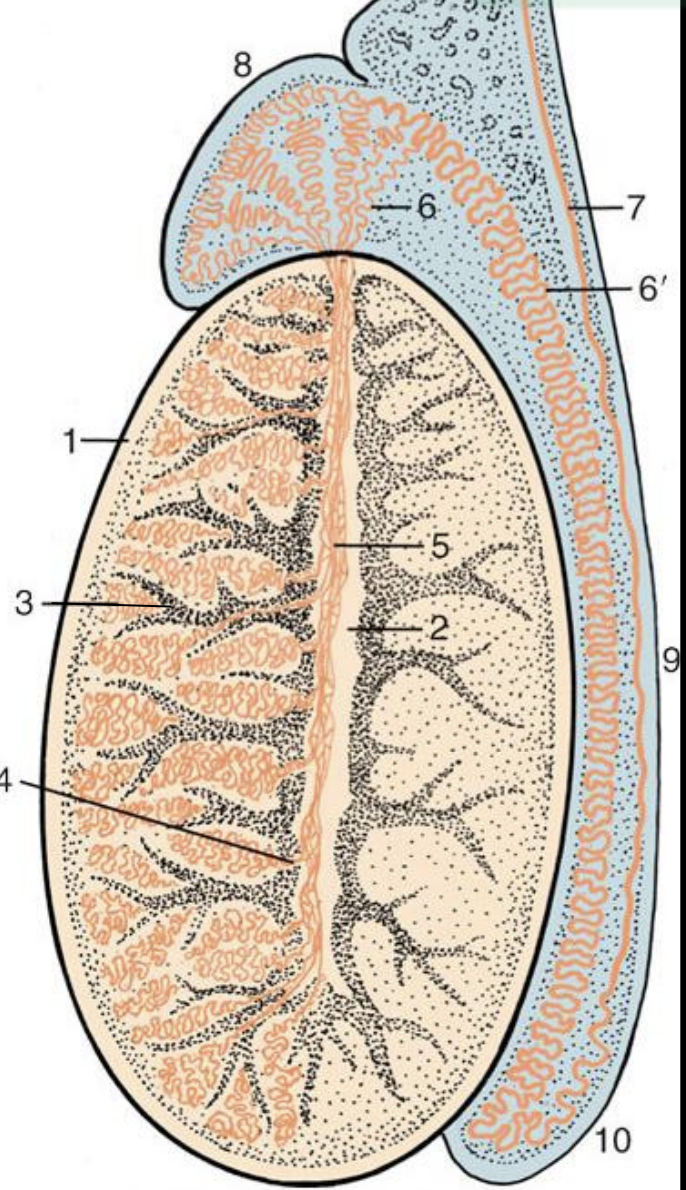
What are the structures of the stroma? #00a5ff
Tunica vaginalis
Tunica albungiea
Septila testis
Mediastinum testis
Interstitial tissue
Stroma: What is
Tunica vaginalis
Tunica albungiea
Septila testis
Mediastinum testis
#00a5ff
Tunica vaginalis: Serosal peritoneal layer of scrotum
Tunica albungiea: Dense, irregular collagenous CT (1)
Septila testis: Internally radiated tunica albunginea to form lobuli testis (3)
Mediastinum testis: Central emerging of tunica albuginea to form tiny cavity (2)
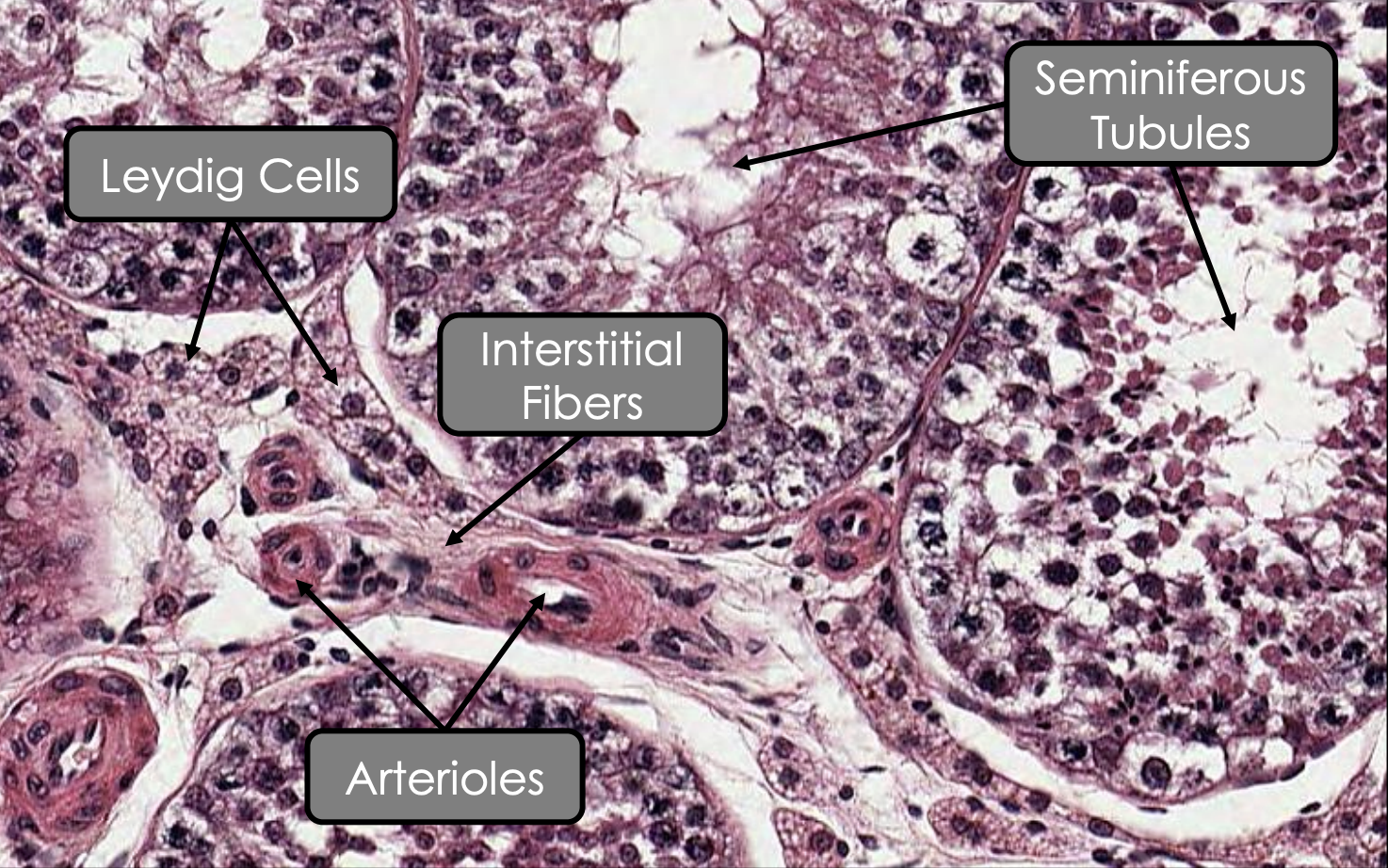
Interstitial tissue of stroma #00a5ff
Interstitial fibers
What
From
Surrounds
Interstitial cell
Name
Arrangement
Adjacent to
How they connect
Cytoplasm
Shape
Nucleus
Abundant of which organelles
Function
Interstitial fibers
What: Infiltration of loose connective tissue
From: Septula testis
Surrounds: Seminiferous tubules
Interstitial cell
Name: Leydig cells
Arrangement: Clusters or cords
Adjacent to: Capillaries
How they connect: Gap junctions
Cytoplasm:
Pale due to acidophilical cytoplasm
Shape: Polyhedral
Nucleus:
Spherical
Euchromatic
Abundant of which organelles:
Lopid vacuoles
