QUIZ 2 [PE1FPF]
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Cardiorespiratory endurance
Ability of the heart and lungs to deliver oxygen to working muscles during continuous physical activity
Physiological Adaptation CRF (Cardiorespiratory Fitness)
Structural and Functional adaptations leading to a better oxygen transport system
Functions of Physiological Adaptation CRF
[1] Improved Stroke Volume
[2] Improved Lung Efficiency
[3] Increased Capillarization
[4] Enhanced Mitochondrial Density
[5] Decreased Resting Blood Pressure
Lower risk of cardiovascular disease
Benefits of CRF
[1] Improved Stroke Volume
[2] Improved Lung Efficiency
[3] Increased Capillarization
[4] Enhanced Mitochondrial Density
[5] Decreased Resting Blood Pressure
Functions of Physiological Adaptation CRF
Lower risk of cardiovascular disease
High level of CRF is associated with a blank, and all-cause mortality
High level of CRF is associated with a blank, and all-cause mortality
Lower risk of cardiovascular disease
Better Stamina
Benefits of CRF
Better Stamina
Enhances cardiovascular efficiency
Better Stamina
This leads to greater endurance by improving oxygen delivery to muscles
Better Stamina
This makes everyday activities easier and less tiring
Managed Weight
Benefits of CRF
Managed Weight
Regular aerobic exercise helps improve calorie expenditure
Managed Weight
This contributes to long-term blank by boosting metabolism
Boosting Metabolism
Long-term weight management is brought on by management of blank
Excess Post Exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC)
This is the graph used to illustrate the relationship between Oxygen Consumption and Exercise Time
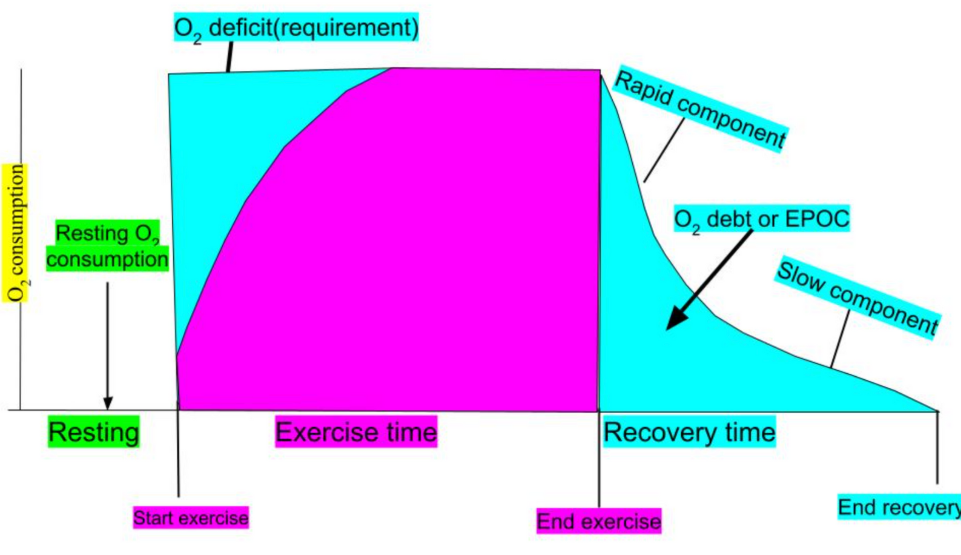
Stronger Bones
Benefits of CRF
Stronger Bones
Weight-bearing and high-impact cardiorespiratory exercises stimulate this
Strengthened bone structure
This is brought on by increasing bone density
Risk of Osteoporosis
Stronger bones by strengthened bone structure and increased bone density reduces blank
Reduce stress / Better Mood
Benefits of CRF
Reduced Stress / Better Mood
Regular cardiorespiratory exercise can help manage anxiety, depression, and improve overall emotional well-being by lowering stress hormones and releasing endorphins
Endorphins
Natural pain relievers or mood enhancers
Natural pain relievers or mood enhancers
Endorphins
Cortisol
Example of stress hormone
Aerobic Training
Exercise that improves cardiovascular efficiency
Aerobic Training
This uses large muscle groups in continuous, rhythmic movements and relies on oxygen for energy
Oxygen
Where does Aerobic Training rely on for energy
Continuous, Rhythmic movements
What kind of movements are present in Aerobic Training
Sports Administration Ministry of Education of Taiwan
SAMET
Exercise frequency: At least 3-5 days of aerobic exercise per week
Exercise Intensity: 60-80% of the maximum heart rate
Exercise Type: Aerobic Exercise
Exercise Time: 20-50 mins per exercise
What does SAMET’s official guideline for cardiorespiratory endurance state
At least 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per week
OR at least 75-150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity per week
OR an equivalent combination of moderate-and-vigorous-intensity activity throughout the week
What does WHO’s official guideline for Physical Activity state
Steady State Cardio
Form of aerobic exercise in white the intensity remains relatively constant throughout a long duration without significant fluctuations in intensity
Jogging/running
Biking
Elliptical Bike
Swimming
Dancing
Playing sports recreationally
Examples of SSC
High Intensity Interval Training
Form of cardiovascular exercise that alternates between short bursts of intense exercise and periods of rest or low-intensity exercise for recovery that is repeated for a set duration
Circuit Training
Tabata
Interval Running
Playing competitive sports
Examples of HIIT
SSC: [1] Improves Endurance, [2] Mental Relaxation, [3] Beginner-Friendly
HIIT: [1] Improves Endurance, [2] Efficient Format, [3] Greater Fat Loss (EPOC)
Difference between SSC and HIIT
10-50%
Range of Intensity for Little to no physiological changes
60-70%
Range of Intensity for SSC
80-90%
Range of Intensity for HIIT
90-100%
Range of Intensity for High Injury Rate
Target Heart Rate (THR)
Associated with the level of your exercise intensity
Obtain values for its lower and upper limit
How to calculate THR zone
208 - (0.7 x age in years)
Heart Rate Max Formula
HRMax - HRRest
Heart Rate Reserve Formula
(HRR x Percent Intensity) + HRrest
Target Heart Rate Formula