sER
Mitochondria
Function: Synthesise testosterone under influenced of LH
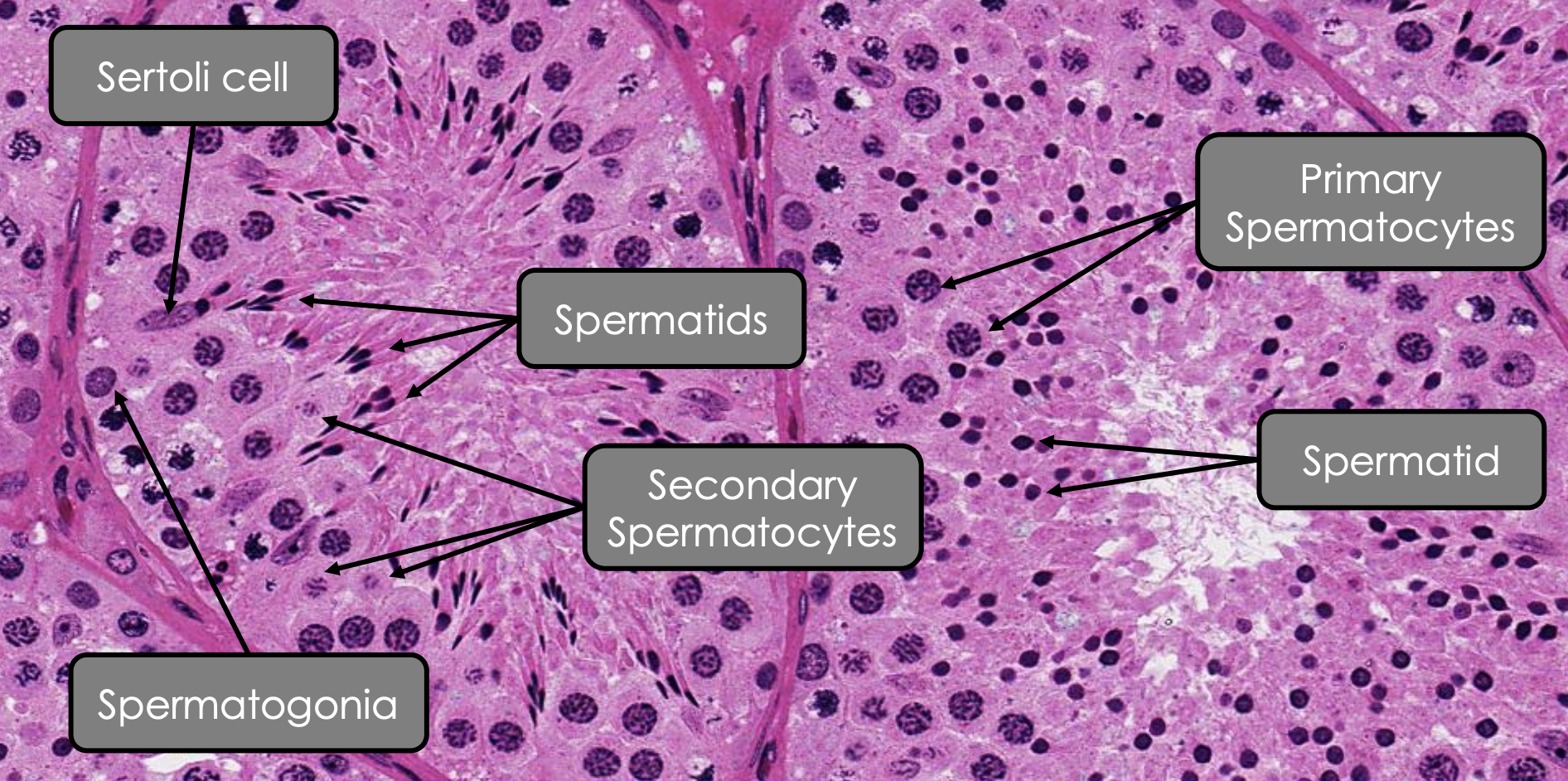
What are the structures of parenchyma? #ff8300
Convoluted seimiferous tubules (forms sperm)
Straight seminiferous tubules (forms sperm)
Rete testis (sperm transport)
Efferent ductules (sperm transport)
Parenchyma: Seminiferous tubules #ff8300
Shape
Location
Straight seminiferous tubule is formed
What is ductuli efferentes
What is lamina propria
Myofibroblaat
What
Why needed
Function
Lined by
Shape: Tightly convoluted
Location: Within pyramidal lobuli testis
Straight seminiferous tubule is formed: Prior merging with rete testis within mediastinum testis
What is ductuli efferentes: Duct that empties the spermatozoa into epididymis
What is lamina propria: Fine collagen and elastic fibers
Myofibroblast:
What: Peritubular contractile cell with actin bundles
Why needed: For contraction
Function: Important for spermatogenesis
Lined by:
Stratified spermatogenic epithelium
With Sertoli cells
Parenchyma: How is secondary spermatocytes produced? #ff8300
Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis I
Parenchyma: How is spermatid produced?
Secondary spermatocytes undergo meiosis II
Parenchyma: Spermatogonia #ff8300
Closely associated with
Shape
Nucleus
Closely associated with: Basement membrane
Shape: Round, pear-shaped
Nucleus: Heterochormatic
Parenchyma: Primary spermatocytes #ff8300
Nucleus
Abundant of what organelles
Nucleus: Varying chromatin density of nucleus
Abundant of what organelles:
Mitochondria
rER
Large GA
Parenchyma: Secondary spermatocytes #ff8300
Location
Shape
Nucleus
Location: Near luminal surface of seminiferous tubule
Shape: Spherical
Nucleus: Weakly stained
Parenchyma: Sertoli Cell #ff8300
Shape
Location
Nucleus
Abundant organelles
How do they communicate with adjacent cells
Function
Shape: Pyramidal cell
Location: Extend the entire height of spermatogenic epithelium
Nucleus: Ovoid and euchromatic
Abundant organelles:
Cytoplasmic projections to all spermatogenic epithelium
GA
Mitochondria
sER (surrounds periacrosomal region of spermatid)
Fat vacuoles (at cellular base)
How do they communicate with adjacent cells: Tight junction and desmosomes
Function:
Structural and nutiritonal support
Intra-tubular fluid secretion
Formation of blood testis barrier